Spiders usually evoke either subconscious horror or disgust in most people. Arachnophobia, oddly enough, is common to many people. Theoretically, because spiders are poisonous. But! Of the several thousand of their poisonous varieties, at most one and a half hundred are scraped together, the rest are safe for people. The second explanation is the disgusting appearance. However, the most dangerous spider, the tarantula, resembles a plush toy. And his small fellow tribesman, Argiope Brünnich, generally has an elegant, almost festive appearance. So arachnophobia is something irrational, and spiders themselves are worthy of attention and interest, like any other work of nature.
Argiope's appearance
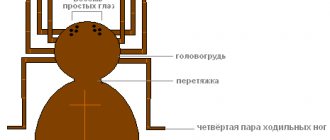
Even fierce opponents of arachnids find the Argiope Brünnich spider beautiful. It is more popularly known by other names: wasp spider, tiger spider, and less commonly, zebra spider. And all thanks to the bright, original, memorable coloring. While fully consistent with a spider's physique, the animal has a characteristic wasp (or tiger) coloring: yellow and black stripes. If you look closely, they are interspersed with white lines, but from a distance the coloring completely matches that of wasps. The spider's legs are also ringed with contrasting stripes, creating a clear impression that they are wearing stockings. Clearly on the fourth stripe, if you count from the cephalothorax, there are two noticeable tubercles, and along the edges of the abdomen there are notches (always six, but colored differently: shades vary from inexpressively dark to bright orange).
The arrangement of the limbs of the wasp spider is also non-standard. Two pairs are oriented strictly forward, the remaining two are oriented strictly backward. Visually, there are no lateral supports, which is not typical for most arachnids, in which the legs are located perpendicular to the surface.
Argiope Brünnich cannot boast of impressive size. Males never exceed seven millimeters in “height” - most people will not notice them, especially since their coloring is rather dull. Females will be larger: they can reach 2.5 centimeters, distinguished by bright colors that are noticeable from afar.
Are house spiders dangerous for humans?
The danger of house spiders to humans largely depends on the type of individual and its habitat. Any insect that lives on trees and shrubs in a given region can reach a person.
In total, there are about 1,000 species of arthropods in Russia, the vast majority of which are absolutely harmless.
The most dangerous insects for the human body are exotic insects that escape from terrariums.
The black street spider is relatively safe for humans. It is poisonous, but the amount of substance it releases when it bites will not be enough to infect people or pets. Insect venom only affects small animals: flies, beetles, etc.
Arthropods pose a problem for humans when they actively reproduce and spread throughout their homes.
To combat the problem, emergency measures are taken: they carry out wet cleaning, collect cobwebs in the corners.
The arthropod itself does not attack a person, but can sting him if he fears for his life. The insect bite site will need to be treated with an antiseptic.
Spiders - tramps and karakurts - are the most dangerous among the representatives of arthropods for humans. When bitten, the latter may develop signs of allergic reactions on the skin and problems with the respiratory system.
Insect bites present with symptoms of varying degrees of intensity. The bite of poisonous creatures is especially difficult for small children and people with immune deficiency.
How do these spiders live?
The range that the Argiope Brünnich spider has confidently mastered is quite wide. It includes many countries of Europe, the south (and, more recently, the middle zone) of Russia, Crimea, northern Africa, South Asian territories, Japan and China. These spiders settle in meadows, along the sides of even fairly busy roads, on forest edges, and in the beds of dry rivers. Argiope is a hunting spider; It does not hunt from ambush, but waits for prey in nets. The basis of its diet are grasshoppers, flies, fillies and wasps.
What causes spiders to appear at home?
The main habitat of arthropods is forests, fields and gardens. There they find food, weave webs and lay eggs. These residents settle in the house if there are favorable conditions for existence.
The main reason for the appearance of a spider in an apartment is a large amount of food. If there are midges, mosquitoes or flies in the room, then the arthropod will firmly settle in one of the dark corners.
Spiders love darkness, humidity and coolness. Therefore, in the house they are often located behind sofas, armchairs or under radiators. In this case, you can get rid of insects by frequent cleaning - removing cobwebs in all corners.
