Science does not know exactly when mammals acquired such a wonderful thing as a penis.
But one thing is clear: it arose along with the mechanism of bisexual reproduction. It was he who helped some living beings send their genetic material into the depths of other living beings. Evolution has chosen and blessed precisely this path and such organs for the reproduction of the highest representatives of the animal world. And man is no exception here. We decided to expand the understanding of the owners of phalluses on planet Earth and will tell you who knows what in the animal world.
In contact with
How long is the penis of animals?
Animals were able to develop in all sorts of ways. Turtles, birds, snakes, and bats have a penis somewhat reminiscent of what we have. Mollusks operate with a tentacle that proudly carries the functions of a reproductive organ. Fish have a cunning tube with a hook at the end, etc. Our list includes those who were the luckiest.
Blue whale
Among all marine mammals, the blue whale has the most amazing phallus on the planet. The size of his reproductive instrument exceeds an enchanting 12 meters. Still, it’s significant! If you stack five strong acrobats on top of each other, the animal's organ will still be larger.
Elephant
The African elephant's "manhood" is S-shaped and reaches 2 meters. It correlates with the body size of this animal as 1:4. If a person possessed such a thing, it would reach 45 cm in length.
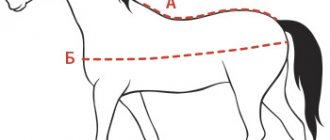
Horse
The size of the horse's penis is well developed in diameter and has a shocking size of 50-80 cm. The whole thing is crowned with a mushroom-shaped head with a diameter of 12-15 cm. Despite the size, the horse has no bends.
Bear
Male brown and polar bears have a bone at the base of the phallus. The average length of the baculum of the largest land mammal is 18.6 cm. And this does not count the cavernous bodies and membranes that cover it.
Monkeys and gorillas
Even the largest male gorilla cannot boast of an impressive penis size. When ready for combat, its organ does not exceed 2.5-3 cm. However, females are content with this, because the priority for this species is the size of the scrotum with its contents.
Dolphin
These mammals have no bone in their penis, but they have an excellent cone shape like a blue whale. The dolphin's trunk is carefully hidden in the genital fold and falls out as needed to a length of 25-33 cm. The girth is also not bad - 27 cm.
a lion
An interesting story about lions begins with the fact that they have spikes on their penises. These things are directed in the opposite direction in the direction of movement and cause the lioness to ovulate. The predator's penis is 28 cm.
Donkey and pony
Nature gave these mammals straight genitals with a mushroom-shaped head and developed thickness. When ready for combat, their trunk hangs merrily just below the donkey’s knee. Some males give out all 45 cm in erection.
In the animal world, about 20% of erect phalluses stand strictly horizontally
Dog
Males have an interesting feature - at the base of the dog’s phallus there is a bone 8-10 cm in size. This cute detail helps the dog to be in almost constant combat readiness. The bone itself is generously covered with cavernous bodies and is equipped with a head with a pointed end. During erection, the dog’s “instrument” increases 5 times compared to rest and often reaches 12 cm.
Walrus
These fellows have a robust 50-55 cm length. In absolute size of the phallus, they are second only to whales. When it comes to the size of the phallus in relation to the body, walruses are ahead of the rest. It is not without reason that the walrus baculum has become part of a well-known phraseological unit (in other words, a strong folk expression).
Hedgehog
With the shocking size of their reproductive organs, our ranking is completed by hedgehogs. These are real sexual giants, measuring an impressive 4.5 cm. This is significant compared to the average animal’s body of 20 cm.
Population and species status
The giraffe, as the most widespread representative of the savannah, has a peaceful character and gets along well with people. Local residents only occasionally hunted giraffes, using all its parts for their intended purpose. The meat was used for food, the tendons were used to make musical instruments, reliable shields were made from the skin of a giraffe, tassels were made from the hair, and bracelets were made from the tail.
Until white people appeared in Africa, giraffes were distributed throughout the African continent. After their appearance, the number of these artiodactyls began to decline significantly.
Interesting to know! Giraffes are listed in the International Red Book under the status of “least concern”.
Until recently, these animals were hunted en masse by Europeans, mercilessly shooting for pleasure, organizing safari. The result of such barbarity is a decrease in the number of giraffes by almost 2 times. Nowadays, hunting for giraffes has been banned, but the populations of these unique animals continue to decline, but now due to the fact that they are being forced out of their usual habitats.
