Chipmunks are small, striped rodents from the squirrel family. The word “chipmunk” is translated as “household manager” or “housekeeper.” This genus of rodents includes 25 species that are common in North America, except for the Asian or Siberian chipmunk (Tamias sibiricus), a resident of Eurasia.
Description of the rodent
— Advertising —
The weight of chipmunks ranges from 30 to 120 g, body length from 5 to 15 cm, tail length from 7 to 12 cm, depending on the species. A distinctive feature of all species is the five dark stripes located along the back, which are separated by white or gray stripes. In general, the color of chipmunks is red-brown or gray-brown and is characteristic of all species, which makes it quite difficult to distinguish them.
Reviews
Daria Albycheva, 23 years old, Omsk.
Before, I didn’t even know that chipmunks were sold in pet stores. Now such a miracle lives in my home. It is not so difficult to tame a chipmunk - you need to hand-feed it various fruits and dried fruits, without making noise or making sudden movements. Now my Jay has become attached to me, he’s used to it, he calmly runs around the apartment, stealing various goodies and cheese. It’s very entertaining to watch him from the outside, but he’s so nimble! I’ll say right away that the chipmunk is not suitable for families with small children; you won’t be able to cuddle him.
Sergey Shustov, 56 years old, Tver.
Chipmunks cost about 2-2.5 thousand rubles. From my own experience, the minimum cage size should be: 60 – width, 60 – length and 80 – height. But all the same, the animal will not have enough of this; if possible, you need to buy a larger cage. Buy him a house with dimensions of at least 15 × 15 × 15 cm. The larger the house, the better, the chipmunk is very thrifty, constantly begs for food and usually puts it in his shelter.
Maria Abramova, 34 years old, Ulyanovsk.
In general, chipmunks are unpretentious animals, but you need to spend a lot of effort to make them tame. But if difficulties don’t frighten you, then you can safely start it. Chipmunks are very noisy. Our cage has a metal wheel. When he trains on it, the noise fills the entire apartment, you can hear it even through the closed door. If you get really tired, we put a stopper in the wheel, and silence and tranquility sets in.
What does it eat?
The basis of the chipmunks' diet is plant food, to which they occasionally add insects. In general, the composition of the feed is varied, including seeds of wild plants, buds of trees and shrubs, young branches, herbs, various berries, as well as acorns, pine and hazelnuts, and mushrooms. Near fields and vegetable gardens, chipmunks willingly feast on cereal grains, buckwheat, corn, flax, sunflowers, peas, cucumbers, plums, apricots and other crops grown by people.
For the winter, chipmunks also store a large variety of different foods: wheat, oats, buckwheat, flax, sunflowers, wild seeds, acorns, nuts, dried berries, apples, mushrooms. At the same time, the chipmunk never mixes different foods, but carefully puts them on a bed of dry grass in separate piles, or separates different foods using dry leaves. The amount of reserves in one burrow sometimes reaches 6 kg, since chipmunks are engaged in creating food reserves throughout the entire period before hibernation.
— Advertising —
The method of harvesting grain is interesting. The chipmunk climbs into a not very dense crop, selects a good ear, grabs a straw and jumps up. Because of its weight, the straw bends and the animal moves along it, holding it between its paws, and thus reaches the ear. Then he bites it off, selects the grain in a few minutes, hides it in his cheek pouches and leaves. In dense crops, where it is not possible to tilt the straw, the chipmunk bites it from below, biting off fragments and gradually reaching the ear.
Repellers
You can scare away animals in various ways.
Cats and dogs
Cats and dogs can be the best defenders of territory. As a rule, rodents even avoid the smell of these animals, which mark the territory. Dachshunds, being burrowing animals, manage to hunt chipmunks, as well as mice and voles. What can we say about cats?
Sprays with capsicin
If there are no pets, you can use other repellers. For example, capsicin sprays. This substance makes peppers hot, its smell can scare away anyone. The spray is used to spray the fence, tree trunks, and the foundation of the house.
Rodent spray
In gardening stores today you can find rodent sprays with a wide variety of ingredients. It could be castor oil, the urine of predators, or a tar smell. It must be taken into account that all sprays wear off over time. It is necessary to repeat the treatment periodically. And be sure to do this after the rain.
