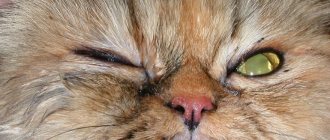
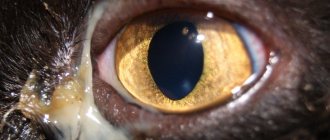
In addition to squinting, the animal may exhibit additional symptoms that indicate trouble:
- A dog or cat scratches its eyes with its paws or tries to rub its muzzle against some object.
- The behavior of animals changes - they refuse affection and can show aggression.
- The animal loses its appetite and sleeps poorly.
- The third eyelid falls out.
- The surface of the eye becomes cloudy.
- Tears flow profusely from the eye, and pus may be discharged.
If you notice such symptoms, then try to take your pet to the vet as quickly as possible, because he is in pain and needs urgent help!
Reasons why it does not open completely
As a rule, the animal’s behavior is not limited to squinting its eyes. In addition, the Spitz may refuse affection and show unreasonable aggression. You can observe how in some cases the dog rubs against objects in the house, trying to eliminate unpleasant sensations. Sometimes photophobia appears.
In addition to squinting, excessive lacrimation and redness may appear. The affected organ may swell slightly or become swollen.
The animal may refuse solid food. This is associated with pain.
The most common causes of squinting may be:
- Conjunctivitis is viral or bacterial.
- Trauma to the organ of vision. A Spitz can get it while walking as a result of mechanical damage from a blow from a branch or during a fight with other animals. A less common option is to get a bruise at home.
- You may be allergic to the use of chemicals at home (deodorant, air freshener, detergent, etc.). When the allergen is eliminated, symptoms usually disappear.
- Inflammation of the tissues around the eyes.
- Entry of foreign objects . A speck or eyelash in the eye can cause inflammation.
- Thermal and chemical burns of the organs of vision. A pet can get a thermal burn as a result of exposure to high temperatures.
- syndrome .
- Increased sensitivity to wind or cold. If a Spitz's eyes water after a walk, especially in cold weather, it means that he reacts this way to strong winds and temperature changes. If this happens, you must refuse or limit your walks.
- Acute respiratory infection .
Factors contributing to eye squinting
All of the above are not all possible causes of squinting:
- Dogs often become “Chinese” in regions with a very dry and hot climate. Squinting in such cases is the body’s natural defense against drying out of the cornea and dust, which can be abundant in dry air.
- This can often be observed in spring and summer, when there is a lot of pollen and fluff in the air. Not all dogs cause an allergic reaction, but getting them into the eyes irritates the cornea and causes constant squinting.
- An extremely dangerous cause of “shrinking” eyes can be... heart disease. More precisely, pathologies accompanied by the development of cardiac edema.
Blushed
The cause of redness in one or both eyes can be a fairly common disease - conjunctivitis.
In the catarrhal form, the membrane of the eye is red and swollen. There is lacrimation. The discharge is serious.
This form begins acutely, and after transition to the chronic phase it is very difficult to treat.
In the purulent form of conjunctivitis, the discharge is first liquid, and then yellowish and thick. The eye becomes red and swollen.
With the follicular form, follicles can be seen on the surface of the eyelid. They look like raspberries. Often this form has a chronic course with remissions and periodic exacerbations.
When the first signs of conjunctivitis appear - watery eyes, you should regularly wipe your eyes with a cotton swab dipped in boiled water. Any physical activity is excluded and communication with other animals is limited, since the disease is contagious.
If symptoms do not go away and only get worse, you should immediately consult a doctor. Anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotic-based ointments are most often prescribed.
The cause of redness may also be overheating of the animal. It can occur if the Spitz has been in a room with too high a temperature for a long time. If your dog overheats, he or she may experience shortness of breath, fever, and vomiting. The animal must be taken out into fresh air.
The eyes may become red due to a head injury. This is accompanied by lacrimation and closing. When the owner tries to pet the animal, aggression occurs. A Spitz can get injured in a fight with a cat. Her scratches are dangerous because there are a large number of microbes under the claws.
If the animal has severe lacrimation, redness, and the whites are filled with blood, these are signs of a burn to the pet’s eye. The dog becomes restless and tries to scratch its face. The eyelids do not open in this condition.
If you do not notice the Spitz's contact with chemicals, then the burn can be confused with conjunctivitis. The diagnosis can only be made by a veterinarian by examining the cornea.
A change in the color of the sclera can occur as a result of drying out of the mucous membrane or the ingress of dust.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
A complete ophthalmological examination includes:
- Schirmer test;
- fluorescein staining of the cornea;
- tonometry;
- examination of the eyelids and surface of the eyeball with magnification (for example, slit-lamp biomicroscopy);
- detailed examination of the front and back of the eye.
A thorough examination is only possible after local anesthesia has been applied. Some types of diseases are very painful and it will not be possible to examine the eye without this. An ultrasound examination is prescribed if the eye is too opaque or if there is suspicion of disease in the back of the eyeball. Cytology (cell analysis) is carried out for damage to the cornea, incl. with an ulcer. A blood test is done if other diseases are suspected. X-rays of the skull are prescribed to identify fractures. Computed tomography - to assess the condition of tissues around the organs of vision.
Did you know? The color of blue eyes in a husky (or any other dog or person)
—
just an optical illusion. The blue tint is caused by the way light enters and leaves the eye, creating the appearance of blue.
What to do?
If squinting is detected, the owner should immediately contact a veterinarian.
In order to make a correct diagnosis, special equipment is required. This allows you to identify the disease with high probability.
At home, if there is sudden squinting, it is necessary to examine the dog's eye. If foreign bodies get in or there is damage, you can try to rinse it with sterile saline solution.
Important! Do not rub your eye with a tissue. Otherwise, a foreign object can be rubbed into the mucous membrane.
If your Pomeranian becomes aggressive when trying to treat the eye, you should immediately contact a veterinarian. Before being examined by a doctor, it is advisable to place the animal in a dark room and ensure peace.
In case of a chemical burn, it is necessary to rinse the eye with plenty of water from the pear. This neutralizes the effect of the chemical. If the Spitz owner notices how the burn was caused, then it is necessary to inform the doctor when contacting the veterinary clinic.
Important! You cannot use ointments and drops yourself.
The main causes of the “mysterious squint”
Let us immediately list the main pathological causes of squinting, often encountered in veterinary practice:
- Inflammation of the conjunctival cavity, also known as conjunctivitis. Dogs of all breeds and ages suffer from this pathology very often. Squinting of the eyes is one of the specific signs of the disease. In this case, it is caused by the development of photophobia: it is painful for the pet to look at any light sources.
- Traumatic injuries to both the eyes themselves and other organs of the visual system. This happens especially often with overly “fighting” and cocky dogs, as well as with service and hunting dogs, which are often in forests, fields and other “traumatic” places.
- Getting foreign bodies into the eyes , be it dust, pollen, sand, dirt, etc.
- Inflammation of the cornea , eye vessels, eyelid pathologies (including entropion) and similar pathologies.
- Allergic reactions.
- A rare but serious pathology is lens luxation.
- For severe dermatitis and eczema.
- Due to burns to the skin of the eyelids or the eyes themselves. It must be remembered that burns can be not only thermal, but also chemical.
In puppies
In Spitz puppies, the cause of squinting of the eyes is most often congenital anomalies. In this case, you should immediately contact a veterinarian, who will decide which treatment to choose. If not treated in a timely manner, puppies may be left without an organ of vision.
If the puppy has lacrimation from birth, and daily toileting and medications prescribed by a specialist do not help, then the baby may have an obstruction of the tear duct.
In this case, a probing procedure is prescribed - cleaning the canal. This manipulation is done under general anesthesia and is painless for the puppy.
Basic drugs used in first aid
To do this, you can use a not too wide range of ophthalmic drugs:
- 1% tetracycline ointment. It should be noted that 3% of the drug should not be used; it is intended for external use on other parts of the body.
- 1% hydrogen peroxide. Can be used both for washing and for removing dried exudate from the skin around the eyes.
- Saline. Used to wash the eyes, it is better to preheat it to a temperature of approximately 37°C.
- For pain relief, you can use a lidocaine solution. If it is not there, a 3% solution of novocaine will do. These drugs are used in ophthalmology to reduce the pain response during severe inflammation.
- After preliminary consultation with a veterinarian, you can use healing ointments (eye ointments, of course) based on anti-inflammatory corticosteroids.
Associated symptoms
Depending on the cause, squinting may be associated with other worrying symptoms. These include:
- apathy or aggression;
- poor appetite and sleep disturbances;
- redness and inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- excessive tearing or the appearance of purulent discharge;
- clouding of the iris, strabismus and prolapse of the third eyelid;
- increase or decrease in temperature;
- enlargement of the pupil and the appearance of a greenish cataract;
- gluing of eyelashes and formation of erosions on the cornea;
- repeated vomiting and bloody diarrhea with the smell of rot;
- yellowing or blanching of the mucous membranes.
Because there is a wide range of possible causes, do not rush to make a diagnosis before contacting your veterinarian. Even an ordinary blade of grass can lead to quite serious consequences if an infection gets into the scratched wound. Limit your actions to first aid and be sure to take your pet for examination.