Spiders in Latin are Araneae, Aranei. They belong to the animal kingdom, the phylum of arthropods, the class of arachnids. There are 42 thousand modern species of spiders in the world, about 1.1 thousand fossils. They are widespread, inhabiting almost all continents of the globe. Obligate carnivores - feed on insects, small animals, and amphibians. An exception is the jumping spider Bagheera kiplingi, whose diet consists of the green part of the acacia tree. On the territory of Russia and the former CIS countries there are 2888 species. The science of spiders is called arachnology.
Description of the spider
The spider is the most ancient creature on the planet. It is much older than humans; these organisms arose in advance. The remains of vital activity, spider webs, were discovered in the structure of amber, which is 100 million years old.
Arachnids lived on the globe back in the Paleozoic era, and this was 2.5 billion years ago. During this period, these creatures practically did not change in appearance.
To understand who spiders are, it is worth considering their features and description of their appearance. They have 6 pairs of limbs. However, the person notices 4 pairs. This is due to the fact that the first 4 limbs are transformed into organs of nutrition and touch.
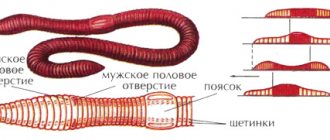
- The body of arthropods is divided into two parts - the cephalothorax and abdomen. They are connected using a short jumper;
- the cephalothorax is divided by a groove into the head and thoracic parts;
- on the chest part there are the limbs of the spider, due to which it moves and weaves a web;
- on the surface of the head there are two pairs of limbs, eyes and a mouth opening.
The number of eyes may vary. Most arthropods have 8 visual organs. But in individuals living in the darkness of caves, they may be absent.
How do they breathe
Respiratory system of spiders
Depending on the species, spiders may have the following variations of the respiratory system:
- one pair of lungs;
- two pairs of lungs;
- a pair of lungs and a pair of tracheas;
- pairs of sieve and tubular tracheas;
- pair of sieve tracheas.
Getting inside the spider through special holes, oxygen is transported through the hemolymph to the respiratory organs with the help of hemocyanin. The lung sacs are located in the front of the abdomen. They saturate the body with oxygen through the circulatory system. Also behind the pulmonary sacs are bundles of tracheae, which are small tubes. They exit through a single breathing hole. During exhalation, the spider releases the resulting carbon dioxide into space.
Why are people afraid of spiders
In science, a pathological fear of arachnids is called arachnophobia. The disease is accompanied by severe attacks of fear that develop when meeting individuals of any size.
Attacks may be accompanied by fainting, headaches, sweating, dizziness, nausea, and a desire to run away from the animal. Experts have found out an interesting fact about patients with a similar deviation - many of them are not able to explain their fear.
In many cases, arachnophobia is a consequence of experiences with arachnids that a person had in childhood. Today, deviation is considered the most common and difficult to treat phobia.
Is a spider an insect or not?
Many people wonder whether a spider actually is an insect or an animal. Most will immediately answer that it is an insect, but this is not the case. Even if in appearance this organism looks like crawling small inhabitants, it is in no way related to them and has distinctive features.
They are animals; among the inhabitants of the fauna they are classified as invertebrates. These are arthropods that have jointed limbs, a hard chitinous cover, which is a hard exoskeleton.
Therefore, the question arises why spiders are not insects and animals. And also interested in what exactly connects mammals, what common features they have with insects and differences from them. This is worth considering carefully.
General signs
The family of spiders and insects share some common characteristics. This is due to the fact that arachnids belong to the class of arthropods.
They have the following characteristic qualities:
- creatures have a chitinous skeleton to which muscles are attached;
- the structure of the eye in arthropods is formed from many ocelli; it is often called facet;
- females reproduce by laying eggs.
Main differences
To understand what a spider is - an animal or an insect, it is worth carefully considering its main characteristics.
- spiders have 8 legs, and insects have 2 fewer;
- Insects have 3 body segments, and arachnids have 2;
- spiders are able to weave webs;
- In nature, insects have a huge number of species and subspecies;
- arthropods produce poison, which is required for external digestion of food;
- unlike insects, arachnids do not have metamorphism (transformation) in their life cycle;
- The communication system and nervous system of insects is much more complex than that of arthropods.
