Pheasants are amazingly beautiful birds that are bred not only for decorative purposes, but also for meat. Pheasant eggs are a delicacy and contain a set of micro- and macroelements, vitamins A, D, as well as an almost complete composition of B vitamins. The hunting season for this bird is one of the most anticipated events among hunters.
The Romanian pheasant has emerald plumage
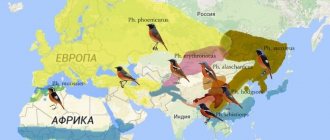
Pheasant appearance
The pheasant is not a very large bird and here are some facts that confirm this:
- body weight on average - 1.5–2.0 kg;
- the body length of the bird can reach up to 90 cm;
- wingspan - 75–80 cm.
Some subspecies may have greater or lesser weight and length.
The pheasant has a pear-shaped body, a small head and a tail, which in the male can reach 55 cm in length, in the female - only 30.
Pheasants are characterized by sexual dimorphism, manifested in differences in size and color.
Females are smaller than males, their plumage is much more modest, so they do not attract attention.
All males have a variegated color with a slight metallic sheen. The males usually have spurs on their legs. The plumage colors of birds vary greatly and depend on the species. The Argus, Golden and Diamond pheasants have the most impressive appearance.
Pheasant Argus named so by Carl Linnaeus
Description and features
the Caucasian pheasant is included in the order Gallinae. It is larger than its relatives. The body length is 90 cm, weight is 1.7 - 2.0 kg. Females are not as large as males.
Long, pointed tails. The wings are rounded. Males are armed with spurs and always have bright plumage. The areas around the eyes and cheek areas are leathery. When the time comes for mating, these places turn red.
Male pheasant
The color of the males includes rich colors, the design seems to have been created by a painter. The pheasant in the photo is like a magical firebird. The main tone of the plumage is yellowish-red. The head is blue-green. The back of the head is decorated with feathers edged in green.
Below is a blue-violet drawing. In front it resembles a scaly pattern. Neck and chest with a metallic sheen. The belly is often brownish in color. Legs and beak are gray-yellowish. The color of males varies depending on their habitat. Subspecies differ in the characteristics of their shades.
The outfit of females is much more modest - nature protected them from the attention of predators so that there was a greater chance of bearing offspring. The motley pattern on a dull brown background perfectly camouflages birds against the background of vegetation. The beak and legs of females are gray. Beautiful birds are bred in special pheasant farms and subsidiary farms. About 50 countries have acquired feathered predators to adapt to their territories.
Pheasant habitats and lifestyle
The pheasant lives from Turkey to the Primorsky Territory, including China, as well as Central and Asia Minor.
Pheasants are “generalists” and can live almost anywhere, with the exception of dry places. They prefer to live in dense bushes or in forest belts with undergrowth. They try to stay near water, so they can often be found in thickets on the banks of lakes or rivers. In some regions, the pheasant is well acclimatized and, where there is stable, dense snow cover, finds food near farms.
As a rule, pheasants are social birds, so in the fall they prefer to gather together over a large area.
The pheasant has a high running speed, it is the best sprinter among galliformes - the bird stretches its neck and head forward, which creates a minimum of resistance when running. The pheasant does not fly well, so it rarely does this - on average, it can fly about 200 meters, and then it gets very tired and when startled again, it already runs. The pheasant is so shy and cautious that it almost always hides. In captivity, a bird can live from 12–15 years, and in the natural environment - about 7.
Purchasing pheasants
When it comes to purchasing, it is better to give preference to nurseries or well-known breeders.
It is advisable to buy birds from different people to avoid inbreeding, as this will lower the immunity of future birds and make them infertile.
Cormorant - how to recognize where it occurs, reproduction, appetites + 103 photos- Crane - origin, description, habitat and lifestyle, nutrition and reproduction + 79 photos
Heron - 89 photos of a very beautiful and rare bird
First, buy 2-4 pairs of birds, and then, once you get involved in the process of keeping them, you can buy more.