Mothballs
The traditional method of rodent control is mothballs. They are placed both around the perimeter of the site and around the house, in the house itself and even in the attic. If there is a chipmunk hole on the site, then it is worth placing it near it. The smell of mothballs does not kill, but rather scares away animals. It forces you to leave even your favorite place.
Plants
You can scare away chipmunks with the help of flowers - daffodils. For some reason, rodents do not like both their smell and the taste of the bulbs. By planting these flowers among other bulbous plants, you can scare chipmunks away from the entire area with future flowers.
Important! Chipmunks also don’t like elderberries. The plant itself on the site can scare them away. Cut elderberry branches will also help, both on the site and in the house.
Chipmunk distribution
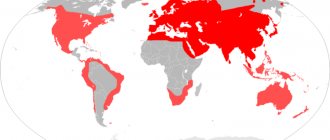
Chipmunks are found throughout North America, from the Arctic Circle to central Mexico. The Eastern American chipmunk (Tamias striatus) lives in the east of the continent. 23 species of the subgenus Neotamias are distributed in the western regions. The Siberian chipmunk lives in Northern Europe to the Korean Peninsula and the northern regions of China, on the island of Hokkaido. In Central Europe, there are feral chipmunks that escape from their breeding farms.
Chipmunks prefer forested areas to live. Thus, the eastern American chipmunk lives in the deciduous forests of New England, the Siberian chipmunk in the taiga, and the little chipmunk in the subarctic coniferous forests of Canada. Some species are also found in open areas overgrown with bushes.
Preventive measures
It is more humane not to fight chipmunks, but not to allow them onto your territory. The simplest and most reliable way is to fence the area with mesh around the entire perimeter. If the mesh cell is no more than 6 cm, the rodent will not be able to get through it. To prevent undermining, the same mesh can be buried 15-25 cm.
The mesh should also be used to cover all potential places where the animal can enter the house - ventilation holes, basement windows and vents.
The chipmunk will be happy to visit the house if he has the opportunity. Chipmunks do not like open spaces. If you constantly mow the grass in your area, the chipmunks will feel uncomfortable and are unlikely to stay long.
Most often, chipmunks are afraid of people. It has been noticed that dachas where people live all summer are less susceptible to attacks by striped rodents than those where the owners appear only on weekends and holidays.
Kinds
Eastern chipmunk
- Latin name: Tamias striatus
- Synonyms: Eastern American chipmunk
- Body length: 14-19 cm.
- Tail length: 8-11 cm.
- Weight: 70-140 g.
The back is reddish-brown with five short white stripes, which are bordered by dark fur. The tail is reddish-brown.
The species' habitat covers the eastern United States and southeastern Canada, where the chipmunk is found in deciduous forests, bushes, and among rocks.
Asian chipmunk
- Latin name: Tamias Sibiricus
- Synonyms: Siberian chipmunk
- Body length: 12-17 cm.
- Tail length: 7-12 cm.
- Weight: 80-111 g.
- Gestation period: 28 – 35 days
- Life expectancy in nature: 3-4 years
- Lifespan in captivity: 7-10 years
The legs are short. The color is variegated. The back is grayish-brown or reddish with five longitudinal black stripes, which are separated by light ones. The belly is whitish. The tail is gray above, red below. The coat is short and rough. Molting occurs once a year, in July-September. The ears are small, without tufts. Cheek pouches are well developed.
The species is distributed in the taiga zone of Eurasia (Russia, the Far East, Northern Mongolia, Sakhalin Island and Hokkaido). The species acclimatizes well and independently spreads to new territories.
Townsend's chipmunk (Tamias townsendii)
The body length is 23-29 cm, the tail is 10-13 cm long, the body weight is from 65 to 89 g. The upper body is light or dark orange-brown, on the back there are five dark stripes, which are separated by four orange stripes. The belly and throat are white to cream colored. The top of the tail is blackish-gray or silver, the bottom of the tail is bright orange. In winter the fur is darker than in summer.
The species lives in Canada (British Columbia) and the USA (Oregon, Washington), in dense forests.
