Forest or black polecat, as well as common, dark or black polecat - all these are the names of a small animal of the mustelidae family, an order of predators. He is widely known among lovers of exotic pets, gets along easily with people and feels comfortable both in the wild and at home. Read more about the forest ferret and its features below.
What does a wood ferret look like?
The ferret is small in size and in appearance is a typical representative of its family.
Constitution
The body is elongated, flexible, squat with short but strong legs. This structure allows it to silently sneak up on its prey. The ferret has an elongated neck, a small oval head, an elongated muzzle, slightly flattened towards the nose.
Basic parameters of the forest ferret:
| Body length | Weight | Tail length |
| 29-46 cm | 650-1500 g | 8-17 cm |
Color
The animals have long fur, which can reach 6 cm, and different colors - from dark gray to black. However, in the wild there are also individuals with brown, reddish, yellow colors, and there are also albino representatives.
Color is never monotonous. Thus, the tail, belly and paws are always darker than the body, and on the muzzle there is a white mask, which is a characteristic feature of a ferret.
In winter, after molting, the color of the forest ferret becomes darker than in the warm season.
Structural features
The main structural features of the animal include:
- the small head smoothly transitions into a flexible and elongated neck;
- the ears are small, low, with a wide base;
- the eyes are brown, shiny, bead-like;
- the paws are short and thick, even in the largest individuals the length of the hind legs is only 6-8 cm;
- the paws have 5 toes, between which there are membranes;
- the forest ferret has 28-30 teeth, of which 4 canines, 12 premolars, 12-14 incisors;
- next to the tail of the animal there are special glands, which, in case of danger, secrete a secretion with a fetid odor.
Traps for the safe capture of animals
There are several types of traps that will allow you to catch a ferret alive. Some of them are offered in specialized stores, but most can be made independently.
In addition to the trap itself, you will need the following list of items to catch a wild predator:
- gloves made of thick fabric;
- canvas or camouflage clothing;
- meat as bait;
- infusion of wormwood.
Overalls are needed to protect against sharp teeth and claws of the animal. Ferrets always resist human capture and can bite through the skin. The bait most often is killed mice or chicks, which predators feed on.
These animals actively react to the strong smell of blood. The trap should be treated with wormwood to repel the human smell.
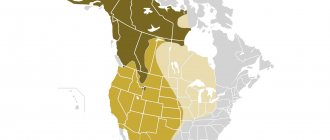
Where does he live?
The habitat extends to the territory of Eurasia and the northwestern part of the African continent. Most often found in Russia, China, England, and Ukraine.
Not long ago, black ferrets were brought to New Zealand to reduce the rodent population; as a result, they took root there and feel more than comfortable.
Animals live in small forests and isolated groves. They prefer not to go far into the forest; they like to settle on the edges and clearings. Forest ferrets lead a sedentary lifestyle and are very attached to their chosen place. They occupy a small area and most often use natural shelters as permanent shelters - stacks of firewood, rotten stumps, haystacks, dead wood. They almost never dig their own holes; they can live in offshoots of badger or fox holes.
They will never choose dense taiga or open space for living; in extreme cases, they settle near human settlements.
Habitat
Black ferrets live in Western Europe and the northwestern forests of Africa. In Europe, representatives of the species can be found throughout the European part of Russia with the exception of the Caucasus, Karelia and the Lower Volga region. A small population lives in England and Western Siberia.
It is fashionable to meet the steppe ferret in Ukraine, the south of the Czech Republic and Yugoslavia. And also in the territory of Moldova, Trans-Baikal Territory, the Far East and China.
The kinship between all species of ferrets is so strong that they can interbreed and have common offspring. Therefore, in adjacent areas where black and steppe ferrets live, researchers often come across populations of mestizos that are simultaneously similar to both varieties.
Lifestyle and behavior
By nature, the ferret is aggressive and fearless; it can rush at an animal that is larger than it in size if it senses danger. The animal sleeps during the day and rarely leaves its shelter during daylight hours. At night the predator goes out hunting. He watches for the prey at the entrance to the dwelling or rushes after it, sometimes even catching prey on the move. The ferret is a good swimmer, so you can find it near small rivers or other bodies of water.
Types and their features
The forest ferret has 2 domesticated species:
- Ferret is a colored ferret. A decorative representative of the species, it has fluffy fur of sable, golden or pearlescent hue. A very sociable, active and inquisitive animal. Body length is 25-50 cm, weight is 800-2500 g. Frets love to sleep, they can doze up to 20 hours a day, especially in winter. The animal can be trained; you can train it to use a tray and even walk it on a leash. The diet includes food mice, mealworms, porridge with meat, and dry food. You cannot give raw food and feed at the same time; choose one or the other.