Pheasant species diversity
Pheasants are a subfamily that includes 4 genera: lofurs, junglefowl, long-eared pheasants and true pheasants.
The following types of jungle fowl include: Ceylon, Bank, green and gray.
The genus of eared pheasants includes 4 species: Tibetan, blue, white and brown.
There are only 2 types of real pheasants: common and green.
Lofurs have the most species - 9.
Pheasant Argus or Stood-eyed Argus (Argusianus argus). It is the largest representative of pheasants and owes its name to Carl Linnaeus, who named it in honor of the many-eyed giant Argus. The reason for choosing this name is simple - on 12 long tail feathers and wings, in addition to the marble pattern, there are “eyes”, the color of which imitates a convex shape. Males acquire an unusual color only in the third year of life. The female does not have such an impressive ocellated pattern of feathers. In appearance, Argus resembles a peacock.
Due to its large weight, which sometimes reaches 2.7 kg, and long plumage, the pheasant does not fly.
Argus leads the life of a hermit and prefers dense thickets. Each male has his own territory, while females do not have one and roam the “lands” of all males. Currently, the birds are at great risk from the deforestation of tropical forests in Southeast Asia, which is depriving them of their usual habitats - which is why they are classified as Near Vulnerable.
If Argus senses danger, he leaves so quietly that it is very difficult to see him in nature.
Common or Caucasian pheasant (Phasianus colchicus). Currently, up to 32 subspecies of common pheasant are distinguished, differing from each other in color.
Male common pheasant
The common pheasant is a common object of hunting and is a domesticated bird. Farmers breed it for its rapid weight gain, unpretentiousness in food, tasty meat and nutritious eggs. In nature, pheasants are hunted by almost all birds of prey and animals, so up to 70% of the young die in the first year of life. Humans also pose a threat to pheasants. People appreciated the exquisite meat of this bird, which is why pheasants are now hunted all over the world.
In Russia, due to the reduction in the number of pheasants, hunting is not permitted in all regions. As a rule, the hunting season falls at the beginning of October and ends towards mid-December. For hunting, a person often uses dogs, which frighten the bird and force it to leave its shelter, rising into the air - it is at this moment that the person shoots at the pheasant. Experienced hunters know that pheasants never stray far from the place of food, therefore, if they attack the trail, they look for birds near this place. In addition to hunting with a dog, the following methods are popular:
- shooting while feeding birds from a blind;
- stalking;
- drive hunting by a group of hunters;
- hunting with decoys - imitating the sounds of pheasants, hunters lure birds or force them to show their location.
Diamond pheasant (Chrysolophus amherstiae). The male diamond pheasant is considered one of the most beautiful birds in the world. The male has a bright red crest on his head, his body is partially decorated with green-blue feathers, and his tail, which is longer than the body, is white and black. The weight of a male can reach 800 grams, and the length is 170 cm. Females are inconspicuous and smaller in size. The diamond pheasant is common on the mountain slopes of southwest China, eastern Burma, some regions of Tibet and several counties in England. In China, the pheasant usually hides in bamboo forests, and in England - in coniferous forests.
In the natural environment, the diamond pheasant has many enemies: foxes, raccoons, snakes, hawks, kites, etc. But most of all, pheasants suffer from the hands of humans, who not only hunt them, but also cut down forests, reducing the bird’s habitat. The diamond pheasant is saved by the fact that it reproduces well and lives in captivity, so nothing threatens its species. In nature reserves, the diamond pheasant can live up to 20–25 years.
White eared pheasant (Crossoptilon crossoptilon). Eared pheasants live in small groups and obtain food by tearing the ground with their strong legs. They feed in the morning and evening, and during the day they like to rest near water sources. In winter, pheasants gather in “flocks” of up to 250 birds, in summer - up to 30, and in spring they live only in pairs. Due to human development of new territories and hunting, experts note a decline in the white pheasant population.
