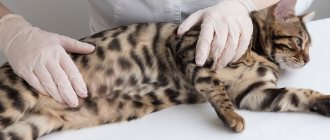
A cat's dense belly should alert owners, because this is a common symptom of digestive diseases and a reason to contact a veterinary clinic. But it also happens that in some situations, abdominal hardness is a natural phenomenon.
Hardness causes tension in the abdominal muscles, which is unnatural. Very often, in addition to this, the cat experiences bloating and other gastrointestinal disorders.
A natural explanation for the changes is the female's pregnancy. In the later stages, the uterus enlarges and the abdominal muscles tighten. The tense peritoneum protects kittens from injury. After birth, it remains hard for several more hours, after which the muscle spasm goes away and the wall returns to its normal state.
Sometimes the reason for a cat's tight belly is fear due to the owner's touch. Not everyone likes tactile contact - some experience stress in such a situation. You need to leave your pet alone so that he calms down.
Organ enlargement
Various abdominal organs may increase in size, resulting in bloating.
Liver, spleen or kidneys
Enlargement of the liver, spleen or kidneys can occur as a result of a benign or malignant neoplasm. This can happen either as a result of tumors growing into the walls of organs, or as a result of solitary lesions, certain types of infections (especially fungal infections), accumulation of inflammatory cells, or a reaction to a disease in another part of the body.
Bladder
An enlarged bladder and difficulty urinating may be signs of a urinary tract blockage, a potentially life-threatening condition. It is more common in males, but can also occur in females.
Gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract can be filled with gas, fluid, foreign material, and even food. This leads to bloating. The most dangerous of the above is blockage of the gastrointestinal tract by a foreign object.
Uterus
In unspayed cats, the uterus may become enlarged due to pregnancy or as a result of the accumulation of fluid or pus. The latter can be life-threatening.
After spay surgery, your cat may experience temporary bloating if she is overly active after surgery or if she has a reaction to the stitches. Therefore, it is important for your pet to rest while recovering from surgery. If the owner notices signs of inflammation, contact a veterinarian immediately.
Natural cause
A cat may have a tight belly for natural reasons. So, in late pregnancy, due to a serious enlargement of the uterus, tension in the peritoneal muscles occurs. This phenomenon is necessary to prevent injury to the kittens. In this case, the cat does not require treatment, since this condition is natural.
The abdominal wall becomes especially hard before lambing, since at this moment all the muscles begin to tense, preparing the body for the birth of kittens. After their birth, the abdomen may remain hard for several hours, thus causing muscle spasm, which is a consequence of severe overload.
Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity
A bloated abdomen in a cat or kitten can be caused by the accumulation of moderate or large amounts of fluid in the abdominal cavity. Typically, in this case, the veterinarian may observe fluctuations when touching the area.
The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity can be a consequence of many diseases:
- Hemorrhage: Bleeding into the abdomen can be caused by bleeding tumors, trauma to internal organs, low platelet counts, or platelet dysfunction. Another cause is poisoning from rat poison, which is called anticoagulant rodenticide.
- Cancer: A buildup of fluid and possibly blood in the abdomen can be caused by cancer.
- Heart Failure: Right-sided heart failure can lead to an inability to pump blood out effectively, resulting in fluid accumulation in the abdomen. Any concern about heart failure should be considered an emergency and require immediate diagnosis.
- Protein deficiency: Decreased protein production usually occurs due to liver failure or kidney or intestinal disease. When protein levels are too low, blood vessels in the body can begin to “leaky,” causing fluid to accumulate in the abdomen and other parts of the body.
- Inflammation: Fluid accumulation and inflammation in the abdominal cavity can be caused by, among other things, pancreatitis.
- Viral diseases: Feline infectious peritonitis, a viral disease in cats, usually results in abdominal fluid and bloating.
- Rupture of a hollow organ: A rupture of the bladder, gallbladder, or gastrointestinal organ can result in fluid from the organ in question leaking into the abdominal cavity and requires immediate veterinary attention. This pathology can occur against the background of conditions such as bladder stones and obstruction of the gallbladder or intestinal tract.
Symptoms of pancreatic inflammation
As we have already said, the pathology has vague symptoms - it is difficult to immediately make a correct diagnosis.
- Profuse diarrhea is sudden, uncontrollable diarrhea.
- Dyspeptic symptoms - rapid saturation, heaviness in the stomach.
- Vomit. Most often it appears in advanced forms of the disease and during exacerbations.
- Cat feces have an unpleasant, sour smell. They contain particles of undigested food.
- Chronic constipation.
- Dehydration: dull, brittle coat, decreased muscle tone, dry skin and mucous membranes.
- Severe pain syndrome. The animal is worried, meows loudly, screams. Doesn't allow you to touch his stomach - he might bite.