Types of spiders of medium poisonousness
Among the large number of species of spiders, there are those that release a certain amount of poison during the bite process, but its concentration is not enough to cause serious harm to prey that is several times larger than them.
banana spider
Banana spider
These spiders live in America and are able to run quickly across the surface, which allows them to catch up with almost any prey. The color of individuals can vary from gray to black and white. It feeds on insects and small animals.
Fun Fact : Banana spider venom can be used for therapeutic purposes in the right concentration.
Giant tree spider
Giant tree spider
Also known as the nephilus orb weaver. It grows up to 4 cm in length, with a paw span of 12 cm. It hunts various creatures, from insects to birds. The spider attacks everyone who ends up in its web and cannot get out. Individuals have a wide variety of colors, most often combining black and orange.
Interesting: Bee: description, reproduction, lifestyle, habitat, nutrition, enemies, how honey is made, interesting facts
Tarantula
Tarantula
The color of this spider varies from light gray to black, the body is covered with small hairs. Tarantulas live in burrows and hunt insects. Adults grow up to 10 cm in length. Currently, 221 species of tarantulas are known, and each has certain characteristics. They live almost all over the globe.
Signs of insects
The insect's body is divided into head, thorax and abdomen. The head consists of five fused segments. There are antennas on the head with receptors for touch and smell. The eyes are compounded, that is, they consist of many simple ocelli. There are mouthparts for chewing food.
The chest includes segments: anterior, middle and posterior. Each segment carries a pair of motor limbs. In addition, the middle and hind ones each include a pair of wings: chitinized elytra and, in fact, wings. The abdomen also consists of segments, on the sides of which paired respiratory openings open.
Interesting facts about spiders
Unusual facts about spiders will amaze many who do not yet know about these creatures. But they conceal many mysteries, secrets, and have unique features that other organisms living on the globe do not have.
Let's look at 15 interesting facts about spiders:
- The web is not only a trap for insects, it is capable of deflecting several millimeters in order to grab and stick an insect to itself. This phenomenon is carried out due to a static charge, which appears during the flight of the insect.
- The bite of the Brazilian wandering spider is not always fatal, but it often causes impotence in men.
- With the help of its limbs, the spider can determine what has reached it in the web. But edible or inedible helps him establish the olfactory organs, which are located on his legs.
- The animal has a durable shell. Its strength can withstand a nuclear explosion.
- The web is very light. If you take a spider thread the length of the earth's equator, then its weight will be only 340 grams.
- Spider web is considered a powerful and durable material. If its thickness is increased to the thickness of a pencil, then such a web could stop a Boeing. In New Guinea, fishermen use this material to catch fish, and in South America there are spider web bridges that support monkeys.
- The lifespan of arthropods is 30 years. But they rarely die of old age.
- At one time, the female can lay up to 20 thousand eggs, from which spiders hatch.
- In nature, there are varieties of spiders that, after being born, eat their mother.
- There are varieties of arachnids in which the brain occupies the largest part of the body, so other organs are forced to be located on the legs. The smaller the spider, the larger its brain.
- In the Netherlands there are more spiders than people. For 15 million human population there are 5 thousand billion arthropods.
- In Cambodia, people enjoy eating tarantula spiders. They are also brought up at home, they learn to dance, and play willingly. And if necessary, they can protect the owner.
- There are types of spiders that do not weave webs - the jumping spider, the lynx spider. They do not catch prey with webs, but hunt it.
- Tarantulas can live without food for about two years.
- The gladiator got its name due to the fact that it weaves a web in a square. He does not leave her until the prey falls into her; he himself abruptly throws the net on her, thereby leaving no chance to escape.
Interesting Facts
Spiders inspire fear in people, but at the same time they inspire interest. Therefore, they are studied and even raised at home as pets.
Flying spiders
There is evidence that some species of spiders can fly. And this is not to instill fear in the impressionable. This method is a protection and a method of movement.
Spiders with a tail
There were individuals that had a tail. Unusual tailed spiders and their descendants.
Web
Spider web is a strong and stable material; it can stretch several times and return to its original position.
How to get rid of house spiders
The first step is to remove those insects that serve as food for spiders, which is why it is first necessary to destroy cockroaches, bedbugs, flies and other unpleasant insects. Next, you should remove the cobwebs. It is very convenient to do this with a vacuum cleaner, the bag of which is emptied outside the home after the procedure. You can fight cobwebs with an ordinary broom. However, if there are a large number of arthropods, this may indicate the presence of masonry, which can be gotten rid of using household chemicals - these creatures do not tolerate strong aromas. If possible, surfaces regularly inhabited by arthropods can be painted.
