Praying mantises are large insects with a narrow, elongated body. Born predators and masters of camouflage, they ambush their prey, blending completely into the foliage and branches. By exterminating phytophagous insects, they benefit agriculture. The common praying mantis is a typical representative of the order of praying mantises, living in Europe. A characteristic feature of insects is their front legs, equipped with tools for grasping and holding prey. There are sharp spikes on the thighs and lower legs, which, like a trap, catch an unwary victim. Many people know about the mating cannibalism of praying mantises. This amazing feature has become a source of inspiration for writing scary stories and making films.
Description of the species
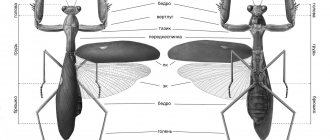
The common praying mantis (Mantisreligiosa) belongs to the order Praying Mantis, which includes 2,800 species. The insect's body is narrow and elongated. Males grow up to 43-52 mm, females are much larger - 50-75 mm. An anatomical feature of mantises is the structure of the forelimbs. Grasping legs with spiny elongated femurs and tibiae are designed for holding prey. The thigh and lower leg in a ligament function on the principle of scissors. On the inside of the coxae of the forelimbs there is a dark spot with a white mark in the middle.
Interesting fact. Despite the fact that females are larger than males, males have longer antennae and larger eyes.
The head is triangular, mobile, the insect is able to look back. On the sides there are large, convex compound eyes. In European mantises they have a black pupil. On the forehead there are long thread-like antennae and three simple ocelli. The mouthparts of the gnawing type are directed downwards. The common mantis has two pairs of well-developed wings. Light males and young females are capable of flying over considerable distances.
The forewings are narrow and leathery, they replace the elytra. The hind wings are wide, and when at rest they are folded on the back like a fan. The pronotum expands in the upper part, but never covers the head. The abdomen is elongated, soft, consists of 10 segments. On the last segment there are appendages - cerci. There are 10 pairs of spiracles on the sides of the body.
The color type of the common mantis is protective. Body color can be green (in 80% of cases), yellow, light or dark brown. Camouflage coloring allows you to blend in with the environment. When the insect is motionless, it completely mimics foliage or a twig. Camouflage serves two functions: it allows you to hunt from ambush and hide from enemies.
Information. When attacked by an enemy, the mantis opens its wings to increase in size. It sways from side to side and raises its front legs and the edge of its abdomen threateningly. All actions are aimed at scaring away the aggressor. If the enemy is too large, the mantis flies away.
Quick Facts
There are more than 2,000 species of praying mantises in the world. Some of them are almost identical and have small distinctive features.
Lives in European countries and Asia, rarely in Africa. It is large and the color consists of green and brown spots.
Chinese mantis . Some of the remaining flightable species. They have a pupil-like pattern on their legs that frightens his enemies.
Indian mantises . They live mainly in Asian countries. One of the smallest praying mantises in the world. There are spikes of different sizes on the hips. Thanks to its miniature size, it can move without flying.
Malaysian shield bearer. Distributed in the Asian tropics, with high humidity. This species is often grown at home. This pointed-eyed mantis is very large, almost 14 cm, and lives mainly in African countries. It is visually indistinguishable from tree branches and leaves because it has a similar appearance. There are bulges in the form of spikes on the eyes.
Arabian mantis. This is a friendly and harmless insect. Unlike its predatory relatives, it does not attack animals that are larger than itself.
The Asian subspecies of mantises is often used to get rid of parasites, pests and insects that carry dangerous viral diseases.
Distribution area
The Mantisreligiosa species is thermophilic and cannot be found beyond the 50th parallel. The northern border of distribution in Europe runs through southern Germany, Austria, the Czech Republic, and France. The common praying mantis is often found in southern European regions, on the islands of the Mediterranean Sea, in Sudan, and in the Middle East. Predatory insects were brought to remote parts of the world - New Guinea, the USA, and the south of Canada was partially inhabited. Climate warming is promoting the expansion of the habitat to the north. Adult Mantisreligiosa is recorded in Belarus and Latvia, where it did not live before. In Russia, insects live in large numbers on the Black Sea coast, in the Crimea and the Caucasus.
