Many people underestimate the importance of the work of earthworms. These representatives of the invertebrate kingdom are best known for crawling out of the ground in large numbers after heavy rain. They are often used as bait by numerous fishing enthusiasts. Darwin also noted the fact that worms perform an important function in nature, acting as a kind of agricultural technicians. In the process of creating an extensive system of tunnels, which the earthworm digs through, excellent aeration is formed by supplying air to the inner layers of the soil.
Thanks to excellent aeration, the respiratory activity of many plants is facilitated. Feeding on organic matter and waste, worms ensure the grinding of soil components, enriching them with their secretions. The amazing ability of representatives of this species is the ability to disinfect large areas of soil, sterilizing it from harmful bacteria. Thanks to countless holes, forming a kind of capillary system, ideal drainage and aeration of the soil is ensured.
Features of earthworms and habitat
The body of an earthworm can reach three meters in length. However, on the territory of Russia there are mainly individuals whose body length does not exceed 30 centimeters. In order to move, the worm uses small bristles, which are located on different parts of the body. Depending on the variety, there can be from 100 to 300 segments. The circulatory system is closed and very well developed. It consists of one artery and one central vein.
The structure of an earthworm is very unusual. Breathing is realized with the help of special hypersensitive cells. The skin produces protective mucus with a sufficient amount of natural antiseptics. The structure of the brain is quite primitive and includes only two nerve nodes. Based on the results of laboratory experiments, earthworms have confirmed their outstanding regeneration abilities. The severed tail grows back after a short period of time.
The genital organs of the earthworm are also very unusual. Each individual is a hermaphrodite. She also has male organs. Based on biological factors, all such worms can be divided into several subgroups. Representatives of one of them search for food on the surface of the soil layer. Others use the soil itself for food and emerge from the ground extremely rarely.
The earthworm is a type of annelid. Under the skin layer there is a developed muscle system, consisting of muscles of various shapes. The mouth opening, from which food enters the esophagus through the pharynx, is located on the front of the body. From there it is transported to the area of the enlarged goiter and the small size of the muscular stomach.
Burrowing and bedding earthworms live in places with loose and moist soil. Preference is given to moist soils of the subtropics, marshy lands and the banks of various reservoirs. In steppe areas, soil varieties of worms are usually found. Litter species live in the taiga and forest-tundra. The coniferous broad-leaved strip can boast the highest concentration of individuals.
What kind of soil do worms like?
Why do earthworms love sandy loam and loam soils? Such soil is characterized by low acidity, which is best suited for their life. Acidity levels above pH 5.5 are detrimental to the organisms of these representatives of the ringed type. Moist soils are one of the prerequisites for population expansion. During dry and hot weather, worms go deep underground and lose the opportunity to reproduce.
Interesting Facts
The table below contains answers to the most frequently asked questions.
| Question | Answer |
| What do earthworms eat? | The diet of these animals consists of organic plant matter and soil fragments. |
| How long does this individual live? | No more than 10 years. |
| How many hearts does an earthworm have? | The heart, as an independent organ, is absent. Its function is performed by ring channels that contract to ensure blood circulation. |
| Is the earthworm hermaphrodite or dioecious? | These individuals are hermaphrodites. |
| Does an earthworm develop with metamorphosis or direct? | In animals of this species, development is direct. |
| Is the earthworm a decomposer or a consumer? | They belong to the category of decomposers. |
| Is the earthworm autotrophic or heterotrophic? | These animals belong to a separate group - saprotrophs. |
Earthworms are part of the first tier of the food pyramid of the biosphere. Sexually mature individuals participate in the decomposition of plant waste, loosen the soil, and eat rotting products with a high concentration of nitrogen. The body of these animals is covered with a layer of thick mucus, which consists of enzymes with pronounced antiseptic properties.
Character and lifestyle of the earthworm
The active and productive life of an earthworm occurs at night. As soon as night falls, many individuals crawl to the surface of the ground in search of food. However, the tail usually remains in the ground. By morning, they return to their holes with prey, dragging pieces of food into them and masking the entrance to their shelter with blades of grass and leaves.
