Pets need to be well looked after. Otherwise they may get sick. In the animal world it is not like in humans. We feel that we feel bad and can help ourselves or ask for help. But with animals everything is not so simple. They will not talk about illnesses or when something hurts them, they will not ask for help. Therefore, we must do everything for them. We are responsible for those we have tamed. Monitor behavior and signs that indicate something is wrong with the rodent. Today we will talk about serious illnesses. If one eye is larger than the other, or an eye has protruded into the hamster, what should you do?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to say for sure what is the reason that the hamster’s eye fell out. Therefore, we will consider only the main reasons. These can be various diseases and irritations. The main ones are an advanced form of conjunctivitis and an abscess in the retro orbital cavity of the eye. In simple terms - various inflammations of the mucous membrane of the eye with all that it entails.
Symptoms of eye diseases
It’s easy to understand that your pet child is sick. The animal's behavior is not the same as always:
- the hamster refuses food and sometimes water;
- little mobile and lethargic;
- the fur is tousled and has a dull, unkempt appearance;
- the rodent quickly loses weight;
- appears to be asleep or sleeps most of the time, even at night.
One of the main symptoms of eye diseases in hamsters is the appearance of any discharge from the eyes of the rodent. Cloudy discharge indicates an infection, and clear discharge indicates an allergic reaction.
Also, the animal’s eyelids may be wet, stuck together, partially open or not open at all.
Inspect your animal's eyes daily, this way you will protect your pet from serious eye diseases.
Hamsters' eyes should be clean and shiny. If you notice dullness, discharge from the eyes or incomplete opening, start sounding the alarm, such symptoms are warning signs.
Having discovered at least one such symptom, place the animal in a dark room, because diseased eyes are very sensitive to bright light.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of diseases that can lead to eye loss, preventive measures should be taken in a timely manner. These include:
- Regular cleaning of the bedding in the hamster's cage;
- Avoid free walks around the apartment without a special ball so that the animal does not hurt itself on sharp corners or falls from a height.
- Avoid spraying chemicals or aerosols near the hamster's cage;
- Regular cleaning of dust near the animal’s cage;
- Balanced feeding and timely hygiene procedures;
- Regular examination of the animal and timely contact a veterinarian at the first signs of illness.
Disease Prevention
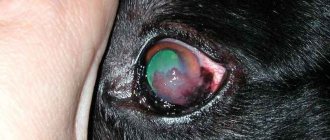
If a hamster's eye bulges out, this may indicate a serious illness, but this does not happen immediately, but gradually. This terrible illness was preceded by the following processes: inflammation, which is expressed by redness or the appearance of purulent plaque, swelling of the eyelids, one eye becomes larger in size than the other, or the eye cannot close at all.
The animals cannot understand the harm of the current inflammatory process and sway on the bedding poured at the bottom of the cage. These actions of the rodent will cause repeated injury to the organ of vision and the loss of the eye will become inevitable.
To avoid any infectious diseases of your pet's eyes, provide him with high-quality food that will contain all the necessary vitamins and nutrients. Also pay attention to keeping your pet clean. Most often, inflammatory processes begin from a lack of any vitamins. Another reason why a hamster's eye bulges out is injury and infection.
Take care of your hamsters, feed them in a timely and balanced manner, carefully monitor the health of your beloved pets to avoid diseases of the eyes and other organs of the rodent. Do not try to pamper your animal with various exotic fruits, which can lead to allergic conjunctivitis.
Check out the articles in which we talked about what is best to feed the dwarf and what should definitely be excluded from the rodent’s diet.
Preventive measures
Agree, it is better to prevent any disease in domestic hamsters than to treat it later. And for this you need to create the necessary conditions for your pet.
Considering the causes of such diseases, caring owners should:
- Use cage mats specifically designed for hamsters. Such material should not contain piercing or cutting objects, as well as a lot of dust.
