For many rural residents, horseflies are a real problem. I remember that even Pushkin lamented in his novel in verse that flies and mosquitoes interfere with enjoying the red summer. Probably, the great poet had not yet encountered a bullfly, otherwise he would have been given a special place in his poems. Or maybe Alexander Sergeevich simply included him in the category of flies. After all, both of them belong to the same order - Diptera.
Description and habitat
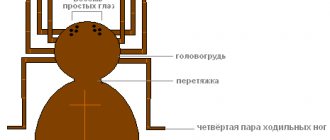
Horseflies are flying arthropod insects from the Diptera family. It is most active in wetlands and pastoral agricultural areas.
Externally, the horsefly looks like a large fly about 2 cm in size. The color is dominated by natural shades - gray, brown. Looking at what a horsefly looks like, you can notice eyes that change shade, an impressive piercing-cutting mouthparts and a fleshy proboscis.
The horsefly has a slightly elongated body with a thin chitinous covering. Behind the transparent wings are the halteres, thanks to which the insect can balance during flight and make characteristic sounds.
View from above
Common types
Although the species diversity of the subfamily is great, in temperate climates the following types of horseflies are more common:
- The bullfly lives throughout Europe. It is distinguished by its large size, because it reaches a length of 2.5 cm. When flying, it makes a loud buzzing sound. The chest of the bullfly is decorated with dark stripes and yellow hair, while the body of the insect is dirty brown. Representatives of this species are found even at an altitude of 2 km above sea level.
- The horsefly lacewing, which is also called the moth, does not exceed 1.5 cm in length. It differs from its relatives in its bright, almost contrasting color: a black chest combined with yellow patches on the abdomen. But the real wealth of the insect is its attractive eyes, painted in shades of emerald and gold, shimmering spectacularly in the rays of the sun.
- The rainfly looks more ordinary: its faded color cannot be called elegant. But the insect has a significant difference from its fellows: its activity increases in cloudy weather, while other horseflies prefer sunny days.
These are the three most popular types of horseflies that can be encountered in the CIS countries.
Lifestyle and nutrition
The horsefly spends almost its entire life in flight. Flight usually begins in the second half of May. The activity of horseflies, which occurs mainly during daylight hours, increases sharply before rain, but during rain the insects do not fly. The exception is the raincoat, which is why it got its name. They do not like horseflies and windy weather. The flight range of a horsefly is 2-4 km. The insect can reach speeds of up to 60 km/h.
Horseflies feed on the blood of mammals. However, this only applies to fertilized females, since they need blood to procreate. As for unfertilized females, they are quite content with a plant menu, just like male horseflies.
Life cycle and reproduction
The life cycle of a horsefly includes four main stages:
- egg (the female lays from 400 to 1,000 pieces);
- larva;
- chrysalis;
- imago (adult).
The total duration of complete transformation is 4 years.
The method of reproduction of horse flies is similar to that of other dipterans. After mating, the female lays eggs on leaves and stems of plants, in water and moist soil.
The horsefly larva hatches in 3-8 days. This stage lasts about a year. In the spring, the larvae begin to pupate, having first moved to a drier place. This process may take several weeks. As a result, an adult horsefly is born.
Varieties
Currently, over 4 thousand species of horseflies are known. Often the characteristic features and lifestyle of an insect are indicated by its name:
- bullfly (one of the largest dipterous insects),
- deer horsefly,
- gray horsefly,
- ordinary raincoat,
- lacewing,
- forest lacewing, etc.
Gray horsefly
Not just bitten - infected with a disease!
The bullfly is an extremely harmful insect. In addition to the fact that this bloodsucker annoys cattle with its bites, it spreads various diseases. This includes tularemia, anthrax, filariasis, trypanosomiasis, and polio.
The bull horsefly does not hesitate to taste the blood of three-day-old corpses. And this is even worse than the transfer of infection from one living being to another. After all, if an animal died precisely as a result of a fatal disease, then there is no guarantee that the insect will not infect a person or livestock with it.
Differences between horseflies and gadflies
Differences between horseflies and gadflies are manifested both externally and in the lifestyle of insects. The horsefly has a discreet color, while the gadfly is brighter. The gadfly is smaller in size than the horsefly. It has four wings, while the horsefly has two.