How to properly pick up a praying mantis?
For humans, praying mantises do not pose a danger, but, like any living creature, if threatened, they either run away or try to defend themselves. Therefore, when you examine an insect, pick it up without making sudden movements, otherwise the mantis may run briskly and fall. Adult mantises are able to protect themselves from injury when falling - they spread their wings, thereby reducing the speed of their fall. But for a young nymph, the fall usually ends with a rupture of the abdomen. If the mantis takes a threatening pose, it is better not to touch it: the thorny spines on the front legs can scratch you.
Lifestyle
The praying mantis lives and hunts like a typical ambush hunter. The predator freezes until the prey is within reach. It grabs prey with its front legs and starts eating from the head. Males are careful in choosing hunting objects; they attack flies, locusts and other small insects. Large females often attack victims almost equal in size to them. Aggressive individuals attack lizards, birds, and frogs. They jump on the reptile's back and bite its head. The fight continues for several minutes, in the process the hunter can become the victim. If the outcome is successful, the prey is eaten within 2-3 hours. The female remains well fed for up to 4-5 days.
You can meet Mantisreligiosa in the forest, steppe herbs, and meadows. Insects do not even avoid large cities, where they have adapted to live in grass, parks and gardens. The favorite habitats of the common mantis are tall trees and bushes. Insects prefer a sedentary lifestyle. They do not leave their usual territory, they move between tiers. For movement, four limbs are used, less often wings.
Given enough food, they spend their entire lives on one plant. Insects have excellent vision; they detect the slightest movement in the environment. Camouflage coloring allows you to get closer to your prey unnoticed. Hunting takes place during the daytime. All soft tissues of the prey are eaten, leaving chitinous legs and wings. How long a common mantis lives depends on the amount of food and gender. The age of females is longer; on average, representatives of the species live 2-3 months in natural conditions. In captivity, the life expectancy of insects increases several times and is 12-13 months.
Like any insect, the praying mantis has many natural enemies. It is hunted by birds, snakes, small mammals, and bats. The arthropod runs slowly and takes off heavily. Its terrifying dance with its wings spread like a fan scares off only inexperienced young birds. For other large hunters, the mantis is easy prey.
The female praying mantis eats the male after mating - is this true?
mating season is well known
when individuals mate to reproduce their own kind. But it is often said that this process can be used for making horror films.
The difference between their mating games and other species is that the female devours the male during mating. She turns 180 degrees and bites off the male's head
. In this case, mating does not stop, nothing changes. Males then either receive severe damage and pretend to be dead, or more often lose their heads altogether. Their vital activity ceases and death occurs. Death occurs in half of the cases.
The fertilized female then lays eggs in the ootheca
. This is exactly how the population of these strange individuals develops in a unique way.
The reason for this phenomenon is still unclear
, but according to biologists, everything can happen for the reason that the male cannot copulate while he has a head; mating begins only when the male loses his head.
A female can also eat a male because she has a strong need for proteins at the initial stage of testicular development.
Next in the video is the process of the female absorbing her partner after mating:
For fertilized individuals, everything ends just as tragically; they lay eggs in a nest, which they previously made from their foamy mucus. After laying eggs they die. Couples give lives to others, giving their own in return.
Meaning in nature
The biological significance of the common mantis is associated with its lifestyle. He is a predator that destroys harmful insects. Adults and larvae eat phytophages on trees and shrubs. Attempts have been made more than once to organize the protection of agricultural lands with the help of praying mantises. Large-scale plans to use predators as biological weapons against pests have not been successful, but many farmers buy Mantisreligiosa oothecae. They are placed in gardens to safely kill aphids and thrips.
The predatory behavior of mantises has its downsides. They differentiate between insects that are beneficial and harmful to humans. Praying mantises catch and eat honey bees, so the appearance of the species near an apiary creates problems. In most cases, people owe it to predators to control the number of pests and parasites, so as a form of gratitude, it is worth preserving the habitats of the insects themselves.
