Depending on the type of reproduction, fish are divided into egg-laying, ovoviviparous, and viviparous.
Egg-laying fish are the main group of fish that spawn eggs into the water column, where fertilization occurs.
Ovoviviparous - internal fertilization, the embryo develops in the female’s body in special extensions of the oviducts, but is nourished by the nutrients of the yolk sac, and the mother’s body serves only as protection from external factors.
Viviparous - in these fish, the union of the egg and sperm occurs in the female’s genital tract, the formation of the placenta occurs, which ensures the connection of the mother’s body with the embryo and supplies nutrients.
Viviparity is a rare phenomenon, typical for aquarium fish (guppies, swordtails), and sharks. There is no larval stage; an embryo develops in the oviducts of the female, and an already formed fry is born, which is capable of independent existence.
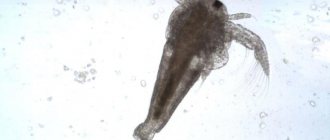
The process of development of an adult fish from an egg
How do aquarium fish reproduce?
There are several natural ways to reproduce fish:
Sexual method
The most popular method of fertilization. It involves the insemination of eggs that mature in the body of females with the seminal fluid of males. It can be both internal (when fertilization occurs inside the female) and external (the eggs are inseminated outside the mother’s body). At the same time, the process of the birth of babies depends on the method of bearing the eggs.
The sexual method of fertilization can be both internal and external. There are spawning, viviparous and ovoviviparous females. Approximately equal numbers of each sex hatch from the eggs.
Parthenogenesis
This method involves the development of eggs without fertilization by the male. This is how commercial fish, cyprinids, usually reproduce. It is extremely rare in aquarium conditions. Such offspring die at the egg stage; even with successful birth, the fry are weak and non-viable.
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is one of the types of reproduction in which the sperm does not take part in the fertilization of the egg. Moreover, this method is considered to be sexual, because one sexual gamete is involved in the process of reproduction. In this case, the egg can develop autonomously until the division stage. After this, it begins to interact with the fertilized eggs and is activated. Thanks to this feature, unfertilized eggs do not have a negative effect on the masonry and do not rot. Parthenogenesis occurs in the following species:
- sturgeon;
- carp;
- salmon.
Types of fish
Fish breeding activities depend on the type of gestation and birth of fry of a particular phenotype.
Viviparous
In viviparous breeds, fertilization of eggs occurs internally.
After this, a kind of placenta is formed, with the help of which the embryos are nourished at the expense of the mother’s body. There is no larval stage, and the fry are born ready for independent life. It is recommended to use a fish tank for viviparous fish. The process of fertilization occurs by introducing the seed using the gonopodium, the male genital organ. The seminal fluid enters the expectant mother in portions (in bags). The remains of sperm remain viable inside the female’s body for a long time. Thus, she can simultaneously carry within herself the seed from different males and give birth to offspring several times during her life without their help.
This method allows you to preserve the embryos, which are protected by the mother’s body. However, most livebearers are bad parents, prone to cannibalism. Therefore, the fry preserved inside the mother's womb can easily be eaten by their own parents.
Viviparous fish are the most popular unpretentious aquarium fish, as they are easy to keep and easy to breed. These are the well-known aquarium fish guppies, swordtails, mollies, formosas, platies, and gambusias.
Stages of fish development
Depending on the method of birth, there are several stages of formation of an adult individual:
- In egg-laying fish, during fertilization, sperm enter the egg cell through the micropyle, an opening in the cell membrane. After the fusion of two germ cells, a zygote is formed, in which active cell division begins and the body of the embryo is formed. Elements of the yolk remain in the abdominal cavity, which will serve as food for the young during the first time after hatching.
- When the time comes, the walls of the eggs are destroyed and larvae are born. Externally, they differ significantly from their parents: a teardrop-shaped body, huge eyes, and no scales or fins.
- After the nutrients in the yolk sac are used up, the larvae begin searching for food. Unicellular organisms, plankton, and algae are suitable for them as food. If the future fry at this moment could not find food for themselves, then with a high probability they will die at this stage.
- Gradually the larvae turn into fry. Their body is covered with scales, fins appear, their shape becomes elongated and in appearance they become similar to adult individuals, only much smaller in size.
