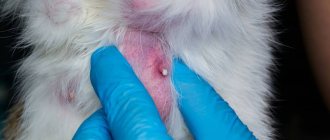
Most often, a cat goes bald during the period of molting, which occurs seasonally. The process is natural, associated with the regular renewal of living tissues. But if hair loss becomes unnaturally abundant, suspicious symptoms appear, or the pet exhibits restless behavior, then veterinary attention is needed. The reasons why a cat has bald spots can be serious pathologies.
What is alopecia?
Alopecia in cats is a pronounced loss of hair.
It does not stop until the negative impact factor is eliminated or appears intermittently. If, during seasonal molting, a cat's hair falls out without consequences and grows back, with alopecia, accompanying negative symptoms are often observed. Their character depends on the causative agent of the disease. Alopecia is pronounced hair loss
Causes of alopecia in cats
Alopecia in cats occurs for various reasons. In this case, negative factors can be not only physiological, but also mental. Hair loss in cats can also be congenital or acquired.
Congenital causes
This group includes factors that negatively affected the fetus through the body of a pregnant female, such as:
- stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- starvation.
Unbalanced diet and fasting lead to alopecia
Anomalies are related to congenital causes. Most often they arise due to mating of related individuals. Sometimes anomalies occur after a pregnant female is irradiated or exposed to chemicals.
Stress and serious mental disorders can cause hair loss in cats
Acquired reasons
Acquired causes of hair loss in cats include:
- dermatological problems. Skin diseases, such as dermatitis, are acquired due to various negative external effects on the skin;
- seborrhea. In this case, alopecia occurs due to overactive sebaceous glands;
- parasites. Ticks, fleas and other parasitic organisms cause itching, which causes your pet to pull out hair, and damage the integrity of the hair and skin.
Due to the presence of ticks and fleas, the cat's coat is damaged.
Provocateurs of alopecia, implying disruptions in the body
Cats lose hair due to problems in the body such as:
- inflammation;
- avitaminosis;
- postpartum period;
- malignant tumors;
- blood diseases;
- infections;
- allergic reaction;
- hormonal imbalance.
Cat with vitamin deficiency
Other causes of bald spots and hair loss
Listed are the main reasons why a cat’s coat may most often thin out. But veterinarians, upon careful examination of the animal, can detect other sources of baldness.
The thickness of the coat in pregnant females changes, and problems with hair can also arise in diseases such as ringworm, solar and neurogenic dermatosis, folliculitis, acne, erythema multiforme .
ATTENTION! All causes are serious and self-medication is excluded. Even if the doctor sends the cat for treatment at home, he will diagnose and prescribe professional, effective treatment.
Why does a cat lick its fur down to its skin, what should I do?
A cat licks its fur down to its skin. Usually a cat washes itself after eating or sleeping - this is its normal, healthy state. Licking the fur down to the skin can signal illness.
If skin is visible in areas of excessive licking, and especially if there are several such foci of baldness, you should treat the animal as soon as possible, but it is also worth determining the cause of this behavior and trying to eliminate it.
Licking a cat's fur can occur due to:
- Nervous overstrain. In such a situation, the animal cleans its nose and whiskers, at the same time nervously moves its tail, while the pupils are dilated, as if the cat was frightened.
- The presence of an unpleasant odor for the cat. It could be a perfumed product or some kind of strong smell.
- Exacerbation of claustrophobia. Cats are terribly afraid of enclosed spaces, so any punishment of the animal by placing it in a space behind a closed door can provoke attacks of licking fur, up to the appearance of wounds on the skin.
- Development of helminthiasis. This infection with parasites, both subcutaneous and internal, is also associated with licking: with this disease, small wounds form on the animal’s body.
- Manifestations of stress and apathy towards the outside world. To stop your cat from frequent licking, you should create the most calm environment for her that does not cause fear, and try not to disturb the cat. After some time of rest the animal will return to normal.
Be sure to read:
Bald patches in a cat near the ears and above the eyes: reasons, what to do, how to distinguish normality from pathology
Features of treatment
You can eliminate bald patches in a cat above the eyes or in another problem area by addressing the root cause of the disease. If parasites are the cause of the skin disease, it is necessary to provide the pet with proper treatment. The use of special ointments, gels and sprays that effectively affect parasites will help improve the condition of your pet. The cat owner should give the animal vitamins that will increase its immunity.
If local baldness occurs as a result of allergies, then it is necessary to limit contact with allergens. A hypoallergenic diet will improve your cat's health. In this case, the veterinarian prescribes the animal to take antiallergic drugs and immunostimulants.
When an animal has problems with the endocrine system, then it is recommended to select special treatment. Taking hormones will improve the cat's health and return its coat to its previous appearance.
Skin diseases
The presence of diseases can also affect the condition of the cat's fur and its loss. Let's list the ones that often occur and cause severe loss.
