The thorn belongs to the sturgeon fish. Therefore, the appearance of the thorn is characteristic of all representatives of this family. The snout has a conical shape.
On the back there are oblong bugs with sharp edges. The color of the thorn is lighter than that of the sturgeon; therefore, it is also called the white sturgeon.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-BRny9hnSL8
The body length of this fish can reach 2 meters, and its weight exceeds 20 kilograms.
Description of the spike
The body is torpedo-shaped. The spine differs from other species of sturgeon by having a continuous lower lip that is not interrupted in the middle. The mouth is lower, transverse, exceeds half the width of the snout, and extends into a proboscis. The antennae are fringed. Dorsal bugs 11-17, lateral (49) (52) 55-66 (70) (72), ventral (0) 12-16. There are 24-42 gill rakers. There are 45-57 rays in the dorsal fin and 23-37 in the anal fin. There are no bone plates on the body between the rows of bugs. The gill membranes are attached to the interbranchial space. The Caspian population has a more massive body and caudal peduncle, a smaller eye diameter and a larger postorbital distance. Forms crosses with stellate sturgeon, Russian sturgeon, and beluga.
Spawning time and lifespan
The thorn can live for a very long time - up to 30 years. But external circumstances often do not allow the thorn to reach this age. Females mature only at the age of 13, sometimes later; males - for 9-12 years. They spawn in the spring, at a water temperature of at least 10°C, optimally around 20°C, for which they migrate to inflowing rivers, looking for muddy water and a pebble bottom. The Kurinsky thorn is more prolific than the Ural thorn.
Thorn Reproduction
In Kura, thorn spawning begins in late April - early May. In the upper reaches of the Syrdarya, the first thorns appear in early September, and the peak of the course occurs from the end of September to the end of October. In the lower reaches of the Syr Darya, the thorn does not lie down for the winter and does not spawn here. Thorn spawning in the river. The Urals begin at a temperature of 12-13°C and usually end at 18°C. Spawning of the Aral thorn began in March at a water temperature of about 10°C, and ended in the second half of May at 21-23°C. The Balkhash thorn begins to reproduce at a water temperature of 10-12°C in sections of the river with rocky, pebble and coarse sandy substrate at a depth of 0.7-2 m. Spawning is extended and ends at a relatively high temperature - 21-24°C.
It spawns no more than once every two years. The fertility of the thorn depends on the age, size and body weight of the fish. The lowest fecundity is 101 thousand eggs, the highest is 1032 thousand. The average fecundity of fish maturing for the first time is about 314 thousand eggs in size. The eggs are about 3 mm in diameter and stick to the pebbles. Spawned individuals roll into the sea.
The size of the running thorn in the lower reaches of the Syrdarya is from 100 to 180 cm (on average 140 cm), age from 11 to 30 years, the main mass is at the age of 15-20 years, the maximum falls on 18-year-olds. The average weight of the Syrdarya (non-gutted) thorn from the lower reaches is 19 kg (1925).
Maturation and nutrition
The lifespan of a thorn fish is 30 years.
The lifespan of this sturgeon fish can exceed 30 years. The body length can reach up to 214 centimeters, and the weight is about 30 kilograms. In the Aral Sea, most fish live to the age of 12-21 years. And they reach sexual maturity when they reach the age of 12-14 years.
In Kura, thorns aged 6-23 years are mainly caught, with most of the females being up to 19 years old, and the males up to 16 years old.
The average weight of thorns caught in the Aral Sea is about 16 kilograms, and on the Kura River larger specimens weighing up to 20 kilograms are caught. One female Aral thorn brings about 216-388 thousand eggs, and among Caspian thorns the fertility ranges from 280-1290 thousand eggs.
The sturgeon is the closest relative of the sturgeon.
In the Aral Sea, these fish feed mainly on mollusks, and in the Caspian Sea, in addition to mollusks, they also eat other types of fish. The thorns living in Lake Balkhash lead a completely predatory lifestyle, while only the winter race lives in the lake, as in the Aral Sea.
In 1933, 289 adult thorns from the Aral Sea, which weighed from 6.7 to 30 kilograms, were artificially released into the Ili River. These fish laid eggs in the Ili River in 1934. The offspring that appeared returned to the Ili River again at the age of 14. In Lake Balkhash, the size of 11-year-old spikes is approximately 130 centimeters, and the weight reaches 9.5 kilograms.