A man brings small spiders on his clothes and shoes from the street. But if the house does not have suitable living conditions, then they will not stay long.
Help prevent spiders in your home
Repellers will help prevent the spread of arthropods in the house. The most effective device will be the Yastreb company, which is plugged into an outlet. It is easy to use and not dangerous to humans and animals.
In addition, you need to take out the trash in a timely manner, throw away old things and faulty equipment. All this attracts arachnids and gives them a wonderful place to live.
Skilled braiders
Like all web spiders, Argiope Brünnich prepares traps stretched between blades of grass and low branches of bushes. The networks of this species of arachnids are circular, in the center they have a zigzag-like pattern, characteristic of the weaving of all brothers in the genus Argiope and called stabilimentum. Despite the small size of the hunter, his traps are very durable, capable of holding a grasshopper, which is 2-3 times larger than the predator. Argiope Brünnich spends only an hour creating nets that are woven at sunset, in the approaching twilight.
Appearance and characteristics
At first glance, the karakurt seems cute and harmless. A small black spider does not cause fear like, for example, a tarantula. His body resembles a construction set. The cephalothorax and abdomen of the spider are ball-shaped. Thin limbs come from the belly. These are four pairs of legs and a pair of jaws. about twenty-two species of karakurt spiders . But among them there are two most common ones: the black widow and the white karakurt.
Karakurt spider or black widow
The color of the spider's body is black, with a slight tint. Often on the body you can see red spots of various shapes, edged with narrow white stripes. It is worth noting that when karakurts become fully mature, the spots may completely disappear. Therefore, it is better to avoid all black spiders.
A person with poor eyesight can easily confuse a spider with its legs tucked in with a black currant berry. The abdomen of the karakurt consists of an anal lobe and eleven members. The female karakurt has chelicerae (upper jaw) on the other side of which there are poisonous glands. Its venom is fifteen times stronger than that of a rattlesnake . They are significantly larger than males. The body of a male individual can vary from four to seven millimeters. The female one grows up to two centimeters.
After the mating process, the karakurt black widow eats her spouse and goes to seek shelter for her future offspring. The spider eggs will need to hang in the cocoons all winter until April.
Gallery: karakurt spider (25 photos)
White Lady
The white karakurt can scare even an adult. But these fears are not entirely justified. Undoubtedly, this spider poses a danger to people , but its venom is not as toxic as the venom of a black widow. However, for a weakened person, an old person or a child, it poses a mortal danger. The white karakurt has a yellow head and abdomen, and four black dots on the back. The female of this species of spider is considered quite large. The paw span can reach ten centimeters.
The White Lady is often called the dancing spider. He received this nickname due to his peculiar manner of movement - the characteristic tapping of his paws. Many believe that in this way they communicate with each other, warning of danger. Despite poor eyesight, white karakurts have perfect hearing. When meeting him, you should not make noise and attract his attention. You can see such a handsome creature in natural conditions in the Naimb desert. There are practically no people there. Therefore, there are practically no attacks of white karakurt on humans. is considered less dangerous than the black widow .
Spider Hunting Rules
For an argiope waiting for prey, it is not enough to simply weave a net. The owner of the trap sits in its center, in that very zigzag segment, and waits for the victim, holding a skein of created threads in his limbs. When the prey is caught, the hunter entangles it in a web and bites it. The insect dies from the poison; at the same time, it begins to be partially digested, while not yet in the spider’s mandibles.
Wolf spiders of the family Lycosidae
We are already familiar with the crab spider, and we will meet the eight-legged wolf for the first time in this book. Although many members of the wolf spider family are gray and brown and hairy, the family did not get its name from its resemblance to a wolf. Wolf spiders lead a nomadic life, not burdening themselves with the construction of complex nets with architectural delights. The nomadic lifestyle is also reflected in the appearance of lycosids - their small, lean body on eight long and powerful legs perfectly matches the wandering lifestyle of wolf spiders. Every summer resident is probably familiar with representatives of this family, because from early spring these spiders run around dug up beds, and already in early summer they acquire a white cocoon, which they wear under their abdomen. But representatives of this family lead not only a terrestrial lifestyle. Some, for example spiders of the genus Pirata, live on the edge of two great elements - water and air, settling on the surface film of water.
