The Brazilian poisonous traveler spider is one of the most dangerous arthropods. It even occupies a certain place in the Guinness Book of Records as the most dangerous species of the squad.
After a bite, the victim dies within 20-30 minutes without assistance, and small animals die even faster. The wanderer lives in South and Central America.
But because of its love for bananas, it can be transported to another continent in a shipping container along with fruit. Despite its venomous nature, the Brazilian spider attacks humans only in self-defense. But if he bites once, he will immediately try to attack again.
Description of appearance
The Brazilian wandering spider grows to a size of 15 cm, which is equal to the size of an adult's hand.
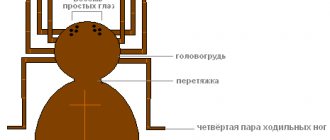
Ranked among the largest spiders. The color is varied - gray, brown, black, red, brown. The body is divided into the abdomen and cephalothorax, connected by a thin bridge. Long powerful legs in the amount of 8 pieces. Well visible mandibles. The photo is located below. The entire body is covered with small, dense hairs. Legs serve as instruments of movement and are organs of smell and touch. The spider has 8 eyes on its head, providing a wide range of vision.
On a note!
The wandering spider sees in different directions, but does not have good vision. Perceives silhouettes, shadows, and responds well to movement.
Brazilian wandering spider
Nutrition
The Brazilian wandering spider hunts at night. Having captured prey in a trap, thanks to its legs it feels well all the vibrations around it.
Having chosen a victim, the animal grabs it with its limbs and injects a deadly poison that instantly paralyzes the victim. Attempts to get away from him usually do not work; while hunting, the spider can reach speeds of up to 5 km/h.
The most common food sources are insects, other spiders, small rodents, frogs and lizards. Small prey dies instantly, larger ones live for a few more minutes.
Simultaneously with the poison, the spider injects its own saliva into the victim’s body, which liquefies the insides. Subsequently, the food is already absorbed in the stomach.
Sometimes arthropods leave the caught insect as a reserve. To do this, the prey is wrapped in a web, like a cocoon.
Wandering soldier spiders, one of the most poisonous spiders on Earth
Correctly called: “Brazilian soldier spiders”, or “Brazilian wandering spiders”. In books and publications we often come across the “banana spider,” a name that denotes many different spiders of the genus Nephila (N. clavipes) and Phoneutria, to which the Brazilian soldier spiders belong. Representatives of the genus Phoneutria are the most poisonous spiders. Their favorite habitat is the banana plantations of Latin America, so they have another name given to them by the people: “banana spider.” The genus of spiders Phoneutria Perty is widespread on the American continent. Habitats of species of this genus:
· Phoneutria bahiensis – eastern Brazil, forests on the coast;
· Phoneutria boliviensis – South and Central America;
· Phoneutria eickstedtae – Brazil;
· Phoneutria fera - Suriname, Peru, Ecuador, Guyana, Brazil;
· Phoneutria keyserlingi – forests of the eastern coast of Brazil;
· Phoneutria nigriventer – northern Argentina, eastern Brazil, Uruguay;
· Phoneutria pertyi – eastern coast of Brazil;
· Phoneutria reidyi – Peru, Brazil, Venezuela, Guyana.