The gadfly has much more habitats because it needs living organisms to reproduce. The horsefly always strives to be closer to the reservoir, since it needs a stable, moist environment to lay eggs and breed offspring.
The gadfly does not drink the blood of mammals, but bites them in order to introduce its larvae into a living organism. For a female horsefly, blood is an essential nutrient she needs for reproduction.
There is also a difference in the way of eating. Adult gadflies do not eat at all. They exist due to the nutrients that were accumulated by the body in the larval state. They have no oral apparatus at all. The horsefly must regularly nourish its body.
Insects also have different methods of reproduction. Horseflies lay their eggs in water, grass, or moist soil. To reproduce, a female gadfly needs to implant her larvae into the body of an animal or human, which then actively parasitize it.
Life activity of an insect
Although in an unfertilized state, females are also not averse to feasting on nectar. But after fertilization, they become aggressive, since they need the blood of animals for the process of egg development. In one horsefly bite, an animal can lose up to 200 milligrams of blood. The described insect uses its proboscis to so-called cut the skin, after which the horsefly begins to directly consume the blood from the resulting wound.
Interesting! Only female horseflies feed on the blood of warm-blooded creatures, while males, on the contrary, eat exclusively flower nectar, as well as sugar-type secretions from worms and aphids.
Horseflies may be attracted to the following features:
- Dark color,
- The emanating smell of sweat from the future victim,
- Wet body, for example, a person after swimming,
- Movement of the source of the attack.
Although it would still be preferable for these insects to have a victim in an immobilized state.
The horsefly larva most often develops in water or in soil saturated with moisture; the described insects can often be found near bodies of water. Especially many horseflies can be found in hot weather; the peak of their activity is summer, which is in full swing.
Horsefly mandibles
So to speak, having eaten the blood of a female horsefly, I digest it quite quickly. After 2 days, only remnants of digested blood can be found in the intestines of insects. The female will feel hungry again, along with the eggs gaining weight. After 3-4 days after the female has consumed blood, she begins to lay eggs from 500 to 1000 eggs at a time. As a result of repeated consumption of blood (female horse flies can carry out up to 6 such cycles), insects can lay up to 3,500 eggs.
Horsefly bite and its causes
While in nature, you can easily become the target of a horsefly bite. The insect senses the smell of sweat from several tens of meters away.
Consequences of a bite
When a female horsefly bites a person or animal, through a puncture in the skin, she introduces a special substance into the blood that thins and prevents clotting. A horsefly bite is dangerous for two main reasons:
- It can provoke an allergic reaction to the insect substance injected into the blood. In some cases, allergy sufferers may even experience death after a bite;
- A horsefly bite can cause an infection; treatment in this case is much more difficult.
First aid for a horsefly bite
Providing first aid for a horsefly bite should begin with washing the affected area with cold water and soap and treating it with an antiseptic to prevent secondary infection from entering the wound. To reduce pain and swelling, it is recommended to apply an ice compress to the bitten area. Baking soda lotion works well against itching and redness. Pharmacy creams against insect bites, for example, “Rescuer,” also help well in these cases.
If the victim of a horsefly bite has a tendency to allergies, it is necessary to urgently take an antihistamine.
Attention! If the bite lands directly on a mole, you should definitely visit a doctor without delay, since such damage can cause the mole to degenerate into a malignant form.
In any case, you need to start providing first aid for a horsefly bite immediately, so as not to provoke any complications that require serious medical intervention.
Meaning in nature
Many people, especially rural residents, who are bothered by these evil blood-sucking flies and interfere with the breeding of livestock, have a question: why not lime the bullfly at all? But it turns out that this is absolutely impossible to do. After all, this insect, like all others, is a component of natural communities. By wiping it off the face of the Earth, the established balance can be disrupted. This will definitely have a negative impact.
In fact, horseflies serve as food for dozens of groups of animals: birds, fish, reptiles. It is not without reason that many fishermen use this particular insect as bait. And quite successfully, by the way.
The corpses of insects, falling to the ground, fertilize it, which is also one of the reasons for the inexhaustibility of our soils.
Another question: how to reduce the harm caused by this vile? As it turns out, horseflies cannot tolerate the smell of wormwood. Therefore, it is recommended to hang bunches of this fragrant grass on door jambs and window frames during the period when these insects are especially active (June-July). It is unlikely that there will be a horsefly who dares to overcome such an obstacle.