- Hard belly.
- The animal hides in secluded places, avoids active games and communication with people, and becomes apathetic and lethargic.
- In the acute form of the disease, an elevated temperature appears.
- Jaundice color of mucous surfaces.
- A sharp decrease in appetite, exhaustion, anorexia.
- Lethargy.
- Respiratory failure: tachypnea (rapid breathing), shortness of breath.
Other symptoms of pancreatic inflammation are also possible. In the acute form of the pathology, the picture of the disease is clearly expressed. The chronic form is sluggish, the picture is blurry.
Intestinal parasites
Causes of bloating in cats may include gastrointestinal parasites, notes the Cornell Feline Health Center. This is more common in kittens, as they are more likely to become infected with worms. Your veterinarian can identify intestinal parasites by testing your cat's stool. Treatment usually involves taking oral antiparasitic medications.
Why do cold sores appear on the lips?
Those who suffer from herpes have noticed that exacerbations begin along with ARVI. Herpes occurs when immunity decreases, the protective forces of which are used to suppress ARVI. Colds on the lips also appear when the body’s defenses are weakened: with chronic fatigue, lack of sleep, frequent stress, poor diet, alcohol abuse and active smoking, in women at the beginning of pregnancy and in the first 5-7 days after childbirth.
Photo: Colds on the lips can only appear if the immune system is weakened
Abdominal masses
Why does my cat have a bloated belly? Perhaps your pet has a tumor in one of the abdominal organs. Such pathologies are more common in adult cats. A neoplasm in the abdominal cavity can be benign or malignant. To make an accurate diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is necessary.
Depending on the location and type of tumor, treatment may include surgery to remove the tumor, chemotherapy, or observation and supportive care with medications.
Medical nutrition
After diagnosis and all therapeutic measures, sick cats are prescribed a therapeutic diet.
In the first days after therapeutic fasting, only liquid mucous porridges with water are allowed: Hercules, buckwheat, rice. Gradually, it is allowed to supplement the diet with steamed egg white omelettes, vegetable purees (zucchini, carrots) and low-fat lactic acid products (yogurt, kefir and cottage cheese). The food should be warm. Give it in small portions 5-6 times a day.
Industrial feed
Animals that are accustomed to dry food are prescribed medicinal food of the “super-premium” and “holistic” classes for life.
Their formulas consist of easily digestible ingredients and contain moderate amounts of fat and protein.
Medicinal foods for pancreatitis:
- Royal Canin Gastro Intestinal Moderate Calorie;
- Hill's i/d;
- Eukanuba Intestinal;
- Purina EN.
What is prohibited to feed:
- raw vegetables and fruits;
- smoked products;
- whole milk;
- fatty meats and fish;
- canned food, salty foods;
- sweets;
- bakery products;
- strong meat broths;
- fatty fermented milk products;
- cereal products;
- industrial feed of the "economy" class;
- dry food containing corn.
A therapeutic diet promotes a speedy recovery of the animal and prevents relapse.
Diagnosis of bloating in a cat
If your cat has a hard, distended abdomen, an examination and diagnostic testing should be performed to determine the cause. Typical types of diagnostic testing for bloating include a complete blood count, urinalysis, ultrasound and/or x-ray of the abdomen, chest x-ray, fluid testing, and biopsy (in the case of a mass). Sometimes more special diagnostics are required if an infectious disease is suspected or an assessment of the condition of specific organs. The examination recommended by your veterinarian will depend on the individual case.
Probability of death
The likelihood of death depends on the situation. The exact indicator is determined only by diagnostic results.
Remember that complications are possible even with non-hazardous factors. The bloating puts pressure on the chest, preventing normal breathing. There is also a high risk of gastric volvulus, intestinal rupture, tissue necrosis and sepsis. To avoid unpleasant consequences, contact your veterinarian if you have any alarming symptoms.
Bloating in a cat: treatment
Treatment for bloating in a cat or kitten depends on the underlying pathology and may include, but is not limited to, removing abdominal fluid, medication, and/or surgery. In any case, it is important to monitor the pet’s condition and consult a veterinarian. Any physical or behavioral changes must be monitored. If an owner is concerned that their cat's belly looks bloated, the easiest thing to do is call a veterinarian and get their expert opinion on what to do next.
Bacterial infection of the deep layer of skin
Occurs when microbes enter deep into the dermis.
Read also: How to make a hookah with milk
Furuncle
First, a painful node appears, then an abscess matures in its center. After 5–7 days it opens, a purulent-necrotic core is released, and the wound is scarred. When there is more than one lesion, they speak of furunculosis.
Carbuncle
These are several boils united into a common infiltrate. The place looks like a purple-bluish tumor. Pain increases, well-being suffers, body temperature rises. After opening the formation, a deep ulcer remains, healing with a scar.