Spiders were also called “wandering” because of their dietary preferences, which affected their lifestyle. Soldier spiders do not weave webs. These fast creatures are very active. They constantly move and do not stay in one place for long. They do not use or weave webs. They spend their days searching for food. The most poisonous spider, oddly enough, loves to feast on bananas. Therefore, there are many of them on banana plantations in tropical America. In search of food, the banana spider often ends up in residential buildings, turning into a formidable source of mortal danger. The poisonous spider, the photo of which you see, is found not only in the wild. Quite often they end up in people's homes straight from a bunch of bananas from the store. He can be found anywhere in the house. They find temporary shelter in folds of clothing, boxes of fruit, and inside furniture. Although bananas are a delicacy for the most poisonous spiders, soldier spiders are still predators. Their main diet is insects and other types of spiders. The size of the spider is small, with elongated legs they reach about ten centimeters. But despite its modest size, the most poisonous spider is an excellent hunter. It attacks small reptiles: lizards, snakes, frogs. It can even attack small birds that are much larger than it. Therefore, we can say that soldier spiders are aggressive and very dangerous creatures for humans. Death from a spider bite occurs after 2-6 hours. Although the banana spider is one of the most poisonous spiders on Earth, deaths from their bites are fortunately not the rule. The fact is that the toxicity of its venom is inferior to that of, for example, poisonous snakes. And its effect greatly depends on the body weight of the victim. The greater the mass, the weaker the effect. Spiders of the species Phoneutria fera can release a fairly significant dose of poison into the human body. But this does not always lead to death. The poison is produced by special glands located at the tips of the chelicerae. Getting under the skin, it causes a severe allergic reaction. If a person is healthy and adult, then usually the bite of the most poisonous spider does not lead to death. But when a child or a sick person with a weakened immune system is bitten, death can occur quickly if medical assistance is not provided. The most powerful neurotoxins contained in the venom and extremely aggressive, fearless behavior have given the banana spider the reputation of not only “the most poisonous spider,” but also “the most dangerous” to humans. A spider bite is very painful. The poison causes symptoms of severe intoxication, then, after a certain period of time, the respiratory muscles are paralyzed. A few hours after the bite the person dies. But, if medical assistance is provided immediately, death can be avoided. This is how the lucky ones who received such help in time describe the bite of the most poisonous spider. Doctors administered an antidote to them, which saved their lives. The bite is compared to the prick of a sharp thorn that penetrates very deeply. Dizziness sets in. There is a strong pressure in the chest, making it difficult to breathe normally. The pressure in the vessels of the circulatory system increases sharply. You can feel your heart beating strongly. But in Latin American countries, tragedies still happen today. An incident that occurred in Brazil: children were playing and climbed into the attic of their house, where they saw a spider. But they were not afraid, but decided to play with him. The soldier spider bit the girl. Her brother rushed to her aid. He wanted to throw it aside, but he was also bitten by the most poisonous spider. The children's parents immediately called an ambulance, which arrived half an hour later. But for the girl this time turned out to be fatal. Only thirty minutes, but she could not be saved. The behavior of the most poisonous spider is aggressive, but at the same time it does not attack large animals or humans. Bites occur more often due to the fact that a person simply does not notice the spider, which is hiding in a shelter. Or, out of ignorance that the spider is poisonous, they are caught and picked up. It is common knowledge that snake venoms are used in medicine. They make effective medicines. The banana spider has venom, which also has interesting properties. According to the testimony of men who suffered from the bite of the most poisonous spider, during the action of the poison they felt a strong, painful erection (priapism). And after recovery, they claimed that the quality of their sex life had improved greatly. This gave scientists a reason to begin researching the venom of soldier spiders. Research is underway suggesting that the spider toxin Tx2-6, which causes this reaction in the body, can be used to create medications to stimulate erections.
Body size and structure
Banana spiders look terrifying - the body is from 1 to 4 centimeters, the paw span reaches 12 centimeters. The females that weave webs are of such enormous size; the males are several times smaller. The body is covered with small hard hairs, the color is gray, brown, almost black.
The female lays eggs in cocoons, which she attaches to the web in secluded places. Each female has up to a dozen cocoons with 10-50 eggs.
The legs of the Nephila spider are powerful and equipped with hooks. Females quickly weave a web, secreting a liquid secretion of different composition. The network in one row contains absolutely even cells, which increase in size in the rows farthest from the center.
If the trembling prey destroys the cocoon, the female quickly runs up and restores the net. The prey has no chance of escaping.
Goliath tarantula
Tarantula Goliath
The spider is of impressive size, can reach 170 grams, its height including legs is 30 cm, belongs to the tarantula family. Lives in the tropics of South America. It builds burrows up to half a meter deep with the entrance covered with cobwebs. Females can survive up to 25 years, males - up to 6.