Nutrition
The praying mantis may look harmless and calm, but appearances can be deceiving. The praying mantis is a predator, and as mentioned earlier, females can eat the male without remorse.
Orchid mantises primarily eat moths, flies, bees, butterflies, grasshoppers and other winged insects. Mantises are known to attack much larger animals rather than insects. They mainly hunt small snakes, birds, frogs and mice.
Thanks to its strong jaw, the praying mantis can easily hunt and process food. A homemade diet is different from a diet in a terrarium. The main advantage is “live” food in small sizes. You can use plant foods that are high in fiber. As a rule, these are non-acidic, dense fruits.
Features of reproduction
Sexual dimorphism of insects is clearly expressed in the sizes of male and female individuals.
The sexual behavior of insects is closely studied by scientists. Relations between partners are divided into two stages:
- pre-court;
- pairing.
In temperate climates, the breeding season is August–September. At the end of the abdomen of males there are sensitive olfactory organs - cerci. With their help, insects capture the pheromones of females. The courtship process involves carefully approaching the object of passion. The male slowly and carefully moves towards the female, trying to walk around her from behind. When she turns her head, she freezes in place, taking advantage of the fact that mantises do not react to motionless figures. Courtship takes several hours, but allows you to remain alive until mating.
Having reached a potential partner, the male jumps on her back. It supports itself with its legs, placing them in special grooves on the sides of the female’s mesothorax. In this safe position, he begins copulation. The process can last 4-5 hours. In 50% of cases the male manages to escape. Having run away from his partner to a safe distance, he freezes for several minutes. This is necessary for relaxation.
Praying mantises are insects with incomplete metamorphosis. The development of an individual occurs in 3 stages: egg, larva, imago. 10-11 days after fertilization, the female common mantis lays eggs. The masonry is 100-300 pieces. A sticky secretion is released along with the eggs. After the liquid hardens, an ootheca is formed - a protective capsule in which the masonry is not exposed to external influences. The ootheca is yellow or brown in color and is attached to branches or stones. The eggs remain overwintering.
Larvae
The offspring of praying mantises appear in the spring. The larvae are born with many spines on the body and two filaments on the abdomen. The spines help the young to get out of the capsule. The larvae hang on the tail threads, this is how the first molt occurs. They will have to go through 4 more molts before they mature. Wingless larvae are similar in appearance to adults. They feed on fruit flies, aphids, and thrips.
Cannibalism during mating
During the breeding season, under the influence of sex hormones, the aggressiveness of females increases. The partner is in danger if the female has been fasting for 2-3 days. She may attack the male before copulation. This will provide the necessary nutrients, plus the size of the prey is larger than regular insects. The partner runs the risk of dying during mating; loss of the head does not affect copulation. Eating the male after accepting the spermatophore has the same reasons. The female praying mantis provides nutrition for future offspring, increasing the chances of producing a large number of eggs.
Interesting fact. Males choose large, well-fed females to mate with, this reduces the risk of being eaten during fertilization.
How to choose a praying mantis?
It is best to purchase praying mantis larvae (nymphs). When you take an adult mantis into your home, you cannot know its age. It is possible that the insect will quickly die without producing offspring. Unfortunately, the life of mantises is short - only 5-9 months, rarely, with proper maintenance and care, 1 year. Adults live only about two months. Males are usually the first to die - after the breeding season, they lose the desire to hunt, they become exhausted and lethargic.
When choosing a nymph, give preference to active ones. Inspect the limbs for damage. The abdomen should have a full appearance.
What signs can be used to determine that a praying mantis is an adult?
Adults have wings, while nymphs do not. However, there are also completely wingless species of mantises, for example, the ground mantis (Geomantis larvoides).
Tips on maintenance and nutrition
The domestic praying mantis is an exotic pet that can live at home for about a year. Insects are smart, sociable, and quite large in size. To house your pet you will need a terrarium. They come in two types: plastic and glass. The second option is preferable. Air access is provided by a mesh lid. The length of the dwelling should be 3 times the size of the praying mantis’ body.
