Flea dermatitis in cats is one of the most common problems faced by lovers of these animals and from which not a single pet, even a carefully groomed pet, is immune. A similar reaction occurs as a result of an allergy to substances contained in the saliva of blood-sucking parasites. The initial manifestations of the disease can be noticed within ten to fifteen days after the flea bite, and the insects themselves may no longer be on the animal’s body by this time. It has been noticed that a cat with hypersensitive skin can react with a case of dermatitis after just two, or even one, flea bite. In this case, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately before the disease spreads to large areas of the body.
What is flea dermatitis?
Dermatitis is manifested by inflammation of the skin resulting from exposure to an irritant, that is, they are considered allergic diseases. For flea dermatitis to occur, it is not at all necessary that the pet be covered in fleas, since a couple of bites from random insects are often enough for its development. Young cats between nine months and three years of age, as well as those with short hair or hairless breeds, are considered to be most sensitive to such a reaction.
Up to two dozen different allergens can be simultaneously present in a flea's saliva, one of which is likely to lead to an allergic reaction.
The disease develops as follows:
- flea saliva containing the allergen after a bite gets on the skin or under the skin of the cat;
- the allergen penetrates the layers of the epidermis;
- subsequently it penetrates into the lymph;
- Together with the lymph, the allergen spreads throughout the animal’s body;
- in response, cells of the immune system initiate a protective reaction.
It has been noticed that manifestations of dermatitis occur not only at the internal level; quite quickly they also manifest themselves in the form of external rashes, which quickly progress and, if urgent measures are not taken, cause significant discomfort to the cat and even change its behavior.
What should you do first?
In order to prevent further development of the disease, the owner must take a number of actions for the treatment to produce results.
- Examine your pet.
- Heat treat all animal toys.
- Get rid of your cat's old bedding and beds.
- If other animals live in the premises, they must also undergo appropriate treatment.
- Disinfect all carpeted areas in the room.
Some veterinarians recommend initially isolating an animal affected by fleas in a separate room and trying to limit its movement. All furniture, equipment and objects with which the animal interacts should be treated with a special antiparasitic substance.
An infected animal must be isolated from other pets
Symptoms of flea dermatitis in cats
An allergic reaction caused by flea dermatitis cannot have a long latent period; diseases of this kind appear quickly and are quite pronounced.
The cat's behavior will begin to change, it will become restless, and upon careful examination of your pet, you can find the following:
- severe itching in a cat causes the animal to constantly itch; scratching in certain places with rashes can merge into limited weeping areas;
- changes in character are noticeable, the cat becomes restless, nervous, and may lose interest in food;
- in areas with rashes, hair loss, deep scratches and redness are observed;
- fleas and traces of their vital activity in the form of dark feces can be found on the skin;
- the rapid development of the disease leads to the formation of scabs in areas of scratching;
- the addition of a secondary infection threatens inflammation with purulent discharge.
A disease such as flea dermatitis can have an acute form, which can become chronic. The most affected areas of the skin are those located on the abdomen, around the ears, and on the back, and they tend to increase and gradually cover more and more new areas. If dermatitis occurs in a chronic form, then exacerbations of the disease are most often observed in the summer.
Mechanism of infection
Did you know that, according to numerous testimonies from veterinarians, in 90% of cases, the majority of skin lesions in their patients are caused by representatives of the blood-sucking order? For some reason, many owners zealously deny the presence of fleas on their four-legged pets, which causes bewilderment among experienced specialists. Owners of small dogs, who “relieve themselves” in a litter box at home, like cats, especially suffer from this misconception. In their opinion, if a pet practically never appears on the street, then this unpleasant problem has nowhere to come from. It's time to dispel dangerous misconceptions.
The flea is a hematophagous insect and, as you probably know, they feed not only on the blood of animals, but also on people. Sensitive tiny insects are able to penetrate apartments and houses:
- from the street;
- from the entrance;
- through windows and cracks.
For the most part, you don't have to be the owner of a furry friend to attract a flea's attention. Without even meaning to, you yourself bring a parasite into your home, for example, on your clothes or dirty shoes.
As a rule, blood-sucking insects hide:
- in sofas;
- mattresses;
- in dust;
- under the parquet;
- in tile cracks;
- behind the baseboards;
- behind the wallpaper and in other secluded corners.
Almost the entire population of tiny bloodsuckers consists of larvae. For a whole year they exist unnoticed in human homes, waiting for their finest hour. And although the main period of outrage of insatiable creatures is considered to be spring, summer and autumn, it is the long stay in the pronymph (pupa) stage that makes these insects very viable and increases the likelihood of flea infestation even in winter.
As you have already understood: fleas are extremely tenacious and dexterous creatures. If a doctor suspects a tailed couch potato is infected with parasites, do not be reckless and deny the diagnosis.
Kinds
Allergic flea dermatitis in cats can occur with varying intensity and some differences in the symptoms shown. Based on these features, the disease is classified into three types:
- Sharp look . Characterized by severe skin itching.
- Subacute appearance . It is an intermediate stage between the acute nature and the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
- Chronic appearance . It is characterized by the formation of nodules on the skin, also accompanied by itching. On damaged skin, hair loss occurs with the appearance of bald areas.
The acute form of flea dermatitis in cats can quickly become chronic, which occurs in the absence of timely treatment or if it is carried out incorrectly. The disease will return until the correct way to eliminate it is found.
Consequences of infection
For some reason, some owners are in no hurry to show their constantly scratching dog to a doctor. Unfortunately, in addition to the above-mentioned flea dermatitis with all the ensuing skin irritations and restless behavior of the pet, small bloodsuckers will cause much more serious damage to the health of a mustachioed pet:
- Chronic form. This type of allergy is characterized by constant relapses, provoked by the owner’s connivance towards the problem and unwillingness to treat the pet well. In the end, insect bites will no longer be necessary for painful manifestations.
