The forest pipit, or forest squirrel, is a small and funny insectivorous bird belonging to the wagtail family. The forest songbird is very often confused with sparrows, but the wood sparrow is smaller in size than the city sparrow and is also distinguished by its peculiarly slender body.
Forest pipits are considered useful birds from the point of view of forestry, which is due to the ability of the wood pipit to destroy a significant number of insects - plant parasites - in the process of feeding.
Description of the bird
More than forty species of small songbirds, distributed on all continents, are united by the genus pipits of the wagtail family. Externally, the skates are very similar to each other and only an experienced ornithologist will be able to distinguish them.
These are slender birds with an oblong body up to 18 cm long, agile, with high legs, pointed or slightly rounded wings, and a notched tail.
— Advertising —
The plumage of skates is usually dark brown on the back and off-white on the belly. The plumage is also characterized by streaks and special patterns that differ among different species. Among its relatives, the spotted pipit stands out for its color - its back is olive green.
In general, it is much easier to distinguish different types of pipits by their unique song than by their external appearance.
Nesting
Forest Pipits are monogamous birds that live in pairs separately from others. In April-May, the female chooses a place for a nest within 1-2 weeks. The nest is usually far from bushes and trees and is located in the grass in a small hole. A complete clutch has 4-6 eggs of a regular ovoid, less often flattened shape.
Eggs can have a wide variety of colors: from light green to rusty purple. On top they are covered with a pattern of spots of varying contrast, color and clarity. The color of the chicks is dark gray, with yellow beak ridges and a red oral cavity. The chicks leave the nest before they can fly. Parents feed them for 9-10 days.
Distribution of skates in nature
— Advertising —
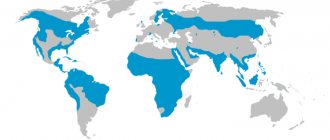
The habitat of skates is very extensive. Various species of this small bird are found on every continent except Antarctica, and in a wide variety of geographic areas.
The homeland of the northern representatives of the genus (Siberian, spotted, red-throated, American pipits) is the Arctic tundra of North America, Europe, and Asia. The large pipit lives in the subantarctic region.
Many species of pipits prefer high alpine meadows for nesting, such as the spectacled and pink pipits.
Interesting Facts
- In neurological centers during rehabilitation they often offer to listen to the sounds of nature. Among the voices of birds there is always the singing of a pipit. His performance acts as a sedative.
- In the old days they said that if you hear the singing of a skate after winter, the whole next year will be happy and easy.
- There was also such a belief: you need to find and pick up a skate feather, and then put it under the threshold, then your house will be protected from fire. And if you throw a feather up and let it fly away with the wind, expect pleasant changes in your personal life throughout the year; the feather will lead your destiny to you.
- Some pipits fly north to England rather than south for the winter, “hoping” for a warm oceanic climate in the Gulf Stream region.
- They usually keep a forest or meadow pipit in a cage; their singing is similar to the singing of a canary, only the melody is even more varied. It's a shame that the song lasts only 3 months a year, from April to July. But for the sake of the beauty of singing, many agree to such short tours.
Types of skates
Certain types of pipits are very similar in appearance to each other; distinguishing them is not an easy task even for an experienced ornithologist.
Steppe Pipit
One of the largest species with a body length of 17 to 20 cm. The bird also has unusually long fingers and legs, and a very long and straight rear claw. The back is painted brown and decorated with dark transverse stripes. The breast and sides are beige or brownish, dark stripes are visible on the neck. The belly is white.
The steppe pipit lives in the steppes of East Asia (Kazakhstan, western Siberia, Mongolia). The bird lives on flat, damp and damp steppes, and sometimes on mountain slopes. Migratory species. Winters in southern Asia.
Field Pipit
The species is distributed in North Africa and Eurasia.
The size of the bird is slightly smaller than the steppe pipit. The plumage on the back is yellowish-sandy-brown with dark streaks, except for the lumbar and rump areas. The belly is buffy-whitish in color with a brown tint on the sides and chest. A light eyebrow on the head is noticeable. The young are distinguished by a peculiar scaly pattern on the upper part of the body, and streaks on the sides, chest and belly.
Godlevsky's Horse
Outwardly, it resembles a forest pipit, but its plumage is colored red, especially noticeable in the chest area. The bird also has light-colored legs and an almost straight hind toe claw.
The bird lives in shrubby and rocky steppes. For life, it chooses the steppes of plains and mountains in the center and east of Asia (eastern Altai).
Canary Pipit or Berthelot's Pipit
Despite the name, the species is found not only in the Canary Islands. The bird nests, for example, in Madeira. And it is always found in open spaces.
This is a small species of skates with a body length of up to 15 cm. The color of the plumage is grayish-brown. Young animals have a rich chestnut color. There is no sexual dimorphism.
Forest Pipit or Forest Pipit
The body length of this type of skate reaches 16 cm. The back is brownish-gray in color, decorated with black-brown streaks. The belly is light and buffy. Dark streaks are also noticeable on the sides and chest. Legs beige-pink; short claw of the hind toe. In young birds, the black streaks on the back are more pronounced.
The forest pipit is widespread in Europe, Northern and Central Asia.
Siberian Pipit
The bird's body length is up to 15 cm. The wingspan is from 23 to 25 cm. The weight reaches 25 g. The Siberian pipit is very similar to the red-throated and meadow pipit.
The plumage on the back is yellow or olive-brown with vague, black longitudinal stripes that are clearly visible on the heads. The tail and rump are greenish in color. The belly is creamy to white and decorated with stripes on the sides. A slightly noticeable light eyebrow is visible above the eyes. Legs are red.
