The appearance of a small pet at home imposes a special responsibility on the owners. Caring for a puppy is expressed not only in proper nutrition and physical activity. Comprehensive animal care includes timely veterinary intervention.
Healthy newborn babies require a visit to the veterinarian for vaccinations. The puppy's first vaccination is given already in the second month of life. Subsequently, the puppies are re-vaccinated and other planned measures are taken.
Timely vaccinations help protect your pet from infections, which prolongs their life and allows you to raise a healthy and happy dog.
What types of vaccinations are there?
Before the puppy is one year old, it is necessary to receive a number of different vaccinations. Each of them is aimed at combating a specific virus. Depending on the region and the presence of certain infectious diseases in it, the types and quantities of required vaccines may vary. But there are a number of mandatory vaccines that are administered to dogs regardless of their geographic location.
There are different types of vaccinations:
- From viral hepatitis.
- From parvovirus enteritis.
- From the plague.
- From parainfluenza.
- From leptospirosis.
- Against rabies.
- From piroplasmosis.
- Against lichen.
The mandatory vaccination schedule does not include tick vaccination; this injection is given at the request of the owners. There are no vaccinations against coronavirus; veterinary medicine treats this infection depending on how it was acquired.
Vaccinations for puppies according to age are given in strict accordance with the established schedule. The final decision on the number of vaccines administered and the types of diseases to be prevented rests with the veterinarian. By following the recommendations of a specialist, up to 90% of diseases can be prevented. In the remaining 10% of cases, the disease is mild and does not cause death to the pet or severe damage to its body.
Types of modern vaccines
When choosing a vaccine for puppies, take into account the place of its production and the breadth of its application. These indicators affect the final price, so it is necessary to understand their main differences.
What to choose: domestic or imported product?
Domestic products are always cheaper than foreign analogues. The main advantage of imported samples is their longer existence and a large number of positive reviews. Veterinarians recommend choosing a domestic manufacturer when vaccinating against rabies. After the use of foreign drugs, outbreaks of diseases were recorded.
Mono-vaccines
Single vaccines are aimed at preventing one disease. Their advantage lies in a more gentle effect on the body and better production of antibodies to the selected infection.
When vaccinated with mono-vaccines, it is easier to choose an individual schedule, but the pet will have to undergo many injections. If your four-legged pet experiences stress when visiting a veterinary clinic or you have too little free time, use polyvaccines.
Polyvaccines
Polyvaccines include up to 6-7 fragments of different viral codes. They are more difficult to tolerate by the body, so multicomponent formulations are indicated only for adult animals. For children, drugs containing up to 4 different viruses are used.
The disadvantage of polyvaccines is the possible suppression of some antibodies by others. The rabies virus is considered the most aggressive, so the body directs all its forces to fight this particular agent. In other cases, immunity to several diseases is achieved simultaneously with just one injection.
Effect of the vaccine on the body
When dead or weakened fragments of the viral code are introduced into the body, active production of T-lymphocytes begins - antibodies responsible for destroying the invading pathogen. These antibodies are called memory cells, so if successful, they remember the method of fighting the infection. In case of infection, they give an immediate response, preventing further spread of the virus.
This method of combating infectious diseases is used only for preventive purposes. In case of direct infection, the infected animal is injected with serum - a preparation with ready-made antibodies that forms short-term passive immunity.
Vaccination schedule by age
When a small puppy or adult dog appears in the house, you should immediately contact a veterinarian. He will conduct an initial examination of the pet and set a vaccination schedule, taking into account the types of mandatory and recommended serums.