- Anemia. Some insensitive dogs do not react in any way to the presence of fleas, which, by the way, multiply at lightning speed. For your information, about 70 females per day are capable of sucking about 1 ml of blood, imagine what will happen if they multiply greatly. Often, after being infected by dangerous flukes, dogs, especially representatives of small breeds, suffer from posthemorrhagic anemia.
- Cucumber tapeworm. Another name for this dangerous disease is dipylidia. Hematophages are spreaders of this serious disease, which also affects humans. The dog endlessly licks the itchy spot and accidentally swallows annoying parasites. The causative agent of the disease penetrates the intestines of the animal along with the insect that previously swallowed the larva of a dangerous worm. An adult reaches a length of one meter. Cestodes developing in the intestines absorb nutrients and irritate the internal walls. Their vital activity leads to intestinal bleeding, obstruction and volvulus, which, in turn, will most likely lead to the death of the animal.
Who is most susceptible?
Despite the fact that flea dermatitis is considered a fairly common form of allergy and is seasonal, not all animals suffer from this disease. For many of them, flea bites pass without a trace, causing only anxiety from the direct bite and not causing flea dermatitis in the cat. Cat breeds with short hair or completely hairless are more predisposed to such a reaction to substances contained in the saliva of parasites.
Particular attention should be paid to your pets during the warm season; it is during this period that the possibility of flea bites increases. Moreover, for this it is not at all necessary to be on the street; the owners themselves can bring them home on street shoes and infect the pet.
Definition of disease
Cat dermatitis is a disease that manifests itself as a common allergic reaction. The animal becomes a target for the insect in two ways:
- Contact with any street animal, dirty shoes, outerwear.
- Weakening of the immune system and contact with a carrier.
Most often, infection occurs in summer or early autumn.
By piercing the upper layer of the dermis, the flea secretes saliva, which gets inside. Scientists claim that such saliva contains about 15 types of irritants. The substances in its composition contribute to the development of an allergic reaction. Most often, animals with weak immune systems are susceptible to it. Kittens under the age of 1 year also become targets of the disease.
Dermatitis in a cat is a disease that manifests itself as a common allergic reaction.
How to diagnose fleas?
Flea dermatitis can be suspected in a cat based on some specific signs that are easy to detect if you pay close attention to it. You just need to take a closer look at the animal and pay attention to changes in its behavior.
If the flea infestation has not yet reached scale and is at the initial stage, then you can check your cat for their presence as follows:
- Place the cat on a clean sheet of white paper.
- Using a comb or brush, comb the animal's fur in different directions.
- Particles of skin, fur, or small black grains resembling dirt may appear on white paper.
- If these particles are crushed, brown or brown marks remain on the paper.
- These particles are flea feces, and the color confirms that the fleas are feeding on the animal's blood.
Such confirmation serves as direct evidence that the cat has fleas, even if there are no other symptoms of infestation. Only a veterinarian can confirm whether their presence is a cause for dermatitis. It is impossible to independently diagnose the flea form of dermatitis, since completely different diseases that do not depend on the presence of skin parasites often exhibit similar symptoms. If, during examination by a specialist, the diagnosis of flea dermatitis is confirmed, then the animal will be prescribed treatment in accordance with the breed and age of the pet, as well as taking into account the form of development of the disease and the degree of damage. Correct prescriptions will not only stop the external manifestation of the disease, but will also prevent its relapses.
How to identify pathology and distinguish it from others
The flea form of the disease is easy to distinguish from other types of dermatitis, since parasites are present. They can be seen with the naked eye. If you have vision problems, you should use glasses or a magnifying glass, since fleas are very small. In the initial stages of the development of the disease, the neck area is affected, so it is necessary to carefully examine this area, carefully moving the hairs apart.
If fleas are not found in one place, this does not mean that they are not found in another. The fact is that in the initial stages of the disease there are very few parasites, so you need to inspect all areas carefully.
If there are fleas, the cat not only itches, but also tries to bite into the skin. If your pet does this regularly, this is a warning sign.
Photo
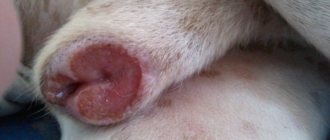
As a rule, most cases of flea dermatitis can be easily diagnosed by external signs. If you carefully examine the skin of an animal, it reveals the characteristic manifestations of this skin disease.
So, in a photo taken from the affected area of skin you can see:
- characteristic scratches in the form of bloody deep scratches;
- swelling of the skin with the presence of nodes, blisters, and ulcers;
- areas of skin with excessive dryness;
- redness of the skin with pronounced inflammation;
- purulent discharge may be noticed, which is characteristic of an infection.
Despite the obvious severity of symptoms consistent with the development of flea dermatitis, the final conclusion about the type of disease must be made by a veterinarian. Therefore, treatment of the disease should be carried out under his control and with the help of medications prescribed by him.
Treatment of dermatitis
Drug treatment of flea dermatitis in domestic cats is carried out according to a standard regimen, which involves the use of the following medications:
- drugs with anti-inflammatory effects;
- medicines with antibiotic properties;
- antiphlogistic nonsteroidal drugs.
When treating, you need to focus not only on the choice of medications that can cope with the flea form of dermatitis. It is equally important to create the necessary living conditions for the animal.
Antihistamines
To treat cats with symptoms of flea dermatitis, medications containing calcium sodium thiosulfate and hormones are used. With the help of calcium in the drug, it is possible to reduce vascular permeability, eliminate swelling and reduce itching. However, their disadvantage can be considered some features of application, when their administration involves only intravenous injections, which can only be done by a specialist.
The use of sodium thiosulfate is also carried out only intravenously and strictly in accordance with the prescribed course. Thanks to it, the allergic reaction is stopped, which relieves the cat of disturbing symptoms. Moreover, if you seek help early and start treatment in a timely manner with such a drug, you can completely get rid of allergies.