- After reaching sexual maturity, the fish is considered an adult. It has all the systems, external and internal organs, scales covered with mucus. Such specimens are ready for further reproduction.
Stages of formation of an adult, using the example of an angelfish.
Livebearers do not need a larval stage, since they immediately give birth to fully viable offspring.
The longer the life cycle of a fish, the later it reaches sexual maturity. Large breeds are usually ready to breed at 4-5 years of age, while cichlids can become parents as early as 3 months. Males, as a rule, are ready for this process earlier than females.
How do guppies mate?
Guppies do not swim very fast, so it is easy to notice that they are in mating season: at this time, their movement speed increases. Small males begin to chase the females and try to snuggle up to their sides. Guppies mate using the gonopodium, a tube-shaped anal fin. Thanks to the movable structure of this genital organ, seminal fluid flows directly into the abdominal cavity of the female - this is how fertilization occurs.
One of the most important conditions for reproduction is that for every male guppy in the aquarium there must be at least two females. If there are more males, they can drive the female until exhaustion and even death. It is advisable that there are no aggressive neighbors nearby, otherwise they will pinch the guppies, preventing them from mating. It is optimal when the male and female are in a separate container.
This is interesting! Having mated once, a guppy can become pregnant and give birth several times in a row.
What kind of development do fish have: direct or indirect?
Depending on the stages of fish maturation, direct and indirect development are distinguished.
Direct implies the birth of babies identical to their parents, having a similar appearance and structure of all organs. This development is typical for viviparous and ovoviviparous varieties.
With indirect development, the individual goes through several stages, and the hatched baby does not resemble its parents. This type of development is characteristic of egg-laying varieties and includes the larval stage on the way to adulthood.
Differences between male and female
The main condition for the successful reproduction of fish in an aquarium is the presence of specimens of different sexes. Most of them have clearly distinguishable sexual characteristics, so it is quite easy to separate them outwardly.
Most of the fish have clearly distinguishable sexual characteristics
Males, as a rule, are more beautiful, bright, colorful, and have lush and large fins. Female specimens are usually more massive, have an inconspicuous appearance and a more rounded anal fin. Sex differences appear in all fish species as they approach their first spawning. It is extremely difficult to distinguish fry from the outside. Therefore, in order not to make a mistake, they immediately purchase a flock of 5-6 specimens. Among them there will probably be individuals of both sexes.
As for internal differences, the main differentiation is the development of germ cells. In the female, eggs (eggs) are formed in the ovaries, which have a thin membrane for the unhindered penetration of the male reproductive cell. When mature, the eggs are released through a small opening located next to the anus.
In males, milt is produced in the testes, consisting of millions of sperm located in paired sacs. The seminal fluid comes out through the vas deferens. In nature, the maturation of cells of both sexes occurs simultaneously.
Angelfish
Angelfish are extremely difficult to determine exactly what gender they are, especially when they are young. Sometimes fully mature males develop a small nuchal protuberance, which is a bump on the head just above the eyes. However, don't expect it to be present in every case. The best way to create a pair is to buy half a dozen immature angelfish and raise them together. When they are mature enough they will split into pairs and you should have at least one breeding pair from the group. Once they start mating, it will be very obvious which one is male and which one is female, since she will be the one who will lay the eggs with the ovipositor. The ovipositor is a short tube extending from the female's opening that she uses to lay eggs. Has a rounded tip. The male will use a pointed tube that extends from his opening to fertilize the eggs after the female has laid them. Both parents will take turns hovering over the eggs, fanning them with their fins to oxygenate them and keep them clean.
Matching
An important factor in the successful appearance of fish offspring is the selection of a pair. For some phenotypes, partners are selected by the owner, while other species mate only with those they choose themselves, for example, discus fish. Having formed a strong couple, they will remain faithful to each other forever.
In order for the union to be successful, it is recommended to purchase an established pair at once, or to populate a flock of fish, in which, with a high degree of probability, at least one couple will be formed. You can find out about this by the behavior of the pets: they always swim nearby, the male seems to be flirting with his partner.
In order for the union to be successful, it is recommended to purchase an existing pair immediately
Male African cichlids are very insatiable and will tirelessly chase females, forcing them to have intercourse. If the female is weak or not ready to mate, she should be housed separately, otherwise such persecution will end sadly for her.