- Skin mites. A skin lesion that is very unpleasant for an animal, causing discomfort with severe itching, rashes, and inflammatory phenomena that appear in areas of the skin affected by mites. You can recognize the disease by the first symptoms, which appear in the form of dull fur and bald spots on the face, ears and front legs.
- Fungal diseases (ringworm, mycosis). Having discovered the first signs of such lesions, you cannot take any measures on your own; immediately contact a veterinary clinic. We must remember that they are very dangerous for people. A sign of a fungal disease is that the hair falls out in round bald spots, which then form entire lesions. Inside them, scaly formations on the skin are noticeable. After diagnosis, the veterinarian will prescribe treatment, which must be strictly followed.
- Flea dermatitis. Flea saliva can cause an allergic reaction in cats. In addition to extensive hair loss, it can lead to severe redness and itching of the skin. With this disease, most often cats may lose hair on their back.
- Allergic dermatitis. Cats can react to irritants such as household chemicals, pollen, dust, etc. All these substances can cause quite severe allergies, which, in addition to hair loss, causes discomfort to the pet in the form of itching, redness of the skin, and the cat develops sores in areas where it is scratched.
- Psychological reaction to external factors. The sensitivity of cats to external stimuli is not new. Any phenomenon that causes stress in an animal can make the cat not only timid and even aggressive, but also encourage him to pull out his fur with his teeth in those areas where he can reach. This includes the stomach, the back, and the paws. At the same time, bleeding wounds and ulcers appear on bald skin, which can become a gateway for various infections.
- Seborrhea. This skin disease is characterized by particularly severe hair loss on any part of the body. The skin becomes inflamed, oily, and foul-smelling.
shutterstock
Only a competent veterinarian can determine the exact reason why a cat’s hair is falling out, because the same symptoms can be a manifestation of various diseases. To make a diagnosis, you will need to undergo a series of examinations and tests. Based on the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe treatment that will help restore the pet’s skin and coat.
Contacting a veterinarian
Alopecia cannot be ignored; immediately take your pet to a veterinary clinic. Only a veterinarian can determine the cause of baldness. Self-medication of a cat is prohibited. The owner may give the wrong medications, which will worsen baldness and weaken the body.
Diagnostic procedures and tests
To find out why a cat is going bald, the veterinarian prescribes laboratory and instrumental tests.
| procedure | why is it carried out? |
| blood analysis | determining the state of the body, identifying inflammation and hormonal imbalance |
| radiography | studying the condition of internal organs, identifying malignant tumors |
| Ultrasound | |
| microscopic examination of wool | detection of external parasites |
| skin scraping | |
| black wood lamp |
Memo for the owner
When you bring your pet in for an appointment, your veterinarian will begin by taking a history. You need to tell in as much detail as possible about the cat’s diet, living conditions, and heredity. You cannot withhold information: this will complicate the diagnosis. Don’t lie if you feed your cat poor quality food and allow your child to abuse him.
If you tried to treat your pet for baldness on your own, tell us about it. Remember what medications were used and how the cat’s body reacted.
It is not difficult to prevent pathological baldness of a cat, you just need to remain a caring owner:
- buy quality food, maintain a balanced diet;
- do not provoke stress;
- promptly vaccinate against infections and carry out antiparasitic treatment;
- regularly take your cat for preventive examinations;
- do not allow your pet to come into contact with homeless relatives.
Remember, a quiet life and good nutrition are the main factors for the health of a cat’s coat. React to the slightest changes in the animal's condition. Timely and competent treatment prescribed by a veterinarian will protect your pet from complications and stress.
Causes of baldness in cats
The causes of baldness in cats can be congenital or acquired.
• Congenital include those that affected the body of a pregnant cat:
- lack of vitamins and minerals in the animal’s diet;
- stress;
- diseases of various nature;
- unbalanced diet;
- starvation and, as a result, exhaustion.
Exposure to these same causes even before pregnancy can serve as a prerequisite for the occurrence of alopecia in the future generation, as a result of which the fetus experiences disruption of the endocrine glands and disruption of the formation of hair follicles.
This should include hereditary anomalies that arise, among other things, from inbreeding
However, it is important to clarify: if hereditary anomalies are accompanied only by the absence of hair (partially or completely), and not changes in the anatomical location of organs or disruption of their functioning, then we can talk about individual, and in some cases breed, affiliation. It is these anomalies that underlie the creation of cat breeds: Sphynx, Bambino, Elf, Ukrainian Levkoy, Cojona
• Acquired baldness in cats can be a symptom of a disease of the skin itself:
- dermatitis (inflammatory skin diseases);
- seborrhea (increased secretion of the sebaceous glands);
- parasitic diseases (scabies) or fungal infections (ringworm, favus, trichophytosis).
This also includes alopecia, as a result of aging hair follicles, or from constant injury to certain areas of the hairline.