But are they really such tramps as they say? To find out, let's observe spiders of the genus Trochosa,
quite common in our area.
Several species of this genus are found in the central zone. I will not immerse the reader in details, since all spiders of the genus Trochosa
are similar in appearance and lead the same lifestyle. These spiders are quite large, their body length reaches one centimeter. They are colored a smooth brown color and have a dark pattern on the upper side of the abdomen. But few people know this spider by sight, since it undeservedly remains in the shadow of the fame of its brother, the tarantula. Of course, the tarantula is somewhat larger than its northern relative, but in appearance and behavior they are not much different from each other.
Trochosis spiders use their web not only for insurance when they go hunting, or for better grip on the surface. For these spiders, webs are comfort. Trochoses dig shallow holes, up to several centimeters deep, weaving webs around the walls. But the spider does not stop at creating comfort inside the hole. He, as a true zealous owner, is also concerned about the appearance of the approaches to the hole. That is why the trochosa also lines the area leading to the shelter with its web. Sometimes spiders don’t bother digging holes, but instead find natural recesses and make the lining and ceiling themselves. A kind of spider-like cosmetic renovation! The cobweb site in front of the hole is the first step towards a catching web. The spider sits in its burrow, and exposes its two pairs of front legs to a web mat in which signal threads extending from the burrow are stretched. The shaking of these threads indicates that some kind of insect has landed on the tarantula's carpet. The owner of the trap does not keep himself waiting long, jumps out from his hiding place, quickly crushes the game under him and kills with a bite to the back of the head.
A spider of the lycoside family, a representative of the pirate genus, sometimes settles on the water
And if the game is caught with a caliber larger than the hunter himself, then the spider simply retreats, because the shelter is just a stone’s throw away. “What kind of wolf is this? This is some kind of homebody!” - you say. But wait to draw conclusions, let's watch the spider further. A day passes, then another, but no insect comes close to the wolf spider’s hole. That's when the spider leaves its hole and goes to wander, looking for profit. If suitable game comes across on the way, the trochosa quickly and without much difficulty kills and eats it. Well, if she is strong and agile, then she runs away from her. Moreover, if at this moment the spider is not far from its hole, it goes straight to the shelter. And if it is far away, then he quickly builds a new hole for himself. This is how hunger makes this homebody a tireless wanderer and seeker of food.
In June, after the last molt, male trochoses mature. They differ from females by being lean and slightly widened on the last segment of the pedipalps, in which males transfer reproductive products to females for mating. There is one more difference: the first segments of the male's front legs are painted black, contrasting with the coffee color of the spider's body. This coloration of the front legs is given to males by nature for a reason. The waves of these very legs, with which he warns the female of his appearance, help the latter not to confuse him with an insect and not to eat him even before mating. I note that it is better to keep females in captivity (and this applies to all spiders), since they are larger in size and live longer. At the same time, females are ruthless and voracious hunters, which also has its own explanation. Who else, if not females, needs in their body reserves of protein necessary for the development of future offspring. But male spiders are delicate and timid creatures, and they feed on smaller insects. So it was not in vain that nature deprived the males of aggressiveness, namely so that the female lycosids themselves would not suffer from the successors of the family.
After mating, the female lays eggs and weaves them into an arachnoid cocoon, which she wears under her abdomen, attached to arachnoid warts. It is precisely by the position of the cocoon that the Lycosid family differs from the Pisaurid family, which wears its cocoon in the pedipalps and holds it with chelicerae. After leaving the cocoon, the babies move to the mother's back, where she carries them until the first molt. And only after molting, the babies leave their mother’s back and go in search of their spider happiness.
Like tarantulas, Trochoses do well in captivity. To keep them, I use a typical standard cage with peat at the bottom, and without my “signature” corner, since lycoside spiders are terrestrial and do not like to climb. Spiders weave part of the soil with their web, creating a platform. Spiders are unpretentious in feeding and will take any insects appropriate to their size.
