Funnel web spiders, whose Latin name is Agelenidae, belong to the family of araneomorph spiders. There are 42 genera and 515 species of funnel-web spiders known in nature. There are 26 species common in Russia, which belong to 9 genera.
The name of this spider comes from two words - age and lenis, which translated from Latin means “to move unclearly.” This name is due to the peculiarities of movement of these individuals. Their running, unlike the smooth, straight running of other spiders, is intermittent and inconsistent. But, despite this feature, the insect received the name “funnel”, or “grass”. In Eastern European countries, the most common species of this spider is the house spider. In Russian colloquial speech it is often called a house spider.
What does a spider look like?
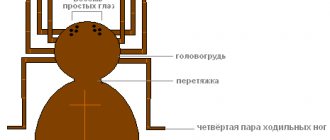
Spiders are medium in size - from 6 to 21 millimeters in leg span, oval abdomen, carapace - pear-shaped or ovoid, not flattened. Females are larger than males, but the latter have a larger carapace.
Body color can range from light brown to black. The body is covered with hair. There is a pattern on the abdomen and carapace. The front legs are longer than the rest. The legs are covered with powerful spines and sensilla. The paws have three claws covered with spines, with which it weaves webs.
Individuals of the family have six simple and two complicated eyes. They are almost equal in size and are located at the same distance from each other. Vision is poor and spiders navigate using their senses of touch. Powerful chelicerae are directed downwards.
On the underside of the abdomen there are two pairs of arachnoid warts, the front ones are widely spaced, the rear ones are elongated and often protrude forward, like tails. One spiracle opens in front of these warts; they breathe with the help of two lungs and a pair of tracheas.
What do funnel web spiders eat?
Grass spiders weave a horizontal dense web that converges downward in the form of a funnel. The network is supported by vertical support threads. The web of these predators is not sticky, but loose: small insects caught in it get stuck in it and cannot get out. The horizontal upper network turns into a hidden lower one, which in turn transforms into the spider’s refuge - a tube enveloping the burrow. In it, the spider waits for a signal from the catching net, after which it abruptly runs head first (which is typical for stray spiders) and bites the victim. He takes the caught prey into his tube and eats it there, or rather sucks it out.
Photo credit: Apdency, Public Domain
Spiders catch and bite only moving animals. If the victim caught in the web freezes and does not move, the funnel web spider will provoke it by tugging at the web, wait patiently, but will not touch it. Some agelenids may lack a cloth, but all have a living tube (burrow). The webs quickly become clogged with dust, and therefore the spider does not stay in one place for long. After 2-3 weeks, he changes his place of residence and weaves new networks. Funnel web spiders are mainly active at night; only representatives of the genus Malthonica hunt both day and night.
Funnel web spiders feed on a variety of arthropods, sometimes even dangerous to them. In addition to softly chitinized flies, mosquitoes, leafhoppers and small spiders, they catch honey bees, orthoptera, beetles and ants. When a prey gets caught in a web, the owner instantly runs out, moving along the web, and inserts chelicerae into the body of the prey. At the ends of the chelicerae on the claw, glands open, which inject poison and enzymes into the body: they turn the insides of the victim into liquid porridge. Grass spiders do not put the victim in their mouth for better digestion, they simply suck out the already dissolved entrails, waiting for the enzymes to finish their work.
Photo credit: Andy Murray, CC BY-SA 2.0
What species are found?
The most common and well-known types:
- The Sydney funnel web spider is one of the most dangerous and poisonous members of the family. Attacks the victim quickly and furiously. It has long and powerful fangs, with which it bites through skin, nails and other integuments. Another name is the Sydney leukoweb spider, which bites very quickly, several times, and its venom can kill a child fifteen minutes after the attack. Timely medical assistance can save the life of the victim. It is quite large in size; the female, including her limbs, can reach seven centimeters. Males are more poisonous. The body color is dark and black. They dig shelters in the ground or make a home in a hole in trees, and cover the entrances with cobwebs on the inside. Habitat: New South Wells.
- Northern tree funnel-web spider - body length up to five centimeters, color dark brown or black. Lives in Australia, New South Wales. Nests are located in tree hollows and rotting wood. It leads an active lifestyle at night and feeds on tree pests. It is also dangerous for humans, because the poison is toxic and can cause severe intoxication of the body.
