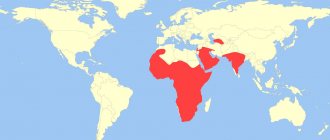
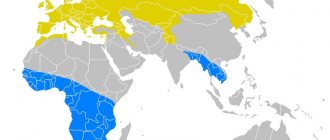
Hedgehogs are unusual animals that are easily recognized by the dense layer of spines on their backs. Living over vast areas, they play an important role in the ecosystems of forests and plains. The animal has many features that attract the attention of biologists and are studied with great interest. He also regularly becomes the protagonist of cartoons and other creative works. There is now a large amount of information about hedgehogs, so anyone can get a detailed understanding of them.
Origin of the species and description
Most hedgehogs have a black nose that is always wet.
It is believed that hedgehogs appeared about 60 million years ago - this is exactly the age of the oldest discovered remains.
They adapted well to the surrounding world and quite quickly divided into several families. However, 33-23 million years ago, all but one ceased to exist for unknown reasons. The species now living on the planet belong to the surviving family Erinaceidae. Interesting fact : three main types of hedgehogs live in Russia: steppe, Eurasian and long-eared.
Hedgehogs are mammals and belong to the order of insectivores. The most common is the European one, which also has a second name – “ordinary”. The animal has common ancestors with moles and shrews. But the hedgehog has no relationship with the porcupine, whose back is also covered with quills .
Family
These funny animals belong to the hedgehog family, and the class is mammals. In addition to this information, it can be noted that there are also different types of hedgehogs. But we are most familiar with the common hedgehog, because it is the one that lives in our surroundings.
The reference book "Mammal Species of the World", which was released in 2005, indicates that the family in question includes 10 living genera, in which 24 species are distinguished.
Not many people know that hedgehogs usually contain two subfamilies:
Appearance and features
All types of hedgehogs are characterized by spines located on their backs. In adult individuals their number can reach up to six thousand, in young individuals - no more than three. The body length ranges from 25 to 35 cm, and the weight does not exceed 800 g. The tail grows up to 4 cm.
The animal's head is elongated, at the end there is a black nose, which always shines due to the moisture accumulating on it. The black eyes are set high, and round ears are visible above them.
A hedgehog's eyes look like black beads
Interesting fact : in the mouth of a hedgehog there are 36 teeth, with 20 located on top and 16 on the bottom. This distribution is necessary so that pairs of incisors growing on both jaws do not interfere with each other and do not disrupt the bite.
The paws have five toes equipped with claws; the forelimbs are shorter than the hind limbs. The back is covered with needles, their length is 3-4 cm. Inside they are hollow and filled with air. Their color contains white and brown areas, which is why the top of the animal looks heterogeneous in terms of color. The hedgehog also has fur: they grow between the needles, but in small quantities, so you can only see them close up.
The head and belly of the animal are covered with hair. It can be gray, brown and yellow-white.
Listen to the hedgehog's voice
Hedgehogs have good hearing, but their vision is poor. However, this is compensated by the fact that sensitive vibrissae are located on the sharp elongated muzzle closer to the nose. Thanks to them, hedgehogs have an excellent sense of smell.
Hedgehog spines are modified hair, but unlike fur, they never change. Only small hedgehogs or sick animals can lose spines.
Of course, the most interesting thing about hedgehogs is their spines, which never fall out. They are modified hairs and cover not only the back, but also the sides and forehead. The most unprotected place is the belly, because the fur on it is soft. Almost all species are gray or brown, only the spines at the tips are white. It is very rare to see hedgehogs that are completely white.
The long-eared hedgehog (Hemiechinus auritus) is a typical desert inhabitant
The hedgehog can curl up into a ball in times of danger. In this he is helped by the circular muscles located in the places where the spines grow.
Habitat - where hedgehogs live
Habitat of hedgehogs
The hedgehog has a fairly large habitat. The animal species live in Europe, Asia and Africa. Also, the found remains indicate that they once inhabited North America, but due to unfavorable conditions, local populations ceased to exist.
As mentioned above, the most common species is the common hedgehog. It is found in most European countries, the British Isles, and also in Kazakhstan. In Russia, it lives in the northwestern part and in Siberia. Relatively recently, the common hedgehog was artificially brought to New Zealand, where it quickly adapted and began to increase its population.
The animal prefers to live in forests and in areas where there are a large number of trees nearby. But it can also be found in plains, near bodies of water and on land overgrown with bushes.
Hedgehog in his hole
Interesting fact : hedgehogs do not live near swamps or in coniferous forests. But they meet regularly in cities.