Also, if spiders begin to appear frequently, you can place containers with flavored liquids around the room. Thus, arthropods cannot tolerate the aromas of chestnut, citrus, mint, and eucalyptus. The number of spiders will sharply decrease, and after some time the unpleasant neighbors will leave your home.
However, if the spiders have managed to breed, you will have to purchase special chemicals aimed at destroying them. First of all, these are products based on pyrethroids.
An excellent preventive measure would be to keep the room clean and regularly remove dust and dirt, especially in hard-to-reach places. It is not for nothing that spiders are considered indicators of cleanliness: in those rooms where a lot of them have accumulated, the conditions are far from complete sanitation.
Species and subspecies
Answering the question of what kinds of spiders there are, it is worth noting that these creatures are divided into species and subspecies, which have some distinctive features.
In nature, there are about 35 thousand species of archanids or arachnids, which differ in appearance.
Different types of spiders have characteristic forms of life activity, which include reproduction, feeding habits, habitat in natural conditions, and size.
- their body consists of two parts - the abdomen, which can have different shapes, it all depends on the type of arthropod, as well as the cephalothorax;
- characterized by the presence of 4 pairs of legs, 2 chelicerae and pelipalps;
- spiders do not have whiskers;
- the main feature of the creatures is to weave webs for various purposes, and its design may have some peculiarities;
- there are poisonous glands, the poison of which has a paralyzing effect on the victim;
- prefer to lead a solitary lifestyle. Most females, after fertilization, eat a select few.
It is impossible to know exactly how many spiders there are in the world, because there are many of them.
At one time, a female is capable of laying 15-20 thousand eggs, most of which hatch into spiders, so it is difficult to imagine how many dozens of females can lay and give birth at a time.
The classification combines many types. In nature, there are exotic representatives of arthropods that do not pose a danger to humans; they are preferred as pets.
It is worth paying attention to the dangerous and poisonous breeds of spiders; they inhabit the tropics and other hot areas, for example, deserts.
What types of spiders are there?
Large pink tarantula.
There are more than 40 thousand species of spiders. They can live in grass, near human habitation and in remote places.
There are very miniature spiders, but there are also large representatives that do not fit on a plate. But all species have the same structure.
Conventionally, types of spiders can be divided into:
- woody;
- domestic;
- safe;
- poisonous.
In Russia, according to the latest data, there are about 2,400 species. More and more of them are opened every year. They are distributed in different regions and climates.
A detailed acquaintance with the spider fauna of Russia.
Distribution and habitat
Spider in the forests of Russia Spiders live on all continents except Antarctica. Being invertebrate animals, they cannot control their body temperature and are susceptible to cold, however, in northern Canada, Greenland and northern Russia they get along well.
They are one of the few species of animals that get along well in the highlands. There are certain species that feel great even in an aquatic environment.
The main factor that limits their habitat is the availability of food.
Place in nature
Spiders are an important and irreplaceable part of the ecosystem. They are of great importance and perform important functions:
- When feeding on a variety of insects, regulate their quantity;
- They themselves are food for many animals.
Among those who eat spiders:
- insects (mantises, blackbirds, scolopendras, wasps);
- spiders (representatives of some species feed on their own species);
- reptiles (snakes, lizards);
- amphibians (toads, frogs);
- small mammals (hedgehogs, rats, mice, noses).
And, of course, birds eat spiders, some of which rely on arachnids as their main food.
What order and class do spiders belong to?
If we talk about what class spiders belong to, then this is the class “arachnids”. It stands apart from all others, which is associated with the characteristic features of the body structure of arthropods.
They have it divided into two parts - the abdomen and the cephalothorax, but in representatives of other classes the body has a slightly different structure.
There is another characteristic difference - the number of legs. Arthropods have 8 of them instead of 6. They have chelicerae, which are located on the front of the cephalothorax.
They also have pedipalps, which look like tentacles. They are located on the sides of the body and perform the same functions as the paws.
These organisms belong to the order Spiders, the family Arthropods. Spiders are often called "archans", this name comes from the name of the suborder to which these creatures belong - Orthognatha.