Another large group of factors that cause alopecia in cats are disturbances in the functioning of the body itself:
- stress: the cat itself intensively licks and plucks areas of the skin;
- allergies to food, medications, flea bites, odors, low-quality pet cosmetics, etc.;
- hormonal status disorders: diabetes mellitus, insufficient or excessive levels of thyroid hormones, adrenal glands, etc.;
- intoxication (acute or long-term infectious disease);
- inflammatory processes;
- blood diseases;
- condition after difficult childbirth;
- lack of vitamins, especially groups A, C, B;
- malignant tumors of internal organs.
In some cases, the cause of hair loss in a cat remains unknown, then we are talking about the unknown nature of baldness.
Prevention
You can avoid hair loss in your cat's ears with the following tips::
- Diet. The cat's diet should be balanced, varied and appropriate to its health.
- Self-treatment. In some cases, owners resort to this method, confident that they have made the correct diagnosis. It's better not to take risks.
- Stress. It is necessary to protect the cat as much as possible from emotional turmoil, especially if it is prone to long experiences.
- Regular inspection. It is necessary to visit the veterinarian every few months to prevent the disease or to prevent it from spreading throughout the animal's body.
There are two types of hosts. Some do not pay attention to any symptoms, including those cases when the cat's ears begin to go bald. Others, on the contrary, examine their pets four times a day and, at the first abnormal formation, run to the veterinarian screaming that their kitten is dying. Which one is right? Neither one nor the other. You need to find a middle ground in caring for your animal.
Causes of hair loss on the back legs of cats – How to create a happy home for your pet
Hair loss in cats can occur in many different situations, including but not limited to poor nutrition, autoimmune diseases, fungal infections, allergies and/or parasites.
For example, your cat may be experiencing hair loss due to an allergic reaction caused by fleas or food, or have a bacterial infection such as folliculitis. However, the most important thing to look for in your cat is the condition of its skin.
You want to see if the skin is inflamed, fragile, “normal,” or full of scabs. If your pet is experiencing hair loss, it is recommended that you take him to the vet to determine the cause.
Causes of Hair Loss in Cats
Most often, cats that lose hair on their back legs experience stress and anxiety. When a cat obsessively licks and scratches in a certain area, it is called psychogenic alopecia. Many cats with this condition pick at their stomachs, sides, and legs. This pattern is especially popular with purebred women who have nervous personalities.
This is globally recognized as an obsessive-compulsive behavior in which the cat continually "burrs" an area. Your cat may need an antidepressant or environmental changes, such as keeping other pets away or high perches. Additionally, cats experiencing pain in a specific area may lick themselves compulsively.
Alopecia and baldness in cats
Baldness, also known as alopecia, is not particularly normal in animals. However, some breeds, such as the Chinese Crested dog, are hairless. Since hair loss in pets is generally rare, hair loss should be brought to the attention of your veterinarian so that he or she can look good.
Severe itching combined with licking, chewing and biting can cause hair loss (known as traumatic alopecia). This can also be seen as blunted stubble in the affected area.
When the skin appears normal and not red, inflamed or seemingly troubled, there may be a hormonal imbalance at play. For example, hypothyroidism can happen to cats, but is more common in dogs.
Read also Dr. Elsie's Precious Cat
There are other conditions of feline hair loss, such as eosinophilic granuloma complex (ECG). This is an allergic skin condition, often with accompanying scabs.
Most often, you will see a mass or nodular lesion on the back of your cat's thighs, on the face, or even in your cat's mouth. This type of infection is limited to cats only, and the type of breed does not matter. Typically, granuloma is observed in cats under 2 years of age.
However, those over two years of age are more likely to be female and are more likely to develop symptoms than males.
folliculitis
Folliculitis causes red bumps on the face and body in kittens and cats. This can cause itching, inflammation and infection. This primarily occurs from damage to the hair follicles. You may see raised, red, pus-filled or crusty bumps on the skin. Hair loss can occur due to your cat scratching when hit.
This can easily be seen as miliary dermatitis or skin allergies like atopy. Typically, folliculitis occurs during illness as a secondary symptom. If your cat has problems with its immune system, bacterial infections such as feline immunodeficiency virus may occur.
Additionally, medications such as steroids can cause an allergic skin reaction leading to folliculitis.
Other conditions that cause baldness
There are many conditions that can cause hair loss with or without itching in cats and dogs. Other conditions not mentioned above include non-flea parasites such as Demodex and Notedres mites
Regardless of your cat's symptoms, it is important to take your pet to the vet immediately if your cat shows any signs of illness
Fleas and food allergies can also be reasons why your cat is going bald. Fleas can cause bald patches on your cat's fur due to their relentless biting.
Of course, your cat will naturally lick, chew, and tug at the area, which can cause additional problems such as ulcers and hair loss.
There may also be allergies to fish, wheat, mold or other factors that can cause itching, scratching and excessive grooming.
Read also Black Mouth Cur: Dog Breed Profile
Where do bald spots come from?