- Brown - females of this genus are caring parents; after birth, the spiderlings take care of them for another month. If the peace of the family is disturbed, the mother will quickly attack the offender and then eat him. Small spiders touch the female and thus make it clear that they are hungry.
- Brownie or meadow - one of the most common species, found everywhere in basements, closets, barns and other human premises. Some spiders have a dark brown pattern on their backs. Females are larger than males. They weave trap webs and install them in the corners. They lead an active lifestyle and do not pose a threat to humans.
- Labyrinth spider - lives in meadows and steppes. It stretches the web directly on the grass and attaches it to the stems. Yellow body tint. An adult can reach a length of up to two centimeters. The abdomen is dark, the hair is not thick and forms a specific ornament. There are two dark stripes on the back.
Read on topic:
Why signs of arachnophobia appear and what to do about it
14.11.2020
The most popular types of Australian spiders
14.11.2020
The main types of spiders living in a house or apartment
05.02.2020
The appearance of a tarantula and the consequences of a spider bite
03.07.2019
Sydney leukoweb spider
The fauna of Australia is very diverse, comfortable conditions and climate allow many spiders to exist and actively reproduce. The Sydney funnel-web spider is a clear example of this.
This is one of the most dangerous inhabitants of the mainland. He has long fangs, high speed, he is aggressive and merciless.
Sydney funnel web spider.
The size of females is about 7 cm, males are smaller but more poisonous. The color of the animal is black, almost glossy, the scutellum is not covered with hairs. The species lives in tunnels up to 40 cm long, completely shrouded in cobwebs inside.
Males actively move throughout the summer in search of females, so they are more frequent guests in human homes. They may hide among debris or things on the floor.
Sydney funnel web spider and people
The spider is very aggressive and when meeting people it immediately rushes to attack. It raises its front legs and bares its fangs. It bites quickly, even lightning fast, maybe even several times in a row.
The bite force is such that the spider can bite through a human nail. True, there is not much time to inject poison, because the pain pierces immediately and people, out of a sense of preservation, immediately throw it off.
Symptoms of a bite are:
- pain;
- muscle twitching;
- numbness of the limbs;
- tingling of lips and tongue;
- intense salivation;
- shortness of breath.
If an antidote is administered, coma does not occur. There have been cases of children dying when they did not seek help in a timely manner.
What does he prefer to eat?
Depending on the variety, spiders weave webs in different places, some in the grass, others indoors, others in hollows and wood. But they only catch moving animals and insects. The arthropod itself freezes while waiting and prepares to jump. Attacks quickly and swiftly.
Introduced funnel-web spiders are most often nocturnal. They eat:
- softly chitinized flies;
- mosquitoes;
- leafhoppers;
- small spiders;
- honey bees;
- Zhukov;
- ants.
When prey falls into the trap, the host quickly runs out and eats away the prey's body with poisonous chelicerae. It is at the ends of these organs that there are glands that inject a dangerous substance. It turns the insect's insides into a liquid porridge, and the spider sucks out the contents.
Description of the arthropod
Appearance
The size of this spider is considered to be medium or small.
The size of females varies from one and a half to three centimeters, males are usually a centimeter smaller. The color of the spider has beige-brown shades, sometimes black. The most distinctive feature is the presence of 2 dark longitudinal stripes on the back of the spider. But these stripes appear only after the first three molts of the insect. Striping can also appear on other parts of the body. The front legs of the funnel-web spider are long, and in some cases even longer than the hind legs. It has 8 eyes, 2 of which are on top, 2 on the sides, and the remaining 4 in a single row are located in front. Only 2 eyes located on top are fully functional; the remaining eyes are simple. Therefore, the spider moves using its front legs, relying on motion sensors.
Reproduction
The mating process among agelenids is quite simple. It all begins with courtship, during which the male, having discovered the female’s web, begins to tap monotonously on it, thereby putting the female in a state of trance. Then the spider takes the unresisting female, indifferent to everything that is happening, to a place convenient for him and mates. After this, the male and female live together for several weeks.
Nutrition
For food, all known species of funnel-web spiders hunt various arthropods. These are mainly soft chitinized arthropods - small spiders, flies, mosquitoes, leafhoppers. But individuals are also often found feeding on such potentially dangerous and well-protected insects as large Orthoptera, ants, beetles and even honey bees.