Goliath suddenly sneaks up and quickly pounces on its prey, poisoning it with its poisonous fangs. It feeds on frogs, small snakes, mice and birds.
The Goliath tarantula is capable of producing powerful sounds with its chelicerae, which can be heard even 5 meters away. To defend themselves, they use their bright brown hairs, which irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, which the spider shakes off its body towards the enemy.
Bite and its consequences
A Brazilian wandering spider bite can cause full-blown poisoning or be limited to a few painful punctures in the skin. The two most famous and dangerous species of wandering spiders are Phoneutria fera and Phoneutria nigriventer.
Brazilian wandering spiders are known for their aggressiveness, as well as their highly venomous bite. However, it is interesting that this behavior is actually a defense mechanism.
When threatened or attacked, they raise their first two pairs of legs, signaling to their predators that they are ready to attack. Their biting is thus an act of self-defense, and they only do so when provoked, either accidentally or intentionally.
If you find yourself in a situation where you are bitten by one of these spiders, you may experience symptoms such as sweating, goosebumps, and severe burning pain at the site of the bite.
Within 30 minutes or so, an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) occurs, blood pressure increases, abdominal cramps occur, body temperature drops below normal, nausea, dizziness, blurred vision and seizures begin.
If you are bitten by a wandering spider, you should immediately seek medical attention from an appropriate facility, regardless of whether there are initial symptoms. This is very important as the poison can threaten your life.
The venom of these spiders is a complex cocktail of toxins, peptides and proteins that affects ion channels and chemical receptors in the neuromuscular system of the victims.
It so happens that the venom that the Brazilian spider Phoneutria nigriventer injects into its prey contains several toxic polypeptide fractions. Some of them have been purified and shown to contain the very potent neurotoxin PhTx-3 and six neurotoxic peptides (Tx3-1-Tx3-6).
The experiment showed that PhTx3 and one of the named peptides, TX3-3, act as calcium channel blockers, reducing its amount. A decrease in the amount of calcium affects the entry of glutamate3 and acetylcholine2 into the rat brain.
In simple terms, the venom of Brazilian wandering spiders affects brain function and disorients the victim.
Habitat and lifestyle
The Brazilian wandering spider lives in the Amazon basin and tropical forests along the Atlantic coast. Found in Brazil, northern Argentina, Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela. It was introduced to Uruguay and Paraguay, where it took root and began to reproduce.
In Russia, banana spiders are found only in large terrariums and in some people who like to keep exotic animals at home. Once released into the wild, they die because the climate is not suitable for their existence. Theoretically, spiders could enter Russia in banana boxes, but there have been no officially confirmed cases yet.
This poisonous arthropod is solitary by nature. In search of prey, he walks around his territory, attacking any relative who tries to hunt in his domain. During mating games, he can brutally fight with a rival for the future mother of his children. Cannibalism is not alien to this genus. Larger representatives eat their smaller counterparts; after mating, females are not averse to snacking on a male specimen.
Brazilian travel spiders do not have permanent shelters, choosing temporary shelters during the day to go hunting again at night. Therefore, they become dangerous to humans when they climb into a house, outbuildings, or hide among clothes or in shoes. They can also get into the car.
These tramps still weave a web, although they do not stretch it, waiting for the victim. They use it to swaddle caught prey, lay eggs, or as a device for quickly moving through trees.
In nature
In captivity, the banana spider lives noticeably shorter than in the wild. He needs free space to move. Otherwise, the arthropod begins to wither and quickly dies.
Tegenaria brownie
This type of spider is widespread throughout Europe and is also called the large house spider. It also inhabits the countries of Central Asia, Africa, as well as Uruguay and Argentina. The length of its body is about 7 and a half centimeters, and together with the limbs - about 15 cm maximum. The body is pale gray in color, and the front legs are brown. Females of this species constantly carry a cocoon with eggs with them until the spiders are born. Tegenaria moves quite quickly. Prefers to live in caves, as well as in abandoned outbuildings. Since this species also chose hot countries for its life activities, it is very difficult to meet it.