Vaccination table from birth to one year:
| Name of the disease | 1st vaccination | 2nd puppy vaccination | Comments |
| Plague | at 2 months | at 3 months | are done comprehensively |
| Viral hepatitis | at 2 months | in 21-28 days | included in the complex |
| Parvovirus enteritis | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks | included in the complex |
| Parainfluenza | 8-10 weeks | at three months | included in the complex |
| Leptospirosis | at 2 months | at 3 months | included in the complex |
| Rabies | 11-13 weeks | — | the only vaccination that is mandatory in the Russian Federation |
| Piroplasmosis (carrier tick) | at 6 months | in 3 weeks | There is a lot of debate about the guarantee of protection after the introduction of the vaccine |
| Lichen | individually | a month later | the effectiveness of vaccination is controversial, since lichen mutates quite quickly and is easier to treat after the disease has occurred |
| Trichophytosis (ringworm) | between 1 month and six months | In 2 weeks | helps prevent infection in 100% of cases |
| Microsporia | 1-6 months | in 10-14 days | recommended for use, but the disease can be easily cured with ointments, without the use of injections |
At 1 month, newborns can be given the PUPPY vaccine. It is not mandatory and is only used if there is a high probability of infection, such as quarantine in a shelter.
Revaccination of all listed diseases is carried out when the dog reaches one year. The frequency of subsequent injections is once a year.
Vaccination of adult dogs
Adult dogs are vaccinated against the same infections as small puppies. After primary vaccinations, the animal’s body has good protection against viruses for a certain period of time, but gradually it weakens, so revaccination is necessary.
Revaccination schedule for adult dogs
Against plague, parovirus enteritis and hepatitis Revaccination every 3 years
Coronavirus enteritis, microsporia, parainfluenza Annual revaccination with an interval of 12 months.
Leptospirosis Revaccination once every 12 months annually. According to indications, the terms may be reduced.
Vaccination calendar: vaccination of dogs against rabies
Rabies is a dangerous infectious disease that cannot be cured. If infected, the dog dies painfully. The disease also poses a threat to humans. To protect the whole family, be sure to vaccinate your pets against rabies according to the vaccination schedule.
Rabies vaccination and revaccination schedule for dogs
First rabies vaccination 12-13 months
Revaccination Every year with an interval of 12 months.
Vaccination schedule depending on breed
Vaccination of puppies is carried out in order to develop stable immunity to certain diseases. The first weeks of babies’ lives are protected by antibodies that enter their bodies with mother’s milk. By 2-3 months, the level of antibodies drops, so it is during this period that dogs are subject to primary vaccinations.
Read Method of use and cost of Advantage for dogs
Vaccination table for puppies of small breeds - Jagdterrier, English cocker spaniel, Shiba in, beagle, pinscher, etc.
| Name of the disease | first vaccination | puppy's second vaccination |
| Plague | 8-9 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Rabies | 6-8 months | — |
| Viral hepatitis | 8-9 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Parvovirus enteritis | 8-9 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Parainfluenza | 8-9 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Leptospirosis | 8-9 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Piroplasmosis (carrier tick) | 8-9 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Lichen | 8-9 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Trichophytosis (ringworm) | up to six months | In 2 weeks |
| Microsporia | up to six months | In 2 weeks |
Vaccination table for puppies of medium breeds - miniature schnauzer, Russian spaniel, giant schnauzer and others:
| Name of the disease | first vaccination | second vaccination |
| Plague | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Rabies | 11-13 weeks | — |
| Viral hepatitis | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Parvovirus enteritis | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Parainfluenza | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Leptospirosis | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Piroplasmosis (carrier tick) | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Lichen | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Trichophytosis (ringworm) | up to six months | In 2 weeks |
| Microsporia | up to six months | In 2 weeks |
Vaccination table for large breed puppies - Alabai, Austrian pit bull, VEO, Drathaaru, Malamute, Akita Inu, hounds, etc.
| Name of the disease | first vaccination | second vaccination |
| Plague | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Rabies | 11-13 weeks | — |
| Viral hepatitis | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Parvovirus enteritis | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Parainfluenza | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Leptospirosis | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Piroplasmosis (carrier tick) | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Lichen | 8-10 weeks | in 3-4 weeks |
| Trichophytosis (ringworm) | up to six months | In 2 weeks |
| Microsporia | up to six months | In 2 weeks |
Small dogs are given injections at almost the same time, regardless of their breed. German puppies and other varieties of kittens can receive additional vaccinations at the age of 4-6 weeks, only if there is a high risk of possible infection with a particular disease. Mutts are vaccinated according to standard principles.
The exact vaccination schedule is prepared by the dog’s attending physician. The vaccination dates set by the veterinarian cannot be changed.
How does the vaccine work?