Spike fish in an aquarium with lampreys.
In nature, thorns interbreed with sturgeon, beluga and stellate sturgeon. A cross between a thorn and a stellate sturgeon is called a “stellate thorn”. On the Kura, crosses between thorn and sturgeon and thorn and stellate sturgeon, which are distinguished by their high vitality, were artificially bred.
Development
The incubation period, depending on the water temperature, lasts from 80-90 to 140-150 hours. Ten-day-old thorn larvae, in which the yolk has already been absorbed, have a length of 15.5-17.2 mm, month-old juveniles - 24.6-37.2 mm . The thorn larvae switch to active feeding at a length of 20 mm. The hatched juveniles roll into the sea. A significant number of juveniles winter in the river. It lives mainly in large and deep holes (10-18 m), where current speeds are much lower than in reaches. After moving into the sea, the spike does not go far from spawning rivers and mainly sticks to pre-estuarine desalinated areas to a depth of 50 m, where it fattens.
The size of juvenile thorn in the Syrdarya in July - August ranged from 3.4-8.2 cm. The speed of the downstream of prelarvae and larvae is close to the speed of the river flow. The thorn is characterized by retention of a significant part of the juveniles in rivers for up to 3-4 years or more. Grows quickly. The North Caspian thorn is distinguished by greater precocity than the Aral thorn.
Related article Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii)
Habitat of the thorn fish
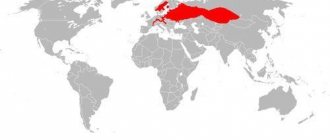
The thorn is found in the river basins of the Caspian Aral Sea. It can also be found in the basins of the Azov and Black Seas, but only in rare cases. The thorn is an anadromous fish. In the Caspian Sea they are found mainly in the southern part, and from there they enter the Kura River during the spawning season. In the Iranian part, they go to Sefidrud to spawn. This fish is not often found in the Volga. But there are quite a lot of thorns in the Ural River.
Thorn (Acipenser nudiventris).
Previously, in the Aral Sea, thorn was a fairly numerous species and was the only representative of the sturgeon, but after people bred sturgeon in the sea, the number of thorn decreased. During spawning, the thorn rises high into the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers, a distance of approximately 2,600 kilometers. The thorn also lives in the Ili-Balkhash basin.
Economic importance
The thorn is the most valuable commercial fish. They are caught using cast seines and smooth nets. Stocks have been severely depleted. It is prepared chilled and frozen, and is also used for preparing dried and smoked products. In the Urals, thorn nuts are used to make granular caviar, which in value is between sturgeon and stellate sturgeon.
The species is characterized by a naturally low abundance throughout its entire range. The species is included in the Red Book of the Russian Federation, the IUCN Red List 2000 , Appendix 2 of CITES, and the Red Book of the Saratov Region. The main limiting factor is the unfavorable hydrological regime and poaching.
Literature: 1. Lebedev V.D., Spanovskaya V.D., Savvaitova K.A., Sokolov L.I., Tsepkin E.A. Pisces of the USSR. Moscow, Mysl, 1969 2. L. S. Berg. Freshwater fish of the USSR and neighboring countries. Part 1. Edition 4. Moscow, 1948 3. Fishes of the north of the Lower Volga region: In 3 books. Book 1. Composition of ichthyofauna, methods of study / E.V. Zavyalov, A.B. Ruchin, G.V. Shlyakhtin and others - Saratov: Sarat Publishing House. Univ., 2007. - 208 p.: ill. 4. Fishes of Kazakhstan: In 5 volumes / Mitrofanov V.P., Dukravets G.M., Peseridi N.E. et al. - Alma-Ata: Science, 1986. T. 1. Lampreys, Sturgeons, Herrings , Salmonidae, Pike. — 272 p. 5. Atlas of freshwater fish of Russia: In 2 volumes. T.1. / Ed. Yu.S. Reshetnikova. -M.: Nauka, 2003. - 379 pp.: ill. 6. Commercial fish of Russia. In two volumes / ed. O.F.Gritsenko, A.N.Kotlyar and B.N.Kotenev. - M.: VNIRO publishing house. 2006.- 1280 p. (Vol. 1 - 656 pp.).