However, antihistamines occupy a special place in methods of therapy aimed against flea dermatitis. With their help, you can quickly cope with itching, and intended for animals, they do not have a harmful effect on their body. These medications are usually given to your cat for three to five days, after which only your veterinarian can decide whether to continue treatment or stop it. The most effective antihistamine medications for cats are prescribed Suprastin, Tavegil, Diphenhydramine or Zyrtec. Chlorpheniramine, which is taken orally twice a day, 2 ml, copes well with this task.
In some cases, antihistamines are not effective enough against allergies, then it is recommended to treat flea dermatitis using glucocorticosteroids.
Hormonal
Hormonal medications are very often prescribed for severe forms of allergies in animals. Typically, Prednisolone is used for these purposes, starting the course of treatment with a high dose and gradually reducing it. The dosage depends on the weight of the cat and its age, due to which the expected result with the elimination of the symptoms of an allergic reaction occurs in a short time. When carrying out treatment with hormonal drugs, it is necessary to take into account their downside, that is, their adverse effect on the vital processes of the animal’s body. Thus, their use may reduce immunity, disrupt metabolic processes, and complicate the processes of digestion and assimilation of food. It is for this reason that hormonal drugs should be used only if indicated for this type of treatment and not used for a long time.
Often a sick animal is offered local hormonal agents as a cream or ointment. Such a prescription is justified in case of contraindications to the use of systemic drugs.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of allergic irritation are most often observed in pets with sensitive skin.
The main signs of allergic dermatitis caused by a flea bite are:
- severe and incessant itching - the dog is restless, constantly spins in place and tries to bite the affected area of the body, frantically scratches the skin with its claws, whines;
- the bite site is hot to the touch;
- due to scratching there are abrasions and scratches on the body;
- hyperemia, suppuration of the affected area of the body;
- baldness;
- the pet’s behavior is ambiguous - lethargy and apathy are replaced by irritation and aggression;
- the dog loses weight, refuses to eat, and cases of gastric upset, such as diarrhea or vomiting, cannot be ruled out.
In rare cases, the general symptoms of flea dermatitis are accompanied by secondary signs - the wounds become covered with seborrheic scales, the skin around them becomes dry and tight.
Video - How to give a cat a pill
Often there is a need to treat a pet with tablets and then the question arises: what is the best way to do this?
To do this, you can use the recommendations of specialists or watch the video:
- Carefully study the instructions for the drug and determine the prescribed dosage.
- Decide on the permissibility of giving the medicine with food or dissolved in water.
- Limit the animal's mobility by wrapping it tightly in a thick blanket or towel.
- Raise the cat's head and open its mouth.
- It should be taken into account that the animal will struggle, so it is necessary to hold it still with your free hand.
- By pressing on the lower jaw, it is necessary to open the mouth. Moreover, if you are supposed to give a pill, the mouth must be opened as wide as possible.
- The tablet is inserted with two fingers, trying to get as far as possible to the root of the tongue.
- You must make sure that the tablet is swallowed. To help with this, you can blow lightly into your cat's nostrils, which will trigger the swallowing reflex.
- Release the cat from the blanket and offer it water.
If the animal is strong enough and actively resists, and the fear of inserting fingers into its mouth turns out to be stronger than the desire to help it, then you can insert the tablet using special plastic tweezers, which can be bought at a veterinary pharmacy.
Top 4 best drops
Drops containing insecticides help achieve the best results in the fight against annoying bloodsuckers. Check out the highest quality, most effective and modern products:
- Bars AVZ. A universal remedy, suitable for both adult dogs and puppies. The protective effect lasts for a month. Does not cause side effects.
- Advantix for large breeds from Bayer. It does not penetrate into the pet’s blood, but remains in the sebaceous glands. Designed for large mature dogs weighing over 25 kg, as well as for growing young animals from seven weeks of age.
- Advantix for medium breeds from Bayer. Does not leave excess oil on the coat, protects against any midges and is considered a hypoallergenic product. It is better to use it together with a flea collar from the same manufacturer.
- Frontline Combo S Merial. It is also not absorbed into the blood and destroys eggs and larvae. Using a special bottle, it is convenient to apply the solution directly while walking.
It is important that after using antiparasitic agents, it is better to put a special collar on the animal, which will prevent the dog from licking the strong-smelling liquid.
Diet
When relieving a pet of the symptoms of an allergic reaction to flea bites, it is necessary to help the body cope with this change in its condition with the help of special nutrition. Thanks to this, the skin healing process will happen faster, and inflammation and itching will disappear. If the cat eats natural food, then it is necessary to add Omega-3 acid, for example, Nordic naturals Omega.
If you prefer dry ready-made food, it is better to use Royal Canin Skin or Econuba Dermatosis. For a while, it is necessary to give up chicken-based food and not give chicken as food, since it is this type of food that most often contributes to allergies.
Description of the problem
Flea dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that occurs as a result of flea bites and an allergy to the saliva produced. The severity of symptoms does not in all cases depend on the number of fleas; sometimes a few bites are enough. According to statistics, an allergic reaction is the main cause of itching in pets. There is no pronounced seasonality, but symptoms are often observed in summer and autumn.
Drops
To eliminate the discomfort caused by flea dermatitis in cats, you can use special drops designed for this purpose and approved for the treatment of allergies in animals. In this capacity, veterinarians advise using the following types of liquid preparation:
- Essential 6 - with the help of this product, the animal quickly gets rid of itching, and they also serve as a guarantee to prevent repeated cases of infection. An additional advantage is the packaging with a small dosage;
- Stronghold are drops that can be used for adult cats and kittens from three months of age.
Using these remedies, you can get rid of parasites on the animal’s body within 24 hours, thereby it will stop suffering from itching and anxiety.