The vaccine, due to the content of antigenic determinants, creates artificial acquired immunity in the animal's body.
In other words, the dog’s immune system recognizes a weakened infectious agent, produces antibodies and creates clones of protective cells that are capable of destroying it. In the future, when encountering an infectious agent, the pet’s immunity will quickly destroy it, preventing the manifestation of clinical symptoms.
Preparing for vaccination
Dog vaccination is a multi-step procedure that must be performed regularly, strictly in accordance with the schedule. The process is complicated by the fact that the pet must be properly prepared for vaccination, and then undergo a certain quarantine after the injection.
The main recommendations for preparation are the need to carry out preventive measures, namely, give anthelmintic drugs before administering the vaccine. It is extremely important not to inject sick puppies. The dog’s condition is usually assessed by a veterinarian, but the pet’s owner must also monitor his well-being.
When preparing your baby, you should follow these tips:
- Treat the wool with special preparations to remove fleas.
- After a few days, give an anthelmintic drug. It is purchased taking into account the actual weight and age of the puppy. If necessary, a repeat appointment is made after 10-12 days.
- A visit to the clinic is planned no earlier than 10 days after the last anthelmintic dose.
When re-administering primary injections, the procedure does not need to be repeated. But in the future, with annual vaccination, preparation is carried out in full.
How does the procedure work?
To avoid complications, it is recommended to follow the recommendations for preparation for the procedure and mandatory quarantine after it. In this case, you don’t have to worry about the health of your four-legged pet.
Preparation at home
Preparation begins 2 weeks before the event. The owner needs:
- Make sure there are no diseases. Check your temperature and stool quality daily. If alarming signs occur, contact your veterinarian.
- Maintain your usual diet. The change is expected only on the immediate day of vaccination. If the procedure is scheduled for the morning, refuse feeding. In the case of an evening recording, reduce the usual portion by ½ with natural feeding and by ⅓ with dry feeding. The last feeding should be no later than 4 hours before vaccination.
- Treat your pet against helminths, ticks and fleas. If infected with parasites, the vaccination period is shifted, and the pet is treated again.
Before the first vaccination, walks and contact with people dressed in outerwear are excluded. An unvaccinated baby should be next to his mother, away from the corridor with street shoes. For preventative purposes, regularly carry out wet cleaning and wash your shoes after going outside.
Choosing a veterinary clinic
Choose an institution that has received a special license to carry out veterinary activities. This guarantees the safety of the services provided.
The procedure can be performed directly in the clinic or at home. The advantage of the first option is a wide selection of equipment needed for complications and the absence of the risk of damage to the drug during transportation. The second option minimizes the stress factor and eliminates the transmission of infection from other four-legged patients.
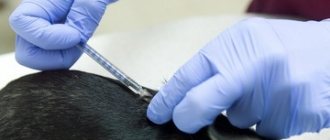
Vaccine introduction
Typically, the most painful part of the procedure is the needle piercing the skin and/or muscle. The injection itself does not cause pain, so most dogs tolerate the injection calmly.
If a puppy is being vaccinated, it is enough to hold it firmly in your arms. You can wrap a particularly active baby in a towel. But an adult dog of any breed must be muzzled. Even very calm individuals who are not receiving an injection for the first time can become nervous and bite the doctor or owner. Therefore, follow all the rules for visiting the clinic: short leash, muzzle, and sometimes you will need an assistant.
Dangerous and non-dangerous side effects
Due to the activation of protective mechanisms, a temporary decrease in immunity occurs, causing a number of side effects. Non-hazardous ones include:
- one-time vomiting or diarrhea;
- lethargy and fever (not higher than 39.5°C) during the first 3 days;
- loss of appetite (fasting is permissible for no more than a day);
- pain accompanied by barking and whining, or temporary lameness (no more than 4 days);
- the formation of a lump at the injection site, which disappears on its own within a month.
If a month has already passed and the lump has still not resolved, contact your veterinarian. This phenomenon is typical for a benign tumor. Surgery is used to remove it.
Mandatory assistance from a veterinarian must be sought in case of progressive deterioration of the condition, growth and suppuration of the lump, as well as the development of anaphylaxis (allergy).
