Symptoms
Symptoms of subcutaneous mites in dogs begin with severe itching. The pet itches for several hours in a row. As the pathology develops, the signs of demodicosis become as follows:
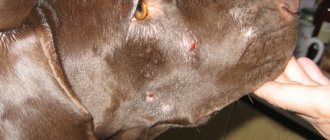
- The hair begins to fall out. The absence or thinning of hair appears spontaneously. Hair falls out predominantly on the face, paws, chest area, and along the spinal column. But it is possible that the problem will also affect other parts of the body.
- On bald areas of the skin comedones or blackheads appear that cannot be squeezed out.
- In pets with long hair, follicular casts are formed. The scales cover the hair shaft, causing the hair to stick together at the roots.
Secondary signs of subcutaneous mites in dogs also include the appearance of blisters, pustules, abscesses or fistulas leading to pyoderma (purulent skin lesions). In advanced forms of the pathology, the pet is depressed and refuses to feed.
Sources of infection
An adult dog becomes infected through contact with sick animals, swimming in ponds with stagnant water, or through contaminated accessories. The disease is transmitted to puppies from mothers who have previously been ill, but the main clinical signs appear in babies at the age of three months.
There is a breed predisposition to infection with subcutaneous parasites in purebred smooth-haired dogs, including such breeds as:
- Shar Pei;
- dachshund;
- Rottweiler;
- Doberman;
- Dogue de Bordeaux;
- kurtshaar;
- bull terrier;
- bulldog (English, French, American);
- Staffordshire Terrier;
- pug;
- miniature pinscher.
The disease becomes noticeable only a few weeks after the initial infection.
What does a subcutaneous tick look like in dogs?
You can see what the parasite looks like in the photo of a subcutaneous tick. Demodex visually resembles a small cigar, the size of which does not exceed 0.4 mm. You can see it only with the help of optical devices and in close-up photographs.
Dog demodicosis: photos before and after treatment
If you contact a specialist in a timely manner and follow the recommendations, the dog may well be cured. And here is the evidence for this:
This is how a dog is transformed beyond recognition after treatment for demodicosis
Even a dog seriously ill with demodicosis can be cured with qualified help.
Forms of the disease
The first signs of the disease become noticeable when the demodex mite in dogs, against the background of active reproduction, creates large populations. Pathology can occur in different ways, so there are several forms:
- focal (local);
- pustular;
- generalized.
Juvenile demodicosis in dogs is diagnosed when the animal is not yet 1 year old.
Focal
The mildest form of pathology is considered to be focal or scaly demodicosis. In sick dogs, 3 to 5 small flaky areas of skin without hair are visualized, having a chaotic location. Affected lesions are found on the head, chest, abdomen or limbs. Under favorable circumstances, the disease goes away on its own after 4-16 weeks.
However, some veterinarians still insist that even with this form, pathologists are better off treating with topical drugs. This will help avoid relapse and also reduce the risk of developing a more severe form of the disease. Some parasites begin to multiply actively when the animal experiences hormonal fluctuations, is stressed, or has recently been vaccinated.
With local demodicosis and the absence of other diseases, 8 out of 10 pets are cured on their own. But relapses of the disease cannot be ruled out.
Pustular
Skin mites often provoke the pustular form of the disease. It is a complication of the scaly form or develops independently.
Dense nodules of damaged lesions change and red-brown or black pustules appear in their place. A month after the onset of the disease, the pustules lose their integrity. And the purulent contents coming out of them have blood inclusions.
During laboratory tests, large colonies of acne glands are found in such secretions at various stages of their development. The wounds emit an unpleasant odor. When the pustular discharge dries, the wound becomes covered with a scab. It is a crust formed by coagulated blood, pus and dead tissue.
Generalized
Generalized demodicosis is the most severe form of acariasis. With it, the same symptoms are observed as with focal or pustular. The difference is that larger areas of the skin are affected.
Generalized demodicosis is diagnosed if more than 5 foci of alopecia are found on the animal’s body.