Diagnosis at the veterinarian
An accurate diagnosis can only be made in a veterinarian's office. You must contact specialized institutions that have the appropriate license. During the examination, the veterinarian must exclude other diseases that have similar manifestations:
- pediculosis;
- psychogenic alopecia;
- staphylococcus;
- drug allergy.
An accurate diagnosis can only be made in a veterinarian's office.
When the possibility of infection has been ruled out, samples will be taken from the animal for various allergens. The veterinarian draws up a treatment plan.
Powder
You can alleviate the condition of an animal when it develops allergic dermatitis as a result of a reaction to flea bites using powder. Most often, powders such as:
- Tsamaks - has wound-healing properties;
- Synthesis - when applied to damaged skin, accelerates its healing, and also effectively relieves inflammation and swelling.
The combination of components in these powders allows you to quickly cope with a problematic situation.
Additional Notes
As you can see, a seemingly harmless disease can do serious things. That’s why prevention is “our everything.” The simplest and most effective means of preventing flea infestation is a collar. Today there are dozens of varieties on the market, from a wide variety of companies. Don’t forget to change the collar on time, and your cat will be reliably protected from small bloodsuckers. Insecticidal drops and simple wormwood oil have also worked well, which also repels fleas well; you can use tar soap.
In addition, do not forget to clean the room more often, paying special attention to wet cleaning of the most remote corners of the apartment. In this case, it is very useful to add insecticidal preparations or simple chlorine bleaches in good concentrations to the water for washing floors. This way you are guaranteed to destroy all the larvae, and the flea population will not increase.
Collar
Using a collar will not get rid of parasites, but it will protect a clean and healthy animal from their penetration. Most often, the following types can be purchased in veterinary pharmacies:
- Leopard - capable of reliably protecting a cat from fleas for seven months, since its characteristic smell repels parasites;
- Baffo - the impregnation of this collar is distinguished by a large number of anti-parasitic components, but they can only be used on animals older than three months.
You should not assume that using a flea collar does not pose any danger to the animal itself. There are cases, however, so far isolated, that the composition used for impregnation can also cause allergies.
Allergic contact dermatitis: basic approaches to diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Allergic contact dermatitis is a classic form of delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction mediated by sensitized lymphocytes. According to a number of authors, this pathology affects 1% to 2% of the population in various regions. The prevalence of the disease is higher in industrialized countries. It is increasing as more and more new chemical substances are introduced into use in medicines, cosmetic products, medical implants, household chemicals, and industrial reagents.
Unlike simple contact dermatitis, in which an irritant causes inflammation in all people when exposed to the skin, allergic dermatitis occurs only in sensitized individuals, that is, in people who have immune cells specific to this substance - T-lymphocytes. Contact dermatitis is often caused by harmless chemicals that, under normal conditions, do not cause any clinical symptoms in healthy people. But allergic dermatitis is also known when in contact with aggressive agents - components of hair dyes, hair growth products, dyes for fabrics, fur and leather, detergents, medications, juice of poisonous plants.
A classic example of allergic contact dermatitis is dermatitis caused by plants of the genus sumac (in particular, poisonous sumac - Rhus toxicodendron), in which the rashes often have a linear shape and are located on exposed areas of the body.
The pathogenesis of allergic contact dermatitis is based on a tuberculin-like delayed (cellular) hypersensitivity reaction, the inductive phase of which begins with local exposure to the skin of low molecular weight chemicals of organic or inorganic nature. Their sensitizing (allergenic) properties depend on their ability to penetrate the skin and form stable covalent bonds with the proteins of the host organism. Thus, dinitrochlorobenzene forms complexes in the epidermis with proteins containing a lot of lysine and cysteine. Skin lipids can also serve as an adjuvant.
In the formation of hypersensitivity, the leading role is played by professional macrophages of the epidermis - multi-processed Langerhans cells. The resulting delayed hypersensitivity is directed not only to the chemical itself, but also to the carrier protein.
Typically, at least 10–14 days pass from the moment of skin contact with the allergen until the development of the first clinical manifestations. The duration of the sensitization period is usually shorter for aggressive chemicals. Thus, according to our observations, drug allergens when applied to the skin can cause manifestations of contact dermatitis as early as 7–8 days. The most common allergenic medications are local forms of antibacterial drugs; contact allergic reactions to local anesthetics, antiseptics and latex are less common.
The location and configuration of the lesion is determined by the causative factor. The most common form of the disease is eczematous dermatitis. The disease is easy to diagnose and, as a rule, is characterized by a favorable course. The rash disappears when exposure to the pathogenic factor ceases. To accelerate the regression of clinical manifestations, local anti-inflammatory drugs, mainly topical glucocorticosteroids, can be used.
Etiology
According to our observations, the most common cause of allergic contact dermatitis is stainless metal alloys from which household products are made - kitchen utensils, jewelry, watches, denim rivets, zippers, keys, as well as medical supplies - dental crowns, braces , devices for focal and extrafocal osteosynthesis. Thus, having analyzed 208 cases of allergic contact dermatitis that we encountered in practice in the period from 1999 to 2009, we came to the conclusion that the metals nickel, cobalt and chromium, which are part of stainless alloys, were the cause of inflammation in 184 (88.5% ) patients.
A list of the most common, according to our data, causes of allergic contact dermatitis is given in
.
Pathogenesis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a delayed-type allergic reaction. An allergen that gets on the skin binds to tissue proteins, forming a compound that can cause an allergy - an antigen. Langerhans cells absorb antigen in the membrane molecules of the major histocompatibility complex class 2 by T lymphocytes. Activated T lymphocytes and Langerhans cells produce gamma interferon, interleukins 1 and 2, which enhance the immune response and inflammatory response. Activated T lymphocytes migrate through the lymphatic vessels to the paracortical zone of the regional lymph nodes. In the lymph nodes they undergo antigen-dependent proliferation and differentiation. Some of the “specialized” T-lymphocytes take part in the immune response, while the rest turn into memory cells. They cause the appearance of a rapid, pronounced response after repeated contact with the allergen. After the first contact with the allergen, T-lymphocytes recognizing it accumulate, which usually lasts 10–14 days. After this, T-lymphocytes leave the regional lymph nodes into the blood and populate all peripheral organs of the immune system. Upon repeated contact with the allergen, memory cells are activated and rapid accumulation of delayed-type allergic reaction effector cells—macrophages and lymphocytes—occurs.