Species characteristics of the penis [ edit | edit code ]
Despite the variety of forms, studies in the field of embryology have shown that the penis in vertebrates developed once, and not several times, as previously thought. [1]
The structure of the penis in mammals [edit | edit code]
The mammalian penis consists of a root, a body and a head, which in turn is distinguished by a corolla and a neck. The penis begins on the tuberosity of the ischium of the pelvis with two legs. The legs form a body, which is located in the perineum. On the upper surface of the body of the penis there is a small groove in which nerves, arteries, and veins are located, and on the lower surface there is a groove for the genitourinary canal. The body of the penis ends with the glans, which is equipped with a large number of nerve endings, giving it increased sensitivity. In some animals, the penis forms an S-shaped curve that straightens during erection. The basis of the penis is made up of three cavernous bodies. Two of them, starting from the tuberosities of the ischium, unite to form the body of the penis, the third is the cavernous body of the urethra, surrounding the urogenital canal and smoothly passing into the spongy body of the glans. The cavernous bodies consist of a dense tunica albuginea, forming numerous partitions inside, between which there are large communicating spaces that are heavily filled with arterial blood during sexual arousal. In some animals, at the base of the penis, a genital bone is formed from fibrous tissue, which performs a supporting function (carnivores, pinnipeds, cetaceans). The shape and structure of the glans, the size of the penis, the degree of development of its cavernous and spongy formations in different species of animals have characteristic differences, but in all animals the glans of the penis is in a calm state in the cavity of the preputial sac.
Horse-like [edit | edit code ]
The stallion's penis is very thick; the head in an erect state is a mushroom-shaped formation with a diameter of 12-15 cm due to the well-developed cavernous body of the head of venous origin. On the lower surface of the head there is a fossa with a process of the urogenital canal (length 1.5 cm). The length of the penis is 50-80 cm, there is no S-shaped bend. The prepuce sac is double, consisting of an outer and an inner prepuce (leaves). [2] [3]
Donkeys, zebras, and other members of the family have a similar structure with variations in size.
Proboscis [edit | edit code ]
Proboscis preserved the primitive method of reproduction of the first ancestors of mammals. Despite its impressive size, the elephant's S-shaped penis, sometimes reaching more than a meter in length, is not intended for insertion into the vagina, but only for leaning against its entrance. The sperm is sprayed with considerable effort and enters the vagina on its own (another archaic feature: the testicles of proboscideans are located inside the body, next to the kidneys).
Bulls [edit | edit code ]
The bull's penis is thin and long, with a point at the end, and has an S-shaped bend. At the tip of the penis there is a neck of the glans, a process of the urogenital canal and a weakly defined glans. On the neck of the head there is a suture - a ligament twisted to the left. During erection, the diameter of the penis increases slightly, but when the bends are straightened, its length reaches 100-150 cm. During ejaculation, the tip of the penis bends and turns around its axis, describing an almost complete circle with a diameter of 12-14 cm. The terminal part of the penis is placed in the prepuce the sac located in front of the scrotum, closer to the navel. [3]
Goats [edit | edit code ]
In a ram and a goat, the penis is thin and long, at the tip there is a process of the urogenital canal 3-4 cm long (in a ram it is S-shaped, in a goat it is straight), which vibrates during ejaculation, spraying sperm into the vagina during natural insemination . During erection, the diameter of the penis increases slightly, but when the bends are straightened, its length reaches 30 cm. The body of the penis, without any special boundaries, passes into the head, which at its pointed end has a left-handed spiral twist. [2] [3]
General information [ edit | edit code]
The structure of the penis in animals is quite diverse, but it always starts from the anterior wall. In turtles, crocodiles and some birds, the penis is unpaired and is a groove-like thickening of the ventral wall of the cloaca. Under the groove there is a fibrous body and an accumulation of cavernous tissue, when it swells, the groove turns into a tube. At the end of the tube there is an organ separate from the wall of the cloaca, which is blown out like a head. The tubes of reptiles fused in the middle form the penis of oviparous animals, which in a calm state hides in a pocket of the abdominal wall. In viviparous women, due to reduction of the posterior part of the cloaca, the penis is placed externally. In marsupials, rodents and insectivores, its apex is turned backwards. The penis of elephants, hyraxes, rhinoceroses and tapirs is oriented similarly in a calm state, but during an erection in these animals it turns forward. The position of the penis with the apex forward in placentals is caused by the development of the perineum. Gradually, a number of animals developed cavernous bodies of the penis. Marsupials, cetaceans, predators, pinnipeds, rodents, bats, prosimians and some monkeys have an unpaired bone in the terminal part of the penis - the baculum. Also, in accordance with the two vaginas of females, the penis of marsupials is often forked, with each half having its own branch of the genitourinary canal.