Hedgehogs have their own den, which they build at the roots of a tree, in bushes or holes. If necessary, the animal is able to dig a hole, but it is always shallow in depth and does not contain forks.
Description of the animal
A hedgehog is a small animal that feeds on insects. Its weight can reach up to 1.2 kg, and its length can be 20 centimeters. Most often, males are slightly larger than females. The hedgehog's muzzle is elongated and quite large.
The animal's eyes are small and lack the ability to see normally. But, in return for vision, the hedgehog is endowed by nature with excellent hearing and sense of smell. There are small ears on the top of the hedgehog's head, and short whiskers near the nose.
For ease of movement, its hind legs are slightly longer than its front legs. The hedgehog has thirty-six sharp teeth and long nails on each of its five fingers. These are his tools that allow him to get his food.
How long do hedgehogs live?
In the wild, hedgehogs live no more than 5 years . A three-year-old individual can already be considered an adult. But in captivity, life expectancy increases to 8-10 years . Since in this case a person takes care of the animal, he does not need to regularly get his own food and think about how not to fall into the clutches of a predator. And since the hedgehog’s body is not subjected to significant stress, it lives several times longer.
Interesting: Monkeys - Species with photos and videos, names, features, description, food, where they live
What do hedgehogs eat?
Hedgehogs are omnivores. They are able to eat both vegetation and meat. But most of their diet consists of various insects. Caterpillars, larvae, slugs, earwigs, worms, beetles, spiders - all these living creatures are quickly caught by the animal and eaten.
Despite their cute appearance, hedgehogs are able to cope with fairly large creatures. When necessary, they eat frogs, lizards and toads. And sometimes they penetrate bird nests, where they attack newborn chicks and eat the contents of the eggs. Hedgehogs also attack mice, but since rodents are quite agile and can run quickly, such collisions rarely occur. In addition to living creatures, hedgehogs also love vegetation. The animal is unlikely to pass by berries and fruits and will not deny itself the pleasure of trying them.
The hedgehog happily eats nuts and other fruits
Different species have different diets. For example, the New Zealand hedgehog prefers mainly plant food, but the ordinary one primarily looks for insects. Snakes can also become food for this animal. The poison in the cold-blooded fangs does not affect him. It is also unable to break through thorns. Thus, the hedgehog rushes at the snake without fear and wins if it does not decide to crawl away.
Due to its lifestyle, the animal is very voracious. Coming out of hibernation in the spring, it eats away to gain weight. And closer to autumn, he again begins to eat intensively to gain weight before the cold weather.
Contrary to popular belief, hedgehogs should not be given milk. They do not tolerate lactose well, but people often pour it into their pets.
Nutrition
Having described the external features and vital functions of these animals, let us now consider what hedgehogs eat . Naturally, in matters of diet, everything largely depends on the habitat. The main menu consists of a wide variety of insects. But in fact, such cute creatures are omnivores.
Hedgehog eats snake
They can feed on earthworms, wood lice, slugs, and caterpillars. Ground beetles, spiders, beetles, and locusts should also be considered suitable for food. Among larger prey, some small vertebrates are suitable for hedgehogs as food. They also love to feast on bird eggs. Species that live closer to the northern regions prey on small rodents, frogs, lizards and toads.
An interesting feature of hedgehogs is their innate immunity to natural poisons. Therefore, by eating scorpions and snakes, the animals described do not cause harm to the body. These omnivorous creatures are not poisoned by food waste, and therefore they are also the best choice for hedgehogs as food.
Little hedgehog eats a big apple
Plant nutrition greatly complements the diet of such creatures. Delicacies of this kind include a variety of berries and cereal seeds. Therefore, settling close to people, in their gardens and orchards, the hedgehog has the opportunity to eat to its fullest. In forests, hedgehogs feed on mushrooms, moss, and acorns.
Features of character and lifestyle
Hedgehogs are most active at nightfall, when they crawl out of their holes in search of food. At dawn they return back to the den, where they spend the whole day. Their homes are usually well hidden in bushes or in empty holes of other animals.
The hedgehog does not like uninvited guests in its territories
Hedgehogs are clean animals. They regularly remove debris stuck between the needles and lick their belly. And to get rid of the parasites that live on its back, the animal rolls in apples so that the acid from the fruit scares them away.
Interesting fact : poisons have practically no effect on hedgehogs. Arsenic, acid, mercuric chloride - all this has a weak effect on his body.
Each hedgehog has its own territory in its domain, which it carefully marks. If another individual invades these lands, a real fight begins, which continues until someone escapes.
The animal has poor eyesight, but it has well-developed hearing and sense of smell. It also has excellent spatial orientation, can swim, jump, and even run at a speed of 11 km/h.