Habitats
Representatives of the family Agelenidae can be found in northwestern Europe. Tegenaria domestica
is the most common species of this insect, which can be found throughout the region. The habitat of the species Tegenaria agrestis, Agelenopsis, Allagelena, Alloclubionoides, Tegecoelotes was found in the south of the Far East; Agelena Paracoelotes - in Siberia and the south of the Far East; Iwogumoa interuna - on Sakhalin, Moneron and the Southern Kuril Islands.
Usually funnel-web spiders can be found near people's homes or in the grass. But their appearance is especially frequent in the autumn, during the mating period, when the male is looking for a female on the walls of buildings.
What are the features of reproduction?
Breeding season is summer, warm months. The spider finds the female's nest and taps her web with certain movements. Because of this, the female falls into a stupor, and the male takes her to another place for mating. Then the couple lives together for some time, a couple of weeks, and after that the female eats the male.
At the end of summer, the mother will make a cocoon and place it in her tube or a new chamber nearby, where she lays eggs. House species make several coconuts and hide eggs in them, then hang them on a net.
Nutrition
The Sydney spider is a real predator, and quite voracious. In one day, one spider can catch about 100 insects in its web. The vast majority of them are flies. In addition to them, the diet of spiders includes other types of insects:
- insect larvae;
- cockroaches;
- beetles;
- bees;
- cicadas;
- land snails;
- centipedes.
Nutrition
A catching net, a web, is woven from threads that glisten in the sun. Attracted by the shine, the victim sits on the net and sticks to it. The spider, which is sitting in ambush, can only move to the prey and start eating. Spiders eat a lot: every day the Sydney spider eats as much food as it weighs.
What is the benefit or harm
Despite the fact that representatives look menacing, and their webs disturb people in houses, in the grass and cause inconvenience, spiders are simply necessary for the ecosystem and people: they kill a huge number of insects (flies, mosquitoes, midges and others).
The venom of the house spider, which lives in a person’s home, does not pose a threat and cannot harm the family. One of the poisonous ones is the Sydney one, whose habitat is limited to New South Wales.
The common meadow spider can be dangerous to humans, American scientists have discovered this, but there are no recorded cases.
Funnel web spiders live all over the planet, except Antarctica and snowy areas. Some of them are safe, but there are also poisonous varieties, so you need to be careful when traveling to their habitats.
Habitat and lifestyle
The habitat of Australian spiders is, of course, Australia. They do not live throughout the country, but only in certain regions:
- State of New South Wales;
- State of Queensland;
- in the Sydney area;
- in Tasmania, an island state of Australia;
- around Canberra.
The best living conditions for funnel-web spiders are the wooded areas of the Cumberland Plain. The Blue Mountains in the west keep hot air masses out of the desert areas, resulting in a humid climate that is comfortable for spiders.
The basalt and sandy-clayey soils of the southeastern coast of the country retain moisture well. The Sydney spider can make its home wherever there is stable and moist soil that is almost not heated by the sun:
- under stones, fallen trees;
- in bushes;
- under trees in parks and gardens;
- in compost heaps;
- in the cracks of buildings.
But funnel-web spiders prefer to settle most of all in the grass, which is why they are also called grass spiders. The white cobweb network can have a length from 20 to 65 cm or more. A grass spider entwines itself around the entrance to the shelter. The peculiarity of the web is its funnel-shaped shape, which is why spiders are also called funnel spiders.
On a note! Australian spiders can make their home under curbs, on golf courses, in doorways, or in flower beds. There have been cases when a predator was found floating on the surface of the water in a pool, and it remained alive and dangerous for 24 hours.
Interesting facts about funnel web spiders
- People have learned to judge the weather based on the behavior of the house spider. If he sits motionless in the center of his web, it means it will rain. If the spider is actively engaged in construction and stretching new webs, then dry and clear weather is ahead.
- Various types of spiders, not only from the grass family, like to live in people’s houses - in addition to the brownie, you can find the black attic spider and the long-legged spider (Volcus phalangoides). The latter is often confused with the haymaker, which is not a true spider at all.
- The Bible says that when baby Jesus was hidden by his parents in a cave, the spiders that lived there helped them escape from their pursuers. They entwined the holy family with a thick web, and the villains did not notice them. Since then, Christians believe that spiders are under the protection of divine powers and killing them is a great sin.
- At night, sometimes we notice a house spider on our own body. This is a male wanderer looking for food and a female. He passes by and accidentally bumps into us or catches pests on a person’s body. Spiders do not feed on human blood.