Stimulation for reproduction
Simple manipulations will help stimulate the awakening of the reproductive instinct. First of all, for the proper development of reproductive cells, pets need to be fed abundantly with high-protein food.
The animals are provided with conditions as close as possible to natural ones during spawning. They are specially studied for this purpose. For example, Amazonians begin breeding during the rainy season, when river levels are at their highest and flood water contains large amounts of live food. In captivity, spawning is stimulated by adding water and introducing live food.
Some species reproduce during drought, such as killifish. In this case, the water level is reduced and the temperature of the reservoir increases. Then all that remains is to wait for the first signs of the pets’ readiness to procreate to appear.
For killifish, the water level is reduced and the temperature of the reservoir is increased
Caring for fry
Keeping newborn fish safe from their mother is not all you can do. The main thing is to feed the fry often and monitor the water quality. It is optimal if the kids live inside the aquarium in a plastic or mesh tank. Oxygen enrichment will come from a common aerator, then there will be no need to frequently change the water in which the fry swim.
First weeks
The first week will tell whether the newborn guips will be able to survive. This is the determining period during which the fish need increased nutrition. The crumbs are actively growing, so it is recommended to feed them six times a day with “live dust” - crushed food. Then you can move on to a larger diet:
- ciliates;
- microworms;
- crustaceans;
- rotifers.
The balanced composition of starter food in the form of a paste is optimal for growing guppies. The paste contains all the necessary vitamins and microelements and is easy to use. Aquarists independently grow live food and also produce phytoplankton: they pour aquarium water into a jar and place it in the sun. The process of photosynthesis starts, and after 1-2 days tiny algae appear, suitable for nutrition.
Gradually they come to three feedings a day, avoiding overeating. After two months, we can assume that the danger has passed, the fish have become stronger and are no longer in danger.
On a note! In the first month, you should not turn off the light above the aquarium. 24-hour lighting has a positive effect on the fry: they grow faster.
Determination of gender
For beginning aquarists, it is a very difficult task to distinguish a female from a male among guppies. If sorting is required, consider the signs that make it easier to distinguish individuals:
- in young females, closer to a month, a spot forms near the anus;
- By the time of puberty, males stop growing and look smaller compared to females.
Determining readiness
The beginning of the mating season is determined by the intensity of the colors and habits of the fish. The color of males becomes brighter and more saturated, pigment spots appear. Goldfish develop tubercles on their gills.
The behavior of males is characterized by activity and sometimes aggressiveness towards rivals. Fights often occur between males.
Mating rituals and courtship of the female begin. Some males independently prepare a spawning area, where they then invite a female, swollen with ripened eggs, to lay eggs.
Histogenesis
In turn, histogenesis is a method of reproduction involving sperm. In this case, the activation of the egg is stimulated by its interaction with the sperm of a male of another species related to this one. Once the sperm is in the egg, it stimulates its division. However, the entire process takes place without nuclear fusion. It is noteworthy that the egg in this case becomes a female organism. Males are not formed during histogenesis. Histogenesis is mainly found in silver carps and mollies. In this case, the stimulant for them is the sperm of roaches and cyprinids.
Reproduction of viviparous
In viviparous aquarium fish there is no need to stimulate spawning. If the process does not start, then gradually increase the temperature of the environment by 1-2 degrees. The duration of pregnancy also depends on it. For example, at a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius, the “interesting position” of the guppies lasts 4 weeks, and at 32 degrees – only 19 days. However, it is not worth speeding up the birth process in this way. Overheating will cause the offspring to be born non-viable.
During the gestation period, the expectant mother's abdomen will increase and become rounded; a couple of days before the babies appear, it will take on more angular shapes. At this point, the female is placed in a spawning tank.
During gestation, the abdomen will enlarge and become rounded
Most livebearers are capable of breeding in a common tank, but in it the babies will become food for other adult neighbors and even their own parents.
To preserve as many fry as possible, use a spawning tank with a double bottom. It is equipped with shelters or algae in which the cubs can hide from the mother. A couple of weeks after birth, babies develop their first sexual characteristics and are sorted by sex and size.
Reproduction of spawners
Spawners spawn in different ways. Some species form pairs, others form harems or flocks. The spawning tank is prepared in accordance with the characteristics of the producers.