A special feature of the eared pheasant is the absence of sexual dimorphism: males can be distinguished from females only by size. The body length of the male does not exceed 96 cm, of females - 92 cm. The weight of the male is 2.7 kg, the weight of the female is up to 2 kg. Despite the name, these birds have no visible ears. The white pheasant has an elongated body and short legs, which are armed with spurs. His head is decorated with a “velvet” black cap. The tail is less bushy than other species and consists of 20 black feathers. In the wild, the pheasant is distributed in the mountain forests of China, Tibet and India. He prefers to settle in thickets of rose hips, rhododendron and barberry. Despite the fact that the White Pheasant is a good flyer, when danger arises it prefers to run, even from dogs.
Romanian pheasant (Phasianus versicolor). This pheasant is often called green or emerald due to the greenish tint of the wings. This species was obtained by crossing Japanese and European pheasants. Birds are bred mainly for meat, which is considered dietary and delicious in taste, as well as for hunting. Pheasants are ready for slaughter at 6 weeks with a weight of 1 kg. The bird does not live in the wild. Males, in addition to the beautiful emerald shade of their feathers, also have a variegated crest. They are slightly larger in size than a chicken: the body length of a male with a tail does not exceed 1 meter, and the maximum weight is no more than 2.8 kg. Females are smaller in size and have brown plumage without any tint.
Romanian pheasants do not live in their natural environment
Golden pheasant (Chrysolophus pictus). Birds are bred for decorative purposes and for meat. Golden pheasant populations in China are not in danger. However, populations living in other territories are small; for example, in the UK there are only 1000 of these birds. The golden pheasant does not migrate, so it does not leave its homes. Birds are bred in captivity in China, Russia, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Spain, Italy, and Portugal. The males are very beautiful - they have a yellow crest, a burgundy belly and an orange collar with a black edging. Males have spurs on their legs. The body length of the male is up to 85 cm, and the weight can reach up to 2.5 kg. Females are without a crest, smaller and more modest - they only have brown-brown plumage. Body length is up to 50 cm, and weight is less than 1 kg.
Their homeland is China, but in the natural environment they can now be found in Mongolia, Great Britain, Tibet and the south of the Transbaikal region. The pheasant prefers to hide in thickets of reeds, bamboo, dense pine and deciduous forests and even in tea plantations. Golden pheasants do not form flocks, preferring to live alone. They lead a sedentary lifestyle and sleep in trees at night.
Lifestyle and habitat
The pheasant has spread widely as a result of the active introduction of birds and successful adaptation. The settlement covers territories from the Iberian Peninsula to Japan. In the Caucasus, Turkey, China, Vietnam, Primorsky Krai, Europe, and North America, bird acclimatization and domestication have become commonplace.
The bird settles in areas heavily overgrown with vegetation - forests, undergrowth, grass meadows, and the edges of sown fields. Thorn bushes are especially attractive - birds feel protected among them. Tugai thickets and reed banks are favorite habitats for colorful birds.
In case of danger, they do not fly to the tops of trees, like other birds, but rather run into impassable thickets. A large animal will not climb into thorny bushes. A prerequisite for settlement is the proximity of a body of water, so birds can often be found near lakes, swampy areas, and in river valleys. Resistant to frost, pheasants easily tolerate winters if the snow cover does not exceed 18-20 cm. In mountainous areas, bird settlement is observed at an altitude of up to 2500 m above sea level.
Japanese pheasant female
The owner of bright plumage has to constantly hide in the thicket of thickets so as not to fall prey to predators. Some species hide in trees and rest among the foliage. They climb higher when they don’t find food on the ground in cold weather. On the branches they feed on preserved fruits.
Pheasants are cautious when they come to the ground. They do this quickly, in a rush, quickly change the angle of movement, and hide in the thickets. The running speed of pheasants, in comparison with other chicken-like representatives, is record-breaking. To accelerate, the bird instinctively extends its head and raises its tail.