With this form of the disease, the tick gradually invades new territories. His next target is the internal organs. The immune system, hepatobiliary region and digestive tract are greatly affected by the active activity of parasites. The pet stops eating. He often experiences vomiting, convulsions, and spatial disorientation. Over time, due to general exhaustion, the animal dies.
There is also a separate type of the disease - generalized juvenile demodicosis in dogs. This is a childhood pathology that develops in puppies. The disease is hereditary (autosomal recessive gene). Juvenile demodicosis in a puppy is transmitted from the mother.
This pathology develops against the background of the fact that the production of oxytocin increases in a nursing female immediately after the birth of her offspring. Ticks quickly pass from the sick bitch to the offspring, provoking the onset of the initial stage of the disease.
Causes and pathogens of the disease
Red scabies or demodicosis is a disease that is dangerous for both humans and dogs. However, they will not be able to get infected from each other, because the type of pathogen will be different.
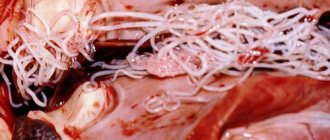
Ticks look like small (up to 0.5 mm) transparent worms with a long body, many limbs and a jaw apparatus. The parasite gnaws its way along the hair, providing passage to the follicle. Demodex lives in the sweat and sebaceous glands at the hair root. It feeds on follicle cells, does not stop at one, but moves throughout the entire epidermis, “eating out” tunnels. The worm lays its eggs at the root of the hair, so up to 250 individuals can live in one follicle.
According to experts, Demodex, as a species, parasitizes almost every animal, but in small numbers, ticks do not cause trouble. Active reproduction of worms begins when the dog’s immune system fails. This often occurs with infectious acute or chronic diseases, with long-term treatment with corticosteroids.
The reproduction of ticks and the exacerbation of the disease are influenced by:
- Age (as a rule, fragile puppies or older dogs suffer from demodicosis);
- Time of year (the most favorable period for the reproduction of parasites is summer, when the development of an individual occurs not in 3-4 weeks, but in 2);
- Hereditary predisposition (most often the disease affects Pugs, Bulldogs, Shar-Peis, Bull Terriers, West Highland Terriers, German Shepherds and Scottish Terriers);
- Improper care and nutrition (gastrointestinal diseases can affect the development of skin diseases, the appearance of bald patches, alopecia, this leads to the defenselessness of the epidermis; fungi and mites most often settle on bare skin);
- Stressful state (depressed, sad or fearful state affects not only the functioning of the cardiovascular system, but also the animal’s immunity);
- Weakening of the immune system;
- Contact with infected dogs.
Such parasites primarily live in the epithelium and do not move throughout the body. When colonies become too extensive, mites look for ways to feed and gnaw through tissue down to internal organs. Then the chances of a cure become minimal.
Empty cavities are filled with intercellular fluid, which becomes an ideal environment for bacteria to live. Demodicosis is also dangerous because it affects the development of other bacterial and fungal diseases.
Complications
Demodicosis in dogs is often complicated by the addition of secondary infections. When the body's defenses decrease, acariasis is accompanied by fungal (ringworm) or microbial infections. The course of the disease becomes noticeably more complicated. In this case, it takes a lot of effort to cure the animal.
Demodicosis of the eyes is not typical for dogs, but the underlying pathology is complicated by the development of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ of vision.
In the generalized course of the disease, pets experience damage to the digestive tract, hepatobiliary region, and problems with the endocrine glands appear.
Forecast
Focal demodicosis disappears without a trace within 1 to 3 months. Treatment of the generalized form lasts from six months or longer. The indicator of clinical recovery is 2 negative tests of skin scrapings with an interval of 1 month. But a complete cure is stated when there are no relapses throughout the year.
With a generalized form in juvenile age, the risk of the disease returning in the future increases, since this often happens due to genetically determined immunity disorders. Such animals require increased attention and painstaking care.