Did you like the article? Share with your friends:
Redback spider (Latrodectus hasselti)
The red-backed spider is originally from Australia, but along with the export of grapes it has already spread to New Zealand, Belgium, and Japan. Judging by the speed of spread, it can also be found in countries far from its habitat, such as Ukraine, Russia or Belarus. Unlike other species, it settles in cities. You can recognize the redback spider by its distinct red stripe on its back. The marking is more noticeable on females than on males.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Victor Ray (@v1cr4v)
The spider is not aggressive, but the female will attack if her eggs are disturbed. The venom is a mixture of neurotoxins called alpha-latrotoxins. Causes pain, sweating, increased heart rate and swollen lymph nodes. The spider is able to regulate the amount of venom injected depending on how hard it is pressed.
Every year in Australia, up to 250 people seek medical help after being bitten. Doctors' opinions regarding the antidote vary. Today it is believed that the antidote does not relieve symptoms or relieve pain. However, the last recorded death from a redback spider bite occurred in 1956.
Types of funnel-web spiders, names and photos
- Labyrinth spider (Agelena labyrinthica) is a typical species of the Agelena family, the body of which, together with the limbs, reaches 13–21 mm in length. The carapace covering the cephalothorax of the arachnid is gray-yellow, red-brown or yellow-brown with two darker concave longitudinal stripes. On the elongated dark brown abdomen of the labyrinth spider there are well-protruding tail-like posterior arachnoid warts. The gray hairs of the abdomen form a herringbone pattern. The legs have no pattern and are dark brown. They have powerful spines and sensilla.
The labyrinth spider is distributed throughout the Palearctic, living in dry, well-lit places: bushes, fields, clearings, meadows, on slopes, near roads, in vegetable gardens and wastelands. It stretches a horizontal dense network with a diameter of 50 cm among grass and bushes, strengthening it with vertical threads. Below he places a small hidden network that turns into a tube: he himself hides in it. The spider covers its living tube with dry leaves. The tube has a curved shape and is open on both sides. On one side she looks at the trapping net, and on the other - at the emergency exit through which the spider escapes in moments of danger.
The predator drags the caught insects inside the tube. Its web is not equipped with sticky threads: victims simply become entangled in the network. In addition, the owner always arrives on time and uses his poisonous glands. In this species of grass spiders, both males and females weave webs of the same shape.
Mating in Agelena labyrinthine occurs in mid-summer. The male comes to the female's web and gives her a signal. After mating, the female can eat the male if he does not have time to escape. Closer to autumn, the female transforms the trapping net into a cocoon and hides it in her shelter or weaves a separate tube for it. The young will spend the winter in it and will come out only in the spring.
Photo credit: Apdency, public domain
- The house spider (lat. Tegenaria domestica ) is a cosmopolitan synanthropic species that lives in people's houses and basements. Those rare individuals that fate rejected from human habitation are forced to settle under the bark of trees, in hollows, in old stumps or under fallen leaves. The house spider spread throughout the world along with humans. The body length of the male excluding legs does not exceed 10 mm, the female is larger in size and can grow up to 15 mm. The color of the teardrop-shaped abdomen of the spider can be beige-brown or yellow with a leopard-like pattern of brown spots. Occasionally the abdomen pattern looks like a herringbone. The male has a darker color tone. The spider's legs are decorated with an ornament in the form of dark rings.
The female house spider weaves a web in the form of a funnel with an area of 3 dm², going to the place where the predator is hiding. These could be dark corners or secluded places. The male tegenaria often makes traps using only single signal threads without a dense funnel. It also happens that the male does not weave a web at all and hunts in the same way as other wandering spiders. The male goes at night to search for a female and food. The house spider cannot store supplies of victims by wrapping them and putting them aside. It eats the caught prey immediately after its insides are dissolved under the action of injected enzymes. The house spider feeds on flies, fruit flies, bed bugs, woodlice larvae, moths, mealybugs and other prey of suitable size. It helps people get rid of harmful insects.
The venom of house tegenaria has been little studied. And although the house spider’s chelicerae are powerful, it rarely manages to bite through human skin. If the spider feels threatened or is caught, it will try to bite, but there have been no cases of infection and poisoning of a person with its venom in history.