Pine chipmunk (Tamias amoenus)
The body length of the species is 19.5-23 cm, the tail length is 6.6-11 cm, the weight is 42-89 g. The fur is colored from red to pink-brown, the back is decorated with five dark, usually black stripes, which are separated by four white or gray stripes. The sides and tail below are gray-yellow. The ears are black in front, white in back. The belly and throat are white to cream in color. In winter the fur is duller than in summer.
The species is found in Canada (Alberta, British Columbia) and the USA (California, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, Utah, Washington, Wyoming). Inhabits coniferous forests and meadows at altitudes up to 3000 meters above sea level.
Red-tailed chipmunk (Tamias ruficaudus)
Body length is 20-24 cm, tail 9-10 cm long, weight from 44 to 79 g. The upper body is orange, on the back there are five stripes from black to brown, which are separated by four gray or yellow-brown stripes . The belly is white or cream. The tail is red below.
The species' habitat includes Canada (Alberta, British Columbia) and the USA (Idaho, Montana, Washington), where it lives at an altitude of 720 to 2400 m above sea level in coniferous forests.
Lesser chipmunk (Tamias minimus)
Body length 10-13 cm, tail length 8-10 cm, weight from 35 to 53 g. The rump is grayish in color, the sides are red-brown, the abdomen is grayish-white. The tail below is reddish-yellow to brown. There are five dark and four light stripes on the back and sides, three dark and two light stripes are on the muzzle.
Found in the USA and Canada, in coniferous and deciduous forests, in the tundra.
Reproduction and lifespan
The rut in animals begins after hibernation. At this time, you can hear something like the whistle of female chipmunks. In this way they let the males know that they are ready to mate.
After mating, pregnancy begins, which lasts about a month and ends with the birth of 3-6 blind and bald babies. The growth of their fur occurs so intensively that after 14 days the little chipmunks have a real and beautiful fur coat.
After 3 weeks, their eyes open. And somewhere around day 120-150, they gradually emerge from their hiding place. Chipmunks reach sexual maturity at 11 months. Animals live for about 10 years.
Chipmunk behavior
The chipmunk is a tree dweller. He can be content with both tall trees and thickets of bird cherry, birch, and willow. It does not live only in open areas, in clean tall forests without undergrowth. Preference is given to places with windbreaks and dead wood, as well as along the banks of rivers and streams.
The chipmunk's burrow is long, up to 3 meters, and contains a nesting chamber, large storerooms for supplies and toilets. The living area is lined with dry grass and leaves. Here chipmunks breed, sleep at night and hibernate.
In the middle of winter, chipmunks sometimes wake up, eat, and then fall asleep again. The chipmunk sleeps, curled up into a ball.
In the spring, chipmunks emerge from their burrows at different times, depending on the weather. If it gets cold again, they go into their burrows, where they wait for warmer weather and eat up their reserves.
In summer, chipmunks emerge from their burrows early in the morning, before the sun rises, and search for food until the heat becomes intense. In the evening, when the heat subsides, they come to the surface again and remain until sunset. In dense shady forests they may not hide all day. In rainy weather they remain in their burrows.
Pet cage
Keeping a chipmunk at home requires the presence of a cage. It should only be metal, large in size, so as not to hinder the movement of the animal. Experts recommend the following cage dimensions: a height of at least 80 cm, with a width and length of about 40 cm, or a width of 50 cm, and a height and length of up to 1 m. It is advisable to equip the dwelling with: a shelf along one of the walls and a running wheel (half the size of for squirrels). Having the opportunity to run, your pet will be in good shape and in a good mood.
It is necessary to install a house on the territory of the cage for the animal to sleep. In addition, he will have somewhere to hide supplies. Approximate size of the house: 30x25x30 cm. The chipmunk sleeps in the nest, so he needs to put hay, leaves and rags inside the house.
Then you will be able to watch with emotion how he takes the bedding out of the house during the day to air it out, and before going to bed he brings it back. Veterinarians advise periodically performing a general cleaning of the house in order to remove old food supplies and disinfect it.
It is better to sprinkle the bottom of the cage itself with large wooden sawdust or fallen leaves. It is better not to use small sawdust.