Dispersal of eggs
Dispersal occurs during school spawning. The eggs scatter randomly and fall onto the ground, leaves and stones. Adult fish do not show parental affection and eat the eggs. To protect the eggs, place the soil in the form of balls with a diameter of 1 cm, cover the bottom with a mesh with small cells.
Masonry formation
The pair form a clutch in a secluded place. The eggs are carefully cared for and protected. Place shelters and broad-leaved plants in the spawning aquarium, where it will be convenient to spawn.
Formation of masonry in caves and gorges
This behavior is typical for fish emerging from aggressive habitat conditions. The spawning ground is equipped with shelters made from piles of rocks, large shells and pots.
Immersion of eggs in the ground
Killie fish, coming from shallow reservoirs with muddy bottoms, form temporary pairs. Pay attention to the soil, choose a substrate based on peat or coconut fibers. Once the parents have spawned the eggs, they can be stored for a couple of months in a warm, dry place. This feature is used when sending eggs by mail.
Nest of bubbles
Labyrinthine fish build nests from air bubbles and pieces of plants. Parents form pairs for life and carefully care for the eggs until the fry appear. When decorating a spawning container, place tall and floating plants. It is imperative to have a tight lid in which an air gap is formed.
Reproduction of ovoviviparous
Ovoviviparous include most cartilaginous species: shark, stingray, katran, sawfish, etc. With this method of reproduction, eggs with young are located in the female’s genital tract, but do not have direct contact with her body. Nutrition of embryos occurs due to the supply of substances in the yolk sac. Some species, such as sharks, feed their offspring with royal jelly, and stingrays with nutrient fluid.
Babies are first hatched in the mother's womb, and only then are born outside.
Babies first hatch in their mother's womb and only then are born
Due to the whimsical nature and large size of cartilaginous ovoviviparous species, keeping and breeding in captivity is extremely difficult.
Peculiarities of reproduction of popular fish
Each phenotype has its own reproductive characteristics, which the owner must take into account when breeding pets.
Veiltail
Having reached sexual maturity by 2 years, veiltails are ready to reproduce. The peak mating season occurs in the spring months. To help the fish show their natural instinct, the water temperature is gradually increased by 3-5 degrees.
The female releases about 2000 eggs at a time. Reproduction of veiltails occurs in a spacious spawning tank, on the bottom of which a net is placed. The eggs are incubated for 4 days, after which the small veil tails hatch into the light.
Guppy
The female guppy is ready to reproduce at 3-4 months. These representatives are completely unpretentious to living conditions and can reproduce even in a three-liter jar. When selecting a flock, you should carefully consider the ratio of female and male individuals. If there is an excess of the latter, the females will be driven, become exhausted and may even die.
Guppies are viviparous fish with internal fertilization. If fertilization is successful, the female avoids male attention and incubates the eggs. Pregnancy lasts on average 24 days. The “interesting position” of the guppies can be judged by the rounded abdomen and the enlarging dark spot next to the anus. Towards the end of pregnancy, the tummy takes on a square shape and protrudes from the sides.
Pregnancy lasts on average 24 days
At this moment, the expectant mother is placed in a container with holes so that she does not eat her babies. The babies slip through these holes into the spawning area, but the female, due to her size, cannot reach them.
During one litter, guppies give birth to about 20-100 babies. Over the course of a lifetime, one female can produce up to 2,000 new fish.
Danio
A few days before mating, the formed pair of zebrafish must be well fed with protein food. To prevent the fish from wasting their strength, the pair is divided into different containers.
At this time, the spawning ground is prepared. Soil is placed on the bottom and covered with a mesh with mesh sizes through which parents cannot reach their offspring. They equip the spawning area with tall plants and let the water settle for several days. After all the manipulations, the couple is released into a container prepared for reproduction.
gold fish
Goldfish are ready to breed at the age of 2 years. When checking in, take into account that for one “lady” there should be 2-3 “gentlemen”. During one litter, the female releases about 3000 eggs.
When setting up a spawning ground, first of all the water is cleaned, settled and disinfected. A mesh is placed at the bottom of the container, lighting fixtures and a compressor are installed. The height of the water layer should be no more than 20 cm.
Goldfish are ready to breed at the age of 2 years
sword bearer
Swordtails, like guppies, are viviparous and are fertilized internally. They reach sexual maturity by six months of age. A month before fertilization, swordtails are fed nutritious protein food.