Alopecia is pathological hair loss in a specific area of the body.
Some cats have normal alopecia. For example, in the area from the eyes to the ears, hair grows there less often and owners often turn to the veterinarian on the topic: “my cat’s forehead is bald.” Pathological alopecia is one of the symptoms of dermatitis - inflammation of the skin.
- Allergy
- Skin and intestinal parasites
- Stress
- Hormonal disorders
- Infectious and fungal diseases
- Lack of some vitamins
So dermatitis can be considered a serious reason to visit the veterinarian, but for now let’s look at the existing diseases in more detail.
Allergic dermatitis
In fact, cats have terrible allergies. An allergy may be to:
- Chicken
- Pork
- Cereal feed components
- Cleaning agent
- Filler
- Drugs
And much more.
The allergy is manifested by severe shedding, ulcerations on the skin, scratching and restlessness of the cat. A runny nose and lacrimation appear for the second time.
Cats with allergies are prescribed medicated food for life. The most popular are the food from the Royal Canin and Hills line.
Skin and intestinal parasites
Skin fleas include fleas. They bite the animal and cause discomfort, and the cat begins to itch intensely. The hair follicles are injured from such pressure, and the hair falls out, and scratches appear on the exposed skin.
Fleas do not live on the cat itself, but only on the litter. But dark spots of bites are visible on the pet’s body. Favorite places for fleas are the chin, base of the tail and lower abdomen.
In the presence of internal parasites, cats do not tend to tear off their skin, but their fur falls out intensively. Simply because there are not enough nutrients for hair.
Treatment involves treating the cat for parasites.
Stress
A cat experiences severe stress if:
- A small child appears in the house
- Other animals appear in the house
- Moving
- Long road
- Going to the vet
The fur flies off the animal's body quickly and rapidly, and if nervous tension continues for a long time, then bald areas appear on its body.
Treatment: eliminate the stress factor. If for some reason this is not possible, then the cat is prescribed sedatives or anti-stress food.
Hormonal disorders
Causes of hormonal imbalance:
- Change of seasons
- Estrus
- Taking hormonal medications, for example, during estrus or to stimulate it
- Disorders of the pancreas, thyroid glands and adrenal cortex
- Long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Treatment consists of restoring hormonal levels, but before this the animal goes through a long journey of various diagnostic manipulations.
Fungal diseases
The most famous fungus is lichen. It is widespread, and you can only get sick when your immune system is severely weakened. It appears as bald spots on the face, with redness and peeling of the skin.
Diagnosed by pointing a Wood's lamp at the affected area.
It is treated by taking antifungal agents on the skin itself and internally.
Why does a cat go bald - reasons
01. The first reason is not at all terrible: it may be physiological reasons or seasonal changes in fur in especially fluffy individuals.
02. The second reason is adenitis. Most often it affects male cats. It appears as follows:
- crusts appear on the head and ears;
- the fur can be pulled out without causing pain or harm to the cat.
Since this disease is extremely rare, it is better to visit a veterinarian so that he can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. While the case is pending, you can purchase a special detergent or shampoo.
03. The third reason is food allergies. Digestion in cats and cats occurs in a special way. Allergies can occur from any product.
If circumstances force you to change food, it needs to be checked for the degree of digestibility, giving the pet a small amount. Read about how and what to feed your cat here.
04. The fourth reason may be injection. The fur will begin to fall off at the injection site. Gradually everything will fall into place; in this case there is no need to treat hair loss.
05. The fifth reason is seborrhea. Because of it, your furry friend suffers from peeling skin and spreads an unpleasant odor. You will have to have your blood tested at the veterinary hospital. Your veterinarian will recommend shampoo and fatty acids.
06. The sixth reason is lichen. To avoid this disease, you need to keep your cat clean. Well, if this happens, the doctor will prescribe medications.
07. The seventh reason is infestation with fleas or lice. It’s easy to get rid of them by using special hygiene products, but you should monitor your cat more carefully.
08. The eighth reason can be considered stress. When can a cat get it? Due to their personality traits, some animals may begin to go bald from stress during moving, changing housing, or participating in an exhibition. The cat is going bald on the hips, abdomen, and inner sides of the paws.
At this time, the pet needs increased attention and care. In addition, you should distract the animal from the constant desire to lick its fur, because in this case this procedure only provokes its loss
09. The ninth reason is hormonal imbalance. Spayed or neutered animals may go bald due to hormonal imbalance. The cat behaves calmly. Treatment of baldness from this cause will be associated with taking hormonal medications, again prescribed by a doctor. The fur will be restored completely.
How to help a cat whose ears are going bald
After determining the cause, the cat owner will have to strictly follow the veterinarian's recommendations . Any deviation from the planned treatment plan is fraught with complications.
If baldness is caused by dermatitis caused by allergies, then you will have to part with even your favorite hyacinths, lilies and other potentially dangerous plants. Their list is not that long. This includes all types of euphorbia, indoor chrysanthemum, hippeastrum, sansevieria, clivia, primrose, poinsettia.