In barnyards, in order to reduce the number of bloodsuckers, they arrange special reservoirs for them, pouring a little fuel oil or kerosene into them. Insects, trying to get drunk while flying, cannot take off and fall into a puddle where they die.
People who are forced to do things in the garden or yard at noon, graze animals in pastures or do work in the fields use chemical repellents as protection against bites. Clothing made of thick fabric also helps them. The face is protected with a hat with a net, such as beekeepers usually use.
Treatment of a horsefly bite
Since the likelihood of an insect attack in nature is high, you need to clearly understand how to treat a horsefly bite.
Chlorhexidine
First of all, during treatment, it is necessary to treat the affected area of the body by washing it with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, or at least clean water. Then you need to carefully squeeze the liquid out of the wound. This will prevent the insect's saliva from spreading under the skin. It is better to cover the bite site with a band-aid.
To prevent allergies, you should take antihistamines (Cetrin, Loratadine). You can take painkillers and antipyretics (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen).
Folk remedies for relieving swelling include rubbing, as strange as it may sound, with Corvalol, soda solution, dandelion juice, grated potato mass, as well as regular ice and iodine. Salt lotions help a lot.
Preventive measures
As they say, prevention is the best cure. Therefore, when going for a walk or a trip to nature, you need to take measures to protect yourself and your loved ones.
When going outdoors, you need to pay special attention to the choice of clothing. It should not be of bright colors, so as not to attract undue attention from horse flies.
It is better to give preference to things that cover the body as much as possible, made of dense, but breathable fabrics, of a khaki color. It is not recommended to use perfume in such cases, as it attracts insects.
Various repellents containing 20% diethyltoluolamide in the form of creams, lotions, and sprays will help repel horse flies. You can also use traditional methods:
- If you are going to live in a rural area, then you need to collect wormwood and tansy in small bunches. By hanging them outside on the walls of the house at the entrance and windows, a person will scare away horse flies that try to approach the home.
- Bouquets of tansy and chamomile in the house would be useful. You can spread tansy stems around the tent if you have to spend the night outdoors. This plant perfectly repels blood-sucking insects.
- When making a fire, it is recommended to burn several chamomile flowers and stems in it. Then evening gatherings by the fire will be safer. You can also use valerian, juniper pine, wheatgrass root, and cinnamon.
- If you treat the body with a solution of carbolic acid, horseflies will never attack.
- To repel blood-sucking insects, an effective remedy is to lubricate exposed areas of the body with fish oil.
- You can sprinkle chamomile tincture on your body and clothes. The most effective in this regard are the Persian and Caucasian species of this plant.
- If there are puddles nearby, you can pour a little gasoline or diesel fuel into them. Flies that want to get drunk on the fly, having landed in such traps, will no longer fly up.
Sometimes it happens that you have to stop for the night in places where there are concentrations of horse flies, mosquitoes and mosquitoes. Then it is better to follow the safety rules:
- you need to set up your camp on a hill, away from the swamps,
- sleep under a mosquito net, and if possible, smear your face with mud (silt), especially before going to bed,
- It’s better to tuck your trousers into your socks or shoes,
- put on all your clothes, especially at night,
- be sure to use a protective mask and gloves,
- Use repellents applied to clothing; they retain their effect for weeks.
There are many recipes on how to avoid insect attacks, but the main thing is to use them in time and correctly.
The horsefly, being a blood-sucking insect, causes inconvenience to both animals and people in the warm season. Many people are familiar with its obsessive buzzing and painful bites. In hot weather, far from cities, horseflies stage real attacks, interfering with comfortable outdoor recreation or work in the garden. They also annoy livestock. What kind of insect is this and why does it attack?
Consequences of a bite
The consequences of a horsefly bite are swelling and allergies. Pregnant women may experience intrauterine fetal death, premature birth, or miscarriage.
Infection of a wound can contribute to the development of an inflammatory and infectious process, including blood poisoning (sepsis) and bacteremia (high levels of bacteria in the body). Tetanus and gas gangrene may develop.
Allergic reaction
A person who is bitten by an allergy may experience an attack of suffocation or anaphylactic shock. There may even be a coma and eventual death.