In search of a female, the male often climbs into people's sinks and bathtubs and cannot get out. The male finds the female's web, carefully touches it with his feet and waits at the edge. If the female confuses him with the victim, he is always ready to run away. If she doesn’t come out, it means she understood the signal, then the male begins to slowly move millimeter by millimeter towards the living tube. Mating usually occurs for spiders: the male inserts the pedipalp legs into the female's genital opening located on the underside of the abdomen and transfers sperm there. Seminal fluid can be stored by the female for some time; fertilization of the eggs does not occur immediately.
Soon after mating, the female lays eggs in several small cocoons she has twisted and hangs them on her funnel-shaped web.
Photo credit: Magne Flåten, CC BY-SA 3.0
- The giant house spider, the large black house spider (lat. Eratigena atrica, until 2013 had the Latin name Tegenaria duellica) is famous for killing its relatives with whom it has to compete for food. It bites reluctantly, and the bite of this funnel-web spider is safe for humans. When in danger, he prefers to flee.
Giant house spiders live in people's homes in North America, Central Asia, North Africa and Western Europe. Both male and female have the same dark brown color and three light spots on each side of the cephalothorax. There are also individuals in gray and even black shades. On the underside of their abdomen there is a characteristic yellowish pattern. The black house spider is somewhat similar in color to the regular house spider, but its legs, tentacles and abdomen are covered with abundant hairs. Despite the name, this species of funnel-web spider is not the largest in the genus: females reach a length of 18.5 mm, males - 15 mm. The paws can be of different lengths: from 25 to 75 mm.
Initially, the habitat of the giant house spider was caves or dry forests. Often he hid under stones. But now he has moved into people's residential buildings. It lives for 2-3 years and builds funnel-shaped webs, sometimes reaching dimensions of one and a half meters. Males can be found wandering around the apartment from July to October, while females sit in the web and are found all year round.
At least 60 small spiders emerge from the cocoon. They stay together for about a month, but are not social creatures; they hunt separately. After 7-8 molts, they become adults and crawl into their corners. A large black house spider can bite through human skin, the wound may hurt, but the venom of this arachnid is not dangerous to people.
For a long time, the giant house spider held the lead in speed of movement among its classmates. He runs at a speed of 0.53 m/sec. Today, in the Guinness Book of Records for this indicator, it is displaced by arachnids from the phalanx order (lat. Solifugae).
Photo credit: Parent Géry, CC BY-SA 3.0
- Thin Allagelena (lat. Allagelena gracilens) looks like a labyrinth spider and lives in the same places, but is smaller in size and rare in occurrence. The genus name translates as “distinguishable from Agelena.” The length of the body, excluding the legs, reaches 9-11 mm in the female and 5-10 mm in the male. The color of the spider is light gray with brown dots. Light brown, barely noticeable stripes are present on the cephalothorax. Thin, slightly transparent legs are gray or gray-beige in color.
Grass spiders of this species live in Europe, Central Asia, and the Mediterranean basin. They build their network among bushes in sunny, warm places.
Photo credit: NobbiP, CC BY-SA 3.0
- Meadow spider , or American house spider (lat. Eratigena agrestis, formerly Tegenaria agrestis) also has the name hobo spider. The species was first described in 1802 in its native Western Europe. Now it lives in the forests and meadows of Central Europe, North America (USA and Canada) and the black earth strip of Russia.
This spider weaves webs in peat, logs, and near human houses, and leads an active lifestyle, moving very quickly. Females, especially during gestation and protection of young, having no escape route, can attack and bite; they can bite through human skin. Previously, it was said about the strong hemolytic effect of their poison, allegedly causing skin necrosis. This assumption was later refuted. A bite from this species can only cause severe local inflammation.
The American wandering spider does not grow more than 5 cm in length including legs, and by this feature it can be distinguished from the similar but larger Eratigena atrica, which prefers to live in human homes. The body of the meadow spider is beige with a dark brown pattern: on the abdomen in the form of a herringbone, on the cephalothorax in the form of 2 longitudinal lines. The diet of this species includes insects and other arthropods.
Photo credit: Géry PARENT, CC BY-SA 4.0
- The brown hermit spider (lat. Coelotes terrestris) is a small arthropod, the average body length of which, excluding legs, is 9-14 mm (in females) and 7-10 mm (in males). The color of the upper part of its body is light, red-brown with dark gray spots on the cephalothorax and abdomen. The spider is distinguished by the dark color of the abdominal part and the absence of a pattern on the red-brown limbs. In females the abdomen is large, expanding at the back; in males it is small.