Diagnostics
The symptoms and treatment of acariasis are well known to veterinarians. But before you find out how to treat subcutaneous mites in dogs, a specialist must examine the animal.
Diagnosis of demodicosis involves a doctor studying clinical symptoms, as well as taking scrapings from pathological areas of the skin.
When making an accurate diagnosis, the factor of heredity is taken into account. And if puppies are sick, the mother is also tested.
To determine the presence of mites, scraping is done so deep that blood leaks out. In the complicated form of the disease, many adult parasites and future offspring of parasites are identified. If no mites are found in the biopsy specimen, but the clinical picture clearly makes it clear that they are present, then a repeat scraping is performed. In this case, the biomaterial is collected from another affected area.
Immunity restoration
For any form of demodicosis, create the most favorable conditions for strengthening the dog’s immunity:
- The pet is examined and concomitant diseases are treated if they are detected.
- At home, the conditions of detention are analyzed. Demodex mites love warm, moist environments. The dog's place is located away from radiators. On the street they do not put you in a damp booth or enclosure. The bedding is kept clean, often washed in hot water or changed.
- Carefully protects from stress. Loud noises, unfamiliar people and new animals in the house, and harsh treatment become sources of nervous tension. Some dogs do not tolerate loneliness or travel well, and take a long time to get used to changes.
- Reviewing the diet. When eating natural food, do not overfeed with carbohydrates - cereals, pasta, bread. They do not give sweets, pastries, sausage, bones, or food from the common table. Avoid dry food with low protein content. Do not mix homemade products and industrial feed.
- To restore the skin and coat, it is useful to take a course of injections of the Catozal stimulating solution, add feed sulfur to food at the rate of 0.04 g per 1 kg of weight per day, but not more than 1 g per dog.
In the focal form, these measures are sometimes enough to restore the immune status and stop the spread of demodex. In difficult cases, Immunoparasitan, Fosprenil, Maxidin are included in complex treatment.
There is no consensus in the veterinary community regarding immunomodulators. Many do not see any benefit from them, since the effect of immunostimulants on the immune system that inhibits demodicosis has not been proven.
Pills
Treatment for subcutaneous mites in dogs often involves the use of tablets. The following drugs are popular among veterinarians:
- Simparica (sarolaner);
- Bravecto (fluralaner);
- Frontline Nexgard (afoxolaner);
Simparika tablets for demodicosis for dogs are used once every 4 weeks for 3 months. This medicine has a liver taste, so pets can take these chewable tablets without any problems. Taking into account the weight, a different dosage is selected for each animal.
Ointments
The treatment regimen for demodicosis cannot be completed without the use of external dosage forms. This disease is treated with ointments, which most often have a auxiliary effect. Effective means include:
- Sulfur ointment is simple. A drug with pronounced antimicrobial and antiparasitic effects. The ointment has a detrimental effect on parasites at any stage of development. Indispensable if mycosis is added to acariasis. Apply the product 1-2 times a day to problem areas and the skin around them.
- Ichthyol ointment. The drug has an antiseptic and disinfectant effect and relieves pain. The product is distributed in a thin layer over painful parts of the skin up to 3 times a day. In this case, after application, a gauze bandage is applied to the wounds.
- Vetabiol ointment. A natural product based on coniferous wood substances has antimycotic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing effects. Apply the ointment to damaged areas of the skin up to 3 times a day, without using a bandage.
Aversectin ointment for demodicosis has a more targeted effect. It is an insectoacaricide that has contact and systemic effects. The pet's fur is first trimmed in the affected areas, and then a fairly thin layer of ointment is applied using a spatula or tampon. After even distribution, rub it in thoroughly. Adjacent healthy areas of the skin are also affected.
Treatment with Aversectin ointment is carried out 2 to 5 times every 5-7 days until the animal recovers completely. This must be confirmed by the results of two tests.
To prevent the pet from licking the medicine during treatment, a protective veterinary collar is placed around its neck or the jaw is fixed in another way.