Acne (blackheads)
- inflammation of the sebaceous gland ducts due to blockage. Pustules form on the face, chest, and shoulders. Their contents dry out to crusts, after which, when rejected, scars or bluish spots remain.
Hidradenitis
Purulent inflammation of the sweat glands. The process often recurs. Favorite localizations are armpits, inguinal folds, under the mammary glands. Deep painful nodes appear, bluish-red on the outside. They are opened with the separation of liquid pus.
Bloating in a cat: treatment
Stomach upset in a cat: what to do and how to treat it
Liver diseases in cats and their treatment with dietary cat food
Is your cat gaining weight?
Recovery of a cat after illness or surgery
What should the owner do
Under no circumstances should you play Aibolit or give your pet medications without consulting a veterinarian. Only a specialist can prescribe medications and set their dosage, based on the severity of the pathology, general condition and age of the animal.
Uncontrolled use of medications can lead to potassium being excreted from the body along with urine. This will worsen the cat’s well-being and lead to complications, even to the point where the animal dies. Human diuretics are especially dangerous in this regard.
Increasing their dosage independently can lead to disturbances in the level of electrolytes and leaching of fluid from the microcirculation network. This is fraught with the possible development of encephalopathy.
At the first opportunity, you should take the animal to the clinic so that the doctor can examine it and prescribe appropriate treatment.
A cat with abdominal hydrops is prescribed a therapeutic diet that involves limiting the consumption of water and any other liquid. The food of a sick pet should be nutritious, balanced in vitamins, minerals and carbohydrates and consist mainly of proteins.
The diet includes meat, poultry, sea fish, cottage cheese, kefir. You can add salt to food, but the amount of salt should be minimal.
All types of diseases of domestic cats: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
When a pet is sick, it is always a difficult ordeal not only for it, but also for its owners. Many diseases are easier to prevent than to treat; other cat diseases can be noticed already by the first symptoms and timely treatment can be started. Of course, it is not always possible to treat a cat on your own, but it is advisable for every owner to know at least the most common diseases and their first symptoms. Conventionally, diseases in cats can be divided into groups:
Infectious. The cause of the disease is pathogenic agents; Viral. Diseases that are caused by viruses; Age. Over time, cats' immunity weakens; age-related diseases include kidney failure, diabetes, and heart disease; Parasitic. These diseases appear when parasites enter the animal’s body; Genetic. Most often found in artificially bred breeds such as Persian cats.
Many diseases develop quickly, so if alarming signs appear, it is better to contact a veterinarian without delay. Convulsions, lethargy, photophobia, changes in temperament, drooling or vomiting, loss of appetite, discharge from the nose or eyes, weight gain or emaciation, poor general condition - it is better to visit a doctor immediately, this way you will save the animal’s life.
Urinary tract infection. Frequent urination, persistent defecation past the tray, the cat meows when trying to go to the toilet, extreme thirst - these symptoms may indicate the development of urolithiasis, cystitis or diabetes. The disease is accompanied by severe pain and can cause complications on the kidneys. Also, urolithiasis can manifest itself by the presence of blood in the urine. Its main causes are metabolic disorders and unbalanced nutrition.
As for treatment, the remedy is prescribed by a veterinarian: in the initial stages, diet correction and light supplements are sufficient; in later stages, surgical removal of stones and cleaning of the ducts may be required.
Prevention of the disease is the correct diet, refuse cheap ready-made food, make sure that the animal has access to clean drinking water. If you provide natural food, balance the diet; often it is the abundance of fish that causes the accumulation of excess phosphorus in the body and the deposition of salts.
Calcivirus infection. A viral disease in which the mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory tract become inflamed, the incubation period is up to one week. If the form is acute, the animal has a high temperature (up to 40 degrees), wheezing, cough, discharge from the eyes, photophobia, and pain in the larynx. There is also a chronic form, which can be accompanied by trembling of the limbs, disruption of the functioning of internal organs, and ulcerations.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are used for treatment, both orally and locally. Limit the contact of other animals with a sick pet; recovered cats cannot be used for breeding, since the kittens become infected during the first feeding. You can get vaccinated to create immunity: the most favorable age is from 3 months to 3 years.
Peritonitis. This is an inflammation of the peritoneum in cats and very young kittens; it is caused by a virus. The disease is accompanied by loss of appetite, dehydration, fever, shortness of breath, damage to the eyes, liver (yellow skin), lungs, and kidneys.
Treatment is possible only in the clinic: fluid is removed from the cat’s abdominal cavity and antiseptic and diuretic drugs are administered. Peritonitis causes a fairly high mortality rate in animals, so a visit to the veterinarian should not be delayed.