If necessary (in case of a lack of one or another sex in the flock), swordtails are able to change sex to the opposite.
Incubation continues for 1-1.5 months, after which the female is placed in the spawning area to give birth. the container must be at least 25 liters; small-leaved vegetation is placed on its bottom. After successful delivery, the female is returned to the general aquarium.
Neon
Neons are tiny creatures that breed in soft, clean water. Avoid bright lighting in the spawning area.
A female neon lays about 200 eggs at a time. After birth, it is removed and the spawning area is shaded. The babies hatch within 1-2 days.
Neon babies hatch within 1-2 days
Cockerel
When choosing an alliance, take into account that the partners must be the same size. To successfully reproduce, they need time to get used to. Cockerels are ready for breeding at one year of age.
The pair is placed in a spawning tank with a partition so that habituation is gradual. a container with a volume of 50 liters is filled no more than 15 cm with clean, settled water. Tall and small-leaved plants that reach the surface of the water are planted in it, because cockerels are labyrinthine fish and they need to build a bubble nest. After giving birth, the female is resettled, and the caring father cockerel remains in the spawning area and protects his offspring.
Angelfish
Heat-loving angelfish form a strong pair for procreation. To induce them to mate, it is necessary to maintain a constant temperature in the tank at 27 degrees and feed the future parents with high-protein live food. As a rule, angelfish do not require a separate spawning tank; they lay eggs in a common tank. Up to 800 eggs can be laid at one time.
Heat-loving angelfish form a strong pair for procreation
Catfish (aquarium)
In species aquariums, relocation of catfish to a separate area for spawning is not required. If other representatives of the fauna are adjacent to the catfish, then they are transplanted into a separate tank with a volume of at least 30 liters. The bottom of the spawning area is covered with soft moss and abundantly planted with vegetation.
For breeding to be successful, one female must have 3-4 partners.
Fish instincts
Fertilization is preceded by a series of events. They are a signal of readiness to reproduce.
Stimulation for mating
Many species approach reproduction very responsibly. Salmonids, for example, migrate from the salty ocean up to freshwater bodies to spawn. They can travel thousands of kilometers, making a dangerous journey up fast rivers, exhausting themselves to the end.
In many cases, males (such as guppies) are brightly colored to attract the female. In a mating dance, they circle around the gray females, trying to attract their attention. The lady will choose which male is the most colorful.
Males of other species can build “houses” from silt, mud and other bottom debris. If the female likes the house, the fish mate.
Certain conditions are required for mating
Changes to terms and conditions
Fish, like other living organisms, are subject to biological cycles. Mating occurs under certain conditions that occur with the change of season:
- change in daylight hours;
- change in water temperature (to be more precise, its increase);
- increasing the volume of food (fry need to eat a lot, for example, daphnia and single-celled organisms);
- increasing the concentration of oxygen dissolved in water.
The duration of gestation of eggs depends on the type of fish and can range from 12 hours to one and a half months. The age at which fish reach sexual maturity also varies greatly (from several months to 15-30 years). This depends on the species size and habitat conditions. The smaller the fish, the faster it reproduces and the faster it reaches maturity.
Number of offspring
The number of offspring depends on the phenotype, as well as on the living conditions of the fish. At one time, several dozen or several thousand young specimens can be born. For example, spawning creatures lay a huge number of eggs. Nature takes into account the fact that most of them will not be fertilized by milk, and some of the offspring will be eaten by their parents. Viviparous fish are less fertile because they carry their eggs inside their body. The fewer offspring are born, the more careful care parents show for their future babies.
The number of offspring depends on the phenotype, as well as on the living conditions of the fish
| Phenotype name | Fertility | Tendency to cannibalism |
| Guppy | 15-25 | Inclined |
| sword bearer | 15-100 | Inclined |
| Angelfish | 700-800 | Declined after 2-3 days |
| Danio | 200 | Inclined |
| Neon | 50-200 | Not inclined |
| Gourami | 150-400 | Inclined |
| gold fish | Up to 3000 | Prone after independent movement of larvae |
| Cockerel | 500-600 | Not inclined |
| Lyalius | Up to 800 | Not inclined |
How to create conditions for reproduction and the necessary equipment
To breed fish at home, you will need not only a spawning tank, but also equipment:
- Filters for water purification. This can be either mechanical, chemical or biological treatment.
