Elephants are the brightest representatives of large mammals that live on land. Their predecessors were mammoths, Meriteria, mastodons and other extinct individuals that had tusks and a trunk. These animals belong to the elephant family, which is divided into three species: Indian, savannah and forest. The body weight of one adult male is approximately equal to the total weight of 100 adults. Therefore, you can easily calculate how much an elephant weighs - about 7 tons.
Appearance of an elephant
Appearance of an elephant Appearance
of an elephant
Appearance of an elephant
Appearance of an elephant
Appearance of an elephant
Elephants can boast of a unique appearance: a long trunk and large ears immediately catch the eye, even against the backdrop of the impressive dimensions of adult individuals. And gray skin is not able to hide a large number of wrinkles located throughout the body.
Ears
An elephant flaps its ears to cool itself.
For an elephant, ears act not only as an organ that allows you to hear sounds around you, but also as an air conditioner. Since most individuals live in hot climates, they need to regularly cool their bodies. And big ears are great for this. Elephants wave them, thereby creating coolness around. Because of this, the blood in the ear vessels cools. It then spreads throughout the body, reducing the temperature.
Interesting fact : Elephants' ears have a unique pattern of blood vessels, just like human fingerprints.
Leather
Close-up of elephant skin
Elephants have thick skin, which is why their body is covered with folds and wrinkles. This helps retain moisture inside the body and prevents temperature rise. However, elephants are quite sensitive to insect bites and sunlight. To protect themselves from them, they roll in the mud and douse themselves with water.
Interesting fact : in some parts of the body, the skin thickness of an elephant reaches 2.5 centimeters.
Tusks and teeth
Elephant tusks close-up
The elephant has two tusks located on the upper jaw. They are also the only incisors. With their help, the animal clears the road from obstacles, obtains food and defends itself from enemies. Tusks are made of ivory (dentine) and are of great value to humans. Deciduous incisors are present in individuals from birth, but when they grow to 5 cm in length, they fall out. In their place, the indigenous ones begin to be cut. Within a couple of years they become so large that they begin to stick out from behind the upper lip. Tusks grow continuously throughout life.
Elephant teeth on the lower jaw
An elephant's molars are located on both jaws. Over time, they are gradually updated, with some individuals changing up to six sets. When new teeth emerge from the gums, they are initially located behind the old ones, but gradually push them out and move forward. In their shape they resemble bricks.
Interesting fact : one adult tooth can weigh up to 2.4 kg, and their total number does not exceed 4-6.
As elephants age, their teeth become deformed and sensitive. Because of this, they gradually switch to softer foods. Adults eat mainly grass near swamps, as it is not so tough.
Trunk
An elephant eats with its trunk.
An elephant's trunk combines the functions of its nose and upper lip. Thanks to the eight muscles contained inside, the animal can turn it in any direction and bend it as it wishes. In most cases, the elephant operates its trunk like a person with its hands: it pulls up tree branches, lifts objects, uses it for tactile sensations, etc.
Interesting fact : the trunk contains approximately 150 thousand muscle lobes, which makes it very strong and flexible.
At the tip of the trunk there are two nostrils. Through them, air enters, passes through long channels and ends up in the lungs. With their help, the elephant also drinks water. True, for this process the animal uses cunning. It lowers its trunk into the liquid and draws it in like air. But when the water reaches the middle of the nasal sinuses, the elephant lifts its head and splashes it into its mouth.
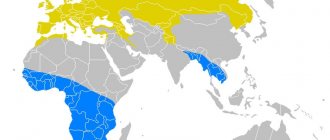
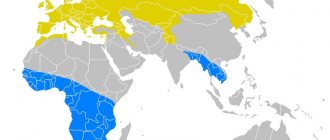
Habitat - where elephants live
Habitat of elephants: African (green) and Indian (red)
For the most part, elephants live in Africa and South Asia, mainly in India. They enjoy the local climate and a wide variety of food. Thanks to these two habitats, two types of elephants are distinguished: African and Indian.
Interesting: Snow leopard