- You should not keep a large number of rodents in one cage. They can injure each other, which will result in various diseases, including eye diseases.
- Genetically predisposed individuals must be immediately excluded from the general “herd.” Such hamsters can be a carrier of an infection from birth, transmitted to them from their mother or father.
- During the keeping process, the cage with rodents must be placed in a bright place, but protected from the sun. Direct exposure to sunlight and ultraviolet radiation negatively affects the health of pets.
- Regular examination of animals will help you at an early stage to identify not only carriers of diseases, but also to prevent the development of an already established disease in hamsters.
Eye diseases in hamsters
Pets lead an active lifestyle in the truest sense of the word, so small pieces of bark from twigs or sawdust, which act as bedding, often get into the animal’s eyes. If several individuals live in a cage, they quite often fight among themselves, establishing primacy.
Getting any object into a rodent's eye causes inflammation, and a fight can lead to injury. The eyes of hamsters have a convex shape, so they quite often suffer from conjunctivitis, cataracts, corneal ulcers, inflammation of the cheek pouches of a rodent or eye disease as a result of diabetes in the animal, and the most terrible and dangerous disease is one of the animal’s eyes is much larger than the other or eye loss .
The hamster's eye has come out, how can we help the animal in this case?
It is difficult to name the real cause of eye loss in hamsters. Several main factors for this disease can be identified. This disease is most often preceded by all kinds of irritations and any infectious diseases. The main causes may be an advanced or untreated form of conjunctivitis, or any inflammatory process of the mucous membrane leading to an abscess.
To the question “what to do?” It’s difficult to give a definitive answer. But we can say for sure: seeing a doctor is inevitable. Most likely, the missing eye cannot be saved, but in order not to lose the second one, urgently take your pet to the veterinary clinic. Delay can cost the rodent’s life.
You won’t be able to do anything yourself; among other things, you need to establish a diagnosis of such a terrible disease, and only a qualified specialist can do this.
Is there no veterinary clinic in the locality where you live? Try to use the Internet to find the coordinates of an agricultural higher educational institution; every such institution has a veterinary faculty, which is what you need. In these laboratories, specialists often do even more than veterinarians in their clinics. Find a way to contact and consult with them. You and your pet will be advised on the necessary treatment.
Possible reasons
If one of your hamster’s eyes has become larger than the other and has protruded from its socket, there may be several reasons for this:
- swelling due to injury;
- eye abscess;
- turning the eyelid inward.
All of them are not particularly pleasant and require medical intervention. In extreme stages, if treatment is neglected, you can leave your pet without vision. And sometimes it ends in death. If you notice that your eyes are different sizes, urgently make an appointment with a ratologist, he will help you identify the correct cause and advise you on further actions.
Swelling due to injury
Although hamsters are often housed in the same cage together, this does not make them pack animals. They are loners. Therefore, they really don’t like it when their personal space is invaded. This leads to fights, during which animals can be injured.
At the initial stage, it is not dangerous, but it can lead to the development of an inflammatory process in the orbit, and this is fraught with serious consequences, including removal of the eye. Therefore, if this happens, immediately get ready and take your pet to a ratologist. He specializes in rodents and will provide all possible assistance in getting rid of swelling of the eyelids and returning the eye to its place.
Abscess of the infraorbital space
This is the same process that an advanced head injury leads to. It develops literally in 2-3 days and leads to loss of vision, and then the eye. At its core, an abscess is a purulent capsule that arises as a result of mechanical action directly in the postorbital space. And not necessarily because of eye injuries, but because of any head injuries.
Abscesses are caused not only by injuries sustained during fights between animals. It can occur due to scratches from hard bedding, or develop due to pricks from wires and toys in the cage. At the site where the skin is injured, support for microorganisms and bacteria appears. They quickly take over the space and move on, causing suppuration and swelling in the eyes. If you start an abscess, then very soon you will see that the hamster’s eye has fallen out.