How to catch flounder
Flounder tackle seems like a rather mysterious device for an amateur in sea fishing. However, anyone who gets the opportunity to catch this mysterious fish must first be prepared for fishing, at least theoretically. Poachers who caught 317 kg of fish were not punished
A group of fishermen revealed the name of the secret bait during interrogation.
Category: regional news.
MORE →
Most “freshwater” anglers will never fish for flounder in their lives. However, in order not to “fall on your face” if such an opportunity arises, you need to know something about this fishing.
The flounder family consists of several dozen representatives. Their habitat is almost all the seas washing the post-Soviet expanses. But amateur fishing for this fish is more common in the Black and Baltic Seas.
Biting periods and location of flounder relative to the shore:
- in spring and summer, the fish is located at a distance of 3-10 km from the coast, so they catch it from a swimming device;
- at the end of August - beginning of September in the Baltic Sea, flounder approaches the shores at a minimum distance and becomes available for coastal fishing;
- flounder approaches the shores of the Black Sea in November and remains with them almost until the New Year;
- in winter the fish move away from the shores;
- Flounder bites most actively in the early morning and at night;
- in the Black Sea, flounder is caught from a boat all year round;
- Flounder often approach the shore after a storm.
Fishing for flounder will be successful if you accurately study its habits and habitats in a particular body of water depending on the time of year and weather, because this fish constantly uses the same migration routes, as well as feeding places.
The bottom lifestyle tells you how to catch flounder. They catch it with bottom tackle both from the shore and from a floating craft.
Basic requirements for gear for bottom fishing for flounder:
- For fishing from the shore - a powerful carp or feeder rod with a length of 4 m and a weight of about 200 g.
- For fishing from a boat, a spinning rod 2.1-2.4 m long is sufficient.
- A marine reel capable of casting 50-80 m and also holding up to 150 m of fishing line.
- Monofilament line 0.4-0.6 mm or equivalent braid.
- Monofilament leashes with a diameter of 0.3-0.35 mm and a length of 20-30 cm.
- End sinker 70-200 g.
- Durable hooks with a long shank No. 8-14 according to Soviet qualification. Multi-colored beads or fluorescent balls above the hooks can activate the bite.
To diversify your fishing, it makes sense to try spinning baits such as jigs, sinking sea wobblers, and also vertical lures from a boat.
It also happens: Feeder method of fishing
Food and bait
Due to the original body structure, flounder has adapted to a bottom lifestyle. The body allows this fish to take the shape of the bottom relief and burrow into the ground, and some species are able to change the color of their upper side. Thus, wherever the flounder lies at the bottom, that’s where its ambush will be.
The food of this predator includes almost everything that can be found in the bottom layer:
- crustaceans;
- shellfish;
- worms;
- small fish.
The following is used as bait for catching flounder:
- mussel meat;
- squid meat;
- anchovy;
- shrimp;
- small bull;
- fish fillet;
- sea worms - neris, sandworm and others.
This is not all that you can use to catch flounder; in fact, it is omnivorous and carnivorous, but sometimes it behaves finicky and requires experimentation with bait.
Flounder should be understood as several species of fish, distinguished by their unusual body structure and body shape itself. Flounder should be understood as “flat” fish species, which is what it means in translation.
As a rule, these types of fish live in close proximity to the bottom and are of industrial interest due to the fact that the meat of these fish has excellent taste. Basically, flounder lives in the seas and oceans, but sometimes enters rivers. Flounder is considered a predatory fish because it feeds exclusively on living organisms. How useful the fish is, its catching and its behavior will be discussed in this article.
In the eastern Atlantic, Mediterranean and Black seas. In winter it goes deeper or into warm waters.
April – October. Stops pecking if the water temperature drops below 15 degrees.
In any weather.
Deep holes 30 - 100 meters from the shore. Prefers rocky coastlines, steep cliffs, piers and sandy soil.
Stellate sturgeon
This species is a close relative of the sterlet, but is much larger in size - up to 2 meters in length. Due to the thin and narrow body, the weight of such huge individuals remains small - about 80 - 100 kg. The head also has an elongated and narrow shape.