- Compressors. They are selected individually based on the phenotype requirements.
- Lighting. The intensity also depends on the individual characteristics of the pets.
- Heater and thermometer to maintain and control temperature levels.
- Automated feeding systems.
The aquarium must have a thermometer to monitor the temperature level
Why don't guppies reproduce?
Aquarium fish guppies are very prolific, they have babies every 1-2 months. But it happens that offspring do not turn out in any way.
- The simplest thing is that all your fish are same-sex.
- It is possible that the female has become pregnant, but this is not visible from her.
- Your guppies reproduce, but without the supervision of the owner, the fry that are born are quickly eaten.
- There is also a possibility that the aquarium is overcrowded and the fish are under constant stress.
- They may not have enough food, so the body does not have time to prepare for fertilization.
- The water hasn't been changed for a long time. A sharp change in water and a rise in temperature stimulates the fish’s desire to reproduce.
- One of the reasons for guppy infertility is obesity of internal organs associated with excess feeding. Even starvation does not affect the ability to reproduce as much as overfeeding.
Attention! It is important for the owner to be able to distinguish a male from a female, because this is the only way to select a successful pair for reproduction.
Possible problems
Breeding aquarium fish at home often ends in failure, especially for novice aquarists. To get the long-awaited offspring, you need to know about the possible problems that await the owner.
Overpopulation
It may happen that more fry are born than originally planned. The higher the number of young animals, the more labor is required to care for them. As they grow, they need to be housed either in different containers or provided with a larger tank. Otherwise, the young fish will begin to suffer from relocation. Oxygen deficiency, excess nitrogen and water contaminated with waste products will lead to pets growing poorly and having health problems.
The higher the number of young animals, the more labor is required to care for them
Display of aggression
Many males are ardent defenders of their territory. For example, Siamese fish and cichlids, when they reach maturity, begin to show aggression, start fights, and injure each other. Therefore, as soon as distinguishable sexual characteristics appear, male territorial fish are separated.
Population degeneration
In species aquariums, the problem of phenotypic degeneration often arises. The fact is that generations that appeared from the same ancestors are related. Mating between them leads to a deterioration in the appearance and viability of the fry. Each new generation should be separated into different tanks.
The same applies to closely related species. By crossing, they form mutating offspring that have pathologies and deviations.
Each new generation should be separated into different tanks
Death of the fry
Improper nutrition often leads to the death of fry. It should be remembered that the food must be finely chopped, otherwise the fish will not be able to eat it and will die of hunger. To make sure that the young animals are eating, you can examine the abdomen of one of their specimens under a magnifying glass. If food remains are clearly visible in it, then everything is fine with feeding. If your tummy is empty, you should be more careful about feeding.
It is necessary to monitor the purity of the water, in which not only food remains decompose, but also the excrement of residents. Insufficiently purified liquid may contain dangerous poisons that cause the death of small underwater inhabitants.
Lack of offspring
Sometimes fish do not reproduce even under ideal conditions. This can be caused by damaged gonopodiums in males or older fish that are no longer able to reproduce. In this case, the male is replaced with a younger one.
Not only the male can be the reason for the lack of offspring, but also an elderly female can lay infertile eggs. This can be understood by the whitish coating, indicating the spread of fungus. This can also be caused by inappropriate water parameters such as hardness and temperature.
An older female may spawn infertile eggs.
Fish superclass
- Integument, musculoskeletal system
- Digestive system
- Respiratory system
- Circulatory system
- Excretory system
- Nervous system
- Reproductive system
The body shape is streamlined, fish-shaped, thereby reducing friction with the water. The surface of the body is covered with overlapping scales (like tiles).
In most species, the scales are ctenoid (from the Greek ktéis - ridge and éidos - view) - equipped with teeth or spines, or cycloid (from the Greek kykloeides - circular, round) - with a smooth rounded rear edge.
The skin contains many glands that secrete mucus that covers the entire body of the fish, thereby reducing friction with the water. Because of the mucus, it is difficult to hold the caught fish in your hands; it slips out.
Fins are the organs of movement of fish. Fins can be either paired (pectoral, ventral) or unpaired (dorsal, caudal, anal).