10 BIGGEST SPIDERS IN THE WORLD.
Watch this video on YouTube
What does it eat?
Common prey for arachnids are insects of various species that get stuck in webs. Banana spiders are considered beneficial because they regulate the population of many pests.
Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes often end up in nets; for tropical areas this is a real benefit, since harmful insects carry different types of fever.
flies
Orb weavers often end up in human homes and reduce the number of flies. Arachnids also prevent flies from multiplying uncontrollably in nature—flying insects often get stuck in webs.
Cockroaches
Infestation of homes with cockroaches leads to an increase in the arachnid population. A random orb moth will breed if there are cockroaches in the house to feed on.
Ants
The ubiquitous ants also get caught in the placed nets, although they can hardly be considered a constant source of food for the arachnids.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Spider Soldier
The wandering soldier spider gets its name because it moves along the ground in the jungle rather than living in a lair or on a web. The roaming nature of these spiders is another reason why they are considered dangerous. In densely populated areas, Phoneutria species typically seek cover and dark places to hide during the day, leading them to hide in houses, clothing, cars, boots, boxes and piles of logs, where they can bite if accidentally disturbed.
The Brazilian soldier spider is often called the "banana spider" because it is sometimes found in banana shipments. Therefore, any large spider that appears on bananas should be treated with due caution. People who unload them should be well aware of the fact that bananas are a common hiding place for this highly venomous and dangerous type of spider.
Unlike most other species that use webs to catch insects, soldier spiders use webs to more conveniently move through trees, form smooth walls in burrows, create sacs for eggs, and wrap up prey that has already been caught.
Brazilian soldier spiders are one of the most aggressive spider species. They will fight each other for territory if there are too many of them in one place. Males are also known to become very combative towards each other during mating season.
They want to have every chance of successfully mating with the chosen female, so they can harm their relative. Soldier spiders usually live two to three years. They do not do well in captivity due to the stress they receive. They may even stop eating and become completely apathetic.
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Spider Soldier
In almost all species of spiders, the female is larger than the male. This dimorphism is also present in the Brazilian fighting spider. Male soldiers roam in search of females between March and May, which corresponds to the time when most cases of human infection from bites occur.
Males approach the female very carefully when attempting to mate. They perform a dance to attract her attention and fight fiercely with other suitors. Representatives of the “fair sex” are very picky, and often refuse many males before choosing the one with whom they will mate.
Male spiders must retreat away from the female in a timely manner after mating in order to have time to escape before her friend’s normal predatory instincts return.
Runners - soldiers - reproduce with the help of eggs, which are packaged in bags made of spider webs. Once the sperm is inside the female, she stores it in a special chamber and uses it only during egg laying. The eggs then come into contact with male sperm for the first time and are fertilized. A female can lay up to 3,000 eggs in four egg sacs. Spiderlings appear after 18-24 days.
Immature spiders can capture prey immediately after emerging from the egg sac. As they grow, they must molt and shed their exoskeleton to allow for continued growth. In the first year, spiderlings undergo 5 to 10 molts, depending on the temperature and amount of food consumed. As they grow older, the frequency of molting decreases.
In the second year of life, growing spiders molt three to six times. During the third year they molt only two or three times. After one of these moults, spiders usually become sexually mature. As they mature, the proteins present in their venom change, becoming increasingly lethal to vertebrates.
Natural enemies of the soldier spider
Photo: Brazilian spider soldier
Brazilian soldier spiders are ferocious predators and have only a few enemies. One of the most dangerous is the tarantula hawk wasp, which belongs to the genus Pepsis. This is the largest wasp in the world. It is not usually aggressive and generally does not attack species other than spiders.