Solutions
To cure a dog, it is also necessary to use specialized liquids to treat problem skin. Doctors often recommend treating subcutaneous mites with Bars Spot-On. The solution contains 2 active components, so it has high antiparasitic activity.
The medicine is applied dropwise to dry skin without damage. The solution is used to treat areas that the pet cannot lick. If the animal is large, then the drops are applied to 3-4 places at once.
To remove the subcutaneous mite with Bars, you need to treat the skin 2 to 4 times. There should be up to 2 weeks between each subsequent application.
Injections
To cure a subcutaneous mite, you need to make a lot of effort. Often therapeutic regimens include injections. Veterinarians prescribe the following injections for subcutaneous ticks in dogs:
- Ivomek;
- Aversect K&S;
- Doramectin;
- Iversect.
Injections against subcutaneous ticks in dogs Aversect K&S contain an antiparasitic active substance from the class of macrocyclic lactones. The drug is administered subcutaneously on the nape, back or lower back. Or they are administered intramuscularly into the buttocks or shoulder.
For demodicosis, Aversect is administered repeatedly (every 7-10 days) until the animal completely recovers.
Shampoos
Treatment of demodicosis in dogs at home is not complete without the use of shampoos.
They remove the outer dead layer of skin from problem areas. Thanks to this, ointments with antiparasitic properties are more effective. Veterinarians prescribe Doctor and Phytoelite shampoo to their patients. Zoological shampoo “Doctor” provides intensive hygienic care, eliminates itching and unpleasant odor. It does not allow the removal of subcutaneous mites, but increases the effectiveness of drugs with antimicrobial and antiparasitic activity for topical use.
With regular use of shampoo, the remnants of the dead layer of the epidermis and pathological secretions are removed, the skin is saturated with oxygen. The shampoo eliminates itching, deodorizes, and suppresses the inflammatory process.
Vitamins
Veterinarians have differing opinions about whether it is worth treating demodicosis in dogs with the use of vitamins. Some argue that this should not be done, since such substances contribute to the active reproduction of parasites. Other experts argue that vitamin complexes can activate the body’s defenses, which help the pet fight the disease.
Most veterinarians prefer to take a middle position and believe that everything is individual. But before giving your four-legged any vitamin medicine for demodicosis in dogs, you need to be 100% sure of them. The pet should not have an allergic reaction to it.
To maintain the general health of the animal, prebiotics for the gastrointestinal tract, hepatoprotectors to support the liver, and immunostimulants are prescribed. Treatment may be costly, but it is better for owners to adhere to all medical recommendations rather than carry out therapy selectively at their own discretion.
You can count on a complete recovery only after completing a full course of treatment.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is permissible only as an additional therapy. Some popular recipes:
- Take the roots of celandine, grind them and fill them with vegetable oil (1:1). Send the mixture over low heat, where the medicine is kept for 3-4 hours. The finished product is applied to areas affected by Demodex once a day.
- Take sour apples or juniper berries. Grind the product until a homogeneous mass is formed and apply to problem areas of the skin.
- In order to carry out hygienic manipulations, ready-made tar soap is used. Birch tar is also applied to pathological areas.
- Prepare a decoction of wormwood (take 3 g of bitter plant material per 250 ml of water). Add 10 g of honey to it. Give the animal this decoction every 2-3 hours.
- Oat baths. A decoction of oats is prepared and added to the water used to bathe the animal. This herbal remedy effectively eliminates itching due to demodicosis.
- To reduce itching, wipe problem areas of the four-legged skin with sea buckthorn oil, buying it at the pharmacy or preparing it yourself.
Folk remedies themselves cannot cope with mites, but they have a good auxiliary effect.
Before using any traditional medicine, it is important to first consult with the veterinarian who is monitoring your pet.
Diet
Treatment at home also involves following a diet. All products given to the animal must be of the first freshness, without the addition of flavor enhancers and dyes.
A large amount of protein products (low-fat meats and fish, eggs) is recommended in the diet. In addition, the animal must eat fresh vegetables, except carrots.