The pheasant has many natural enemies. Among mammals, birds are hunted by foxes, lynxes, pumas, and wild dogs. Feathered predators, such as eagle owls and hawks, are also natural enemies of pheasants. In the first year of life, up to 80% of individuals become food for other forest inhabitants.
Particular danger comes from humans. The pheasant has long been an object of commercial and sport hunting. Specially trained dogs help by driving the game onto tree branches, and upon takeoff, hunters shoot the birds. Population numbers are significantly affected by climate. The natural decline of birds is inevitable in very snowy and frosty winters.
Pheasant populations are actively recovering. A significant role is played by domestic breeding of birds, keeping them in nurseries and in protected areas. In general, the population size does not cause concern.
Fireback Pheasant
Pheasants are gregarious birds that stay in large same-sex groups outside the breeding season. The active time for searching for food is morning and evening. Birds are quiet, their voice can only be heard in flight. This is a sharp, abrupt sound, heard from afar. Birds emit special signals during mating.
The common pheasant, migratory or not, is characterized by its region of habitat. A sedentary lifestyle is characteristic of most inhabitants of regions with an abundance of food. Migratory time over short distances begins after the chicks hatch. Then, in search of food, birds can be found in places unusual for them.
What do pheasants eat?
Pheasants mainly collect food on the ground, raking it with their strong paws. However, sometimes they jump up and pick fruits from bushes. Pheasants are omnivores, so they can eat not only plant foods - berries, seeds, acorns, fruits, nuts, shoots, but also animals - invertebrates, small insects, grasshoppers, larvae, etc. Adults prefer the first option, and pheasant chicks prefer rapid growth and development in the first 4 weeks - the second. By the way, pheasants are the best destroyers of Colorado potato beetles, so they are often released into fields to get rid of this scourge.
In addition to its main food, the pheasant swallows small pebbles, which help it improve digestion. As a rule, birds feed in the morning and evening.
THIS IS INTERESTING! Under unfavorable conditions, the white eared pheasant can eat pine needles, as well as the droppings of hares or deer in the form of balls. Stalwart Argus, in addition to berries, shoots and leaves, does not refuse frogs and snails.
Diamond pheasant - one of the most beautiful birds in the world
Nutrition
The bird of the pheasant family is omnivorous. The diet is dominated by plant foods, but it also includes an animal component: worms, spiders, rodents, snails, and mollusks. Newborn pheasant chicks up to one month of age receive only animal food from their parents.
More than a hundred plants are attractive to pheasants. The food becomes seeds, berries, young shoots, and fruits. Birds obtain food by tearing the ground with their claws. They jump and fly low to collect fruits from tall bushes and trees. In households, pheasants are unpretentious in nutrition.
The best foods are considered to be food waste (without signs of spoilage) and greens (plantain, dandelion). Birds feast on grain mixtures, vegetables, fruits, and berries. Beautiful plumage must be maintained with mineral supplements (lime, chalk, crushed shells). You can activate the work of the digestive organs by adding clean river sand and small pebbles.
Natural enemies and population size
Predators hunt pheasants both on the ground and in the air. Most often, birds are attacked by hawks, owls, foxes, raccoons, lynxes, badgers, wild dogs, cougars, etc. Predators attack not only adults, but also nests in the hope of eating eggs and chicks. A person who does not refuse to feast on delicious meat also poses a threat to pheasants.
Pheasants are widespread and their conservation status is not of concern. Although sometimes bird numbers decline locally due to overhunting and habitat destruction. For example, the number of pheasants in Europe is estimated at approximately 10 million adult individuals, and in Azerbaijan, according to preliminary estimates, no more than three hundred birds.
Often wild populations are supplemented with large numbers of captive-bred pheasants (for shooting).
Product sales market
Pheasant eggs, in addition to those left for the reproduction of other individuals, will naturally be sold. They are more useful than chicken, non-allergenic and recommended as a dietary product.
The pricing policy is quite high, which will bring good profits.
The meat of domestic pheasants is considered a delicacy and is in great demand in the restaurant business, which is why contracts for the supply of carcasses should be concluded in advance.