Female wasps seek out their prey and sting it, temporarily paralyzing it. Then the wasp lays an egg in the abdominal cavity of the soldier spider and drags it into a previously prepared hole. The spider dies not from the poison, but from the hatched baby wasp eating the spider's abdomen.
When confronted with a potential predator, all members of the genus display a threat. This characteristic defensive posture with raised front legs is a particularly good indicator for confirming that the specimen is Phoneutria.
Spider soldiers are more likely to hold their positions than retreat. The spider stands on two hind pairs of legs, the body is almost perpendicular to the ground. The two pairs of front legs are raised up and held above the body, showing off the brightly colored undersides of the legs. The spider swings its legs to the side and moves in the direction of the threat's movement, showing its fangs.
There are other animals capable of killing a soldier spider, but this is usually due to death in a random fight between the spider and large rodents or birds. In addition, people destroy members of the genus as soon as they are discovered, trying to prevent the soldier spider from being bitten.
Due to their toxic bite and intense appearance, these spiders have a reputation for being aggressive. But this behavior is a defense mechanism. Their threatening stance serves as a warning, indicating to predators that the poisonous spider is ready to attack.
Soldier spider bites are a means of self-defense and are only done if provoked intentionally or accidentally. In the soldier spider, the venom gradually evolved, performing a protective function against mammals.
Tarantula
Related article:
What is the most poisonous snake?
These poisonous spiders have always had a bad reputation. At one time, people were convinced that these spiders were the main cause of the spread of all terrible diseases and even madness in people. In the Middle Ages, the poison of tarantulas was considered the causative agent of seizures, which were treated with the help of the tarantella - a dance at a fast pace. However, the terrible legends that have been written about this spider over the centuries are highly exaggerated. Although an encounter with this rather large spider (15–30 cm) will not be pleasant, in any case it will definitely not end in death for a person. The consequence of a tarantula bite is usually a complex allergic reaction. These light brown or dark gray spiders covered with numerous hairs with a noticeable black cap are found in steppe, semi-desert and desert areas at night.
Tarantulas or Mizgiri are widespread in Russia. They can be found, for example, in the Oryol and Saratov regions. The bite of the South Russian tarantula is similar to the bite of a hornet. It causes swelling in the affected area, which goes away quite quickly. But this cannot be compared with the consequences of a bite from another species - the Apulian tarantula, a resident of Italy, Spain and Portugal. In addition to pain in the bite area, the person experiences a condition close to fever, which does not subside for 4 days.
Where does the Brazilian wandering spider live?
Photo: Dangerous Brazilian wandering spider
The main habitat of this species is America. Moreover, most often these arthropods are found in the tropical forests of Central and South America. Representatives of this species can also be found in Brazil and northern Argentina, Venezuela, Peru and Havana.
Spiders are thermophilic; the main habitat of these arthropods is the tropics and jungle. There they are placed on the crowns of trees. Spiders do not build shelters or burrows for themselves; they constantly move from one habitat to another in search of food.
In Brazil, spiders of this species live everywhere, perhaps only in the northern part of the country. Both in Brazil and in America, spiders can crawl into houses, which terribly scare the local population.
They love warm and humid tropical climates. Spiders of this species do not live in Russia due to the climate. However, they can be found accidentally brought from warm countries in boxes with tropical fruits, or by spider lovers for breeding them in a terrarium.
In recent years, this dangerous animal is increasingly being kept at home as pets. At home, they can live all over the world, but keeping them is not recommended due to the extreme danger of this species. Spiders also don’t live well in captivity, so you need to think carefully before getting such a pet.
Now you know where the Brazilian wandering spider lives. Let's see what he eats.
Tarantulas
Tarantula spiders (Theraphosidae) are a whole family of arachnoids found in Africa, Australia and on the ocean islands in South America. These are the largest spiders (up to 20 cm), which some exotic lovers are fond of and even keep them at home in terrariums.
Tarantulas do not pose a danger to adults, although they can cause muscle pain and fever. However, the poison can be fatal for pets or children.