The skull is the seat of the brain and surrounds it on all sides. Characteristic is the presence of a rostrum (from Latin rostrum - beak) - the front elongated part of the fish skull.
The spine consists of two sections: trunk and caudal. There is a hole in the center of each vertebra. Adjacent to each other, the openings of the vertebrae are connected together into a single spinal canal, in which the spinal cord lies.
The skeleton of the pectoral fins is connected to the spine by the bones of the pectoral girdle, in contrast to the skeleton of the pelvic fins, which is not articulated with the spine. There are gill covers that cover the gill slits from the outside (in cartilaginous fish there were no gill covers; 5 gill slits each opened separately to the outside.)
The body cavity is secondary (coelom).
The muscular system is segmented, which is expressed in the appearance of separate (differentiated) muscle bundles. The most striking example of differentiation is the muscles of the oral apparatus and paired fins.
Consists of the oral cavity, pharynx, which continues into the esophagus, stomach, large and small intestines. Many fish have a tongue and sharp teeth located on the jaws in their mouths. Teeth are not designed for mechanical grinding of food, but mainly for grasping and holding prey. There are no salivary glands, but there are taste buds.
The ducts of the digestive glands, liver and pancreas, as well as the gall bladder open into the lumen of the small intestine of fish. There is no spiral valve in the intestine (characteristic of cartilaginous fish), the total absorption area is increased due to blindly ending intestinal outgrowths - pyloric appendages.
The pharynx is closely connected not only with the digestive system, but also with the respiratory system: the gill apparatus of fish is located here. With the help of gills, they have adapted to take oxygen dissolved in it from the water and saturate the blood with it, from where oxygen is supplied to the internal organs and tissues.
The breathing process is carried out due to the fact that water enters the pharynx through the mouth. Due to the movements of the operculum, water from the oropharyngeal cavity is drawn into the lateral gill cavity, washing the gills. As a result of gas exchange, oxygen enters the blood of the fish, and carbon dioxide leaves it and dissolves in the water.
The gills consist of a gill arch on which the gill rakers and petals are located. The gill rakers are directed towards the oropharyngeal cavity and prevent the penetration of food particles into the gills (filtration function). The gill filaments are directed outward and are intertwined with a dense network of blood vessels - capillaries, in which gas exchange occurs.
Like cartilaginous fish, bony fish have one circulation. The heart is two-chambered, consisting of one atrium and one ventricle. Remember that fish have venous blood in their hearts. It is pumped by the heart into the gills, where it is saturated with oxygen, after which the blood becomes arterial.
Arterial blood is directed to internal organs and tissues, blood moves inside the vessels: a closed circulatory system.
It consists of paired ribbon-shaped trunk kidneys (mesonephros, or primary kidney.) They are located on the sides of the body. The ureters begin from the kidneys, merging with each other and forming an extension - the bladder.
Urine containing metabolic by-products is excreted from the fish’s body through the anus in females and through the genitourinary opening in males.
All chordates have a tubular nervous system. The brain consists of the medulla oblongata, midbrain, cerebellum, diencephalon and forebrain.
The development of the same sections in different classes of chordates is not the same, which we will clearly see as we study this section. I recommend that you pay special attention to this topic.
Compared to other classes of chordates, the brain of fish is poorly developed: the forebrain cortex is absent, instead the surface of the brain is covered with epithelium. The midbrain, the main coordinating center, reaches its greatest development.
The cerebellum, which is responsible for coordination of movements and orientation of the body in space, is also well expressed (developed). This is due to the complex movements of the fish, which “soars like a bird” only not in the air, but in the aquatic environment. 10 pairs of cranial nerves originate from the brain.
The sensory organs of a fish are represented by a special formation - a lateral line, stretching in the form of a channel along the entire body on both sides. Sensitive cells (neuromasts) of the lateral line organ respond to changes in the direction and speed of water flow near the fish. With its help, the fish senses the direction and speed of the water flow.
In fish, a specialized hearing organ—the inner ear—appears for the first time. With its help, they are able to distinguish sounds while navigating in the aquatic environment. The inner ear consists of three semicircular canals, the upper and lower saccules. Sometimes the inner ear is connected to the swim bladder (catfish, carp), due to which the hearing in such fish is more developed.