The medicine that caused baldness should be stopped immediately and special attention should be paid to its composition. It is likely that the irritation was caused by one component, and not their complex. Therefore, be careful when giving your pet all other medications with a similar composition, and ideally, their use should be supervised by a veterinarian. It is possible that the baldness was caused by food, in which case the veterinarian will prescribe a diet consisting of specialized foods. Many cat owners neglect it, and after a while a relapse occurs, i.e. after a short-term improvement, the cat begins to go bald again. To exclude this possibility, you need to give your pet only hypoallergenic food recommended by a veterinarian.
Bacterial infections can only be treated with antibiotics, and to get rid of the virus you will have to follow a whole set of rules. It includes diet, filling the animal’s diet with certain groups of vitamins, and the use of medications.
To eradicate the cause of the disturbance in the animal’s mental balance, you will also have to resort to the help of tablets , although in this case these will be mood modifiers and tranquilizers.
Pathological causes of baldness
All hair loss that occurs for pathological reasons requires specific treatment. The therapeutic strategy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease and eliminating symptoms.
Lichen
This is a group of diseases accompanied by the appearance of skin rashes, scales or nodules, and hair loss. Cats with weakened immune systems become ill. Fungal infections are combined with bacterial infections and occur mainly against the background of the underlying pathology
Parasitic factors
Small ectoparasites - lice eaters - feed on the skin along the edges of its microscopic defects - scratches, ulcers. But the main component of their diet is wool. The cat is going bald.
The activity of subcutaneous mites is accompanied by the development of dermatitis, inflammation of the hair follicles, and hair loss. There are demodicosis, notoedrosis, and sarcoptic mange.
Ringworm in a kitten
Allergy
Hypersensitive reactions, accompanied by dermatitis with hair loss, develop to insect saliva, household items, food components, accessories and inhaled irritants.
Imbalanced diet
An important role is played by the ratio of lipids, carbohydrates and protein in a hundred-kilocalorie portion, as well as the saturation of the diet with vitamins. It is known that the condition of the coat depends on the amount and ratio of biological catalysts in the incoming feed. Hair loss is caused by deficiency or excess of vitamins.
The desire to do what is best plays a cruel joke on cat owners. Most vitamins can accumulate in the body's depots. Primarily in adipose tissue and liver. Uncontrolled feeding of a pet with food additives leads to oversaturation of organs and textures with active compounds. There is a perversion of metabolism, toxicosis, baldness and more serious consequences.
To avoid vitamin poisoning, it is necessary to select factory-prepared food in consultation with a veterinarian. The most nutritious food mixture is intended for a lactating cat. But after the end of the feeding period, you need to return to your normal diet.
Hormonal disorders
When the endocrine glands do not function properly, hormonal imbalance occurs, accompanied by hair loss. Seborrhea develops and pigmentation is disrupted. Black dots appear on the skin - acne.
Physical and chemical factors
When a cat's skin is not properly treated against external or intradermal parasites, a chemical burn occurs, accompanied by hair loss. Solar radiation and contact with hot radiators cause inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, accompanied by hair loss.
Acne on the tail of a sphinx
Congenital pathologies
Seborrhea is a pathology of the sebaceous glands that causes excess secretion. The disease is accompanied by itching, dermatitis, and necrosis of hair follicles. The condition, called sebaceous tail, causes clogged pores and hair loss on the back and ends. There are congenital seborrhea and acquired as a result of parasitic influence.
A similar hereditary disease is called adenitis, which occurs in young and older cats.
Hypotrichosis is a genetic disease in which kittens are born with sparse hair and become completely bald by 4 months. A cat that has lost its natural clothes is doomed to constantly freeze and needs artificial ones.
Greasy tail
Chronic intoxication
Accumulating toxins enter the fur. The body gets rid of toxic products by shedding hair. This is a defensive self-purification reaction.
Treating baldness at home
Depending on the reason why your pet is going bald, a course of therapy is selected:
- If the problem is a lack of nutrients and vitamins, it is recommended to replenish the missing microelements and balance the animal’s diet. Specialized minerals and vitamin complexes are required to be added.
- In case of an allergic reaction, it is important to get rid of the allergen and, thanks to immunostimulating drugs, strengthen the animal’s immunity. The fur will recover on its own over time.
- If the cause of your cat’s baldness is liver pathology, then first of all you need to address this particular problem. You need to contact your veterinarian to prescribe therapeutic therapy. In this case, you cannot do without antibiotics. Amoxicillin is most often prescribed. Once the root cause of baldness is resolved, there will be no manifestations of alopecia.
- During the period following a stressful condition, fur may begin to actively fall out on the pet’s belly and paws. In this case, it is recommended to use sedatives.