- Furo is an albino ferret. The fur is white (due to the lack of melanin) or with a champagne tint. There are some individuals with sable and pearlescent colors. The dimensions of the predator are 25-45 cm, weight - about 400 g. A distinctive feature is red eyes. It has the same qualities as the wood ferret. Loves active games and attention to himself. It is recommended to include white meat, chicken eggs, vegetables, veal and fresh fish in the diet. It is forbidden to give furo sweets, as in large quantities they can lead to the death of the animal.
Since in the wild the ferret feeds at night, these species also need to be given food at certain times - around noon, during the day and late evening. Ferrets do not eat well in the morning.
Taming methods
Taming a wild ferret is not an easy task. Predators that are caught in natural habitats will not completely trust a person even after several years. The offspring of wild ferrets born in captivity will be less amenable to training, but in order to produce cubs, the pair of animals must be provided with favorable conditions for mating.
The gullibility of these predators largely depends on age. If a ferret is 1.5-2 months old, then over time it can get used to a person, but it will not become a complete pet. A ferret over 5 years old is not at all tamed and shows aggression towards people. Such animals are very difficult to train, since constant stress can cause a ferret’s heart to break.
At home, wild animals need to be provided with a place to live, similar to their natural habitats. Also, an untamed ferret should be kept in a closed enclosure, since the animal can exhibit a high level of aggression out of fear. The cage for a predator should be multi-tiered, with a system of pipes simulating underground conditions. In natural conditions, ferrets move a lot, so housing that is too cramped can cause prolonged stress. You can make such a cage yourself; to do this, you should watch instructional videos or photos on the Internet.
It is extremely important to exclude possible noises and strong odors: animals born in the wild are extremely sensitive to this.
Ferrets recover after being carried for about 2 months. During this time, the animals should be kept at rest. Initially, the animal will hide in a shelter or corner, will not eat, and will loudly gnaw at the cage mesh at night. Over time, the animal will get used to the new living conditions and human presence. It is also important to stay close to the predator while it is feeding. In this case, the pet will begin to recognize the owner’s smell and associate it with food.
You should give the animal a name and constantly refer to it during feeding: this way the ferret will quickly get comfortable and get used to human speech. There is no need to hand feed a wild predator in the first months: it can easily scratch or bite through the skin.
The taming process takes about a year and requires a lot of effort, but a tamed wild ferret will still not become a domestic ferret and will retain its independent character.
Eating in the wild
Although the wood ferret is relatively large in size, it is a typical mouse eater. The main diet of the animal consists of:
- small rodents - mice, rats, gerbils, voles, moles, gophers and ground squirrels;
- frogs and toads;
- large insects such as locusts;
- hares and rabbits, can penetrate animal burrows and strangle young individuals;
- reptiles - lizards and snakes;
- small birds and their chicks, as well as eggs from ground clutches;
- invertebrates such as worms;
- carrion - if there is no other source of food, then the ferret will not disdain carrion.
One interesting feature of the forest ferret is noted - when attacking a bird's nest or getting into a hare's hole, the animal completely ruins them and strangles all the individuals located there. Although he only eats a small part.
Care
When getting a ferret, it is important to remember the need for vaccination. Diseases such as rabies, plague, leptospirosis will safely bypass the animal if it is given the appropriate vaccinations. It must be remembered that ferrets do not tolerate vaccinations well: they often develop allergic reactions to vaccines. Therefore, in parallel with the vaccine, the ferret needs to be given an antihistamine. Only half an hour after the indicated injection, having made sure that there is no negative reaction, you can leave the clinic and go home.
If keeping a ferret at home does not involve producing offspring, it is better to resort to sterilization of the animal. With this you can reduce the release of unpleasant odors.
Ferrets need to be bathed when kept at home, but this should be done no more than 2 times a month. For bathing, water around +37 degrees and cat shampoo are suitable. If everything is done correctly, then bathing can soon become a ferret’s favorite pastime: animals love to dive and swim. After bathing, the ferret is dried with a towel, and he must dry himself.
It is necessary to trim the claws in a timely manner; they tend to grow back quickly.
Reproduction
Already 1 year after birth, a young ferret begins puberty. The rut begins in April-May, although there are also cases when this period can begin as early as February or end in August, depending on the climatic conditions of the area where the ferret lives.
Females can give birth up to 6 years of age!
Pregnancy lasts one and a half months, the female is able to bear from 4 to 6 cubs at a time. Ferret puppies are born very tiny and helpless, blind and deaf. The weight of a newborn is 10 g, and the length of the body is 5.5-7 cm. Females are very caring and attentive mothers; they rarely separate from the cubs, and if they do have to leave the offspring, they tightly plug the entrance to the home with straw. Females selflessly protect puppies from any danger.
Within a week, the babies are covered with silky white fur. And after a month, the puppies’ eyes open and the color of their fur changes to gray-brown.