It is distinguished by species diversity and specific appearance.
This suborder includes spiders called mygalomorphs. The body of representatives of this species is completely covered with short hairs. They prefer to live in dungeons.
The group includes the following species:
- tarantulas;
- ctenises;
- funnel spiders;
- diggers.
How many eyes does a spider have?
Spider Eyes
The number of spider eyes varies from 2 to 12 depending on the species, but in most cases there are 8. They are located in such a way that the creature's viewing radius is 360 degrees. Spiders see what is happening around them at about 30 cm. The main task of the visual organs is to notice in time the approach of prey or danger. Also, some types of spiders can distinguish between colors.
In the center of the head is the main pair of eyes, which are larger than the others. With their help, the spider focuses on objects. The lateral eyes are motionless and are needed for additional visibility.
What is the body of spiders covered with?
Arachnids are arthropods. The main difference between this type is the articulation of the limbs and the absence of a spine (invertebrates). The exoskeleton (shell) protects and supports the animal’s body. The exoskeleton contains rigid, stable components that perform different functions:
- Protective. Prevents the negative impact of environmental factors on the internal organs of the protostomed animal. The opisthosoma of some representatives is covered with many small hairs. When in danger, the arthropod scratches them off and throws them towards a potential attacker. When the mucous membranes and bristles come into contact with the skin, they cause irritation.
- Tactile. The exoskeleton is covered with many trichobothria (tactile setae). They are scattered throughout the body, especially on the pedipalps and walking legs. The hairs are attached to the bottom of the pits, in the integument, and are connected to sensitive cells. Hairs react to air vibrations. The spider is able to understand the nature of the stimulus by the intensity of the vibrations.
- Musculoskeletal. Ingrowths of the exoskeleton, known as apodemes, serve as sites for muscle attachment. The structures are made of chitin, 6 times stronger and 2 times stiffer than vertebrate tendons. Apodemes are able to stretch to maintain elasticity.
- Protection against dehydration. The shell maintains the balance of moisture in the body during environmental temperature changes.
The body of all arthropods, arachnids in particular, is covered with a chitinous shell. The hardest layer is located in the chelicerae and claws, the more elastic one is in the joints of the limbs. Chitin is a glucose derivative, the main component of the cell walls of the exoskeleton. The structure of the polymer is crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers.
In its pure, unchanged form, chitin is transparent, pliable, elastic and quite durable. Some species of arachnids, such as Pholcus phalangioides, are distinguished by a transparent cover. If you hold the animal up to a microscope, you can see the superficial circulatory system.
Silk nets
Almost all arachnids produce webs, but some do not weave webs from them. These protein strands are used for climbing, hunting, reproduction, protection and other needs of the animal. If you look at a frozen web, it may seem that it is monolithic, but in fact it can be 3-4 separate threads that stuck together when drying.
Surprisingly, the webs are so strong that some spiders use them for travel . One end of the thread is attached to a tree branch, and the animal hangs on the other end and, with the help of the wind, sometimes moves for many kilometers. It is interesting that the owner disposes of the unnecessary network - simply eats it.
Spiders treat insects as food; some large specimens are capable of catching and eating even bats, small birds or small fish.
Some species of spiders have a unique hunting technique, it all depends on the diversity of the fauna around them
Representatives of the orb weaver class catch fish by weaving a kind of fishing net from a web. These creatures hunt prey in very different ways:
- spiders that live in holes jump out of them to catch a passing or flying victim;
- some, having placed sticky snares, sit in ambush on plants, tree bark, under stones and wait for the victim to fall into their clutches;
- more active individuals go in search of prey on their own.
All spiders are carnivores. Their digestion begins long before food enters the stomach. Some representatives inject enzymes directly into the body of the victim, others first break the food with their jaws. Partially digested food is absorbed into the intestines.
Disputes on the topic “are spiders insects, and if not, then why” arise to this day. Although there are huge differences between these groups of living organisms.
In fairness, it should be noted that until the middle of the last century, these classes were indeed united by one biological type.
Features of reproduction
During the process of active growth, spiders from time to time shed their tight shell, which consists of a chitinous structure. They gradually acquire a new, stronger one.
Over the entire period of their life, they can molt up to 10 times . Spiders are heterosexual individuals, with the female being much larger than the male.