The organs of vision are adapted to the aquatic environment: the lens has a spherical shape. The cornea is flat, accommodation (adjusting the eye to the best vision of an object) occurs only due to the movement of the lens.
Fish see well only at close range. There are taste organs on the skin and lower jaw, as well as olfactory organs that open into the oral cavity.
Fish are dioecious. The gonads of males are testes, of females - a single ovary. Fertilization is external and occurs in water: the female lays eggs (eggs), and the male releases sperm into the water, which merge with the eggs. Over time, young individuals develop from eggs.
Development in most fish (teleosts) is indirect, with metamorphosis. Remember that the process of laying eggs and their subsequent fertilization is called spawning, it is seasonal. Freshwater fish spawn in the spring; fishing is strictly prohibited at this time.
Feeding and caring for offspring
As soon as a new generation is born from eggs, even the most caring parent fish leave their young. All care for the young falls on the shoulders of the owner.
The fry are kept in the same container in which they were born. If this happened in a common aquarium, then they are caught and moved to a separate tank so that they do not become an object of food interest.
Ideally, the first food for babies should be single-celled organisms, such as ciliates. However, not everyone has this opportunity. Therefore, they begin to feed them with specialized dry food ground into flour or with brine shrimp and daphnia ground into dust. Meal frequency: 2-4 times a day.
The first food for babies should be liquid. The ground food is mixed with water and dropped drop by drop onto the surface of the water, evenly distributed over the entire area so that all the kids get it.
As the young grow, they are moved to a larger container, separating them by size and gender. You should not allow both large and small specimens to be in the same jar, otherwise the latter may become live food for the taller ones.
Breeding fish at home is a labor-intensive process that is worth the effort of the aquarist. If you follow the rules and recommendations, your pets will definitely delight you with a large flock of young offspring. In addition, fish breeding, if desired, can not only be an exciting hobby, but also grow into a profitable business.
Have you bred fish in your home aquarium? How difficult did you find this whole process? Share your opinions in the comments.
Pregnancy period
The embryos develop in the female's abdomen over 4-6 weeks. The gestation period depends on the age of the “mother” and the temperature of the water in the aquarium. Next, we will tell you how to determine the pregnancy of a female guppy by her appearance and behavior, and also consider the nuances of preparing for childbirth.
Determining pregnancy in guppies
In the early stages, the pregnancy of a female guppy cannot be determined, and it is difficult to tell whether fertilization has occurred. But every day the female’s belly grows, rounds, and her back bends. The guppies' appetite increases. She tries to hide deep in the thick of plants, often sinking to the bottom and licking the muddy sediment. This food supplement serves as a source of microelements that fry need.
By the end of the gestation period, the guppy's abdomen swells significantly and takes on a rectangular shape. A so-called “step” appears between the stomach and head - a sharp drop that indicates a normally developing pregnancy. A dark spot appears in the lower abdomen, the anus increases in size.
Is it necessary to remove the female for childbirth?
For a pregnant fish, changing place of residence is stressful. There are cases of delayed birth in released fish. When you don’t want to interfere with the natural process, you can leave the female in her usual environment and not take any action. However, if breeding guppy is your goal, it is recommended to move the female to a nursery during the birth. The fact is that in wild guppies, after birth, the fry are immediately carried away by the current, but in a home aquarium there is a closed space. Waterfowl look at the miniature fish as food, and even parents can eat their offspring.
Attention! A special tray - a depositor, placed in the aquarium, will save the situation. And the pregnant fish will be able to feel at home, and the babies will be safe. It is easier to place the female in time than to later catch the newborn fry with a glass.
Prenatal behavior and childbirth
Feeling the approach of childbirth, the female tries to move less, because of this she freezes. In search of warmth, it stays close to the heater. She takes in little food and often belches food. At the beginning of spawning, the guppy freezes and its tail trembles slightly. The fry appear one after another, some immediately break the shell and begin to swim, others lay down on the bottom. This is normal - after some time they will gain strength. To prevent a tired mother from eating her fry after giving birth, she must be immediately returned to the general aquarium.
How many fry can be born
It is very difficult to calculate how many fry were born, because they are in constant motion. The number of fish depends on the condition of the female:
- her age;
- size;
- having childbirth experience.
If the female guppy is young, pregnant for the first time, she will give birth to no more than 20 fry. In its prime, the fish gives birth to 50-100 babies.