An allergic reaction is accompanied by swelling and discoloration of the mucous membranes, profuse salivation and difficulty breathing. If these symptoms appear, give the animal an antihistamine and call a doctor immediately.
Cost of vaccine and clinic services
The final price depends on the chosen manufacturer and location of vaccination. Foreign drugs and calling a doctor to your home will cost the most. The most popular vaccines include:
- French Eurican;
- Dutch Nobivak;
- American Vanguard;
- Russian Polivac and Multikan.
The clinic’s services include not only the procedure itself and consumables, but also a preliminary conversation with a therapist. Prices vary greatly by city and region, so it is better to call the clinics yourself and compare the cost of services.
How to vaccinate a dog
Vaccinations for dogs are given intramuscularly. You can inject yourself or at a veterinary clinic.
It is not difficult to vaccinate a puppy at home yourself, but it will require certain knowledge and skills. The procedure for administering the injection at home is as follows:
- Disinfect the vaccine injection site. The injection can be placed in the withers and in the hind thigh. Disinfection is carried out using alcohol or another medical solution intended for this purpose. Do not forget that the “house doctor” himself must also wash his hands thoroughly.
- Mix the vaccine until smooth by shaking and draw the liquid into the syringe.
- Bleed air from the syringe. There should be no air bubbles in the solution.
- Insert the needle into the treated area on the withers or back thigh and slowly inject the drug.
- Remove the needle and re-treat the injection site with a cotton swab dipped in alcohol.
Read Real reviews about Superflex supplement for dogs, price and characteristics
Home injections are not suitable if the dog will take part in exhibitions and competitions or travel with dogs. In these cases, the dog must have a vaccination passport, which can only be issued by accredited veterinary hospitals.
Timing of vaccinations and what to vaccinate against
An individual vaccination schedule is developed for each four-legged patient. Having purchased a kitten, the owner must undergo an examination by a veterinarian, who will prescribe the timing of administration and types of drugs.
Immunization calendar by age
An approximate vaccination sequence looks like this:
- at 7-8 weeks the first comprehensive vaccination is given against parainfluenza, parvovirus, carnivore distemper, leptospirosis and adenovirus infections;
- at 12 weeks of age, the same vaccination is given as the first time, with simultaneous vaccination against rabies;
- upon reaching 6-7 months of age, the puppy is revaccinated against rabies, parainfluenza, parvovirus infection, carnivore distemper, leptospirosis and adenovirus infections;
- At one year of age, the serum complex is administered for the last time, then the dog is vaccinated annually.
The listed diseases are the most common, and vaccinations against them are the most common. However, vaccines are rarely used against other infections, taking into account the epidemiological situation in a particular area.
The only immunization within Belarus, which is mandatory for any dog and is not related to its age, breed, or region of location, is a vaccination against rabies, and this provision is enshrined in the legislation of the country.
The first vaccination against the rabies virus can be delayed until the puppy reaches six months of age, as long as it is ensured that the dog does not come into contact with outside animals.
It is necessary not to miss the prescribed vaccinations until the time of tooth replacement due to the fact that some serums affect the color and condition of the enamel. In the future, vaccinations are carried out after complete eruption of all crowns.
Violating the schedule drawn up by the veterinarian is unacceptable: postponing the dates to earlier or later periods can interfere with the development of the immune mechanism or prevent it from forming in full. An exception is if the puppy is ill before visiting the doctor. In such a situation, vaccination is postponed until the dog's health is favorable.
Under some conditions, the serum is reintroduced to a 4-month-old puppy. This is necessary if the kitten has not developed immunity as a result of the first two vaccinations.
Regardless of what breed the baby belongs to: whether it is a large Newfoundland, Great Dane, Mastiff, Caucasian Shepherd, Chow Chow or a small miniature poodle, Yorkshire Terrier, Spitz, Brussels Griffon, the volume of serum administered will be the same for everyone. Each ampoule includes a strictly calculated number of weakened or dead viruses.
But it is important to note that injections are given only by a veterinarian. You should not engage in amateur activities when buying a vaccine and administering it to your dog. Only a specialist will not violate the requirements for storage and administration of the product.