To breed Trochos, I place a male with a female that has been well-fed and settled in the cage. The area of the cage is 35 x 15 cm. As a rule, courtship and mating take place at night. However, the fact of mating can also be determined by the behavior of the male. So, if in the evening he looks for the smell of a cobweb, freezes, bumping into a female’s web, and trembles with his whole body, and the next morning he runs away from the female and her snare and hides, then it means he is young.
The female takes care of the cocoon herself, and the amateur needs to maintain a sufficiently high level of humidity in the insectarium by spraying the soil every other day. As soon as the young leave the female's back, they can be collected and placed in small test tubes, where, when fed with a newborn cricket, the babies begin to grow quickly. After a couple of molts, the juveniles can be transferred to a standard cage under the same conditions in which adult spiders are kept. And I place only adult females in large cages, where mating takes place.
In conditions similar to those described above, the tarantula (Trochosa singoriensis), other less popular members of the family, as well as a number of species of tropical tarantulas can be bred (but in cages appropriate to their size!).
More interesting articles on the topic:
Bronzeworts (group of species)
Bronzeworts (group of species) For three hours now I have been moving along the edge of the forest. Since then
Karakurt (Latrodectus malmignatha)
Karakurt (Latrodectus malmignatha) In this chapter we will get acquainted with a large group
Seven-spotted ladybird (Coccinella septempunctata)
Seven-spotted ladybird (Coccinella septempunctata) Despite the gentle morning sun, the dark
Red-legged softshell (Cantharis rustica)
Red-legged beetle (Cantharis rustica) These small, bright orange beetles, nicknamed
Magnificent rove beetle (Staphylinus caesareus)
Magnificent rove beetle (Staphylinus caesareus) Under the old cherry tree where there was a large compost pile
Gray grasshopper (Decticus verrucivorus)
Gray grasshopper (Decticus verrucivorus) Having reached the forest, I was a little scared: the forest was dark
Sad breeding
Spiders of the species Argiope Brünnich deal with the issue of leaving offspring during the molting period, when the female has already shed the previous chitin, but has not yet acquired new ones. After the male has done his job, the female in the vast majority of cases eats him. Sometimes the “brave fellow” manages to impregnate the second lady, but, according to scientists, not a single one lived to see the third approach. There is a theory that the cannibalism of spiders is caused by a lack of protein necessary for the development of heirs. However, you shouldn’t sympathize too much with their “men”: the female Argiope does not survive her “husband” for long. After creating cocoons and laying eggs in them (up to 400 eggs in each “little jar”), the wasp spider dies. The offspring spend the winter in the houses she created, and in the spring they emerge from them completely independently.
Spider nutrition and reproduction
The karakurt's digestive system is extraintestinal. When attacking a victim, it pierces it, injecting its poison. At the same time, he pierces it in this way several times so that everything inside is digested. Then it sucks out all the contents. The steppe spider prefers to feed on beetles, grasshoppers, cicadas, locusts and other invertebrate creatures. Small rodents can also become prey.
In one year, the female lays more than a thousand eggs. The male actively courtes the female during the mating season. But after mating, the “karakurt lady” eats her spouse. For this, the Kalmyks nicknamed the female “belbesen-hara”, which means “black widow”.
The black widow weaves a web around her own nest from the inside. There her offspring will be located in the form of cocoons with eggs. After about seven days, the eggs will hatch into spiderlings. But they don't come out right away. They will live in a cocoon until summer. Only the female can bite through human skin. Her upper jaw has glands so sharp that they can even pierce a fingernail. They pose a particular danger during two months: July and August . It's mating season time.
Argiope Brünnich spider: poisonous or not?
The question of the potential danger of the entire crawling brethren worries people in the first place. Argiope Brünnich did not escape a similar fate. Whether this species of spider is poisonous or not is incorrect to ask. Strictly speaking, all arachnids are poisonous; another thing is that not all representatives of the species are able to bite through the skin enough for their poison to reach at least the capillaries. So, even without conducting laboratory tests, we can say with confidence that Argiope Brünnich is a poisonous insect. In the end, it is with poison that she “pacifies” her victims. And it is fatal to insects. Another thing is the person. Its dimensions are not comparable to those of Argiope Brünnich. The bite of this spider is therefore relatively harmless to humans. It can be compared to being stung by a wasp (the spider lives up to its middle name). The sensation is quite painful, and swelling and itching may subsequently occur, but an argiope bite does not pose any danger. Only an allergic person can suffer from it. But the same troubles will be brought to him by the bite of any insect, even a mosquito.