The cost of carcasses is high, which means profit is guaranteed.
When growing steppe or emerald breeds, it is possible to sell them for hunting grounds.
Pheasants get used to freedom quickly, within 4-6 days.
Pheasant hunting is a pleasure only for wealthy people, which is why the cost of the birds sold is too high and amounts to several tens of dollars.
Pheasant nesting and raising offspring
The domesticated pheasant lives in polygamy and can gather up to 10 females around it. In the wild, the pheasant is monogamous, meaning it has only one female.
The mating season begins in early spring, and the male chooses his partner very carefully. The female also evaluates her partner and tries to choose a dominant male who can offer her protection. Studies have proven that the female prefers the male with a long tail.
The mating dance begins when the pheasant rises, opens its tail and begins to loosen the soil, picking up and throwing grains. When luring the female, he makes short intense sounds “kh-kh-kh”, and in the immediate vicinity of her - dull “gu-gu”. Pheasants build nests on the ground and hide them in grass or thorny bushes. The clutch, as a rule, consists of 8–18 eggs of the same color, brownish in color. Males do not take part in incubation, hatching and raising chicks - this is done exclusively by the female.
Hatching of eggs lasts about 20–25 days. The chicks are born covered in down and with open eyes. They can follow their mother as soon as they are dry. They can also look for food on their own, but naturally, only under the supervision of their mother. 14–15 days after birth, the chicks begin to fly, and after 80 days they become independent.
THIS IS INTERESTING! During the mating season, which occurs at the beginning of spring, male golden pheasants attract females by clucking and shouting “chak-chak.”
When a female comes running to the call of a male, he begins to circle around her, stopping from time to time and approaching. The male hangs his wings and opens his tail so that the female can appreciate his beauty. There is practically no information about how nesting occurs in natural conditions.
It is no less interesting to watch the male Argus, who, at the beginning of the mating season, looks for an open place and clears it - the area turns out to be about 4-5 meters in diameter. Next, he begins to call the female with sounds and dance, and then, opening his wings, tries to show her his many “eyes.” The more beautiful the male looks, the more likely he is to succeed. After mating, the female leaves and begins to build a nest. Argus becomes sexually mature no earlier than the fourth year of life.
White eared pheasant
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Pheasant bird
Pheasants are social birds. In the fall, they flock together, often in large groups, to an area with shelter and food. Usually the main winter range is smaller than during the nesting period. Flocks formed in winter can be mixed or single-sex and can contain up to 50 individuals.
These birds move little but may exhibit some migratory tendencies depending on the availability of food and cover. Short-distance migration is observed in northern populations, where cold weather forces the birds to find milder conditions. The dispersal of the group in early spring is gradual rather than abrupt, with males leaving first.
Fun Fact: The bird uses dust for bathing by incorporating particles of sand and dirt into its plumage by raking with its beak, scraping the ground with its paws, or shaking its wings. This behavior helps remove dead epidermal cells, excess oil, old feathers and the sheaths of new feathers.
Common pheasants spend most of their time on the ground and rest on both the ground and trees. They are fast runners and have a "strutting gait." While feeding, they hold their tail horizontally, and while running, they hold it at an angle of 45 degrees. Pheasants are excellent pilots. When taking off, they can move almost vertically. Males often make a croaking call during takeoff. They run when threatened.
Keeping pheasants at home
Pheasants are bred in families: for 1 male there should be no more than 3-4 females - a larger number leads to a decrease in egg production. Pheasants cannot be kept in cages - they require space, so you will need to install high enclosures with a roof.
Pheasants hate drafts, so cracks and gaps in the house must be eliminated. Perches need to be installed on the walls. All drinkers and trays must be firmly secured, otherwise the pheasants will overturn them. It is best to feed pheasants with mixed feed made from corn, barley, shells, yeast and grass meal. You can also give peas, sorghum, soybeans, cottage cheese, clover, nettles, carrots, cabbage leaves, apples and pears.