The mother feeds the offspring with milk until they reach the age of one month, and when they have milk teeth, even before the end of the lactation period, she begins to feed the young with meat. The offspring stays with the mother until autumn, in some cases until next spring. At 3 months of age, ferrets are considered adults.
Young animals can be recognized by the presence of a special juvenile “mane”.
As for males, they participate in the process only at the mating stage, and all care for the offspring is entirely the responsibility of the female.
Description
In terms of external features, the forest ferret is not much different from most mustelids of the genus Mustela: squat with short legs armed at the end with sharp long claws. The body is elongated and flexible. The weight of males is 1000-1500 g, the weight of females is 650-815 g; the length of males is 350-460 mm, the length of females is 290-394 mm. The color of an adult ferret is black-brown, the belly, legs, chest, throat, and tail are almost black (there are color variations, pure red and white). The head has a contrasting pattern reminiscent of a mask. Under the tail, ducts of specific anal glands open, the secretion of which has a pungent odor. It differs from the steppe polecat in the dark color of its fur, the absence of a sharp contrast in the black color of the legs and fur, the black color of the entire tail, and from the minks and kolin - in color (minks are chocolate brown, the kolin is red). Geographical variability in color, fur quality and body size is insignificant; about 7 subspecies are recognized as real, 2 of which live in the territory of the former USSR. It produces fertile hybrids with the steppe polecat and European mink (see Honorik).
Natural enemies of the forest ferret
Since ferrets are small animals, in the wild they have enemies that pose a mortal danger:
- Wolves. Although ferrets run fast, they rarely manage to escape from a wolf in open areas. Therefore, they try to avoid open spaces and settle where there are a lot of bushes and similar shelters.
- Foxes. Another terrestrial predator that is not averse to feasting on the forest ferret. Especially in winter, when foxes are short of food. A cunning fox can get a ferret even in its own hiding place if it is really hungry.
- Lynx. Being an insidious “master of ambushes”, the predator does not leave the animal a chance to survive. And sharp teeth can bite a ferret in one bite.
- Stray dogs. If a forest ferret gets close to a human settlement, then a dog may lie in wait for it.
- Predator birds. At night, when the ferret goes hunting, he is also hunted by eagle owls or owls. During the day, golden eagles and falcons pose a danger. Although often a fight with a bird ends in victory for the ferret, since it is capable of aggressively and fearlessly counterattacking.
- Human. The human factor cannot be excluded from this list, since it is humans who are able to reduce the population of an animal by illegally hunting for valuable fur. Human activities, such as deforestation, also cause damage to ferrets.
Character
Like any predator, the ferret prefers to stay awake in the dark, that is, at night. Owners of pets notice this feature in them. It is unusual for animals to migrate from one place to another: they dig holes for themselves and can live their whole lives in one place. Only something unexpected and serious can force them to leave their familiar and familiar territory.
The burrows of animals are characterized by increased comfort. The inside of the hole is covered with dry grass and leaves. The animal will happily take a ready-made hole dug by another animal, for example, a fox, and arrange it to its liking. Ferrets are not afraid of people. If necessary, a basement or barn in a person’s home can be suitable for housing.
Often hunger drives these predators out of the forest; they approach human habitation in search of food. After their visit, chickens and other small poultry disappear from barns and farmsteads.
Females can be distinguished by their activity, restlessness, developed intelligence, and playfulness. Females are much easier to train. At the same time, males are distinguished by increased affection for humans, they are calm and can sit still for a long time.
Interesting facts about the beast
There are several interesting facts that are worth knowing about this animal:
- among rural residents, the forest ferret has gained a negative reputation because it attacks poultry;
- belongs to valuable fur-bearing animals, but hunting for it is not carried out and is prohibited by law, since the number of ferrets is small;
- listed in the Red Book;
- in the wild it lives for 3-4 years, at home life expectancy doubles;
- the sensory system is well developed, but does not distinguish colors;
- in the wild, hybrids of a forest ferret and a mink are often found, they are called honoriki;
- the ferret is depicted on the coat of arms of the city of Boguchar (Voronezh region) and the city of Oboyan (Kursk region);
- an angry or frightened ferret may make a strange sound, similar to a hiss;
- the ferret's stomach is not able to digest organic fibers;
- to prevent domestic ferrets from emitting a characteristic musky odor, a special gland is removed;
- Leonardo da Vinci’s painting “Lady with an Ermine” depicts not an ermine at all, but a furo ferret;
So, for now, the resourceful and tenacious ferret manages to maintain its population. However, the main threat to its existence is still considered to be man and his activities. Perhaps very soon the animal will survive only in its domesticated forms.
0
0
Copy link
Lifespan
Ferrets do not live very long; in the wild they can live at most 3.5 years. This is due to the huge number of dangers that await predators from everywhere. A pet will live much longer - about 6 years, and sometimes 10 years. In order to achieve this result, it is necessary to provide your pet with quality care and adequate nutrition.