This type of funnel-web spider lives in Europe, China and Turkey, in the central and southern part of the USA, and in Australia. It often settles in the moss litter of forests or under the roots of coniferous trees. Less commonly, it inhabits old stumps and weaves a funnel-shaped web about 5 cm wide under tree bark or stones. The brown recluse spider's favorite prey is insects and their larvae: butterflies, beetles, mosquitoes, flies.
Photo credit: Bernard DUPONT, CC BY-SA 2.0
- Tegenaria parietina is a species of funnel web spider that is found in Africa, Europe, Central Asia, Jamaica and Sri Lanka. Lives near humans, weaving webs in the corners of barns, basements and houses.
The average body length of a female excluding legs is 20 mm, of a male – 17 mm. The legs of representatives of this species are 3 times longer than the body. The spider's cephalothorax is yellow, light brown or yellow-brown, and contains a pattern on top in the form of two wavy black or dark brown lines. The edges of the cephalothorax are outlined by a thin stripe of the same color as the lines in the middle. In some individuals these stripes are clearly visible, in others they are barely noticeable. The beige, brown or yellow abdomen of the male is oval, while that of the female is round. The pattern on it may consist of spots of a darker or lighter color, contrasting with the main coat.
Photo credit: Géry PARENT, CC BY-SA 4.0
Brown
Females of this species of spiders are very caring mothers who look after their spiderlings for a month after birth. No one dares to disturb their peace, otherwise the female mercilessly kills the troublemaker, whom she subsequently eats. The spider also feeds its children with the killed victim.
This type of spider has its own communication system. For example, when cubs want to eat, they touch their mother with their limbs. Thus, the female understands that it is time to feed them.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Black widow (Latrodectus mactans)
The bite of a black widow is feared because its venom is 15 times stronger than that of a rattlesnake. The bitten person feels nausea and pain at the site of the bite. Most people bitten recover without complications. It is believed that the bite is dangerous for a child or an elderly person. But, fortunately, arachnids bite only for the purpose of self-defense. For example, if you accidentally step on it. No fatal bites from widow spiders have been recorded in Russia, although they themselves sometimes occur.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Victor Ray (@v1cr4v)
The black widow spins a small web to hunt flies, mosquitoes, beetles and caterpillars. It settles in woodpiles, in abandoned buildings, and weaves nets on plants that serve as load-bearing supports.
Brownie
This is the yellow funnel-web spider that is most familiar to us, as it can be found in any home, closet, barn and other rooms. Sometimes you can see a dark brown pattern on the back of house spiders. The female is usually much larger than the male.
They place trap webs in the corners. In appearance it looks straight, but its central part drops sharply into the depths of the corner. These spiders are most active at night. The house spider is not dangerous to humans, since its bites are not poisonous.
[custom_ads_shortcode1]
Silver spider or water spider (Argyroneta aquatica)
Silver spider
This is the only European aquatic species of spider, so you will not confuse it with anyone else.
Their body is round, gray or brown, up to 15 mm in length, covered with many velvety hairs. They also differ from other spiders in having long swimming bristles on the hind legs and three claws on the legs of the three hind pairs.
Silverfish are often found in still or slow-moving waters. It feeds on various small animals that become entangled in the threads of its underwater web or which it catches while swimming in the water.
A water spider bites very rarely and only for the purpose of self-defense. A person can be injured accidentally by being pulled out of the water along with fish or aquatic plants. Redness, pain, burning, swelling, and swelling appear at the site of the bite. People prone to allergies, with weak immune systems, and young children may experience a deterioration in their health after a spider bite - weakness, nausea, dizziness, headache, and fever. The condition returns to normal in a few days. To speed up the therapeutic effect, take antihistamines.
In some places, silverfish are included in the regional Red Books of Russia and are protected!
Brown widow (Latrodectus geometricus)
The brown widow spider, like other widow spiders, is equipped with neurotoxic venom. Its effect is manifested in increasing pain, spreading from the site of the bite throughout the body for an hour. The more poison enters the body, the stronger the pain. Spreading through the blood, the poison causes muscle cramps. Nausea is observed, sweating increases, and the person feels restless.
View this post on Instagram
A post shared by Victor Ray (@v1cr4v)
The brown widow has trouble seeing. If it is not in the net, it may bite if it feels threatened. Males are generally less dangerous than females. But they bite if the web is disturbed. To avoid being bitten, it is recommended to shake off poisonous spiders rather than crush them.