When breeding Argus, you need to take into account that they are calm, but very sensitive, so it is advisable to create a peaceful environment for them. Argus also quickly become attached to a person and remember his voice well. For Argus chicks, rats pose a great danger - they do not attack adult birds, but they attack babies at the first opportunity.
The Romanian pheasant does not require special maintenance, so it is enough to build a spacious indoor enclosure, in which there will be 2 square meters per bird. m. It is advisable to provide some kind of perches in the enclosures. Since pheasants have thick plumage, there is no need to additionally insulate the enclosure; it is enough to protect it from drafts. These pheasants are very shy, so they hide at the slightest “danger”. They also have a good memory, so in order not to stress the bird again, it is advisable that they are fed by the same person.
The diamond pheasant is suitable for breeding on farms and in nature reserves, as it feels great in a spacious enclosure. The water should always be clean. Pheasants are kept for decorative purposes, and the feathers are often used to make fishing gear.
Eared pheasants are bred in large poultry farms and farms. They tolerate extreme cold well, but heat, direct sun and damp indoors do not, so it is better not to breed white pheasants in hot and dry regions. The white pheasant is trainable. In captivity, males can be aggressive towards each other, so, just in case, it is better to place them in different enclosures. Trimming one wing helps to pacify the aggressor. Since birds of this species do not have the habit of changing their place of residence, they are quietly kept in open areas. In captivity, females lose interest in hatching eggs, so they can be used as turkey hens or an incubator. Birds are ready to mate in their second year of life.
The golden pheasant is unpretentious - the main thing is to make an enclosure at the rate of 2 square meters per bird. In the enclosure, it is necessary to install perches at a distance of at least 1 meter from the floor and drinking bowl. By the way, the golden pheasant eats often and a lot.
Golden pheasant - decoration of any yard
Handy devices
To properly keep pheasant birds you will need:
- an incubator, since the female does not always hatch the chicks; a nursery for growing chicks of about 20 sq. m.;
- several medium-sized enclosures for breeding couples, about 7 square meters. m., but if there are several females per male, then the area expands;
- a large enclosure designed for a certain number of pheasants.
- for one – 2 sq. m. This means that 50 birds require an aviary of about 100 square meters. m.
Interesting facts about pheasants
There are some interesting facts about pheasants that may surprise you.
- Several golden pheasants brought to the UK have managed to escape from their enclosures into the wild. They were able not only to acclimatize to the new environment, but also began to nest.
- The pheasant uses dust for bathing - it draws it into its plumage by scratching the ground with its feet and shaking its wings. This bathing helps remove epidermal cells and old feathers.
- The Romanian hunting pheasant has thick plumage, so it is not afraid of cold weather, and it is also very voracious, so it quickly gains weight. This bird is bred not only for its meat or decorative appearance, but also for hunting competitions, which are organized by enterprising business owners.
- The game pheasant, bred as a result of the hybridization of several subspecies of the common pheasant, is not found in the natural environment.
- Pheasant and partridge are often confused. However, the partridge is smaller - its body length reaches only 30 cm, and its weight is about 600 grams. It does not have such beautiful plumage as the pheasant, because its main defense strategy is camouflage.
- The common pheasant has an unfeathered circle around its eyes. During the breeding season, this circle turns red.
- Due to the faded appearance of females and chicks, they are practically invisible in the open both in winter and summer, while males, on the contrary, are visible from afar and try to distract the predator from the nest.
- Pheasant meat tastes very similar to guinea fowl meat. However, guinea fowl are smaller than pheasants, which can weigh more than 2 kg. The pheasant also has a trump card - its appearance, which rarely leaves anyone indifferent. Guinea fowl and pheasants can be bred together as they get along well.
- The famous Georgian dish chakhokhbili was originally prepared from pheasant fillet, but then the Georgians replaced it with chicken.
We invite you to watch a short video of how an Argus male tries to win a female by performing his mating dance.