Early vaccination in special cases
It is recommended not to vaccinate puppies under 7-8 weeks of age.
This is explained by the fact that they have protection in the form of passive immunity acquired through breast milk. Its effect lasts 1.5 months.
However, there are special situations when the puppy is vaccinated earlier. At 1-1.5 months of age, the kitten can be given anti-plague and anti-parvovirus vaccines.
The reasons for early immunization of babies up to 2 months can be:
- the occurrence of an epidemic situation in the nursery;
- feeding cubs artificially, and not with mother's milk;
- lack of vaccinations in the mother;
- the puppy is a “foundling”, and there is no way to obtain information about his vaccinations or lack thereof for him and his mother;
- there is a possibility of contact with infected animals;
- planning to move to another region of the country or abroad.
The first vaccination for babies under 8 weeks of age is carried out with specialized products from the Puppy . Use "NobivacPuppyDP" or "EuricanPRIMO" . The cost of each is within 310 rubles.
What drugs are used
Dog owners quite often wonder which vaccine to choose from the variety of drugs offered. Without sufficient experience, it is not too clear what exactly to focus on when choosing. But it is worth understanding that the same type of injection can have many names, depending on who the manufacturer is.
If we talk about the most common vaccines that are used to vaccinate puppies and adults, their list is quite small:
- Monovalent vaccines are aimed at preventing one type of disease. Such drugs are very effective, and they also reduce the burden on the animal’s body when producing antibodies. It is believed that the quality of the immune bodies produced as a result of the single drug is higher. If you vaccinate a puppy with monovalent drugs, it is easier to develop an individual vaccination regimen.
- Polyvalent or complex vaccines can form immunity against several types of diseases at once. The drug contains live viral strains, which allow the puppy to have a mild form of the disease and develop immunity to it. It is better to use a seven-valent drug in relation to already adult pets; they can more easily tolerate its effects, since the body already has immune bodies of this type.
The price of the drug directly depends on the manufacturer, as well as on the type of vaccine chosen.
Domestic
Manufacturers of vaccination drugs are constantly looking for new and improved drugs, so the list of injections is often updated with new items. Today, four-legged pets can be vaccinated using the following domestic vaccines:
| Name | What disease does it fight? | Primary use |
| Aversect | nematodosis, demodicosis, otodectosis, notoedrosis, sarcoptic mange, entomosis | at any time when a disease is detected |
| ASP (antistaphylococcal drug) | staphylococcal infection | as the disease progresses |
| Shchelkovo-51, Vnukovo-32 | rabies vaccine (against rabies) | from 3 months |
| Dipentovac | plague, parvovirus enteritis, infectious hepatitis, adenovirosis, leptospirosis, rabies | from 60 days of age |
| Biovac-D | carnivore plague | from 8 weeks |
| Biovac-R | parvovirus enteritis | from 8 weeks |
| Biovac-RA | adenovirus infection and parvovirus enteritis | from 8 weeks |
| Biovac-PAL | leptospirosis, parvovirus enteritis and adenovirus infection | from 8 weeks |
| Biovac-L | leptospirosis | from 8 weeks |
| Vakderm | microsporia and trichophytosis (lichen) | any age |
| Vladivak-Ch | plague | 8-10 weeks |
| Vladivak-P | parvovirus enteritis | 8-10 weeks |
| Vladivak-AG | adenoviral infection and infectious hepatitis | 8-10 weeks |
| Vladivak-ChP | plague and parvovirus enteritis | 8-10 weeks |
| Vladivak-PAG | parvovirus enteritis, adenovirus infection and infectious hepatitis | 8-10 weeks |
| Vladivak-ChPAG | plague, parvovirus enteritis, adenovirus infection and infectious hepatitis | 8-10 weeks |
| Hexakanivac | canine distemper, infectious hepatitis, adenovirosis, enteritis, leptospirosis | from 8 weeks |
| Ivermek | antiparasitic | as prescribed by a veterinarian |
| Microderm | microsporia and trichophytosis | from 6 weeks |
| Multikan (in various configurations) | plague, infectious hepatitis, adenovirosis, enteritis, leptospirosis | from two months |
| Polivac | ringworm | from 1 month |
| Tetravac | plague, adenovirosis, infectious hepatitis | from 2 months |
| Trivirokan | enteritis, hepatitis, adenovirosis | 8-10 weeks |
| EPM | plague | from 9 weeks |
| Chlamikon | chlamydia | from 9 weeks |
Read Signs and treatment of ataxia in dogs: 3 types of disease
The cost of Russian vaccines is an order of magnitude less than foreign ones. Prices vary by region and distributor.