- When parasites become the cause of baldness, you need to immediately begin to eliminate them. For this purpose, the pet is treated with special pharmaceuticals. Antiparasitic agents are dripped onto the withers. These can be drops or sprays. Additionally, it is recommended to use immunostimulants and vitamin complexes.
Treatment depends on the identified pathology and is applied strictly under the supervision of a veterinarian
Preventive actions
Caring for and properly caring for your pet will help you avoid many problems, including partial hair loss on the belly and hind legs.
Therefore, it is recommended to adhere to some rules:
- constantly care for your pet’s fur: bathe it and comb it;
- Vaccinate the animal in a timely manner;
- provide periodic medical examinations;
- eliminate stress;
- periodically treat your pet's fur for parasites;
- exclude contact of the cat with sick animals;
- be attentive to your pet's health. If problematic symptoms appear, consult a veterinarian.
After all, these are external consequences of various pathologies. There is no need to guess and prescribe treatment on your own. The only right decision is to seek help from a veterinarian.
Symptoms of baldness in a cat
The symptoms of baldness in a cat are different and depend on the reasons that caused them. The owner notices severe hair loss in the pet, especially noticeable near the tail, on the back, on the stomach, and behind the ears. The skin at the site of the loss is pink or red.
In case of allergies, the owner sees the following symptoms:
- Severe itching
- Skin redness
- Papules and pustules at the site of scratching
- Patchy hair loss
Reddened skin with scabs and wounds is observed when the hair is damaged by microscopic fungi. With scabies, your pet suffers from itching, which causes scratching. In advanced cases, purulent inflammation of the skin occurs. When stressed, a cat licks and pulls out its hair. Areas of baldness are located in the back, on the paws, stomach, and thighs.
With hormonal problems, alopecia appears on the stomach, chest, nose, and at the base of the tail. The skin becomes inelastic.
Diagnostic methods
If your cat's ears are going bald, there is brown discharge from the ears and redness of the skin, then you should contact a veterinarian for help. The specialist will examine the area with lost hair and become familiar with the symptoms that are bothering the pet. If it is not possible to visually determine the cause and severity of the disease due to which the bald spot appeared, then additional diagnostic procedures are prescribed. To make a diagnosis, the following manipulations may be required:
- laboratory testing of blood and urine;
- bacterial culture of urine;
- scraping from the damaged area with further microscopy;
- ultrasound diagnostics of internal organs if there is a suspicion of a violation of their function;
- allergic reaction test.
Return to contents
Dangerous complications
Overgrooming is a fairly serious deviation that can lead to negative consequences. Lack of timely and correct assistance can lead to:
- The formation of wool plugs in the stomach and intestines of cats, leading to their obstruction and accumulation of feces.
- The appearance of non-healing wounds, ulcers, scratches, which are open gates for various types of infections. In severe cases, this can lead to the formation of necrotic lesions. To prevent such situations, you need to treat wounds with antiseptic sprays and ointments, cover them with bandages and plasters.
- Disturbances in the natural growth of the coat, as well as deterioration of its protective functions.
Overgrooming is a pathology that requires a special approach, as well as great responsibility. If its cause was physiological health problems, then treatment should be aimed at eliminating them. After recovery from the underlying disease, pathological licking will go away on its own.
In the article I will describe in detail the reasons why a cat licks itself until it becomes bald, and why it licks human skin. I'll tell you what this entails. I will clarify the treatment of overgrooming in cats. I will dwell in detail on why cats lick their owner and whether it is dangerous for humans.
Licking fur is a normal state for a cat. But everything should happen in moderation. If your pet is licking its fur excessively to the point of baldness, you need to think about it. Most often this is a sign of some kind of problem. Let's look at the most common of them.
Stress
Unusual and even inappropriate behavior of a cat is not always a consequence of deteriorating physical health of the animal. Sometimes the reason has an emotional basis.
A number of situations can cause stress in a pet:
- relocation of one of the family members;
- rearrangement of furniture;
- loss of a pet's favorite toy;
- the appearance of another animal in the house and much more.
A cat's life is predictable and orderly, and anything that brings change is not always good for the pet.
Owners often try to impose rules on the cat.
Licking causing increased skin balding is abnormal
But a freedom-loving animal may have its own thoughts on this matter. It is impossible to act impudently here, and you will achieve nothing. It can cause emotional stress. It is better to find contact with the pet, some kind of mutual solution.
Compromise is the only true way out of the situation.
Itching
If your pet feels itchy, it begins to actively lick these places. Moreover, there is a pattern: a cat licks wounds more accurately than itches. If the licking area is large, it means the cat is itching there. Moreover, attentive owners have noticed that when itching, animals most often lick their back, stomach and other parts of the body.
Allergy
Mostly typical for cats. For example, for dry food, which the animal cannot eat in nature, or for its individual components. Sometimes, of course, medications cause side effects. But this happens less often. You can try changing your diet. You need to consult a specialist; you may need to take antihistamines.