The role of earthworms in nature is difficult to overestimate. The worm literally passes an incredible amount of soil mixture through itself, enriching it with beneficial enzymes and killing harmful substances and bacteria. The worm moves by crawling. Retracting one end of the body and clinging to the roughness of the ground with its bristles, it pulls up the back part, making its many passages in a similar way.
How do earthworms survive winter?
During the winter, the vast majority of individuals hibernate. A sharp drop in temperature can instantly destroy worms, so they try to burrow into the soil to a depth in advance, often exceeding one meter. Earthworms in the soil perform the most important function of naturally renewing it and enriching it with various substances and microelements.
Benefit
In the process of digesting semi-fermented leaves, the worms’ body produces specific enzymes that contribute to the active generation of humic acid. Soil that has been loosened by earthworms is optimal for a wide variety of representatives of the plant kingdom. Thanks to a system of intricate tunnels, excellent aeration and ventilation of the roots is ensured. Thus, the movement of the earthworm is an important factor in the task of restoring the beneficial qualities of the soil.
The earthworm is in fact very useful for humans. It makes the soil layers fertile and enriches them with all kinds of nutrients. However, the total number of individuals in many regions of Russia is rapidly declining. This happens due to the uncontrolled introduction of pesticides, fertilizers and mineral mixtures into the soil. Earthworms are also hunted by numerous birds, moles, and various rodents.
What is vermicompost and how is it useful?
Vermicompost is an organic fertilizer that people obtain as a result of processing organic waste with the help of earthworms and beneficial microorganisms.
The use of such natural fertilizer on the site helps solve the following problems:
- reduce the number of pests and weeds on the site;
- bind heavy metal residues and remove residual radiation;
- get a generous and high-quality harvest without the use of chemical fertilizers.
Why do earthworms come out after rain?
After rain, you can see a large number of worms on the asphalt and soil surface, what makes them crawl out? Even the name “earthworms” indicates that they love moisture very much and become more active after rain. Let's consider several possible reasons why earthworms crawl out to the surface of the earth after rain.
Soil temperature
It is believed that worms crawl to the surface in search of warmth, since after rain the soil temperature drops by several degrees, which causes discomfort for them.
Changes in acid-base balance
Another theory says that the worms crawl to the surface due to a change in the acid-base balance of the soil after rain, it becomes more acidic, which negatively affects these diggers. According to researchers, emergency evacuation to the soil surface saves them from death in an acidic environment.
Lack of air
The third theory explains that after rain there is more oxygen in the top layer of the soil, so the worms crawl up en masse. Water enriches the upper layers of the earth with oxygen, and many species of worms love moisture and vitally need sufficient oxygen. And through the surface of the body, oxygen is absorbed best in a humid environment.
Trips
British scientist Chris Lowe suggested that worms crawl to the surface of the earth during rain in order to make a long journey to new territory. On the surface, worms are able to crawl much further than underground, and dry soil causes discomfort when moving, strong friction is created, and grains of sand stick to the surface of the worm’s body, injuring it. And after rain, the surface of the earth is highly moistened, which allows them to freely travel to new areas of the ground.
Sounds of the rain
Another scientist, Professor Joseph Gorris from the USA, suggested that earthworms are frightened by the noise of rain, since the vibrations it creates are similar to the sound of the approach of their main enemy, the mole. That is why some fishermen use a technique to lure bait to the surface: they insert a stick into the ground, attach a sheet of iron to its surface and pull it so as to create a vibration, which will be transmitted into the ground through the stick. When frightened, the worms climb to the surface of the earth and become easy prey for experienced fishermen.
The benefits of worms for humans
Until now, no more effective way of restoring eroded, depleted or contaminated soils has been invented than breeding earthworms. Vermicultivation (growing invertebrates in captivity) makes it possible to produce vermicompost on an industrial scale and enrich large areas of land with it.
Summer residents do not have to propagate vermiculture artificially. Having assessed the importance of worms in agriculture, a farmer can attract worms to his plot in the following ways:
- avoid deep plowing (it is better to dig or loosen with a flat cutter);
- mulch the surface to avoid drying out of the soil and sudden temperature changes;
- leave a minimum area of the site without planting (vegetation prevents moisture evaporation);
- in the fall, leave some plant debris on the beds (worms need food);
- reduce the use of chemicals;
- annually add compost or humus as fertilizer;
- Do not burn plant waste, but compost it and subsequently add it to the soil (especially since worms do not like excess ash).