The pheasant is an unusually beautiful bird that takes root in any climatic conditions and even near humans. Unfortunately, man himself is gradually reducing the number of birds, reducing their range by cutting down forests and hunting not only for food, but also for pleasure.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: Pheasant
This species was first scientifically described by Linnaeus in Systema naturae under its current scientific name. This bird was widely discussed even before Linnaeus established its nomenclature. The common pheasant was simply called “pheasant” in most ornithology textbooks of that time. Pheasants are not native birds to Central Europe. They were brought there during the Roman Empire from Asia, as hunting game many centuries ago. Even today, most pheasants are artificially incubated in some areas and then released for hunting.
Video: Pheasant
Some wild subspecies have long been among the favorite ornamental birds, and therefore have long been bred in captivity, although they could not yet be called domesticated. The homeland of birds is Asia, the Caucasus. They got their name from the ancient Greeks, who discovered birds near the Phasis River (current name Rioni), near the Black Sea and the Georgian settlement of Poti. The common pheasant is the national Georgian bird. The national dish chakhokhbili was made from its fillet. These Caucasian birds constituted the bulk of the introduced stock in Europe until the modern era.
The bird is not found in Africa, except in Mediterranean coastal areas, in the time of Linnaeus, where they may have been introduced during Roman times. These birds had more features in common with the Transcaucasian population than with others. The scientific name is Latin for "pheasant from Colchis", which is located west of modern Georgia. The Ancient Greek term corresponding to the English "pheasant" is Phasianos ornis (Φασιανὸς ὂρνις), "bird of the river Phasis". Linnaeus included many other species in the genus Phasianius, such as the domestic chicken and its wild ancestor. Today, this genus includes only the common and green pheasant. Since the latter was not known to Linnaeus in 1758.
Species Definition
Pheasants are domesticated birds; most species are native to Asian countries. Modern breeds, such as the lemon pheasant, were bred artificially. This is what a pheasant looks like:
- Body length is about 84 cm, weight is 1.7-2.1 kg, males are much larger than females.
- The tail is long, wedge-shaped. Consists of 18 feathers.
- Males have spurs on their paws.
- The color of the male is always brighter and more colorful (golden, orange, green, purple tones), while the females are faded and inconspicuous (usually sand, brown, gray, brown).
The common pheasant is an elegant wild bird that will become the desired prey of any hunter
. Please note! In the common pheasant, a stripe devoid of feathers surrounds the eye. Other species do not have this feature.
Distinctive features
Pheasant is a bird with small wings, rounded into an oval shape. The head has dark plumage, most often with a green tint. The eyes are golden or yellow-orange, the paws are light, in some species deep red.
The base of the tail is red, the feathers on the tail itself are brown, edged with purple or black.
Note! Young males are similar in appearance to females, but with age their plumage acquires its natural beauty.
The average life expectancy is 12-15 years, but in the natural environment these birds rarely live this long, as they become victims of hunters or predators.
Nature itself has painted the plumage in bright, rich shades, while the males are much more elegant than the females
Does the bird fly or not?
Pheasants fly well, but they do not like to do this, preferring to run away from danger on their strong legs. The only species that is predisposed to flight is the large, rich orange satyr tragopan. It can float in the air and rise to considerable distances, which is generally uncharacteristic for chickens.
All other pheasants try to rarely leave the ground, doing this only in emergency cases. This is due to the specifics of the anatomical structure. But birds are endowed with acute vision and excellent running speed - pheasants are the fastest among all chickens.
How much does it weigh
The average weight of a pheasant depends on the breed. For example, the common pheasant in the wild reaches no more than 2-2.3 kg, and we are talking about large males. When raised for meat, it was possible to obtain several productive breeds capable of growing up to 3-4 kg.
Catering
The pheasant is a non-capricious bird in food; it can eat both plant food and insects. Enjoys berries and grain. To have constant access to water, it prefers to settle near the banks of reservoirs.
Diet of birds in the wild
Every hunter knows who a pheasant is, since this gray bird with a long tail is considered a desirable prey. The habits of birds, as well as their diet, have been studied quite well.