Damage to the skin
Animals have no other way to restore health than to do it themselves. And licking wounds is proof of this. The pet instinctively tries to help itself. But if you have already applied the ointment, it is better to exclude this possibility. Apply a bandage or otherwise limit the animal’s access to the wound site. You can wear a special collar.
Movement restrictions
Cats by nature do not like closed doors. They will constantly be tormented by the question of what is happening in the closed area. Imagine that a person was imprisoned in an apartment and forbidden to leave. Over time, he will begin to tear out his hair. Especially if you previously liked to walk outside for a long time. And animals are no exception.
Although a cat can make do with a small space to exist, too little space is also bad. It is recommended to consider the interests of the pet. This is a living creature that also has its own needs.
Consequences of injury
Observing a cat after it has fallen and been severely injured, you will notice that it has also lost a lot of hair on some parts of its body. Sometimes injuries are visible and easy to diagnose, but they can also be hidden, which is even more dangerous.
Hair loss is sometimes the only visible symptom of internal injuries. Therefore, having detected the appearance of alopecia after a fall of a pet, you need to immediately report this to the veterinarian observing the cat.
Bald spots in combination with fearfulness and wariness quite accurately indicate the stress the cat has experienced. With this state of psychological health, the pet does not want to be handled, does not allow itself to be petted, looks for secluded corners, and may flinch from sharp and loud sounds.
IMPORTANT! As you can see, bald spots on a cat’s body always indicate some kind of health problem, so this symptom cannot be ignored.
Alopecia, or feline baldness: what is it?
This is complete or almost complete baldness in certain areas of the skin with the formation of crusts and the appearance of itching. The skin peels, turns red, and the animal constantly tries to lick this area.
What does alopecia look like?
Alopecia in cats can occur as a result of:
- changes in hormonal levels;
- the appearance of fungus;
- mechanical damage;
- stressful situation;
- vitamin A deficiency;
- obesity;
- allergies, food intolerance to certain products.
Only a doctor can determine the cause and prescribe treatment. It is impossible to determine on your own at home why a kitten is going bald and the reason.
How to protect your cat from baldness
It's actually quite simple, just follow these tips:
- Make your pet's diet balanced, rich in essential microelements and vitamins.
- Do not self-medicate; all medications for animals should only be given with the permission of a veterinarian.
- Avoid plants that pose a potential threat in your home
- Protect your animal from stressful situations
- Keep your cat up to date on vaccinations and see your veterinarian regularly. This will prevent baldness, and if there is already a lesion on the ears, it is possible to prevent it from spreading.
Causes of baldness of a cat's tail
The reasons why a cat develops bald patches on its tail are divided in veterinary medicine into external and systemic. The owner of the animal must be able to distinguish between the seasonal process of shedding and total hair loss on the cat's body.
Seasonal molting is a physiological process characterized by the gradual replacement of dead and unnecessary hairs with new ones. The molting process is not accompanied by the appearance of areas of alopecia.
The main causes of tail baldness:
- Ringworm
. A disease often diagnosed in pets, caused by a pathogenic fungal microorganism. When the skin is damaged by fungi of the genus Trichophytum, areas of baldness with clearly defined edges form. The main symptom of a cat affected by lichen, in addition to baldness, is severe itching, which provokes scratching (in some cases until it bleeds). - Disorders of the endocrine system
. Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system provoke hormonal imbalances. Pathologies of metabolic processes lead to obesity in cats and dysfunction of some organs and systems. Also in cats, in the area of the root of the tail, there are glands that produce a specific secretion necessary for hair care. Increased secretion production leads to hormonal imbalances - the tail becomes bald at the base, and bald patches also appear in the area of the animal’s hips, which the animal carefully licks. - Ecto and endoparasites
. Various blood-sucking insects - fleas and ticks - can lead to severe scratching on the body as a result of bites. In their place, severe itching occurs, the cat scratches the skin with its claws, trying to eliminate the cause of the itching. Flea infestation is often accompanied by a bacterial infection. Helminthiasis can also cause baldness. If an animal eats unheated meat or fish, it develops worms, which cause disturbances in the functioning of the entire body. This is reflected primarily in the condition of the coat and skin. - Allergic type reactions .
Nutritional and contact allergies in cats are being diagnosed more and more often, which is associated with improperly selected food or household chemicals used to wash the floor in the room. Allergies in cats are manifested by skin rashes, severe itching and the formation of alopecia areas. - Bacterial and
fungal infections. Damage to the skin by pathogenic microflora is often a secondary disease that develops against the background of allergies, hormonal imbalance or diseases of internal organs. Failure to provide timely assistance for small foci of bacterial infection leads to extensive lesions and baldness of the animal. - Stress factor
. Cats are emotional animals. If an animal experiences severe stress associated with moving, the arrival of a new family member, cat birth, or renovations, the manifestations of stress can be varied. Against the background of a general depressed state, the pet becomes less active, may refuse to eat, metabolic processes are disrupted, and baldness of the tail or other parts of the body is only a symptom.