The chipmunk likes to dig holes in the cage litter, and small sawdust can irritate its mucous membranes. The neat animal chooses one corner of the cage for its toilet. This makes caring for her much easier. You can find a cage with such a design that the floor is made like a drawer. Such cages are even more convenient to clean.
When choosing a place for the cage, you should take into account that in the spring the chipmunk loves to soak up the sun. But he does not tolerate the summer heat very well. At a temperature of +25 C it can die in direct sunlight. In the summer, he definitely needs shade, where he can hide from the heat and feel more comfortable.
Natural enemies
The main natural enemies of chipmunks are small predatory animals and birds of prey. Occasionally, they are also pursued by large predators such as a bear, which seeks to dig up a chipmunk's burrow in search of its winter food reserves.
When people or dogs approach, chipmunks make a jerky “tink” or whistle. At the same time, the animal sits on its hind legs and examines the approaching person. Having allowed him 20-30 steps, the chipmunk runs away and continues repeating the alarm signal while running to notify his relatives of the danger.
Prohibited Products
When it comes to chipmunks, there are no restrictions on grains and seeds that are edible to humans. But each animal may have its own individual preferences. If the animal does not eat oats or wheat, sunflowers or rice, there is nothing wrong with that, but you should not persistently offer it this food. Let the rodent show what he likes and what he prefers to eat.
Products that are strictly prohibited from being included in the diet of chipmunks:
Important! You need to carefully monitor the freshness of products. Moldy or rancid grains can cause digestive problems for your chipmunk.
Occasionally you can give your pet a ripe apricot or plum, cherry or sweet cherry, but only without seeds! The seeds of stone fruit crops contain a lot of hydrocyanic acid, which is deadly to animals.
From a financial point of view, feeding a chipmunk is not too expensive. When choosing a menu for it, you should always ask yourself the question: do rodents eat this product in the wild or not? A mistake can be very costly, because a balanced diet is a guarantee of a long life and good health for a chipmunk.
Source
Interesting facts about the rodent:
- Chipmunks are bred in captivity; it is recommended to do this one at a time, so that there is no rivalry or fights between the animals. Chipmunks that grow up in captivity are easily tamed. Domestic chipmunks choose a varied diet, adding nuts and berries to their diet. The cage should be as large and spacious as possible; its bottom should be lined with a special substrate for rodents (wood bark, sawdust). To maintain physical fitness, the cage is equipped with a running wheel.
- In places where agricultural crops are located near forests, chipmunks are pests of fields. In some cases, these animals are capable of stealing the entire crop from the field.
- Chipmunks are represented in world cinema, for example, Chip and Dale, cartoon characters are chipmunks. The virtual musical group “Alvin and the Chipmunks” from the film of the same name was also loved by viewers.
Traps
Chipmunks are no larger than a rat. Therefore, you can use all the rodent traps you can buy to catch them. Most traps are humane. They simply lock the animal inside without harming it. To bait, scatter nuts (for example, peanuts) or sunflower seeds around the trap.
After catching the chipmunks, it is necessary to take them far enough from the site - 8-10 km - so that they definitely do not return. There is also an inhumane trap - a bucket of water. If you attach a plank to it, along which the chipmunk can reach the rim of the bucket, and place bait on it, then the chipmunk, falling into the bucket, will simply drown.
How to get rid of chipmunks in your summer cottage: the best methods of control
Chipmunks in their appearance do not cause a feeling of threat, they are cute and fluffy, children are happy to have such a pet.
However, not everyone shares this point of view, especially summer residents in those regions where these rodents are found in natural conditions.
If an animal was spotted on the site of a country house, then a real invasion can be expected soon.
Therefore, it is important to take timely preventive measures to prevent rodents from entering, and if this happens, you should clearly know how to get rid of chipmunks.
Favorite food: cereals
The chipmunk loves grain and can severely damage grain crops. The extraction process is unusual: if the spikelet is not tall and there is nothing in the way nearby, the animal jumps on it, holds on with its paws and takes a bite.
If there are other ears of corn nearby, the straw below is snacked on. The chipmunk quickly puts the grain in its cheeks and runs into the hole.