Histological picture
The histological picture of allergic contact dermatitis is characterized by infiltration of the dermis with mononuclear cells, primarily near blood vessels and sweat glands. The epidermis is hyperplastic and also infiltrated with mononuclear cells. Typically, the formation of vesicles in the epidermis combines with the formation of bullae. The serous fluid filling them contains granulocytes and mononuclear cells.
Clinical manifestations
The disease, according to our data, is more common in young and middle-aged people. However, exceptions are possible. Thus, of the people we examined, the youngest was a one-and-a-half-year-old girl with an allergy to cobalt, and the oldest patient was an eighty-year-old man, sensitized to chromium and nickel.
In the clinic, allergic contact dermatitis is distinguished into acute, subacute and chronic forms, as well as mild, moderate and severe.
The interval from the initial exposure to the allergen to the formation of skin hypersensitivity can vary: from relatively short (2–3 days when exposed to a strong sensitizer, for example, urushiol from the juice of plants of the genus sumac) to very long (several months or years in the case of a weak sensitizer, for example, chromic acid salts or chloromethylisothiazolinone). As a rule, in an already sensitized organism, the disease develops acutely 12–72 hours after exposure to the allergen and is manifested by itching, bright hyperemia and swelling of the skin at the site of contact, against which papules, small blisters or blisters are visible, opening and leaving weeping erosions (wetting) . Sometimes skin necrosis occurs.
The subsiding inflammation leaves crusts and scales. In a chronic course, peeling and lichenification appear.
Acute allergic contact dermatitis is characterized by the following stages of development of rashes: erythema => papules => vesicles => erosions => crusts => peeling. For a chronic course: papules => desquamation => lichenification => excoriation.
In severe allergic contact dermatitis (for example, caused by sumac poison), the patient may experience symptoms of intoxication - headache, chills, weakness and fever.
The localization of dermatitis can be any and depends on the place of contact with the allergen. Thus, occupational allergens more often form foci of inflammation on the palmar and lateral surfaces of the hands and fingers, forearms, and metal allergens sensitize the skin and mucous membranes at points of contact with rings, bracelets, zippers, and denim rivets (“jean rivet disease”). , metal dental crowns.
Different areas of the skin are characterized by varying susceptibility to allergic dermatitis. Inflamed and infected tissues become sensitized more often. Friction, squeezing, maceration and increased sweating contribute to the formation of allergies. In this regard, the skin of the eyelids, neck, perineum, and anterior abdominal wall in the area of contact with fasteners and buckles is often sensitized. Often patients do not realize that they suffer from allergies, believing that they simply “rubbed” the skin in the area of inflammation.
Allergic contact dermatitis always begins at the site of exposure to the allergen. Therefore, at the beginning of the disease, the lesion is clearly demarcated, although it often extends beyond the area of skin in contact with the allergen. In sensitized patients, the lesion may spread to other areas of the body or become generalized.
With a single contact, the disease lasts several days or weeks. With frequent and regular contacts - months and years.
Diagnostics
Based on the location of skin lesions, as a rule, possible causative allergens can be assumed. In the future, their role in the pathological process is determined when performing skin patch tests. To conduct a patch test, the test material is applied to the skin for 48–72 hours, and then the size of the reaction caused by the allergen is assessed.
Since allergies are always a systemic process, the skin and mucous membranes of the entire body are sensitized. Consequently, inflammation develops when an allergen is applied to any area of the skin. However, it is technically more convenient to carry out patch skin tests in the interscapular region, the outer surface of the shoulder and the inner surface of the forearm, when fixing the material on which the patient feels most comfortable during the study.
The test materials are applied to dry skin treated with alcohol, covered with pieces of gauze and then attached with adhesive tape (that’s why the test is called “plaster”). It is convenient to use a standard test system with standardized allergens already applied to the adhesive base. Thus, the Allertest system for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis to 24 reagents has been registered in Russia. It is sold in a pharmacy and allows you to diagnose contact allergies to nickel sulfate, lanolin, neomycin sulfate, potassium dichromate, a mixture of local anesthetics - caine derivatives, a mixture of flavoring substances, rosin, epoxy resin, a mixture of quinolines, Peruvian balsam, ethylenediamine dihydrochloride, cobalt chloride, p-tert-butylphenol formaldehyde, parabens, carbamate mixtures, black rubber mixtures, chloromethylisothiazolinone, quaternium 15, mercaptobenzothiazole, paraphenylenediamine, formaldehyde, mixtures of mercaptans, thiomersal and mixtures of thiuram derivatives. This is a simple and ready-to-use patch skin testing system. Allergens are included in a hydrophilic gel, from which the allergen is then released when soaked. "Allertest" contains two plates that are adhesive to the skin, each of which contains 12 allergens. All 24 antigens can be tested simultaneously, or the desired allergen can be cut from the plate with scissors and applied independently.
After 48–72 hours from the start of placement, the flaps are removed, wait 20–30 minutes for the nonspecific mechanical irritation to subside and take into account the severity of the reaction. Changes at the site of skin contact with the allergen are taken into account quantitatively. The gradation of a positive result is carried out as follows: (+) - erythema; (++) - erythema and papules; (+++) - erythema, papules, blisters; (++++) - erythema, papules, blisters and severe swelling.
A true allergic reaction lasts 3-7 days, while a reaction caused by skin irritation disappears within a few hours. Therefore, in doubtful cases, the severity of the reaction should be re-evaluated the next day.