Breeding worms on the site also has a side effect - the abundance of invertebrates attracts moles. Vermicultivation in closed containers will help avoid this. As a useful product, the farmer will receive not only vermicompost , but also worm biomass for feeding livestock or selling.
Reproduction and development
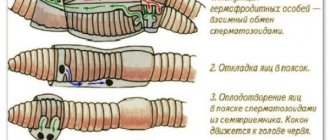
The life cycle of an earthworm is the same for all types of small bristles. Earthworms are hermaphrodites. Every adult has both male and female reproductive organs. Invertebrates reproduce sexually through cross-fertilization.
During the mating process, two mature individuals exchange sperm. At the same time, the cells of the belt (a thickening located in the first third of the body) secrete mucus, from which a cocoon is formed for oviposition and a protein substance for nourishing developing embryos. Together, the secretions form a kind of friction.
The worm crawls out of this formation with its rear end, laying eggs in the mucus. The edges converge, and the eggs remain under the reliable protection of the cocoon, which the worm leaves in the hole. Within 2–4 weeks, embryos develop inside the cocoon, after which small worms are born. After about 3–3.5 months they reach adult size.
How long an earthworm lives depends on the species and environmental conditions. On average, life expectancy is 4–7 years.
Who else lives in the soil?
The well-being of the soil is ensured by numerous soil inhabitants, but most of them are so small that we do not notice them. Healthy and fertile soil is full of life: bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoa, mites, springtails, larvae, worms, ants, nematodes, millipedes, enchytraeids and much more.
All depend on each other, many exist in symbiosis. Manipulations with herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides destroy established connections and the vacated living space is very quickly occupied by aggressive forms, most often pathogenic.
Worms feed on dead organic matter, but without soil microorganisms they will not be able to do this. Thus, the clean land beloved by many without a single weed is half dead, its biocenosis is disturbed, it requires constant labor and investment in the form of fertilizing, loosening, weeding, and watering. Instead of soil biota, gardeners work. And vice versa - if there is organic matter in the zone of plant roots, all soil living creatures will actively work there, providing the plants with everything they need.
Methods of gardening and gardening, of course, are everyone’s personal business. But there are already more than a dozen annelids in the Red Book of the Russian Federation, and behind them in the chain are all those who feed on them.
Popular message topics
- The work of Yuri Yakovlev
Yakovlev Yuri Yakovlevich is a Soviet writer and screenwriter, creator of his own books for children. His son is Ezra Howkin. Yuri Yakovlev was born on June 22, 1922 in the city of Leningrad. - Pegasus - constellation
The vast and unidentified space has always been of genuine interest to people of all ages. The main object of study are stars. Since ancient times, people have looked at the night sky and fantasized, - Interesting facts about the sea
Almost every person, when he hears the word “Sea,” imagines a beach, small waves and a light warm breeze. We always associate the sea with relaxation, vacation and summer.
Internal structure
The internal structure of earthworms is quite complex.
The circulatory system is closed and consists of two main vessels:
- abdominal (blood moves from the front of the body to the back);
- dorsal (blood moves from the back of the body to the front).
The main vessels are connected by ring vessels located in each segment of the body and passing into smaller capillaries. Some annular vessels are thickened and can contract, moving blood from the dorsal to the ventral vessel.
Respiration of earthworms occurs through the surface of the body.
The digestive system is connected in series:
- mouth opening;
- pharynx;
- esophagus;
- muscular belly.
From the stomach and almost to the end of the body runs the middle intestine, where food is digested and absorbed. Undigested residues enter the hind intestine and are then eliminated through the anus.
The excretory system is a set of thin ring-shaped tubes, one end of which enters the body cavity and the other exits. In addition, the worm has special excretory pores.
The nervous system consists of the brain (a large collection of nerve cells) and the abdominal brain with nerve ganglia in each segment, from which we can conclude that each segment is independent, but the work of all organs is coordinated.