The lifestyle of this migratory fish is associated with constant migrations. Therefore, it can be found both in the rivers of the southern seas and in the seas themselves:
- Black
- Aegean
- Adriatic
- Caspian
- Azov
Spawning of stellate sturgeon occurs only in fresh water. Fishing in the wild is completely prohibited, as its numbers have seriously declined in recent years.
Stellate sturgeon is successfully grown in artificial conditions on fish farms. Because of this, the cost of its caviar is low and comparable to the price of the sterlet product.
Yandex pictures
Amur sturgeon
Another name for this fish is Schrenk's sturgeon. It is found only in the Amur River, which is why it got its name. This species is a close relative of the Siberian sturgeon. It is distinguished by a hypertrophied, elongated snout, which makes up almost half of the body. The total length of an individual can reach 1.5 – 2 meters. The fish weighs a little - up to 80 kg.
The Amur sturgeon is on the verge of extinction, so its systematic catch is strictly prohibited in any volume.
Yandex pictures
Cartilaginous or bone
Many people have a question: are sturgeon fish species cartilaginous or bony? It does not arise by chance. Externally, fish of the sturgeon family give the impression of animals with a good skeleton due to the presence of a notochord, a skull and frightening teeth-bugs on the back. However, these parts are not rigid, bony tissue and are composed of tough cartilage. For the same reason - the lack of bone tissue, fish do not have teeth, although they are all predators. Of the bones, only small and thin costal, superficial or fin elements are present.
Due to the fact that most of the skeleton is made of cartilage, these animals are classified as cartilaginous ganoids. The subclass itself, like the entire class of ray-finned fish, belongs to the type of bony fish. But this is just a general name. Therefore, the question arises: are sturgeons bony or are they only similar to such animals. In reality, sturgeon are cartilaginous animals that have a small number of non-core small bones that do not form the basis of the skeleton. But they, along with other similar creatures, are classified as bony fish.
Yandex pictures
Class and subclass
Sturgeons predate bony animals and are one of the most ancient creatures on earth. The basic structure of their body has remained unchanged for several tens of millions of years. Such a long period of residence allowed them to populate almost all rivers and lakes of the Northern Hemisphere. They can be found in freshwater bodies of Europe and North America, including Canada, Norway and Finland. Animals can stay in cold water for a long time and do without food. All representatives of this species are predatory animals that feed on smaller fish and shellfish.
Sturgeons are a phylum of chordates whose body constitution suggests the presence of a skeleton based on a central cartilaginous axis or spine. Chordates are representatives of the highest type of nervous system organization. These fish do not have a hard skull, like vertebrates. The basis of the head here is made of hard cartilage.
The fish species belongs to the ray-finned class, which includes several other orders. The name of the class comes from the Greek words “ray” and “feather”, which denote the special structure of the fins.
Yandex pictures
Interesting! The ray-finned class includes 95% of all modern fish species. This is the most numerous class in the phylum of chordates. Many of them, including all sturgeon, are commercially available.
All representatives of the sturgeon order, which is part of the ray-finned class, do not have large dorsal fins. The main characteristic of the appearance is special spikes or bugs located throughout the ridge. They are also located on the sides. One dorsal fin is located quite low, near the tail.
A large spine is also located on the front fin. By the size of this spike you can determine the age of the fish. All sturgeons have a strongly elongated, fusiform body with a developed, protruding snout and an active, mobile lower jaw. These fish are predators that feed on small animals, shellfish and plankton.
The respiratory system is equipped with two pairs of gills, which are connected by membranes. This allows the fish to more efficiently obtain oxygen from the water, moving faster and more actively.
Yandex pictures
Culinary use
Sturgeon fish species are valued primarily for their tender, healthy meat, which is easily digestible. Sturgeon meat has excellent nutritional characteristics, as it contains about 16% protein, and its caviar contains 29% protein. These products contain no carbohydrates and very little fat. Due to this, sturgeon products are considered dietary.
In cooking, sturgeon is traditionally an expensive, luxurious and royal fish. Sturgeon fish can be prepared in any way:
- bake completely in any form: stuffed, with sauce, on a bed of vegetables;
- fry into steaks;
- bake in pieces;
- use minced meat or fillet to fill pies;
- cook aspic from cartilage and fins;
- cook fish soup from meat, heads and tails;
- make pates and rietas;
- pates, minced meat can be used for filling baskets, rolls and canapés.