Imported
Imported vaccines are quite widely represented on the Russian market. The choice of drugs is huge. Of all the variety, it is worth highlighting the most popular types:
- Nobivak, manufacturer: Netherlands. Manufactured under the brands DHP, DHPPi, KC, Lepto, Piro, Puppy DP, Rabies, RL. Each of the drugs can be used separately. The very first injection in this series is the pappi vaccine, which, if necessary, is administered as early as 6 weeks of age.
- Hexadog is a French vaccine. It is used primarily at the age of 12 weeks. Allows you to develop immunity against plague, parvovirus, adenovirosis, peptospirosis, rabies.
- Eurican, France. Has two forms:
— DHPPI2 – L – from plague, adenovirus, parvovirosis, parainfluenza and leptospirosis;
- DHPPI2-LR - against plague, adenovirus, parvovirus, parainfluenza, leptospirosis and rabies.
- Vanguard, American vaccine. Vanguard is a multivalent antifungal drug that can be used from 8-10 weeks.
- Rabizin, France, against rabies. Primary use no earlier than three months.
- Primodog, France. Monovaccine against parvovirus enteritis, indicated from 5-7 weeks.
- Defensor, USA. Intended for the prevention of rabies, administered from three months of age.
How much each injection costs depends on which drug is used. We must not forget that when receiving vaccinations at a veterinary clinic, the price also includes related services.
Which vaccine to choose
In Russia, the most widely used vaccines are those produced in the Netherlands (Nobivac) and France (Eurican); they are considered safer and more effective than their domestic counterparts.
Nobivac vaccine against rabies has received a large number of praises , since, unlike other drugs, it extremely rarely causes allergic reactions in animals due to the use of herbal remedies to obtain the pathogen antigen.
Other vaccines in the Nobivac series (Puppy DP, DHP, DHPPi) are positioned by many dog owners as potentially dangerous with the highest risk of developing allergies, including anaphylactic shock. Despite this significant drawback, vaccinating dogs with these drugs is very popular and demonstrates a high level of reliability in the development of stable immunity.
Some imported drugs and their domestic analogues can also be used to vaccinate an animal:
- “Multikan”, “Biovac”, “Polivak- (made in Russia);
- “Hexadog” (made in the USA - France), “Duramune” (USA), “Vanguard” (Belgium), “Primodog” (France).
As a rule, the above-mentioned products are characterized by an average level of safety and effectiveness, but are more affordable.
Restrictions after vaccination
When vaccinated, a puppy is injected with the viral strain of the disease against which it is being vaccinated. Accordingly, the pet’s body will be susceptible to the disease, albeit in extremely small doses. It takes about two weeks for complete recovery and the production of immune bodies. But persistent immunity to the disease appears only after the puppy’s second vaccination, and sometimes after the third.
It is important for puppies to undergo strict quarantine for two weeks after each vaccination. During this period, it should not be taken outside, but the house should be kept clean and the pet’s contact with dirty shoes or with other pets that are regularly walked in the fresh air should be minimized.
Necessity
The word “vaccination” means a special vaccine that is administered to an animal at certain periods of life and protects its body from the action of infectious agents.
The vaccine may contain live weakened or killed microorganisms. The introduction of these drugs reduces the risk of possible infection of the pet when encountering an infection, and in the event of a disease, it reduces the severity of complications. Therefore, vaccinating a dog is a top priority for any owner.
Side effects and complications
Injections can cause complications. The most common side effect is an allergy to the vaccine. The reaction is expressed in profuse salivation, lacrimation, involuntary defecation, swelling at the injection site.