Ringworm. One of the most common diseases caused by a fungus. Even if your pet does not go outside, you can transfer microspores on clothes or shoes; ringworm can be transmitted to humans, especially people with weakened immune systems and children.
Symptoms: the appearance of red spots, the hairs in these places fall out, then skin crusts and scales appear. Ringworm is mainly localized on the paws, ears and face of the cat. Ringworm is diagnosed using Wood's lamp or laboratory tests. If you direct the light of a lamp onto the affected area, it will turn emerald. The doctor prescribes antibiotics, topical antifungals, and vaccinations.
Ear mite. A pet can also “catch” an ear mite; the main symptoms are: restless behavior of the pet, the cat often shakes its head and tries to get into the ear with its hind paw; after 1-1.5 weeks, a brown or black coating or crust appears on the inside of the auricle.
You can treat ear mites at home; it is very important to complete the treatment, since the development cycle of the parasite is 21 days. You need to regularly clean your pet's ears, apply special drops, and sometimes use medications that are applied to the withers (the capsule acts against both fleas and ticks or worms). Read more in the article - “Ear mites in cats”
Subcutaneous mite. Ticks are dangerous parasites that can carry various viruses and microspores. It is quite difficult to detect them on the animal’s body until characteristic signs appear. Demodicosis is caused by an endoparasitic mite, the animal's immunity decreases, the skin becomes bald in some places, and rashes appear. Ticks are small, they mainly parasitize on the belly, tail, around the bridge of the nose, eyes and ears of the pet. The skin in the infected area becomes covered with dense tubercles, turns red, peels, and hair falls out. Whether there is a tick or not can only be determined through tests.
To treat mites, special shampoos and ointments are used, and drugs with antiparasitic properties are administered.
Helminths. There can be many symptoms that a cat has worms: loss of appetite, excessive thinness, vomiting, bloating, poor coat condition, chronic diarrhea, apathy - all this may indicate that the cat has worms. Often, the body of cats is affected by roundworms (they cause bloating, increased appetite, decreased activity), nematodes (feed on the cat’s blood, and are therefore deadly to it), tapeworms (often found in animals infected with fleas), heartworms (appear in weakened or painful animals). cats, they are carried by mosquitoes).
Treatment for worms in a cat is prescribed by a specialist after taking tests. Practice good hygiene as some types of worms can be transmitted to people. Feed the animal properly, do not allow the cat to catch rodents, carry out preventive measures, give anthelmintics.
Respiratory tract infections. In cats, they are very similar to colds in humans. Typical syndromes are: fever, sneezing, loss of appetite, runny nose, eye damage, tearing and so on. Depending on the severity of the disease, medications are also prescribed: antibiotics, vitamins, drops, and in some cases injections. Infections can cause complications, so contact your doctor promptly.
Panleukopenia or feline distemper. The panleukopenia virus is quite common in nature. Signs of the disease are: vomiting, depression, diarrhea, deterioration of coat condition, poor appetite, convulsions, fever. In many adult cats, the disease may be asymptomatic or may resemble signs of poisoning. The veterinarian makes a diagnosis after examination and laboratory tests. Upon palpation, you can detect enlargement of the abdominal lymph nodes and thickening of the intestine.
The cat is prescribed a diet, given medications to stop vomiting, and given vitamins and fluids to correct dehydration. It is better to carry out timely vaccination against distemper at 8-12 weeks, and then repeat every year.
Rabies in cats. We would like to note right away that this disease is fatal, so carry out timely vaccination, especially if your cat walks outside. The causative agent of the disease is a neurotropic virus; it is localized in the tears, saliva and brain of the animal; generally, the first symptoms appear a month or two after infection. Cats' mood changes rapidly, they begin to swallow inedible objects, and they salivate profusely. Then the cat begins to show aggression, its voice changes, its swallowing muscles become paralyzed, and as a result the animal goes hungry. Paralysis of the entire body develops within a few days, and the animal dies. The infection is transmitted through contaminated saliva or a bite; such a pet is dangerous to other people and animals. If a cat is bitten by an animal infected with rabies, you need to take it to the clinic and get an anti-rabies vaccination, then isolate it for 60 days and monitor its condition.
Treatment
Treatment can be conservative or surgical. This will depend on the cause of the hard belly syndrome. For example, in case of helminthic infestation, it will be necessary to carry out specific antiparasitic therapy; in case of constipation, a special diet and mild laxatives will be required. Antispasmodics are often recommended as symptomatic therapy. These remedies help relax the muscles of the abdominal wall, but can neutralize many symptoms and complicate diagnosis. Therefore, it is better for the veterinarian to show the animal before trying to help it. The most competent method of first aid would be to provide the animal with rest and deliver it to a veterinary hospital.