Migratory species. The main places of residence are from the Pechora River to the Chukotka Peninsula, Kamchatka, and the Commander Islands. The bird winters in the Philippines and Indonesia. The Siberian end nests in dense thickets along river banks and in the tundra.
Menzbier's Pipit
A small type of skate, painted in dark colors with bright spots on the back. The wings have jet-black stripes in the center and whitish-green stripes on the edges. The belly is bright yellow. Lives in Siberia.
meadow pipit
It is very reminiscent of the forest pipit, but differs from this species in its smaller body size (up to 15 cm). Colored mainly in gray tones, the breast is light yellow with thin stripes. Legs are reddish. The birds are also distinguished by their thin and sharp beak.
The meadow pipit is widespread in Asia and Europe. It goes for the winter south of its usual habitat. The bird nests in swampy places, wet pastures and meadows, and occasionally in the mountains.
Red-breasted Pipit
The species lives in the northern taiga and tundra of Eurasia, on the west coast of Alaska. For life, it prefers open swampy areas with thickets of bushes; in the taiga it nests in swamps.
The bird's body length is up to 15 cm. The plumage on the back is brown, decorated with dark streaks. Adults are distinguished by a reddish-brown throat, sometimes with a reddish pattern on the sides and chest with black speckles. The belly is yellowish-white. Young animals have a white throat. It differs from other species by a white supercilium, a white eye ring, and whitish stripes on the upper part of the body.
Mountain Pipit
Distributed in the mountains of southern Europe and Asia. Migratory species.
The predominant color in the plumage is brown with stripes, lighter on the belly than on the back. The legs and beak are dark, and white feathers are visible on the tail. In summer, the breast becomes pink and the head turns grey. Body length reaches 17 cm.
Shore pipit
Body length - 16.5 cm, weight from 20 to 30 g. Wingspan from 23 to 28 cm. The bird's beak is long, black. Color changes with the seasons. In summer, the plumage on the belly is yellowish or off-white with gray-brown stripes. The upperparts are olive with dark streaks. In winter, the lower part becomes grayish and the back becomes dark. The species has dark legs.
The shore pipit is widespread in Scandinavia, Great Britain, Iceland, Ireland, Russia, and Central Europe. Northern residents migrate to southern Europe for the winter.
American Pipit
The body length of the species is up to 16 cm. The plumage on the back is brown, the legs and beak are dark. The belly is beige, the chest is decorated with dark stripes.
The American Pipit is found in North America (Canada, USA), Greenland, and Alaska. The bird nests in the Arctic tundra or in the mountains. For the winter it goes to the southern countries of America.
Big horse
The species is found only on the South Georgia Islands, and is the only songbird of the Sub-Antarctic. For some time it was endangered due to gray rats brought to the island. Outwardly similar to a shore pipit.
rock pipit
Distributed in South Africa and Lesotho, in high mountain meadows. Body length is up to 18 cm, weight is about 30 g. In appearance it is similar to a mountain horse.
Habitat
Of all the species of wood pipits, forest pipits are most associated with arboreal vegetation, so their summer habitat is represented by small deciduous or coniferous forests surrounded by grassy glades and clearings with separately growing young trees. Most often, the insectivorous bird settles on the light edges of large forests or in small forests.
The forest pipit is widespread throughout the island forest zones of Eurasia. In our country, nesting sites are observed from the northern part of the White Sea to the southern part of Crimea. While in a significant part of their habitat, the silver guinea pig has slight variability in appearance, then in the Pamirs and Tien Shan one can observe a subspecies characterized by the shortest beak. Scientists associate this feature with the type of plumage coloring and the absence of characteristic bright spots on the feathers.
For the winter, the bird migrates to warm countries . The chickweed winters in the Mediterranean, Africa or India. Rare, apparently random, flights of pipit flocks to Madeira, Jan Mayen and the Canary Islands have also been observed. With the onset of the warm season, migratory birds return to the regions of our country in large flocks.
Keeping skates at home
Skates are sociable and friendly birds. Some of the species are kept in captivity due to their sweet singing.
Birds will need a spacious and long cage and food for insectivores. Namely: a mash of cottage cheese, eggs, carrots, gammarus and daphnia. Birds love to feast on mealworms and insects. You can also add grain mixtures to your diet.
Skates are rarely kept at home; breeding them is not practiced.
Diet
Birds mainly feed on insects and small invertebrates. The diet includes butterflies, cicadas, caterpillars, aphids, ants, and grasshoppers. They also feed on various beetles: elephant beetles, weevils, click beetles. Feeding almost always takes place on the ground. The horse deftly maneuvers in the grass, running and catching insects.
From the beginning of August it can feed on the seeds of plants: sedge, sedmichnik, warty birch, and marianberry. Throughout September, it flies away from its nesting sites. Forest pipits very rarely stay until October.
What do buntings eat
The bird uses a long and pointed tongue to collect and eat many ants at one time. But birds don't just eat insects. The bunting sits on an anthill and allows the ants to crawl on its wings. Scientists believe that the acid secreted by ants fights parasites.
Oatmeal feeds on seeds:
- barley;
- ryegrass;
- dandelion;
- amaranth.
Buntings hunt:
- grasshoppers;
- moths;
- caterpillars;
- flies;
- Zhukov;
- aphids;
- bedbugs;
- cicadas;
- spiders
How do buntings behave?
Birds spend most of their time on the ground, in pastures, plowing, crops and stubble, on lawns and gardens. Buntings are monogamous during the breeding season, but gather in flocks ranging in size from a few individuals to thousands of birds outside the mating season. They often fly in mixed flocks with other species, including finches, goldfinches, and sparrows.
Males sing from a prominent branch or perch during breeding, such as a treetop or power line. If the nest is destroyed by predators, then the parents "go crazy", fly and scream.