H1 blockers do not affect the results of application tests. Topical use of corticosteroids on the skin area selected for testing should be discontinued at least one week before the test. Taking systemic corticosteroids in a daily dose exceeding 15 mg of prednisolone can suppress even sharply positive reactions, therefore skin patch tests are carried out no earlier than 7 days after the cessation of immunosuppressive therapy. In rare cases, skin tests are performed in patients chronically taking corticosteroids if the dose of prednisolone does not exceed 15 mg/day. However, it should be borne in mind that in this case there is a risk of obtaining false negative test results.
When performing a patch test, it should be remembered that the procedure itself may cause sensitization in the patient. Among the substances that have the ability to cause sensitization even at the first contact, it is worth noting plant resins, paraphenylenediamine, and methyl salicylate. Therefore, the application test must be justified. In addition, when conducting the test, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of nonspecific inflammation - primary irritation of the skin by the tested substances. To do this, the test materials, if they are not included in the standard test system, must be used in concentrations that do not cause irritation in the majority of healthy people (in the control group). The test should not be performed in cases of acute or extensive contact dermatitis, as increased skin reactivity may lead to a false positive result. In addition, testing with the causative allergen can cause a sharp exacerbation of the skin process. Therefore, before conducting the study, the patient must be instructed in detail, drawing his attention to the fact that if severe irritation occurs, he must remove the bandage with the allergen and contact the doctor.
When receiving a positive result from a skin patch test, it must be remembered that it only indicates sensitization to the test substance, but is not absolute proof that this particular allergen caused the dermatitis, because the possibility of long-term and polyvalent sensitization always remains. In other words, another antigen that you have not tested may also be the cause of your allergy. Therefore, when making a diagnosis, it is also necessary to take into account the history and physical examination.
Differential diagnosis
Allergic contact dermatitis must be differentiated from simple contact dermatitis, seborrheic and atopic dermatitis.
Simple contact dermatitis can develop due to damage to the epidermis by irritating chemicals (croton oil, kerosene, phenol, organic solvents, detergents, caustic soda, lime, acids, etc.) or physical impact (overheating, squeezing, compression). There is no primary sensitizing effect. Symptoms of inflammation occur immediately after exposure to the irritant, rather than 12 to 48 hours later, as with allergic contact dermatitis. The presence of papules in acute contact dermatitis indicates its allergic nature. Occupational simple contact dermatitis is similar in appearance to allergic dermatitis. The patch test allows you to differentiate these conditions.
The distinctive signs of seborrheic dermatitis include oily skin, as well as other signs of seborrhea and typical localization - the scalp and nasolabial folds. The affected areas are covered with greasy crusts and peel off profusely; Itching is usually not typical.
Atopic dermatitis usually begins in early childhood. The skin is dry. Itching is characteristic that appears before the rash, and not after it, as with allergic contact dermatitis. The flexor surfaces are most often symmetrically affected. The edges of the affected areas are indistinct; There is no consistent development of the elements of the rash: erythema => papule => vesicle.
In our practice, we encountered combined skin lesions when allergic contact dermatitis developed in response to ointments and other topical dosage forms for the treatment of dermatoses. Thus, in a 45-year-old woman suffering from microbial eczema, aggravated by the use of Zinerit (erythromycin, zinc acetate), we identified sensitization to erythromycin, an antibiotic from the macrolide group. 3 days after stopping this medication, the symptoms of exacerbation disappeared.
Three of the patients we examined, who received topical Celestoderm-B with garamycin for a long time, complained of the lack of therapeutic effect from the use of this medication. That is, despite the use of an anti-inflammatory drug, the itching and intensity of the rash not only did not decrease, but sometimes intensified some time after applying the medicine. During an allergological examination using the patch testing method, sensitization was established - a drug allergy to the antibiotic gentamicin (Garamycin), which is part of the drug. Replacing the drug with the topical glucocorticosteroid Elocom after a few days led to complete regression of dermatitis symptoms in all three patients.
When carrying out differential diagnosis, it is also necessary to remember about photocontact, phototoxic and true photoallergic dermatitis.
Photocontact dermatitis is caused by the interaction of a chemical and ultraviolet light in the skin. With it, rashes appear only on open, insolated areas of the body. The sensitizing agent is most often drugs (tetracyclines, sulfo compounds, griseofulfin, hormonal contraceptives) or locally applied resinous extracts. In phototoxic dermatitis, skin damage is caused by the action of substances (for example, hogweed juice) that acquire toxic local irritating properties under the influence of ultraviolet rays. In true photoallergic dermatitis, the sensitizing allergen undergoes chemical changes under the influence of ultraviolet rays. In the absence of insolation, it is harmless to the patient's body.
One of the rare variants of contact allergies is contact urticaria. Depending on the pathogenesis, allergic, non-immune and combined forms of this disease are distinguished. The non-immune form develops due to direct exposure of the skin or mucous membranes to an agent, most often nettle, leading to the release of mediators from mast cells. Allergic contact urticaria is caused by the production of specific IgE antibodies and, according to the mechanism of development, is classified as type 1 hypersensitivity. Most often it is caused by food products (fish, milk, peanuts, etc.), pet allergens (saliva, fur, epithelium) and penicillin antibiotics. Little is known about the combined form of contact urticaria, caused by the influence of both immune and nonspecific factors. It is believed that ammonium persulfate, an oxidizing substance found in hair bleach, often causes this type of reaction.
Treatment
The treatment of allergic contact dermatitis is based on eliminating contact of the body with the allergen that caused the disease. In the acute stage, with swelling and oozing, wet-dry dressings are indicated, followed by topical application of glucocorticoids. If the rashes are represented by large blisters, then they are punctured, allowing the liquid to drain; the bladder cover is not removed; every 2–3 hours, change bandages moistened with Burov's liquid. In severe cases, systemic corticosteroids are prescribed.