Yandex pictures
Sturgeon are prepared with virtually no waste. Cartilage and small bones soften when baked in the oven and become suitable for consumption. If desired, they can be removed and used to create soup or aspic.
Sturgeon caviar is highly valued, which is why it is even called “black gold.” Caviar is usually salted and served as is. You can supplement it with other fresh ingredients:
- butter;
- lemon slices;
- mint or lemon balm leaves;
- onion feathers;
- boiled chicken egg white;
- cheese or shavings from it.
With the help of such additions, you can easily create an original presentation of caviar and emphasize its rich protein taste.
Siberian sturgeon
This species of sturgeon got its name from its habitat. Animals are found in the northern, cold rivers of Siberia. Individuals are distinguished by a beautiful gray-gray color and several rows of scutes on the sides and ridge, which makes the appearance very beautiful. It can be mixed with another fish of the sturgeon family - Siberian sterlet. A cross between these species is called a brome.
The Siberian sturgeon is not a very large fish. Its length ranges from 1 to 3 meters and it can weigh up to 150 kg. The average life expectancy of representatives of this species is 50 years. Although there are few Siberian sturgeon left in the wild, they are not yet recognized as an endangered species. Fish spawning occurs once every 3-4 years. This species lends itself well to captive breeding, which is practiced by many farms.
Yandex pictures
Benefits and harms of consumption
The benefits of dietary sturgeon meat are many. First of all, it is high in protein and unsaturated fatty acids Omega-3. Meat and caviar contain all known amino acids, many of which are not synthesized by the human body. Sturgeon products also contain many vitamins: A, C, E, D, group B and microelements: potassium, calcium, iron, copper, phosphorus, manganese, fluorine, molybdenum, magnesium.
Sturgeon fish bring many benefits to the body:
- accelerates metabolism due to the high content of iodine and Omega-3;
- reduces cholesterol in the blood, which reduces the risk of heart attack and blood clots;
- strengthens bones and reduces the risk of fractures;
- helps increase skin tightness and elasticity due to its high protein content;
- strengthens memory and attention;
- strengthens the nervous system and promotes clearer transmission of nerve impulses;
- accelerates regenerative processes in the body and slows down aging.
Yandex pictures
The danger of eating sturgeon consists primarily of botulism pathogens getting into the meat or caviar. To prevent this from happening, the fish are cut alive and gutted immediately after catching. It is for this reason that you should not buy caviar from unverified places, as it may be contaminated with botulism or other infections.
Also, sturgeon is not recommended if you are allergic to fish or have an individual intolerance. This product has no other contraindications. And it brings enormous benefits.
What does the weasel eat, do seasons and spawning characteristics affect its behavior?
The weasel searches for food in its habitats, preferring not to go far. Large schools can destroy everything around them, leaving behind only a rocky, clean bottom without algae. Baby's diet:
- fish caviar (often our own);
- polychaetes;
- diatoms;
- sponges;
- hydroids;
- small crustaceans.
Sea crucian carp leads a sedentary lifestyle in the Black Sea; even a cold snap or strong warming will not force it to move away from its home. Spawning will also not force you to leave your comfortable place.
Photo 1. In the river delta.
Already at the age of one year, fish are ready to breed offspring. To do this, you don’t need to make long crossings - the rocky, comfortable bottom is perfect for spawning. Reproduction occurs at a short distance from the shore, at a depth of three to five meters.
Interesting! For a long time, fish do not have sex, only with age do they divide into male and female individuals. Some of them remain hermaphrodites until their death.
During spawning, sea crucian carp are divided into pairs, which do not complicate their lives by building a nest, because the eggs are securely attached to the rocky bottom. Reproduction lasts throughout the warm season, from late spring until autumn. The female is quite fertile and easily lays up to half a million eggs (this depends on the size of the fish - the larger it is, the higher the fertility). The caviar has a peculiar bright red hue and is clearly visible in clear water, which is why it often becomes food for predators.
Immediately after laying eggs, the couples separate, not considering it necessary to protect their future offspring. The eggs soon hatch into babies, who do not move far from their place of birth for several months. The fry feed on soft algae. Babies grow very slowly, so they often become prey for larger representatives of the huge fish family.