Care and maintenance
Spiny babies require large areas to live in - a hedgehog cage must be at least 80 cm long.
To express activity, the hedgehog will need to purchase a wheel. It is desirable that its surface is solid - this way the animal’s paw will not get stuck between the bars.
There must be a house in the cage - a shelter from which the hedgehog cannot be pulled out by force. Typically, such houses are sold in stores and are made of plastic. Also be sure to install a stable waterer and feeder.
Cat corn litter is best suited for filling the cage - it absorbs odors well, has an optimal structure and is safe for prickly predators.
Daily walks of the animal outside the cage are required. The main thing is not to lose sight of him, otherwise he will find the darkest and most inaccessible corner in which you will have to look for him for a very long time.
Be sure to visit a veterinarian once every six months for a dental examination and cleaning.
How do hedgehogs winter
During sleep, hedgehogs curl up into a ball.
In October, when the temperature begins to drop, hedgehogs hibernate. Beforehand, they actively overeat for a month and try to gain as much fat as possible. This makes it easier for them to survive the cold. If an individual lives in warm regions, then it may not hibernate at all.
When an animal enters a state of suspended animation, its body begins to work completely differently. The pulse drops to 20 beats, and body temperature to 2 degrees. The intervals between breathing in a hedgehog increase significantly: 1-2 breaths per minute.
The animal emerges from hibernation in April. Moreover, having awakened, he can spend several days in the den and wait until the temperature outside rises to 12-15 degrees.
Lifestyle and habitat
The dwellings of these animals are, as a rule, holes dug by them, about a meter long. When the sun is shining, hedgehogs prefer to rest in their shelters. They successfully inhabit wooded areas, where their houses can be seen in the roots of bushes and trees. Hedgehogs comfortably settle in steppes and even deserts.
Such representatives of the fauna are also capable of occupying ready-made dwellings of rodents, once abandoned by them. Hedgehogs also settle in cultivated landscapes, being found in gardens and parks; they often catch the eye of a person in the immediate vicinity of human habitation. Such animals are also found in foothill areas, where they find shelter between stones and in rock crevices.
In general, these creatures do not like to be in plain sight, and communicating with their relatives is usually not their intention. By nature, the hedgehog is a solitary animal. He prefers to be active at night. It is during this period that hedgehogs obtain food by going out to hunt.
But they don’t like to be far from their place of settlement, being cautious creatures by nature. However, many dangers await them nearby. And the big problem here is cars driving on country roads.
Unfortunately, according to statistics, too many of these cute creatures die under the wheels of cars, carelessly crawling into dangerous areas and being invisible to drivers in the dark.
Meetings with predators can also be fatal for hedgehogs. These include foxes, wolves, hyenas, as well as smaller animals - mongooses, martens, badgers and other four-legged enemies. The most dangerous birds for hedgehogs are eagles and owls. They are well protected from many enemies by thorns.
It is known that these creatures have a habit, sensing danger, to curl up into a tight ball, exposing their sharp needles. And in this state, successfully feasting on a hedgehog turns out to be quite a difficult task. However, cunning foxes are able to cope with thorny creatures.
If there is a body of water nearby, they push them into the water. And in order not to drown, the hedgehog has to straighten out from a curled up position in order to row in the water with its paws. It is in this unprotected state that the foxes overtake them.
Hedgehogs that live in areas with an unfavorable climate build a nest in a secluded place for winter, the building material for which is dry leaves. With the onset of cold weather, they curl up into a ball and hibernate.
Social structure and reproduction
In the spring, when hedgehogs come out of hibernation, their mating season begins. Already at the age of one year, individuals are able to have offspring. Having woken up, the males go in search of females, and several gentlemen can lay claim to one female at the same time. Then the fight starts. Its participants hiss and bite until a winner is determined.
After courtship, the male goes to his territory, and the female prepares for the appearance of offspring. Males do not help mothers in any way and do not participate in raising the young. The female is capable of producing offspring once a year.
Newborn hedgehogs under mother's protection
Pregnancy lasts one and a half months, and during this period the hedgehog manages to cover its den with leaves. From 3 to 8 animals are born at a time. The length of newborn cubs does not exceed 2 cm, and their weight is around 10 grams.
Interesting fact : newly born hedgehogs do not have spines, but after a couple of hours the spines begin to appear on the surface of the skin. In a few days they grow and become hard.
All summer the children live in their mother's den. By the 15th day they begin to see, and after a month they stop feeding on milk and switch to regular food. With the onset of autumn, they set out in search of territories that will become their new home. There, young individuals will begin to prepare for hibernation for the first time.
Interesting: Wolf