Their bright, beautiful fur is actually poisonous hairs. The spider combs the hairs from its abdomen and throws it at its prey. If it comes into contact with the skin or eyes, the poison causes pain, itching, and severe vision impairment.
Population and species status
Photo: Dangerous Brazilian wandering spider
The Brazilian wandering spider is listed in the Guinness Book of Records as the most dangerous spider on planet earth. This type of spider is very dangerous for humans, and sometimes spiders enter people’s homes. Insects can often enter the house in boxes of fruit or simply crawl in hiding from the midday heat. When bitten, these spiders inject a dangerous substance, the neurotoxin PhTx3. It blocks muscle function. Breathing slows and stops, and cardiac activity is blocked. The person quickly becomes ill.
After a bite, the dangerous poison very quickly penetrates the blood and lymph nodes. The blood carries it throughout the body. The person begins to choke, dizziness and vomiting appear. Cramps. Death occurs within a few hours. Bites from Brazilian wandering spiders are especially dangerous for children and people with low immunity. If you are bitten by a Brazilian wandering spider, you must immediately administer an antidote, although it does not always help.
The population of this genus of spiders is not threatened. They reproduce quickly and survive changes in the external environment well. As for other species of this genus, they live quietly and reproduce, flooding the forests and jungles of Brazil, America and Peru. Phoneutria fera and Phoneutria nigriventer are the two most dangerous species. Their poison is the most toxic. After their bites, painful conditions are observed in their victims due to the high content of serotonin. The bite provokes hallucinations, shortness of breath, and delirium.
Interesting fact: The venom of this type of spider can kill a child in just 10 minutes. An adult, depending on his state of health, can last from 20 minutes to several hours. Symptoms appear instantly and develop rapidly. Death occurs quickly as a result of suffocation.
Therefore, when visiting tropical countries, be extremely vigilant; when you see this arthropod, under no circumstances approach it or touch it with your hands. Brazilian spiders do not attack humans, but upon noticing danger and saving, they can bite their own lives. In America, there are many cases of people being bitten by Brazilian spiders, and unfortunately in 60% of cases the bites were fatal. Modern medicine has an effective antidote, but unfortunately, the doctor is not always able to get to the patient in time. Young children are especially susceptible to bites from these arthropods, and they are the most dangerous for them. Often children cannot be saved after being bitten by a wandering spider.
The Brazilian wandering spider is a dangerous but calm animal. It reproduces quickly, lives for about three years and is capable of giving birth to several hundred cubs during its life. When living in their natural habitat, they obtain their food by hunting. Young spiders are not very dangerous, but adults, thanks to their poison, are deadly to humans. The danger of the poison depends on its quantity. In recent years, more and more people are keeping these dangerous spiders at home in terrariums, thereby endangering themselves and their loved ones. These spiders are dangerous, remember this and better avoid them
"Black Widow"
This spider earned its grim name due to the extreme gluttony of females, who immediately eat smaller males after mating. Seeing a male is rare and his bites are not dangerous. This spider is black in color with a red spot that visually resembles an hourglass. These are quite aggressive spiders and can easily be provoked into attacking. Despite the not very impressive size (up to 25 mm) of the black widow, its venom is tens of times stronger than that of a rattlesnake.
These spiders, as a rule, inhabit the Central Asian steppes and deserts. Also, black widows, or rather, their variety - karakurt - are also found in Russia (Caucasus and Crimea), but much less frequently. Perhaps this is for the best, since their poison is extremely dangerous for humans. If after a bite the antidote is not administered within half a minute, an attack of nervous excitement occurs, then a spasm occurs in the muscles and blood vessels. Black widow venom is especially harmful to groups such as children and the elderly. These spiders do not attack themselves, but only defend themselves. Due to their small size, a person may not notice the bite at all at first. However, after 15 minutes, a person experiences terrible pain throughout the body, accompanied by dizziness, nausea, vomiting and convulsions. Without timely assistance, a person dies a few days later.