Prevention and treatment of staphylococcal and streptococcal skin infections play an important role.
Allergic contact dermatitis generally has a favorable prognosis. With timely identification of the causative allergen and elimination of contact with it, the symptoms of the disease completely regress within 1–3 weeks, and sufficient patient awareness of the nature and causative factors of the disease significantly reduces the possibility of chronicity and recurrence of dermatitis.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of allergic contact dermatitis, the local use of medications with a high sensitizing ability, primarily beta-lactam antibiotics, furatsilin, antihistamines, sulfonamides and local anesthetics, should be avoided.
In case of frequent and professional contact with low-molecular compounds, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment for the skin, mucous membranes and respiratory tract - special protective clothing, gloves, and protective creams.
Once the cause of allergic contact dermatitis has been identified, the patient must be carefully instructed and all possible sources of the allergen discussed with him, drawing his attention to the need to stop contact with this reagent and cross-reacting substances (the most common allergens, their sources and cross-reactive substances are listed in
). For example, patients with nickel allergies are not recommended to wear stainless steel jewelry or use nickel-plated cookware. For such patients, implants containing nickel are contraindicated, including dental crowns and white metal braces, and steel structures for osteosynthesis. It is also recommended that steel rivets and fasteners on jeans or other underwear be sealed on the inside with adhesive tape or cloth to prevent their contact with the skin.
If dermatitis is caused by rubber gloves, they can be replaced with vinyl ones. It is also necessary to remember that rubber drains and other medical supplies should not be used in such patients. The use of latex condoms is contraindicated for them.
If you are allergic to formaldehyde, the patient should not use certain medications and cosmetics containing this preservative. The patient should be explained that before using medications and cosmetics, it is necessary to familiarize themselves with their composition indicated on the packaging.
In the case of occupational dermatitis, it is necessary to recommend acceptable types of work to the person.
Literature
- Harrison T.R. Internal diseases. Ed. E. Fauci, J. Braunwald and others. In two volumes. Per. from English M., Practice - McGraw-Hill (joint ed.), 2002.
- Patterson R., Grammer L.K., Greenberger P.A. Allergic diseases: diagnosis and treatment. Per. from English edited by A. G. Chuchalina. M., GEOTAR MEDICINE, 2000.
- Popov N. N., Lavrov V. F., Soloshenko E. N. Clinical immunology and allergology. M., REINFOR, 2004.
- Luss L.V., Erokhina S.M., Uspenskaya K.S. New possibilities for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis // Russian Journal of Allergology. 2008. No. 2.
- Fitzpatrick T., Johnson R., Wolfe K. et al. Dermatology. Atlas-directory. Per. from English edited by E. R. Timofeeva. M., Praktika, 1999.
E. V. Stepanova , Candidate of Medical Sciences, Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums named after. I. I. Mechnikova RAMS, Moscow
Key words: allergic contact dermatitis, patch skin tests, preventive dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, drug allergens, occupational allergens, contact allergens, metal allergy, contact dermatitis, metal dermatitis, contact urticaria.
Shampoo
As an effective remedy against fleas, special shampoos can be used, which are presented in a large assortment, namely:
- Kiss shampoo - produced in Sweden, it simultaneously kills insects and moisturizes the skin;
- Rolf Club shampoo is a product considered the most effective against fleas, but its more aggressive composition does not allow its use on animals under three months of age.
Many types of shampoos intended for animals, in addition to getting rid of parasites, gently care for the skin, prevent dryness and flaking, and the coat becomes silky and thicker.
Fighting the disease at home
Traditional medicine is used as alternative treatment methods. However, this method does not exclude the professional prescription of a specialist. Rather, this is regarded only as additional measures to alleviate the condition of a mustachioed patient, but certainly not as a panacea for the disease.
- Soap solution. One of the most popular techniques to relieve itching and remove skin rashes. Essential oils of cedar, tea tree and lavender are mixed in equal proportions with soap foam. The resulting composition is used to treat the animal’s fur before and after bathing. The owner will have to be patient, because the results of such treatment will not appear soon.
- Lotions. Infusions of chamomile, fireweed, celandine, burdock, and plantain will help reduce unpleasant symptoms. Usually a compress is applied to the affected area or the surface of the skin is wiped with a cotton swab soaked in the broth.
- Medicinal ointments. You can also make your own special paste. Take one tablespoon of all the above plants and mix with 400 ml of hay dust brew. The resulting mixture is poured with boiling water and steamed in a “bath” for about 5-7 minutes. Then filter the cake and add about fifteen grams of butter to the liquid and keep it on the fire until the mixture thickens. Then add another 15 grams of glycerin and apply to the damaged areas for a month four times a day.
- Chlorhexidine. Based on this antiseptic, various sprays and shampoos are produced that relieve inflammation, prevent infection and have an antimicrobial effect. It is allowed to use a regular 1-2% pharmaceutical solution. It is enough to gently wipe the inflamed area with a moistened cotton pad.
- Hydrogen peroxide. Popular antimicrobial agent. It is better to buy a 3% solution.
- Nutrition. During the acute stage and until stable remission occurs, the animal can be given hypoallergenic food. But it is better to exclude beef, wheat and fermented milk, which provoke allergies. Suitable natural foods would be: pumpkin, turkey, potatoes.
- Vitamins. Be sure to support the dog’s immunity, which is weakened by the fight against the unfortunate allergen. Here you will still have to consult a doctor, since prescribing supplements to your pet at your own discretion is highly not recommended.
In conclusion, I would like to remind you: if you develop hypersensitivity to flea saliva, it will be impossible to completely get rid of this type of dermatitis. The problem will be relevant until the onset of the first cold weather. Then the temperature outside will become unsuitable for fleas and the insects will go into hibernation.
During the warm season, it is recommended to constantly treat dogs prone to this infection. Try to avoid areas with tall, dry grass, where these obnoxious insects like to settle.