Jumping spiders (Salticidae)
Different types of jumping spiders
You have probably also seen these “fluffy” medium-sized and compact spiders with large eyes and powerful legs. They easily climb vertical surfaces, including “inconvenient” ones like glass. They can often be seen near human habitation on stone and brick walls, where they bask in the sun. These spiders are also found in thick grass. The color of these arachnids can be very different - black, light brown, striped, spotted.
Jumping spiders are active daytime hunters; they do not weave webs, but track prey (insects and the smallest vertebrates) and jump at it, often over long distances.
Jumping spiders that live in our latitudes are absolutely safe and not poisonous to humans.
Crab spiders, or sidewalkers (Thomisidae)
Crab spiders
These representatives of arthropods are distinguished by a very swollen spherical abdomen against the backdrop of thin legs.
The color of their body (up to 10 mm long) can be nondescript white, greenish, beige, or, conversely, very bright - two-color, patterned, striped. The first two pairs of legs of these spiders are usually much longer than the hind ones.
Crab spiders can move sideways, which is why they got their nickname. They do not build trapping nets, but lie in wait for their prey (insects and small spiders), sitting on flowers, on leaves, in litter or on the bark of trees. They are absolutely not dangerous for humans.
Behavior
Atrax robustus lead a terrestrial lifestyle, located in secluded corners under stones and rotting wood. They dig holes in the soil, and near them they stretch trapping nets in the shape of a funnel. Females almost never leave such shelters, and males temporarily part with their homes when they go in search of partners.
The length of the fishing net ranges from 20 to 60 cm. Outwardly, it resembles the Latin letters Y or T and is able to withstand both low and high ambient temperatures. Sometimes animals form a real colony, placing their nets not too far from each other, but at a safe distance. There can be up to hundreds of individuals in it.
During the rains, Sydney spiders are forced to flee from flooding and move to drier places, quite often under the roofs of local houses. This is also the sin of males who are looking for females. They often crawl into clothes and shoes, where they enjoy the warmth and darkness.
The diet mainly consists of beetles, cockroaches and snails. Occasionally small amphibians and lizards become prey. The spider injects poison into the body of the victim with the help of poisonous fangs, which digests its internal organs.
After some time, he drinks the nutritious broth formed from them. All that remains of a hunting trophy is an empty shell.
[custom_ads_shortcode3]
Scary to look at
With all the desire of the Australian fauna, if not to eat a person, then at least take a bite, there are also quite harmless animals there. These are found even among arthropods. Not all huge spiders in Australia are poisonous.
Huntsman Spider
The bite of this arthropod is not dangerous to humans, although it can cause consequences of varying severity. The level of exposure to a hunter's venom depends on the susceptibility of the prey. Or a tormentor, since a hunter rarely bites a person and very reluctantly. It takes a long time to provoke him to bite.
Interesting!
The hunter spider does not weave webs, chasing prey on long legs. The paw span is up to 19 cm. The speed of movement of the arthropod is 1 m/sec. The hunter's lifestyle is nocturnal.
Because of his love for cars, a hunter may be responsible for more deaths than the Sydney leukopachine. The hunter likes to climb into cars under control panels or on sun visors. Not every driver will be able to control the car if a hunter jumps into his lap while driving.
Spiders of Australia
Queensland whistling tarantula (Selenocosmia crassipes)
In the Russian-speaking space, such spiders are usually called tarantulas. In the English tradition they are tarantulas. This species is also called the eastern tarantula.
It can be placed separately, since despite its enormous size (paw span 22 cm), thanks to which it is included in the list of the largest spiders in the world, it has a relatively strong poison. A bite from an eastern tarantula can result in six hours of vomiting. But a tarantula bite does not cause death. It does not need strong poison, since it does not feed on birds. Its prey is invertebrates and small lizards.
The maximum body length of the whistling tarantula is 9 cm. The tarantula has a massive body and chelicerae that grow up to 1 cm in length. The legs are thick. The front ones are thicker than the back ones. The color of the bristles covering the body is dark brown. The eastern tarantula lives in Queensland.
The lifespan of females is 30 years, males up to 8 years. This circumstance makes them desirable “pets” among arachnophiles. As a result of the fact that whistling tarantulas are removed from their natural environment, the species is on the verge of extinction.