The presence of a small amount of boiled cereals is allowed. It is important to exclude fatty, spicy, salty or smoked foods.
If your pet prefers ready-made food, then it is better to give preference to special medicinal ones designed for allergy sufferers.
The diet of a pet should be complete not only during treatment of the disease, but throughout the rest of its life.
If a pet eats mainly dry food, then the owners must be sure that there are no harmful components in it.
conclusions
Ticks pose a danger not only to animals, but also to humans. To avoid infection, follow preventive measures and purchase a special protective suit for your pet. In this case, it will be very difficult for parasites to get into their favorite areas of the body.
Pay attention to the following points:
- The presence of scabies is an important, but not obligatory, point of mite infestation. In rare cases, the dog does not suffer from itching, but is sure to lick small wounds from bites.
- Demodicosis is an unpredictable and dangerous disease that requires constant monitoring. If your pet is on the mend, don’t let your guard down. Any violation is fraught with relapse, so visit the veterinarian for prevention at least 2 times a year.
- All acaricidal drugs are toxic. Dosages are selected individually, and especially strong drugs (Dectomax) are allowed to be used only under the supervision of a doctor. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Be sure to check your pet after finishing your walk. Carry out a more thorough inspection during seasonal tick activity, which increases their concentration outdoors. Remember that if you have any suspicions, professional help is needed. An erroneous diagnosis made independently can lead to the death of a pet due to improper treatment.
Prevention
Subcutaneous ticks in dogs are a disease that is easier to prevent than to treat. Preliminary measures also help reduce the risk of relapse of the disease.
Prevention of demodicosis in dogs should be carried out as follows:
- Make sure that your pet does not come into contact with sick or stray animals.
- Review your dog's diet. Make it more balanced and nutritious.
- Keep your pet's skin and coat dry and clean. Wash and comb it in a timely manner. Such manipulations make it possible to detect the disease at an early stage.
- Before a planned mating, conduct a preliminary examination of both partners.
- Regularly clean the house, including cleaning the lounger, toys (balls, ropes, bones).
- Make sure that the room where the animal lives is dry and draft-free.
- Regularly monitor your dog's general health.
It is also important to carry out deworming and preventive vaccination on time. The Immunoparasitin vaccine is popular among veterinarians. It helps prevent infection with iron mites.
Vaccination is carried out every 6 months. The manipulation is performed in 2 passes. The break between each dose is 2 weeks.
Features of nutrition during the treatment period
The vital activity of ticks is accompanied by the active production of toxins that disrupt the process of food digestion. To restore the functions of the gastrointestinal tract, the patient is put on a gentle diet. It provides:
- Elimination of fatty and heavy foods. The main emphasis is on chicken breast, beef tenderloin and oatmeal.
- Refusal to reheat. Don't cook several days ahead. Food should not only be of high quality, but always fresh. It is also worth monitoring her temperature. When served, it should correspond to room temperature.
- Transition to fractional meals. Reduce the single portion, increasing the number of feedings to 4-5 per day.
- Monitoring adequate fluid intake. Change the water in the bowl regularly and include rosehip infusions in your daily menu.
When feeding dry kibble, it is recommended to switch to a special line for allergy sufferers. It can be found from manufacturers that produce products of at least premium class.
Traditional treatment
Among folk remedies against demodicosis, birch tar is considered the most effective. For home treatments, you can use it in the form of soap. The dog is lathered with it in the affected areas and left for 3 hours. Then the soap should be washed off with warm water and the skin should be dried. Other effective recipes and folk methods against demodex in dogs:
- mix crushed celandine with vaseline in a ratio of 1:4;
- combine 1 part turpentine and 2 parts drying oil or animal fat;
- mix 5 tbsp. mustard oil with 1 tbsp. crushed garlic;
- prepare a mixture of 2 tsp. grated laundry soap, 1 tsp. birch tar, 2 tsp. melted fat and 1 tsp. sulfur.