The mating period lasts quite a long time, its season begins in mid-autumn and lasts until early spring. At this time, the male fills the bulbs, which are located at the ends of the pedipalps, with sperm, then he goes in search of the female.
After performing the “mating dance” and fertilization, the male leaves and dies in the subsequent period.
As soon as 2.5 months have passed, the female lays eggs. After 35 days, spiderlings hatch from them and live in the web until the first molt. Sexual maturity in females occurs at the age of 3-5 years.
How do they winter
Some spiders can lead an active lifestyle in winter.
Spiders are able to hibernate in different ways. Some survive frosts in the foliage and bark of trees. Spiders also try to escape the cold by settling in different buildings. In the cold, the predator produces a special chemical that acts as antifreeze. If a female lays eggs before the onset of cold weather, she tries to hide them in a secluded place where the temperature will still remain above zero in the winter.
Interesting fact : in the cold, spiders fall into a state similar to suspended animation. Because of this, processes in the body slow down and they age more slowly.
Feeding spiders
The spider is considered a predatory creature by nature. Its diet mainly consists of insects, and it can sometimes catch small animals. The exception is the jumping spider; it prefers to eat only plant foods (grass, berries, leaves).
The arthropod hunts using nets that it skillfully weaves from cobwebs. In nature, there are varieties of these creatures that use web shots during hunting, while they hypnotize the prey, leaving it no chance to escape.
Despite the fact that they are considered obligate predators, catching prey on their own, they do not have teeth . To eat prey, they need to dissolve its tissues and make a nutritious broth from it.
For these purposes, spider venom is used; the animal injects it into the victim through hollow chelicerae. This allows you to achieve two goals - killing the prey and obtaining a nutrient solution.
Class Arachnida
- Integument, musculoskeletal system
- Digestive system
- Respiratory system
- Circulatory system
- Excretory system
- Nervous system
- Reproductive system
The body is divided into the cephalothorax and abdomen, covered with a chitinous cuticle, which serves to protect the animal from drying out. The body cavity is a mixocoel. The abdominal limbs are absent (reduced); there are a total of six pairs of jointed limbs. Two of them, closest to the head end of the body, are transformed into chelicerae.
Chelicerae (from the Greek chele - claw claw and keras - horn) are the first pair of head, usually claw-like limbs in arthropods of the chelicerate subtype. Their main function is to grab and tear prey, grind and crush food. The chelicerae consist of 2-3 segments and often end in a claw.
Behind the chelicerae there are leg tentacles - pedipalps (from the Latin pes (pedis) - leg and palpus - tentacle). The pedipalps are the second pair of articulated limbs on the cephalothorax in arachnids. They serve for grasping and chewing food, as well as for the sense of touch. The bristles on the pedipalps prevent solid food from entering the mouth - remember that spiders feed on liquid food and have special digestion. Soon you will know everything 
On the lower abdomen of the spider there are special organs - arachnoid warts (modified abdominal legs). These are paired articulated outgrowths (from one to four pairs), the main function of which is the formation of arachnoid fiber. With the help of arachnoid fibers, spiders build a trapping network, which we call a cobweb (net).
Each spider's web has its own unique pattern; it consists of dry and sticky threads. The spider builds its own web and knows very well which threads are sticky and avoids them. Other animals do not know this secret and therefore get confused easily.
The spider has eight walking legs (four pairs). All representatives of the chelicerate subtype, including the cross spider, are characterized by the absence of antennae: they have neither antennules nor antennae.
Remember that spider digestion is extraintestinal. Having caught prey, the spider inserts chelicerae into its body and injects poison (formed in the poisonous glands). The victim is enclosed in a cocoon of web, after which the spider injects the secretion of the salivary glands into the victim, which begins to literally digest the victim outside the intestines of the spider - hence the name! After some time, the spider can simply suck in the already digested organs and tissues of the victim. The spider does not eat solid food.
The digestive system of arachnids consists of the foregut, midgut and hindgut. The foregut consists of a pharynx, a crop and a sucking stomach, which is equipped with powerful muscles and acts like a rubber bulb. Thanks to its sucking stomach, the spider pulls out the digested organs and tissues of the victim.
The midgut, whose main function is absorption, has numerous blindly ending projections that increase the total area of absorption. The hindgut ends with the anus, through which undigested food remains are expelled.