Karakurt bite
Usually karakurt is active at the end of May and June . Therefore, you should not beware of the bites of this insect in winter. But there are known cases of karakurt bites in winter. As a rule, all spiders sleep at this time of year, but a warm winter can disrupt their biological rhythm. However, July and August can be considered a dangerous period for spider bites.
September and October are the last of the season for them. As a rule, they all die with the onset of cold weather . Only spiders in cocoons, which hatch closer to summer, remain alive. Increasingly, the steppe spider can be found in human habitats. It can settle not only in abandoned houses and barns, but also in the yard or, for example, a wooden restroom. During long rains, spiders also penetrate into living spaces.
Diagnosis, symptoms and treatment
Diagnosing a karakurt bite is quite difficult . After an insect bite, a person does not feel pain. It can be detected by two small red spots. Intoxication manifests itself after some time in the form of burning pain throughout the body .
At this time, a person begins to show severe anxiety. Fear of death may appear. Afterwards, the pain spreads to the chest and abdomen, and breathing problems begin. Severe poisoning can cause pulmonary edema and cardiac arrest .
Twitching of the muscles of the body and face is added to the pain. You can read pain and fear on the patient’s face. Watery eyes or conjunctivitis may occur.
Diagnostics
The manifestation of symptoms after poisoning with karakurt poison lasts up to three days. In some cases (depending on the body) longer. Severe cases of intoxication can lead to death within 24 hours. Death most often occurs in children bitten by this spider, adults with weakened bodies and serious illnesses, and those who seek medical help too late.
The maximum number of deaths from a karakurt bite is 6% of all registered bites. Recovery of the bitten person occurs gradually. The patient will feel weak and nervous for another two weeks. In some cases, problems with the nervous system may appear within two months. Quick recovery depends on the amount of poison that enters the body. When admitted to a medical emergency, the person who has been bitten is often misdiagnosed. Severe pain in the abdomen or heart is often diagnosed as acute gastritis or myocardial infarction.
Protection from karakurt bite
To protect yourself from the bite of the most poisonous spider, you need to be more careful in nature while relaxing. You can prevent contact with karakurt if you follow some rules:
- You need to stop in areas unsuitable for spider life. The selected location should be free of holes for rodents, cobwebs on vegetation or in soil depressions.
- Don't take off your shoes and run barefoot on the ground. So you can stumble upon a web, karakurt, which can be located in the depressions of the earth.
- Never sleep on the ground. For overnight stays, it is best to use an air mattress or tarp. This way you will protect yourself from being bitten at night.
- When collecting firewood or clearing a campsite, be sure to wear heavy-duty gloves and heavy-duty protective clothing. It is best to wear socks and rubber boots on your feet.
- Never feel your way on rocky slopes at night.
- You should not leave your tent open all day. Before going to bed, your sleeping bag or bed must be carefully checked: shake the linen and inspect everything carefully. The same needs to be done with shoes.
- Most bites are caused by people. Many homeowners neglect their yard and do little to control wild grasses. Therefore, spiders settle in vegetable gardens. Many people leave their shoes between the rows in the evening. Karakurt may mistake it for a mink, and if a person uses it in the morning, it is unlikely that he will be able to avoid being bitten.
Treatment after a black widow bite
Treatment after a karakurt bite must begin immediately. But if this is not possible and you realize that you have been bitten by a spider, you need to immediately cauterize the wound. But this must be done no later than two minutes after the bite. This can be done with a match, cigarette or hot metal. .
It is believed that the poison disintegrates when heated . You can also make lotions or introduce a 0.1% solution of potassium permanganate. Treatment after a karakurt bite is carried out using anti-karakurt serum (intravenously). Depending on the poisoning, one or two doses diluted in 1 thousand ml of saline are administered. This serum is produced at the Tashkent Institute. The cost of one dose is 37 thousand rubles. This is a large amount for some hospitals.