- Diseases of internal organs.
Pathologies of the hepatorenal system, digestive tract, and insufficient insulin production lead to various disorders, affecting the general condition of the cat. As a rule, diseases of the internal organs are accompanied not only by alopecia, but also by other characteristic symptoms - eruption of gastric contents, polydipsia, sudden loss of body weight, increases or decreases in body temperature. The diagnosis and treatment regimen must be made by a qualified physician. Self-medication is not acceptable. - Inflammation of the paraanal glands .
Cats have well-developed paraanal glands, which are responsible for the production of a specific secretion. Under normal conditions, its excess is excreted along with feces during the act of defecation. In case of violations, an inflammatory process occurs in the glands, the animal suffers from stool, and the act of urination is disrupted. In the area of the tail root, oily seborrhea and alopecia are observed. - Vitamin deficiency
. The most common cause of bald spots in cats is not only in the tail area, but throughout the body. Vitamin deficiency occurs when there is a constant deficiency of vitamins and minerals. Cat owners whose pets consume natural food are especially often faced with alopecia due to vitamin deficiency. The lack of useful nutrients negatively affects not only the appearance of the animal, but also provokes disruptions in the functioning of all body systems.
Preventive measures
Proper prevention often allows you to avoid problems with hair loss.
- You should carefully choose food for your pet, feed it not only dry food, but also high-quality homemade food (vegetables, dairy products, herbs). The diet should contain a lot of vitamins.
- Vaccination is required, taking into account the schedule for a specific breed.
- It is recommended to protect the cat from stress and injury and provide him with the best living conditions.
- Products for hair care and antiparasitic skin treatment are also needed.
What causes a cat to go bald, what happens to it
Cats go bald for various reasons.
These include:
pregnancy or stress. During pregnancy, lactation, or due to severe stress, a cat may begin to lose fur. But there is no need for treatment; after a while it will grow again;
- baldness above the eyes. At the age of 14 to 20 months, cats, especially dark shorthaired cats, begin to lose hair above their eyes. This process is natural and, if there is no redness, treatment is also not required;
- side effect of the medicine. Sometimes baldness occurs after taking medications;
- consequences of the injection. Sometimes baldness occurs in the area where the injection was given after a couple of months. In addition, there may be skin thickening and hyperpigmentation. Everything also goes away on its own;
- fleas. There are varieties of fleas that cause baldness.
- ringworm. Signs (in addition to hair loss): peeling of the skin, the appearance of crusts, and sometimes itching;
- allergy/contact dermatitis. It happens that a cat develops an allergy from antibiotics or some food component, as well as from interaction with certain materials, metals, and chemicals. In addition to hair loss, redness, bumps, and itching occur;
- solar dermatosis. This reaction to sunlight usually occurs in white cats. It goes away on its own (although the animal will need to avoid sunlight), but sometimes medications are also necessary. Symptoms: hair falls out, redness occurs, crusts and sores appear on the nose and ears;
cheyletiellosis. The causative agent is a tick. The cat itches a lot, but if the disease has not worsened significantly, hair loss is usually minimal;
Important! Ticks easily climb onto other animals and even people.
folliculitis. Infectious disease of hair follicles, occurring on the face, neck, head, accompanied by itching, hair loss;
hyperthyroidism. It happens due to increased secretion of thyroid hormones. With this disease, the fur is easily pulled out and falls out profusely, the cat itches and licks a lot, which causes irritation on the skin;
neurogenic dermatitis. Due to stress, anxiety, or boredom, a cat may lick itself a lot. As a rule, fur loss is symmetrical. To heal, you need to understand the cause of the stressful condition;
alopecia areata. An autoimmune disease that goes away on its own. Fur falls out on the head, neck, body (without itching).
- seborrhea. It can be congenital or acquired (after feline leukemia virus, infectious peritonitis, feline immunodeficiency virus, ringworm, parasites). It manifests itself in different ways: scales appear on the skin, the fur becomes very dry/oily, an unpleasant odor occurs, hair loss occurs;
- hyperadrenocorticism. Caused by elevated levels of corticosteroids (occurs not only for natural reasons, but also as a result of prolonged hormonal treatment). Signs: baldness, thinning of the skin, hyperpigmentation, comedones, bruises;
demodicosis (glandular acne). A tick-borne infection that affects the face and neck. If demodicosis is generalized, this indicates immunodeficiency. Symptoms: baldness, the appearance of scales, redness, itching;
polymorphic erythema. It appears due to increased sensitivity to a medication or infection, and may be one of the manifestations of oncology or other diseases. There is loss of fur, blisters (near the mouth, ears, groin, armpits), and sometimes ulcers. Sometimes the temperature rises and apathy appears.
Important! There are many causes of baldness and medications are not always necessary. But still, do not self-treat; be sure to take your pet to a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis.