Due to the physiological characteristics of the jaw, Chihuahua dogs are predisposed to various anomalies of the dental system. Failure to comply with the standards set by the cynological federations will lead to the unconditional disqualification of the dog from the breed show. In addition, in order to avoid inheritance of the defect by offspring, the dog is excluded from breeding work.
Changing teeth is an important stage in the life of a Chihuahua puppy. And the correctness of the bite depends on its course. The owner is obliged to examine the dog’s oral cavity daily to identify pathologies in the development of the dental system. Their detection requires an immediate visit to a veterinary dentist.
Teething in Chihuahuas may be accompanied by the following defects:
- Retention (delay in the physiological change of teeth);
- Dystopia (abnormal position of teeth in the dental arcade);
- Oligodontia (lack of teeth, insufficient number of teeth);
- Polyodontia (supernumerary teeth, i.e. their number is higher than normal).
The above pathologies can be congenital or acquired.
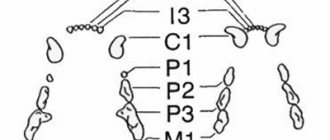
Dental formula of Chihuahua dogs
Forming the correct bite and maintaining the integrity of the teeth plays an important role in breeding work. According to canine standards, toy Chihuahua dogs must have a scissor bite. And the teeth forming dental arches (arcades) are distributed strictly according to the following scheme:
- 28 milk teeth in puppies (6P+2K+6P each on the upper and lower jaws);
- 42 constants in adult dogs (6P+2K+8P+4M in the top row and 6P+2K+8P+6M in the bottom row).
The letters in the formulas indicate the types of teeth:
P ─ incisors;
K ─ fangs;
P ─ premolars;
M ─ molars.
Normally, the upper and lower dental arcades of a puppy consist of an equal number of teeth (14 on each). Adult Chihuahuas have 20 teeth on the upper arch and 22 on the lower arch.
Number of teeth by breed
The number of teeth may vary between breeds. Large dogs such as Labrador, German Shepherd or Rottweiler should have 42 teeth in their mouth. Deviation from standards is considered a vice.
In medium and small breeds, the number of teeth can range from 36 to 40. Sometimes there are individuals with 42 teeth in the mouth among spaniels and dachshunds, which are among the most common representatives of medium and small dogs. It will not be possible to find a terrier with so many teeth due to the fact that as a result of the selection of this breed, the structure of the jaws of such a dog has significantly changed, as a result of which the intercanine space has narrowed.
Here is a table of the number of teeth by breed:
| Breed | Number of teeth |
| Yorkshire Terrier | 40 |
| Chihuahua | 38-40 |
| Toy Terrier | 40 |
| German Shepherd | 42 |
| Retriever and Labrador | 42 |
| Pug | 38-40 |
| French Bulldog | 40 |
| Welsh Corgi | 38-40 |
| Laika | 42 |
| Husky | 42 |
| Cocker Spaniel | 42 |
| Collie | 42 |
| Brussels griffin | 40 |
| Bloodhound | 42 |
| Irish black spaniel | 40-42 |
| Australian heeler | 42 |
| Collie | 42 |
| American Hairless Spaniel | 40 |
| Chinese Crested Dog | 40 |
| Shih Tzu | 38-40 |
| Bull Terrier | 40-42 |
| Doberman | 42 |
| English bulldog | 40-42 |
| Newfoundland | 42 |
| Miniature Pinscher | 38-40 |
| Cane Corso | 42 |
| Tibetan Terrier | 42 |
| Greater Swiss Mountain Dog | 42 |
| Dogue de Bordeaux | 42 |
| Toy poodle | 40 |
| Greyhound | 42 |
| Samoyed dog | 40-42 |
| Siberian Husky | 42 |
| Beagle | 40 |
| Pomeranian Spitz | 38-40 |
When do baby teeth appear?
Chihuahua puppies are born toothless. Milk teeth begin to erupt 2 weeks after birth. Sequence of cutting:
- First, a pair of central incisors emerge in the lower row, then in the upper.
- The lateral incisors are cut next.
- Behind them the fangs change (in any order).
- The premolars are cut last.
The growth of a Chihuahua's milk teeth lasts 2-3 months. Their development ends by 4 months of age.
Treatment
The main goal of treatment is to prevent tooth loss and strengthen bone tissue. Surgical removal is performed once the dead incisor is identified. Thus, further therapy is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process of the gums.
After sanitization, the specialist prescribes regular treatment of the gums. For this, chlorhexidine, Metrogyl Denta ointment, Cholisal or Lugol's solution are used. The course of treatment is about 7-10 days. In case of complications, the veterinarian prescribes antibiotics.
Scheme of changing temporary teeth to permanent ones
At the age of 4 months, the formation of the rudiments of molars begins under the necks of milk teeth. Under the influence of chewing loads, baby teeth become loose and begin to fall out. The change occurs according to the following scheme:
- The incisors are the first to be replaced.
- Then ─ premolars. Simultaneously with their replacement, the eruption of molars occurs.
- The last ones to fall out are the fangs.
Normally, the change of teeth in puppies ends at seven months. Baby teeth that have not fallen out by the age of 9 months are subject to forced removal.
Breed predisposition
Often, diseases and other problems with the jaw occur in small individuals. Chihuahuas, Spitz dogs, Yorkshire terriers, toy terriers and other toy breeds are more prone to such ailments. Therefore, the phenomenon is genetic in nature and can be passed on from generation to generation.
Problems begin at an early age: the puppy develops polydontia. The question may immediately arise: do dogs’ milk teeth fall out on their own? In some cases, everything goes away without medical intervention. However, if the situation has not changed by 9-12 months, then the pet should be taken to the veterinarian. The disease is solved surgically.
In most cases, looseness is a symptom of gum disease. The disease is also characterized by bad breath (halitosis), increased salivation, and complete refusal to eat. When palpated, animals experience pain and excitement.
Periodontitis in toy breeds causes them to experience fractures of the lower jaw. Missing teeth can cause the development of an oronasal fistula, an open opening between the nose and mouth. Oronasal fistula can only be treated with surgery.
O is increasingly observed in large breeds. These include Labradors, Dobermans, Boxers, Rottweilers, South Russian and German Shepherds. It is difficult to say specifically at what time teeth fall out in large dogs. With temporary polydontia, the breasts disappear on their own closer to 12 months. In case of long delays, the help of a veterinarian is required.
Possible pathologies and causes of teething disorders
Teething problems in Chihuahuas occur due to the genetic characteristics of the breed. A dog owner may encounter the following pathologies.
- Retention ─ partial or complete delay in eruption and slow growth of molars. Causes of retention: calcium deficiency, gum disease, underdevelopment of masticatory muscles, weakened immunity, heredity.
- Dystopia is an abnormal (chessboard) arrangement of incisors and canines. Arises as a consequence of retention.
- Oligopodontia is incomplete teeth, accompanied by the formation of voids in the dentition and displacement of adjacent teeth.
- Polydontia is a pathology in which the number of teeth exceeds the norm. It can be false and true.
Teeth grow in two rows: what to do
This defect is rare in veterinary practice. The main reason for its appearance is insufficient chewing load on the jaws. Pathology is observed when the baby teeth have not yet fallen out, but the molars have already begun to form. It can cause damage to the gums, misalignment of the jaw, and malocclusion. Makes it difficult to chew food. The solution to the problem is surgical removal of baby teeth. Performed in a veterinary clinic.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is carried out by a veterinarian-dentist. To determine the causes and prescribe treatment, it is necessary to undergo a series of studies. The patient is given an X-ray of the head to understand the extent of bone tissue destruction. An x-ray can significantly affect the course of treatment itself. Before therapy and other diagnostic procedures, sanitation is carried out - complete cleaning of the mouth from plaque and stone.
Additional methods for diagnosing gum disease are color tests. The Schiller-Pisarev test (reaction with iodine) is used to assess the degree of inflammation. Sometimes it is used to evaluate the course of therapy.
The second color test is needed to determine the degree of destruction and softening of enamel and dentin. After the test, the affected tissue areas are colored red-violet. This procedure is carried out after complete sanitation from stone or plaque.
The third color test allows you to assess the dog’s level of oral hygiene. It reveals soft and hard plaque. After the test, the damaged areas are painted blue.
Should you brush your Chihuahua's teeth and how often should you do it?
Dogs of this breed have very thin and narrow jaws. Because of this, dental problems arise. In the plaque that forms on them, pathogenic microbes intensively develop. Cleaning prevents infections from developing. Therefore, you need to brush your teeth at least twice a week.
It is recommended to accustom your dog to brushing during puppyhood. This is done like this:
- For 1-2 weeks, the puppy is fed by hand, while touching its face.
- At the next stage, his lips are parted and his teeth are touched. The procedure ends with rewarding the pet for obedience.
- When the puppy learns to bare his teeth, begin cleaning. It consists of wiping the gums with a damp cloth in the morning and evening.
Cleaning Methods
Special toys or treats
With the help of such devices you can clean your pet’s teeth quite well..
Before giving a puppy or adult Chihuahua such a toy or treat, you need to make sure that the item does not have sharp edges or corners that could injure the dog, and that the device itself is soft enough and will not harm the teeth.
Toothbrush for dogs
It is not difficult to choose a brush and toothpaste suitable for your Chihuahua: pet stores have a large selection of such devices.
In this case, you need to take into account not only the size of the brush, but also the stiffness of its bristles: for a Chihuahua it should be minimal.
When choosing toothpaste for your pet at a pet store, you need to give preference to one that does not have to be washed off . You should not brush your Chihuahua's teeth at home with anything other than toothpaste intended for dogs.
Ultrasound
This method is suitable for cleaning teeth if plaque has already turned into tartar and it is impossible to remove it with a brush and paste.
To carry out this procedure, you should contact a veterinary clinic.
CAREFULLY!
You should not try to remove tartar yourself, using unsuitable hard or, especially, sharp objects, as you can easily break your dog’s tooth or injure his gums.
How to brush your Chihuahua's teeth at home
Before you start cleaning, you need to let the puppy sniff the brush and let it lick the paste. It is better to brush a puppy’s teeth with a small, soft rubber brush; for an adult dog, with a toothbrush with nylon bristles. Procedure:
- Spread your pet's lips;
- Apply a brush with toothpaste to your teeth;
- Make circular or scraping (top to bottom) movements with it;
- Rinse off the paste with a stream of water (if required);
- After cleaning, massage your gums with a massager brush.
detailed instructions
If your pet’s teeth are being brushed for the first time, then you must first give him the opportunity to get used to the brush: give it to the Chihuahua, so that the dog can be convinced that this object is not scary and does not pose a danger to him.
Next, you need to let the dog lick some of the paste, which will also convince him that nothing bad is happening.
Chihuahua's teeth need to be brushed like this::
- Apply the amount of paste specified in the instructions to a soft brush.
- Part the dog's lips and begin cleaning its teeth.
- In this case, you should not press the brush too hard or move it horizontally. You need to brush your pet's teeth in a circular or sweeping motion, directing the brush from bottom to top in the direction of tooth growth.
- Further, if necessary according to the instructions, the toothpaste is washed off with warm, but not hot water.
- After cleaning your teeth, experts recommend using a gum massage brush.
It is best to accustom your pet to brushing its teeth from an early age, then the sight of a toothbrush will not cause panic in an older dog, which will significantly facilitate the brushing process and make it more enjoyable.
Possible problems
Dental problems can be identified by examining your Chihuahua's mouth daily. The most common of them are malocclusion and early tooth loss.
Malocclusion
It develops in Chihuahuas due to untimely replacement of the temporary incisors of the lower jaw. The defect interferes with chewing food, injures the gums, and disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Reasons for the development of malocclusion: viral infections, deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body. It can be corrected by installing braces by a veterinarian orthodontist.
Early tooth loss
Premature loss of Chihuahua's molars can occur as a result of the development of gingivitis or periodontitis, gum inflammation, jaw injury, tartar formation, lack of calcium in the body, and improper oral care. If your dog's teeth begin to fall out, you need to contact a veterinarian to determine the cause of the disease and prescribe treatment.
Pathologies requiring surgical intervention
- Strongly curved fangs. The pathology is eliminated by grinding. The ground surface is covered with artificial enamel.
- Curvature of the jaws (one side is longer than the other). Leveled by operation.
Possible pathologies
A mandatory examination by a veterinarian is required at the moment when an adult dog’s molars begin to fall out. If her age is far from elderly, then the cause of the disorder lies in pathology.
Oral diseases
Dental diseases affect soft mucous or hard bone tissue. The most common diseases include the following:
- caries
– putrefactive destruction of hard tissues, often complicated by periodontitis and pulpitis;
- periodontitis
– an inflammatory process involving the connective tissue between the hole and the root;
- pulpitis
– inflammation of internal tissues, including nerves and blood vessels;
- stomatitis
– damage to the oral mucosa;
- gingivitis
– an inflammatory process that covers exclusively the gums and does not affect external soft tissues;
- periodontitis
– a complication of gingivitis that affects all surrounding tissues.
All these diseases require mandatory treatment, since very often they are complicated by secondary infections. Also, when the process is running, the likelihood of losing not only part, but the entire dentition increases.
Bacterial and viral infections
Bacteria and viruses that enter the mouth directly or from neighboring organs are usually to blame for the occurrence of the pathologies discussed. Their waste products cause acute intoxication. The body uses an inflammatory response to destroy the pathogen.
Improper feeding
When feeding exclusively soft foods, the gums soften, causing premature loosening. There is also a rapid accumulation of plaque, which gradually hardens into stone. The quality of enamel deteriorates, causing the development of caries.
Eating tubular bones is no less dangerous. They injure soft tissues, opening the way for pathogens.
Injuries and tumors
The cause of the problem can be severe maxillofacial injuries associated with mechanical damage. In this case, the animal loses its snow-white smile immediately upon being hit or bruised.
It is also recommended to check the dog for the presence of tumors. Malignant tumors have a destructive effect on the mucous membranes.
Prevention of dental diseases
Regular preventative measures will protect your Chihuahua's teeth from diseases and other problems. These include:
- Daily examination of the dog's oral cavity;
- Weekly brushing of teeth and massage of gums;
- Enrichment of food with vitamins and minerals;
- Controlling the process of changing teeth;
- Passing a scheduled examination every six months at a veterinary clinic.
The formation of the dental system and bite in a Chihuahua is a complex process. This is due to the miniature size of the dog. The owner needs to monitor how the teeth change. Follow the rules for caring for them. This is the only way to preserve the integrity and health of your pet’s dental system.
Dog dental care
Knowing how many teeth on top and bottom the dog has in its mouth, the owner will be able to receive more information about his pet and properly care for him. Teeth, like a dog's coat, need regular cleaning.
In breeds with a regular bite, teeth cleaning occurs naturally while eating solid food.
Dog breeds with malocclusion require special care for their mouths after eating. In addition to special means of protection and care, you need to monitor your pet’s diet and what he likes to play with.
Balanced food is a source of nutrients for the animal. It does not allow pathogenic microflora to develop in the mouth by maintaining the animal’s immune system in good condition. You should also prevent your dog from chewing on stones or very hard objects that he uses to play on.
Consequences
Complete refusal of therapy can cause a number of serious complications. Bacteria that settle on stone or plaque begin to produce toxic substances. Together with saliva, waste products of microorganisms enter the gastrointestinal tract. This causes infectious diseases of the digestive system.
The resulting microflora gives rise to the development of dangerous infections in the mouth. The inflammatory process can spread to deeper tissues, right down to the skull. The dog has a risk of developing sepsis or osteomyelitis (purulent-necrotic inflammation of the bones).
With periodontitis of the 3rd (last) stage, complete removal of all the incisors of the animal is required. An advanced disease is characterized by the release of pus. Dwarf breeds older than 6-7 years are prone to periodontitis.
How to correct an open bite in a child?
Despite the fact that the consequences are quite serious, open bite is classified as a disorder of moderate complexity. Usually, surgery is not required to correct it - braces or aligners are sufficient.
Fixed braces are an effective way to treat orthodontic problems. Of all the systems existing today, self-ligating (ligature-free) braces have proven to be the best.
In older bracket systems, the arch was secured using rubber ligatures. The ligatures retained their elasticity for two to three weeks after installation, and then wore out and became softer. The force of the arc decreased. Ligature-free systems do not have this drawback: the arch is attached to the grooves of the braces and works equally effectively all the time, from installation to the next activation. Therefore, with such braces, the treatment period is reduced by approximately 30% (compared to ligature ones). In addition, the ligature-free system is easier to clean, and there are much fewer food particles stuck in it.
But braces also have disadvantages: they can cause pain and irritation. Some children and teenagers do not want to wear them, since even aesthetic ceramic systems are quite noticeable on the teeth.
An alternative to braces is transparent polymer aligners, which are created individually for each patient. The aligners are worn on the teeth every day, including at night, and are removed only when eating and brushing your teeth.
Children's aligners are thin, transparent and invisible
Each pair of aligners has its own program for moving teeth. Each tooth moves exactly where it is needed - thanks to computer modeling, the aligners can act in any direction. Therefore, they are not inferior in effectiveness to braces. And in terms of comfort they are much superior, both due to aesthetics (they are invisible on the teeth) and ease of wearing.
Braces have sharp metal parts that can scratch your mouth and cause irritation (although this doesn't happen to everyone). The aligners are smooth, accurately follow the shape of the teeth and adhere to them very tightly, so they do not cause any concern.
Splinting
It is possible to save weak and excessively mobile teeth by splinting. The procedure strengthens them, preventing complete loss. Splinting is performed if pathological looseness, exposed roots or deep gum pockets are diagnosed.
For splinting, special hardening materials are used, such as dental wire or fiberglass. Consequently, the material eliminates the weakness of the incisors and distributes the load throughout the pet’s entire jaw. The more incisors are preserved, the more effective the splinting procedure is.