And finally, I would like to note that properly functioning anal glands in a pet directly affect the barrier function of the skin. It is important to regularly maintain and keep the area clean. If it is difficult to do this procedure yourself, seek the help of specialists. If these glands work well, it will be easier for your pet to tolerate flea dermatitis.
Be attentive to your four-legged friends. Do not neglect taking care of their health and bring your animal to the veterinary clinic for examination on time.
Spray
Topical sprays are most suitable for contact allergies and flea dermatitis caused by a reaction to fleas.
- Nartz spray has the advantages of a large volume and the presence of several types of the drug, allowing it to be used in accordance with the age and weight of the animal. It has hypoallergenic properties and can be used from one month of age.
- Front-line spray - due to its sufficient volume, it allows you to extend use up to one and a half years, and one application protects the cat from fleas for up to 40 days.
The use of a spray allows you to relieve the animal from itching and obtain an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect.
Purpose of therapy
After making a diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment for your pet. Follow the recommendations strictly. Destroying fleas and eliminating the consequences of their outrage on a dog’s body is a rather difficult task, and it is almost impossible to rid the animal of hypersensitivity to saliva.
Of course, the appointment will be made by the attending physician, but the owner would also benefit from information about the most effective treatment methods:
- Lethal dose. Today on the market there is a huge number of all kinds of tablets, sprays, powders, drops, collars that destroy bloodsuckers parasitizing on the dog’s body. You can easily get confused among this diversity. An experienced specialist will select the right products based on the animal’s condition and the severity of symptoms. Preparations based on imidacloprid and fipronil are considered the most effective. The active substances enter the flea through the blood of an infected animal, although they are not absolutely harmless to our tailed pets. In any case, adhere to the veterinarian's instructions and strictly follow the instructions.
- Fighting allergies. Depending on the scale of the lesion and the severity of the form, the patient will be prescribed concomitant medications. Injections of gluconate or calcium chloride, sodium thiosulfate, which is also administered intravenously and, in extreme cases, hormonal preoral drugs such as prednisolone. The listed substances are aimed at reducing the development or completely stopping the allergic reaction.
- External means. The veterinarian will also prescribe special ointments and shampoos that will soothe the unbearable itching and make the four-legged patient feel better.
- Deworming. As previously mentioned, fleas are carriers of worms and other helminths, so this item will definitely be included in the prescription.
Please note that antihistamines such as Tavegil, Suprastin and others, as a rule, are ineffective for dogs and competent doctors do not prescribe them.
Traditional methods of treating fleas in cats
You can try to alleviate the animal’s condition and treat flea dermatitis in cats at home using traditional methods that will complement the main treatment with medications. To do this, they often use a composition of equal parts of olive and lavender oils and soapy water. Soak a cotton pad in the solution and apply it to the surface of the skin before and immediately after bathing the cat.
The same effect, eliminating irritation and swelling, as well as relieving itching, can be obtained by rubbing with chamomile decoction.
However, if your veterinarian does not recommend using such methods on your animal, then it is better not to use them.
Treatment of the territory
Some owners, after treating their dog, forget to disinfest the dog. Here are a few simple rules to follow:
- Thoroughly vacuum all areas where the animal is. Don't forget about your car, bed, and carrier. After cleaning, throw away the bag or filter.
- Treat surfaces with insecticidal preparations. Neostomozan or Butox will do. As a rule, one ampoule is diluted in two liters of water; in any case, it is better to follow the instructions on the package.
Accompanying illnesses
Flea dermatitis is dangerous due to its complications, the most common of which are:
- development of atopic dermatitis, ending in the formation of lesions;
- the addition of bacterial infections, accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea and symptoms of fever.
If this happens and the cat’s condition does not improve within a few days, then you should immediately consult a veterinarian. To prevent the development of concomitant diseases and complications, it may be necessary to review and change the prescribed treatment regimen.
Home diagnostics
There is a way to identify flea dermatitis without visiting a specialist. Unfortunately, fleas are very small and cannot be seen in the animal’s thick fur. To confirm the diagnosis of flea dermatitis, it is necessary to moisten the animal's fur with water. Then the pet is placed on a hard horizontal surface with an A4 sheet placed under it. They begin to comb and stroke the fur, trying to ruffle it.
It’s great if you carry out this procedure not alone, but with the help of another person: most likely, the cat will break out. The movements need to be carried out within a few minutes.
Instead of paper, you can use white cloth
Look at the white sheet. In addition to hair, dust and pieces of dead skin, small black dots will remain on the leaf. These are fleas.
Prevention
Today there are no effective remedies that could completely protect against allergies to flea bites. To prevent their pet from suffering from flea dermatitis and its complications, owners must protect it from the possibility of infection.
To do this you should:
- do not allow street walks;
- when traveling to the country, pre-treatment against fleas is necessary;
- in case of high humidity, it is better to reduce walks in the air to a minimum;
- Carry out a thorough monthly inspection of the animal for the presence of fleas, and repeat treatment with drugs that have not expired;
- carry out wet cleaning more often in the room where the cat is;
- treat upholstered furniture and carpets with antiseptic agents;
- When you come home, do not leave dirty shoes in the hallway, but after washing them, put them in the closet.
If your pet has undergone treatment for dermatitis and it was successful, it is recommended that its condition be monitored by a veterinarian for several months. This is necessary for timely action in case of relapse.
Preventive measures
Given the extent of the flea population, it is quite difficult to completely get rid of the insects.
Measures to prevent infection of domestic animals with ectoparasites:
- Regular sanitary treatment of the room where the pet is, as well as the things it touches.
- Systematic treatment of the dog with antiparasitic agents containing fipronil, selamentin or imidacloprid.
- Using anti-flea collars or shampoos.
- Make sure that your pet does not come into contact with stray animals during walks.
- Regular and thorough examination of areas of the body with high humidity - the parotid, perianal area, inner thighs and withers.