In addition to a pair of lung sacs, the spider has a tracheal system. The spider's lung sacs are modified skin outgrowths and have the shape of parallel partitions.
Tracheas are the respiratory tubes of arachnids and insects, opening on the surface of the body with special openings - stigmas (spiracles), most often lying in pairs. The inner wall of the trachea is represented by a chitinous membrane, which protects the trachea from collapse.
Thanks to the tracheal system, oxygen is delivered to the tissues and organs of the spider, and carbon dioxide is removed from the body.
The circulatory system of the spider, like all arthropods, is not closed (lacunar type). It consists of a tube-shaped heart, the functioning of which occurs in the same way as in crustaceans. The heart lies in the pericardial sac. From the heart there is an aorta, several arteries and a system of lacunae in which hemolymph circulates, washing the internal organs and tissues.
It should be noted that the developed tracheal system greatly simplifies the structure of the circulatory system, which practically does not participate in the transfer of oxygen. It is for this reason that there are no capillaries and small vessels in the circulatory system.
Thus, the main function of the circulatory system becomes the transport of nutrients to the cells and tissues of the body.
The excretory organs are the Malpighian vessels. Malpighian vessels are thin (thread-like) blind outgrowths of the intestine at the border of the midgut and hindgut. The land lifestyle has so increased the value of water for spiders that all the water is absorbed from the urine in the Malpighian vessels, and at the entrance to the intestine, uric acid crystallizes and precipitates, and is excreted in solid form with excrement.
Spiders also have special ones - coxal glands (Latin coxa - thigh), which are modified metanephridia. The excretory duct of these glands most often opens near the base of the first segments - the third pair of walking legs.
Consists of the brain (suprapharyngeal ganglion), subpharyngeal ganglion, connectives connecting these two ganglia - all these structures together form the peripharyngeal nerve ring. From the peripharyngeal nerve ring departs the ventral nerve chain, the structure of which is atypical - all nerve ganglia merge into a single star-shaped ganglion.
The sense organs are represented by the organs of balance - statocysts, and the organs of hearing - auditory vesicles. Spiders have 4 pairs of simple eyes, sensitive hairs - bristles - are distributed throughout the body, their greatest concentration is observed on the chelicerae, pedipalps, around the mouth and on the limbs. Spiders are very sensitive to the slightest vibrations of the web, which allows them not to miss prey caught in it.
Dioecious animals, fertilization is internal. The gonads of males are testes, and those of females are ovaries. Males lay a spermatophore (sac with sperm), which the female captures with the edges of the genital opening. Some spiders inject sperm directly into the female's genital tract using the copulatory organs.
The development of arachnids is direct - without metamorphosis (with the exception of mites). Some spiders lay eggs, from which young individuals subsequently develop, and some have viviparity. Viviparity is the birth of a fully developed baby, free of egg membranes.
Meaning for humans
Only poisonous spiders are dangerous to humans, but they attack in exceptional cases when they feel threatened. The remaining individuals are safe and even useful. They destroy many harmful insects that spread dangerous diseases. Animals living in earthen burrows loosen the soil.
In many countries, scientists use arachnid venom to make medicines. In laboratories, experts are trying to artificially produce spider web, which is a very durable material.
Scorpios
They hunt mainly at night. There are more than 1,500 species in the world. About 15 species are found on the territory of the former USSR. Among them:
- Italian scorpion (body length up to 5 cm) - lives on the Black Sea coast;
- Mingrelian scorpion - from the shores of the Black Sea it spreads along the banks of rivers inland;
- Crimean - found on the southern coast of the Crimean Peninsula;
- thick-tailed scorpion - the largest, up to 10 cm long;
- The motley scorpion lives in the Volga region, Transcaucasia, and Kazakhstan.
Scorpion venom is neurotropic in nature. The toxic proteins contained in it lead to disruption of the functioning of various systems and organs.
The bite is accompanied by severe burning pain, which either subsides or intensifies. Over time, the pain turns into a burning sensation. After 40 minutes, swelling forms at the sting site with a clearly visible dark dot in the center of the bite. Blisters with serous filling may form.
The time period for symptoms to appear ranges from 5 minutes to 24 hours. The headache is growing. Dizziness, convulsive muscle contractions and tremors, tachycardia appear, and blood pressure increases. The victim is agitated and may experience fear. Death from respiratory paralysis is likely within 20–30 hours.