The heat-loving insect requires a temperature of 22-26°C. It can be maintained with a special heater or a lamp installed near the container. Recommended humidity 40-60%. Maintained by daily spraying of the substrate. It is not necessary to install a drinking bowl; moisture on the walls of the terrarium is enough. The pet is picked up without fear; the more often the contact occurs, the sooner it gets used to the person.
Sand or coconut sawdust is poured onto the bottom as a substrate. Twigs and driftwood are placed inside for the insect to crawl on. An important nuance when keeping several common mantises is placing them in different containers. This will prevent cannibalism, which is typical for the species. Food for the predator includes grasshoppers, flies, locusts, crickets, and cockroaches. Pets are fed every 2-3 days. Depending on the size, 1-3 food insects are given at a time. By launching the prey inside the container, you can watch the hunt.
What to feed a praying mantis
Provide your praying mantis with a variety of insects to feed on. The best way to ensure nutritional needs are met is to feed several types of prey: fruit flies and aphids, as well as a variety of flying insects such as moths, fruit flies and house flies.
Occasionally, the praying mantis' menu may include a cricket or mealworm for larger individuals. Feed the mantis prey with a busy gut, giving your pet food enriched with vitamins that are passed on to the mantis.
When drinking water, use a small shallow bowl with pebbles or a piece of sea sponge to avoid drowning. This water will also increase the humidity. Most mantises obtain water by drinking drops of water from fog-formed vegetation, although some may use a water bowl. Make sure the humidity is not too high.
Security measures
Despite the widespread distribution of insects in some regions of Russia, the common mantis is listed in the Red Book. It is classified as a rare species in the Chelyabinsk, Voronezh, Kurgan, Belgorod and Lipetsk regions. The number of insects has decreased as a result of plowing of land, grass burning, continuous hayfields, and the use of pesticides in cultivating fields. In the habitats of mantises, economic activity is limited. To protect the species, plowing land, grazing livestock, using pesticides, killing or capturing insects is prohibited. In Germany, the common mantis is included in the Red List as a declining species. It cannot be caught in the wild and kept at home as a pet.
Where can I buy a praying mantis and how much does it cost?
You can find praying mantises in some pet stores or look for advertisements for the sale of these wonderful insects on the Internet.
The price of a praying mantis primarily depends on the species. Thus, the common mantis (Mantis religiosa) can be purchased for 500-1000 rubles, the orchid mantis (Hymenopus coronatus) - for 3000 rubles, the spiny flower mantis (Pseudocreobotra wahlbergii) - for 1500-4000 rubles. The most expensive species, perhaps, is the “devil’s flower” mantis (Idolomantis diabolica) – 11-12 thousand rubles.
It should be noted that it is better for beginners to pay attention to types that are easy to maintain. For example, the African (large) mantis (Sphodromantis centralis) is easy to keep and the most popular among beginners.
The praying mantis is an insect from another planet, video
And in conclusion, we bring to your attention an interesting popular science film about praying mantises.
Common mantis
, or
religious mantis
(lat. Mantis religiosa) is an insect from the family of true mantises of the order Praying Mantis. A large predatory insect with forelimbs well adapted for grasping food. Reaches 42-52 mm (male) or 48-75 mm (female) in length.
Mantis
- a well-known insect with a characteristic appearance, even residents of those places where mantises are not found usually have an idea of what this insect looks like. The praying mantis is quite popular due to its characteristic “alien” appearance.
It is often shown in popular science films about insects, and for some, the mantis is a real pet, just like a cat or dog. Perhaps someone else knows about the “mantis style” - a style of martial arts named after this insect.
The common praying mantis (lat. Mantis religiosa) is a large insect of the cockroach order, reaching 7 cm in females and 5 cm in males; in addition to the fact that females are longer than their gentlemen, they are also noticeably more massive. The color of the mantis is protective - green or brown - depending on the color of the plant it prefers to hide. The praying mantis is a typical ambush predator. The mantis spends most of its time hiding on a plant and waiting for prey.
The characteristic pose of a hidden praying mantis with folded front grasping legs is what gave this insect its unique name - the folded legs of a praying mantis resemble the hands of a praying person raised in supplication.