Behavior in the wild
Banana spiders are predators. Weaving and using webs is a major part of the life of orb weavers.
To catch prey, they weave huge nets (up to one and a half meters in diameter), in which they can catch even small animals - lizards, mice, birds. The arachnids themselves watch over unwary insects nearby, catching the slightest vibrations of the web with their sensitive paws.
The best time for hunting is at night, when the web shines, attracting many insects with reflected light, which become prey, getting stuck and sticking to the nets.
Banana spiders have glands that produce a liquid secretion to produce web threads. The female injects poison into the stuck prey, then wraps it in a net to firmly hold it until the required time.
In limbo, a half-dead victim can hang for several hours until the spider decides to have lunch. Males do not weave webs; they feed on the remains of their prey. After mating, males often die - the female eats them.
The spider that constantly lives in bananas does not eat fruit. He gets enough of the insects that are attracted to the fruits and foliage of banana groves.
Benefit
Brazilian spiders are quite poisonous and their venom is rarely used in medicine. It was mainly extracted to find an antidote. During the research, it turned out that the substance contains a toxin that increases erection in men.
Now a poison-based drug is being developed to treat impotence. The main problem with previous failures is the need for a strict dosage of the medicine so that it brings the desired benefit and does not harm the human body.
The wanderer spider is one of the most poisonous arthropods. Once bitten, the victim is paralyzed within seconds. Then, in 15-20 minutes, the poison converts the insides of small animals into juice, which is what the killer feeds on.
The Brazilian traveler lives in South and Central America. To provide himself with food, he has to constantly move. It is precisely attempts to find food that can lead to the transportation of arthropods to another continent in boxes of bananas. Fortunately, in Russia, Ukraine and other nearby countries you can meet the Brazilian wanderer only in terrariums at exhibitions.
Danger to humans
The British wandering spider is one of the most poisonous members of its huge family. The toxic substance disrupts the functioning of the nervous system and causes spasms. Possible consequences of a bite:
- abdominal pain;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- dizziness;
- temperature change;
- arrhythmia;
- headache;
- increased blood pressure;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath.
Redness, swelling, pain, and burning appear at the site of the bite.
The situation is especially dangerous for young children, people with weakened immune systems, the elderly, and people with allergies. The venom of the Brazilian wandering spider can kill a child in 15 minutes and an adult in half an hour. Alarming symptoms develop within 20 minutes after a predator attack. However, with the provision of qualified assistance, the condition returns to normal. You should call an ambulance immediately if you experience difficulty breathing.
Important!
Poison in high concentration leads to muscle failure, heart function is disrupted, and breathing becomes difficult. Death occurs as a result of suffocation. There is an effective antidote - Phoneutria. When it is administered, nothing threatens a person’s life.
Lethal dose of poison
It is believed that one bite and an injected portion of a toxic substance is enough to cause death. During a bite, a person may not feel the injection of poison, but after a second the skin begins to burn, the poison enters the lymph and blood. In 80% of cases, you are guaranteed to go into cardiac arrest.
If you determine the amount of poison that is needed to kill your victim, then it is as follows: for a small rodent, 6 mcg directly into the blood is enough and a little more, about 130 mcg under the skin. You can calculate the dose for humans, given that the average weight of a rodent is about 50 grams.
Antidote
Today, medical scientists have nevertheless developed an antidote against the venom of the Brazilian wandering insect.
Obtaining it is a very difficult process, but still it helps many. Due to the presence of antivenom, mortality from bites is reduced. According to statistics, it is 3%.
About this article
Contributor(s): wikiHow Staff Editor
This article was produced by our experienced team of editors and researchers, who reviewed it for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow carefully monitors the work of its editors to ensure that every article meets our high quality standards. This article has had 8,094 views.
Categories: Home Security
English:Identify a Brazilian Wandering Spider
Italiano:Identificare un Ragno Errante Brasiliano
Português:Identificar Uma Aranha Armadeira
Deutsch:Eine Brasilianische Wanderspinne erkennen
Seal