In some cases, after the disappearance of clinical signs of poisoning, a relapse is possible. The victim should be under medical supervision for at least 12 hours after symptoms disappear.
First aid, treatment and prevention
an antidote is injected. In the absence of qualified assistance, the poison is sucked out of the wound, a cooling bandage is applied, and the bite site is treated with antiseptic drugs. The victim needs complete rest.
Scorpions can hide in the grass or burrow shallowly in the sand. Therefore, you must always wear shoes with strong soles. In areas where scorpions live, you should inspect clothing, shoes, and living quarters. Protective nets on windows and doors, sealed cracks in walls and ceilings will protect the house from the penetration of poisonous arthropods.
Poisonous arachnids
Spiders of Russia
In Russia you can meet a wide variety of spiders. It is estimated that the country is home to approximately 2,880 species with specific characteristics. Below are the main and most common ones.
House spider
House spider
This species prefers to live in residential buildings and outbuildings. It eats small insects: bedbugs, moths, flies, etc. If there are no human settlements nearby, it can live in fields and forests, using a crack in a tree or thick grass as a home. The color of the spider is yellow-brown, with a dark pattern on the back. An adult grows up to 1.2 cm.
Orb weaver
Orb weaver
A poisonous spider that lives in nature. The predator climbs trees and weaves a large round web between the branches, into which insects fall, which later become food. Orb weavers can also hunt frogs, rats and other small animals.
Interesting fact : the poison of the orb weaver paralyzes the frog in 15 minutes. For humans, the bite is practically harmless, although there may be discomfort in the affected area.
Argiope arthropod
Argiope arthropod
Males of this species rarely grow more than 5 mm, but females stretch up to several centimeters. The spider is yellow and black in color, which makes it look like a wasp. Argiope is found in central Russia. The spider is poisonous and rarely attacks first in case of danger. Having spread a web, the predator often sits right in its center and does not hide from potential prey.
Hyracantidae
Hyracantids
This species of spider lives in grass and dense thickets and loves temperate climates. Adults grow up to one and a half centimeters. The color is light brown, sometimes there may be a green tint. Chiracantids are nocturnal, do not build permanent housing, travel across territories and hunt insects. The bite is considered highly poisonous.
South Russian tarantula
South Russian tarantula
Grows up to 3 cm, prefers areas with low humidity, mainly steppes. He builds a house in loose soil, digs a hole several tens of centimeters deep. During the hunt, he sits inside and waits. When an insect runs nearby, the tarantula jumps out of the hole and bites the prey. The poison almost immediately paralyzes the enemy, and the spider only has to drag him home.
Silver spider
Silver spider
In Russia, you can find the silver spider in the Far East, Siberia and the Caucasus. The legs and front part of the predator's body are dark brown, the back part is gray. The size of an adult does not exceed 2 cm. The silver spider has a calm character and does not attack without reason. Spends most of its time in water, where it hunts small creatures.
Steatoda
Steatoda
Species is found in the Caucasus and southern Russia; it prefers to settle next to humans and hunt in gardens and vegetable gardens. The spider is black in color with orange-red or gray patterns on the back. It is poisonous, but the bite is not capable of causing severe harm to humans. But it quickly helps to cope with insects.
Black Eresus
The Black Eresus
Spider has a rather unusual color, which makes it look like a ladybug. Eresus lives in the Rostov and Novosibirsk regions. It digs a small hole as a home, to which it is attached all its life. Often the male and female live together to regularly produce offspring. The spider grows up to 2 cm in length.
Solpuga
The Salpuga
Spider lives in the Crimea, has white-yellow legs and a gray body, which is why it is perfectly camouflaged in the sand. It is most active at night and can move quickly. When hunting, it uses long jaws, which help cope not only with insects, but also lizards and rodents. Salpugs grow up to 7 cm in length.
Pouch spider
The pouch spider
is an aggressive predator that is capable of attacking even a large opponent. It has an elongated body of yellow color with a greenish tint. Lives in the Volgograd and Rostov regions. Prefers to live in fields with tall grass, but can also be found near trees. The average length of an adult is 1.5 cm.
False black widow
False Black Widow
The False Black Widow is dark in color and sometimes has red spots on its body. Individuals with light-colored paws are also sometimes found. The spider grows no more than 1.2 cm in length and hunts small insects. Considered highly poisonous. The bite can cause discomfort to a person for 2-3 days. The bulk of the population lives in Dagestan.