The main goal of a bird’s life is to obtain food, and the bulk of the day is devoted to solving this problem. Pheasants move from one tree to another, visiting fields and berry fields in search of food. At the same time, birds are useful for farmers - they do not destroy fields, but destroy insects, thereby saving the harvest.
Interesting fact! Pheasants love Colorado potato beetles, which some farmers use as an alternative method of pest control.
Grass seeds, shellfish, insects, snails, berries and fruits - this is what pheasants eat in the wild. Even a small snake or rodent can be included in the bird's diet.
Pheasants are unpretentious in their choice of food, so they can easily organize their own food
At home
Keeping these birds at home requires proper organization of their diet. Main types of food: greens, grains, small insects. Nutrition must be balanced and of high quality, otherwise the bird will not be able to gain weight normally. The birds are fed three times a day, with one meal consisting entirely of green food. The second and third meals can be based on mixed feed or mash.
Note! Competition among birds is very developed, so feeders and drinkers should be in such quantity that each individual has access to them. The average feed rate per bird is 70-75 grams.
List of approved products for feeding pheasants:
- legumes;
- grains (oats, barley, wheat, corn);
- vegetables (cabbage, carrots, boiled potatoes, pumpkin);
- green grass.
It is important to enrich the menu of domestic pheasants with minerals and vitamins that will help keep the birds healthy. In a separate feeder for them, crushed shell rock is poured, as well as bone meal, fish oil, and cottage cheese.
In summer, the basis of nutrition should be green food, its amount per individual is at least 20 grams. It is recommended to feed at the same time so that the bird develops a reflex. In winter, feed should be given every 6 hours; the green component content is reduced. To make it easier for the bird to tolerate molting, you should give it minced meat and fish oil.
Since birds have a rather sensitive digestive system, they should not be given the following foods:
- black bread;
- millet;
- green potatoes;
- seeds;
- fried and fatty.
All these products will only cause harm and will not contribute to weight gain.
Proper feeding is the key to keeping domestic pheasants healthy and strong.
Natural enemies of pheasants
Photo: Pheasant Author: Svetlana Medvedeva (@msvetlana012018)
Adult pheasants can be hunted either on the ground or in flight. Some of their behavioral responses to danger include retreating to cover or flying, and they may also fly away, hide, or run away depending on the circumstances. Females may display a broken wing in an attempt to lure a predator away from the nest, or will sit very still and quiet. When brood chicks are hunted, often more than one is taken at a time. In addition, exposure to extreme weather conditions is a cause of chick mortality.
Hunting of game by humans is a serious problem for pheasants. They are especially vulnerable during nesting time. Increased rates of pheasant predation are closely linked to habitat destruction. This occurs because habitat degradation makes prey more vulnerable to predators. It was previously thought that coyotes were the main predators of pheasants, but after observing their behavior over several decades, it was discovered that coyotes focus their foraging on rodents and rabbits.
The most common predators that attack adult pheasants or their nests are the common fox, striped skunk and raccoon. Additionally, the wider range and territorial nature of coyotes is leading to declines in the population of these mammals, a more destructive predator.
The most famous predators of pheasants are:
- foxes (Vulpes vulpes);
- domestic dogs (Canis lupusiliaris);
- coyotes (Canis latrans);
- badgers (Taxidea taxus);
- mink (Neovison Vison);
- weasel (Mustela);
- striped skunks (M. mephitis);
- raccoons (Procyon);
- great eagle owls (B. virginianus);
- red-tailed buzzards (B. jamaicensis);
- red-shouldered buzzard (B. lineatus);
- rough-legged buzzard (B. lagopus);
- Cooper's hawks (A. cooperii);
- goshawk (A. gentilis);
- peregrine falcons (F. peregrinus);
- Hen Harrier (C. cyaneus);
- snapping turtle (C. serpentina).
Three quarters of nests and adult birds suffer from attacks by predators, with the exception of hunting.