By the way, the same is true for the Latin species name of the common mantis - which consists of two words mantis, which is translated from Greek as “prophet” and the Latin word religios, which clearly means “religious.” Interestingly, mantises were spotted near the Holy Protection Goloseevskaya Hermitage, where Mother Alypia lived. The other two pairs of legs of the mantis are running; the mantis also has well-developed wings, but flies rather reluctantly; heavier females especially rarely rise into the air. Praying mantises are quite aggressive insects, sometimes attacking large insects of equal and sometimes greater size.
The color is protective, very variable, ranging from green or yellow to brown-gray or dark brown. The pronotum is of moderate length, the front legs are grasping, in addition to obtaining food, they are also used for movement. The hind legs are running. The wings are well developed in both males and females (although females, due to their impressive size, fly very poorly and reluctantly). The abdomen is ovoid, rather long.
A special feature of this species of mantis is its wide distribution: it lives throughout Southern Europe (south of the 55th parallel), Western and Central Asia, Africa, partly Southeast Asia and Australia (where it competes with related species). Introduced to the USA. In Crimea it is gradually replaced by the tree mantis (Hierodula Tenuidentata). Single finds were noted in the steppe and mining zones of the Southern Urals. This is the northern boundary of the species' range. Listed in the Red Book.
Females of some species may eat males during mating. After mating, the female lays from 10 to 400 eggs, which, like cockroaches, are packed into oothecae. Ootecae hang on the grass or on the branches of trees and shrubs. In regions with fairly cold winters, it is the oothecae that are the overwintering stage.
The praying mantis in the first larval stage has a worm-like shape, and after leaving the ooteca, it molts and acquires the characteristic appearance of a praying mantis.
The common mantis sometimes plays a useful role in agriculture as an exterminator of harmful insects (such as flies, mosquitoes or other agricultural pests). But the beneficial effects of mantises are compensated by the fact that they also destroy beneficial insects (bees, other beneficial entomophages).
The common mantis is an insect belonging to the family of true mantises. This is the most common representative of the species in Europe.
Bonus facts about the praying mantis:
- China has several martial arts based on the movements and principles of the hunting mantis.
- The color and shape of the praying mantis can be very different; they can disguise themselves as flowers, twigs, leaves, etc. This phenomenon is called mimicry. Flower mantises are so colorful and convincing that unsuspecting insects come to collect nectar from them... and become lunch in the meantime.
- They can see the movement of other animals up to 18 meters away!
- They are often eaten by bats, so you should be wary of them too.
- The USSR once decided to use praying mantises as a natural weapon against unnecessary insects in agricultural life, but it didn’t work out. And all because praying mantises eat not only bugs, aphids, etc., but also bees, and this has only begun to cause harm.
04/08/201926/08/2019 TanyaVU 1857
Insect specificity
The most specific feature of such a unique insect is its color, which matches the color of individual elements of its habitat: stones, grass, flowers, tree leaves. The most common praying mantises are yellow and brown and green in color, which accounts for 80% of their total number. It is almost impossible to see a motionless mantis in the natural environment. An insect can only reveal its presence by movement.
The mantis moves slowly, but in case of danger it is able to very quickly move to a safe distance and freeze in place again. Because the favorite pose of such a unique insect is expectant. Like spiders, praying mantises are ambushers, ready to wait patiently for days on end for an unwary mosquito.
Praying mantises lead a solitary lifestyle. They are more active during the day, as potential victims are tracked visually. It is precisely because of the long wait that the overwhelming majority of insects have a protective coloring, and some specimens have a special body shape. For example, species of praying mantises that live in grass are painted green and resemble a blade of grass, while brown-colored insects resemble dry twigs. In the praying mantis Choerododis stalii, tiny spots on the body imitate damage to the leaf blade of the plant. Tropical species of mantises that wait for their prey in flowers have a curved abdomen and flat lobes on their feet, reminiscent of flower petals.
The Orchid Mantis, which is white in color when young, is especially striking in its adaptability to natural colors, but as it matures it becomes pink, completely indistinguishable from the flower.