Regardless of where and how the victim was bitten, you need to immediately take him to a medical facility. In case of severe poisoning, the patient must be given a lot of water, warm the limbs during chills and muscle tension. A cool compress and painkillers will help. All this can be done before the ambulance arrives. Do not forget that medical assistance in such cases is necessary!
What does the white karakurt eat?
Photo: White Karakurt
The source of food for the white karakurt is insects that get caught in the web it weaves.
What is the power source:
- Arthropods are small in size;
- Cicadas;
- Locust;
- Grasshoppers;
- Flies;
- Horseflies;
- Beetles;
- Cicadas;
- Small rodents.
White karakurts have an extraintestinal structure of the digestive tract. When a victim enters the web, it pierces its body in several places and injects a poisonous secretion so that the victim's entrails are completely digested by the poison. After this, the spiders eat the liquid part of the body of their victim.
A horizontal web is most often used to catch insects. It is characteristic that the web does not have a typical trapezoidal pattern, but has a chaotic arrangement of threads that does not form any pattern. The white karakurt can create several such webs of traps. Most often they are placed among the foliage in such a way that it remains invisible to most insects or small rodents. Such traps are often left in burrows, small depressions in the ground.
The process of assimilation of food proceeds quite quickly, since almost everything has already been digested under the influence of the poisonous secretion. Among the variety of food sources, locusts and grasshoppers are singled out and given preference. White karakurts literally manage to live without food, or eat a very modest amount of food. White karakurts can live for about 10-12 months practically without food.
Where does the white karakurt live?
Photo: Animal white karakurt
There is an opinion according to which the white karakurt lives only in uninhabited regions of the Naimb desert. However, this is not true. Changing climatic conditions have led to an expansion and change in the habitat of white karakurts.
Geographical regions of arachnid habitat:
- Southern regions of the Russian Federation;
- Northern part of the African continent;
- Southern part of Ukraine;
- Crimea;
- Iran;
- Mongolia;
- Türkiye;
- Kazakhstan;
- Azerbaijan.
White karakurts prefer areas where there is little precipitation and there is no severe frost. Favorite habitats are steppes, ditches, and ravines. They try to avoid flat, open areas in every possible way. Like the vast majority of arachnids, it chooses secluded, inaccessible places.
Likes to hide in burrows of small rodents, crevices, gaps between walls, and other remote, secluded corners. Karakurts do not tolerate severe frosts and harsh climates. They try to avoid excessive moisture, too light areas, and too hot climates.
It is quite possible to meet a white karakurt on the territory of plowed farm lands, abandoned or residential buildings, in attics, under the roofs of houses and barns.
Reasons for the appearance of spiders in an apartment or house
Only a few species of spiders are synanthropic, that is, living near people. For most species, staying in a human home is unnatural; their habitat is wild nature.
There are several main reasons why arachnids appear in houses and apartments.
Among them:
- an abundance of food (since spiders feed on insects, cockroaches, flies, mosquitoes, midges and even bedbugs in the house will attract eight-legged predators);
- suitable temperature and humidity (spiders climb into the house, attracted by warmth, escaping cold, excessively dry air, or, conversely, high humidity).
In the apartment
The factor of chance is also of great importance. A spider can get into a house with a bouquet of flowers or a basket of vegetables collected from the garden, on a person’s clothing or on the fur of a pet. A common situation is that in summer an arthropod crawls into the house through an open window or door.
Pets
Decorative spiders in most cases have a unique color and huge size. Tarantulas have become human pets. They are considered the largest representatives of arachnids. 1500 species are known. The most exotic ones live in tropical countries. Collectors buy them for impressive sums. Hand spiders live in artificial conditions for up to 3 years. Poisonous. Therefore, it is not recommended for people prone to allergies to keep them.
Interesting!
The huge spider naturally weaves a web up to 2 m in diameter. The web is so strong that birds easily get tangled in it. Predators eat insects, beetles, amphibians, birds, and rodents. At home, they are fed insects and kept in large aquariums or terrariums.