After vaccination, they can suffer from a mild form of ARVI; they sneeze, cough, and have a fever. Sometimes complications are expressed in a more complex form. One of the most severe side effects after an injection can be post-vaccination sarcoma. This is a tumor that forms at the injection site. It can only be removed surgically.
Preparing the puppy for vaccination correctly
Preparing your pet for immunization should begin 12-15 days in advance. What to do:
- treat once against blood-sucking parasites: ticks, fleas - 10 days before vaccination;
- treat for worms; if there is infestation with helminths, then twice, if not, then once; the procedure is also carried out 10 days before the injection;
- exclude excessive physical activity, stress, overwork; this requires a 3-week period before vaccination.
On the day of the manipulation, it is recommended to stop feeding the puppy. If your veterinarian visit is scheduled for the evening, you can feed him a small amount of dry or regular low-calorie food.
It is mandatory to carry out anthelmintic and antiparasitic measures before any vaccination of not only cubs, but also older dogs.
What to do if you missed a vaccination
The vaccination schedule established by the doctor cannot be changed without permission, especially when it comes to primary vaccinations. Subsequently, revaccination is carried out every year, but the timing of the first injections is extremely important.
If the owner missed the deadline for administering the vaccine, one should be prepared for the fact that immunity will not be fully developed, that is, it will not be 100% stable. Sometimes skipping an injection is due to the pet's illness.
If you miss the time for administering the vaccine, you will have to take the course of this vaccination again and only after quarantine will the dog be able to go outside for a walk.
The first year of a puppy's life is very important for its entire life. It is possible to form an immune system resistant to infections only through vaccination. The vaccination schedule should be strictly followed; this is the only way your four-legged pet can get a healthy foundation for its future existence.
Recovery after vaccination
Quarantine lasts 2 weeks after the procedure. For the safety of your four-legged pet, it is necessary to exclude contact with the outside world, ensure a comfortable environment inside the house and reduce physical activity.
On the first day there is a slight increase in temperature. It will go away on its own after a couple of days.
When can you go for a walk?
It is recommended to walk your pet only on the 4th day after revaccination. In this case, the likelihood of infection from other animals is minimal. If you are vaccinated for the first time, you will have to stay at home for the entire quarantine, that is, 28 days.
When can you bathe a puppy?
Weak immunity is vulnerable to colds, so any draft can end in tragedy. Avoid swimming for 4 days after the injection.
Feeding during quarantine
When feeding, it is recommended to stick to your usual diet. The introduction of new products is fraught with an allergic reaction. If the animal refuses to eat, there is no need to force feed it - it is better to wait until the appetite awakens.
Why get vaccinated and is it necessary?
For many dog breeders, the question of the need for vaccinations remains a mystery. After all, animals in the wild can do without them and survive just fine.
And this is a big misconception:
- Firstly, dogs are already domesticated animals and their immunity is weaker than that of wild animals.
- Secondly, in the wild, the life expectancy of animals is much lower and they often die from infectious diseases.
- Well, thirdly, our favorite little animals do not live in the forest, where the danger of infection is much lower, but in a city where there is a lot of all kinds of chemical and natural waste, harmful emissions and other stuff. This means that the risk of getting infected in the city is much higher.
This is why the need for vaccination, in my opinion, is beyond any doubt. If the animal gets sick, the treatment will be very difficult and may even lead to the death of the dog. Therefore, it is better to vaccinate and prevent infection than to fight it.
Moreover, it is also necessary to vaccinate those animals that do not leave the apartment, since they can become infected even from their owner’s outdoor shoes or clothes.
Well, if you are going to take your animal with you when traveling by train or plane, then this question disappears altogether. Moreover, in the latter case, all vaccinations must be reflected in the veterinary passport and certified with the stamp of the state veterinary clinic.
Briefly about the main thing
- Vaccinations are a mandatory annual procedure to prevent dangerous infectious diseases.
- It is necessary to vaccinate according to schedule for the drug to be effective.
- A deadly, zoonotic disease on the territory of the Russian Federation is rabies.
- It is better to use an associated vaccine to prevent a number of dangerous diseases
- Weakness and malaise after vaccination are a normal state of any living organism.
- Vaccination against rabies is mandatory and is carried out free of charge in state veterinary clinics.