Top 5 largest spiders in the world
Let's look at the five that were officially recognized as the largest.
5th place. Purple tarantula
One of the huge spiders is the purple tarantula, which lives mainly in the forests of Colombia. It is in this place that its subspecies are most numerous in the world. The largest spider of this genus, which has been officially registered, has a length of 34.5 cm, but the average specimen reaches a length of 26 cm. It is worth noting that this large spider is not dangerous to humans, only its bite can cause an allergic reaction. Distinctive appearance features:
- only its abdomen is covered with thick hairs, and its paws are long and drooping;
- females are dark blue, purple and black in color;
- males are yellow-green in color.
4th place. Camel spider
This type of insect got its name because it has several humps on its head, which is why it has been compared to camels. These spiders prefer to feed on lizards, rodents and small birds. While hunting, it is capable of reaching speeds of 16 km/h. And its size reaches 30 cm including limbs. It is yellow-brown in color and has tentacles on its head that also serve as limbs. Thanks to four eyes, this species is excellent at distinguishing moving objects. Its chelicerae are very sharp and can easily cut the skin and hair of their prey. If a camel spider bites a person, the area may become inflamed because there is an infection on the chelicerae. Habitat is Asia, North and South America, Africa and some European countries.
3rd place. Salmon pink tarantula
Even though this species is considered the largest spider, some people keep it as a pet. The pink tarantula reaches a size of 30 cm and in the wild it feeds on small snakes, lizards and birds. The tarantula has lightning speed, so the victim has no chance of survival. Habitat is Brazil. Distinctive external features:
- the head and chest are covered with a shield, which depicts a design in the form of a 10-pointed black star, while the color itself is salmon;
- at the base of the limbs, which are adjacent to the body, the color is pink, and then it turns into dark gray;
- the belly and legs are heavily covered with hairs.
2nd place. Giant Crab Spider
One of the largest and arthropod insects in the world is the crab spider, or it is also called the huntsman spider. Its size reaches 30 cm and even more. It got its name due to its external resemblance to a crab and its ability to move. Its body is gray or brown, sometimes the color may contain spots or red splashes. The main feature of this giant is that it quickly kills its prey and feeds on insects and small invertebrates. When the victim is in his paws, he immediately injects his poison, which affects the victim's nerve cells. The venom contains a neurotoxin that can cause pain and swelling of the limbs. It attacks a person only in self-defense, but people still try to avoid it. It lives in Australia and Japan.
Harmless species of spiders
If the spider's venom is mildly toxic and causes almost no harm to humans, such species are considered harmless and non-poisonous. There are a large number of species in the world, and the main ones are listed below.
Hunter bordered
Border hunter
Lives in swamps and places with high humidity. To hunt, it enters the water and waits for insects and other small creatures to swim nearby on the surface. Feeling the vibrations, the spider breaks away and runs towards the source of the waves to grab its prey. The hunter's length grows up to 2.3 cm, the paw span reaches 8 cm.
Flower spider
Flower Spider
The spider has long front legs that can effectively grab prey. Males grow up to 4 mm in length, and females grow up to 9 mm. Females are white, sometimes with a yellow tint on their paws. Males are brown with red spots.
Interesting fact : the spider lives in the buds of different flowers, and its color can change depending on the color of the leaves. This helps to remain invisible while hunting insects.
Knitting spiders
Knitting spiders
Representatives of this species live in fields and prefer to settle near a water source. They spread their nets between branches over a river or pond and wait for various insects to get there. Knitting spiders mainly prefer flies, ants and aphids. Adults stretch up to several millimeters in length.
Haymaker
The Harvesting Spider
has a small round body and long thin legs. The color can be dark brown or with a reddish tint. The haymaker lives both in nature and in residential buildings. Builds webs in well-lit places, because... loves sunlight. Hunts small insects, but can also eat plant foods. It is completely harmless to humans.
Goliath tarantula
Goliath tarantula
An adult can grow up to 30 cm, making this species one of the largest among spiders. The body is covered with hairs, the color varies from light brown to dark colors. Most of the population lives in South America. The goliath tarantula is often kept as a pet. It feeds on insects and other spiders.
Interesting: Bumblebee