In addition to the tumor, symptoms include:
pus. It appears due to the abundance of leukocytes at the site of injury;- wet fur around the eye. It occurs due to the fact that the hamster tries to lick the injured area and get rid of crusts of pus on it;
- discharge.
If you see a mature abscess in time, then rejoice. Your hamster may be able to cope with it without surgery. But you shouldn’t postpone your visit to the clinic.
The veterinarian will prescribe antibiotics, blockades and other types of treatment to help your pet cope with the disease. If you take medications in a timely manner, there is a chance that the tumor will resolve and the matter will cost with “little blood.” If you notice an abscess too late, you still need to go to a specialist. Even if one of the hamster's eyes falls out, there is a risk of the second one falling out. You won't be able to save him on your own. Under no circumstances try to open an abscess yourself, you will only make things worse for your pet.
Inward turning of the eyelid or entropion
The eyelid may roll inward and cause the eyelashes to rub against the mucous membrane.
This causes inflammation and the eye begins to protrude from its socket. In addition to the visual enlargement of the eyeball, the eyelid may protrude slightly forward without covering the mucous membrane. This is a rare occurrence and occurs in a limited number of hamsters. It is better not to attempt to cure entropion on your own, but to immediately take it to a veterinarian for examination. To prevent eye protrusion and other eye diseases, provide your pets with proper care and attention. Change the bedding every day, keep individuals separately or avoid fighting between them. If, despite following all measures, it was not possible to avoid injury, do not self-treat, take the animal to a veterinarian. This will allow you to correctly diagnose the disease and take timely measures.
Treatment of eye diseases
If you notice that your pet is in trouble, the first thing you need to do is:
- protect the “little animal” from contact with other relatives, if any;
- all objects in the cage with which the hamster and the cage itself have been in contact should be disinfected with a strong solution of potassium permanganate;
- Treat the area around the animal’s eyes with sterile saline, and drip the eyes themselves with Albucid drops. You need to drip at least 4 times a day, 1-2 drops. Drops can be purchased at any pharmacy;
- switch the rodent to its natural diet, feed the rodent what its relatives eat in the wild: grains and a little (just a little) chicken, because this is a natural protein.
After such procedures, you will see results within 1-2 days. If there is none, the eye does not open or is still festering, do not engage in further self-medication.
Remember! It is almost impossible to cure eye diseases in hamsters on your own. Contact a knowledgeable specialist, and he will try to help the animal.
In the most extreme cases, if you still cannot turn to specialists for qualified help in a timely manner, try, first of all, to clear your eyes of unusual discharge and drip drops containing antibiotics into them, for example Tsipromed, Tsiprpovet or others. You will also need an antibiotic, which is often used in veterinary medicine - Baytril 2.5%. The spectrum of action of the drug is wide, it has an antibacterial effect. The course of treatment with the drug is at least 10 days.
If, nevertheless, the hamster’s eye pops out, then most likely it will not be possible to save him. The case when one eye is larger than the other is a period when the inflammatory process is just beginning and effective treatment will help save the animal not only the organ of vision, but also the life.
Using the simple techniques given above, it is possible to preserve the health and life of your beloved hamster.
Did you like the article? Share with friends: [supsystic-social-sharing id=”1"]
- Related Posts
- Hamster has a cold
- The hamster lies and does not move
- Cheek pouches in a hamster and their inflammation
« Previous entry
If it doesn't open
Only the attending physician - a veterinarian - can help establish the correct diagnosis. Therefore, if the hamster’s eyes do not open, you urgently need to take your pet and take it for examination.
If for some reason you are currently unable to visit a veterinarian, you will need to do the following:
- A hamster whose eyes are sour, inflamed and completely closed should be quarantined, that is, separated from his fellow cagemates.
- The animal’s home, as well as all accessories that are in it, must be disinfected (a solution of potassium permanganate or soda solution can be used as an antiseptic).
- At home, you can drip a rodent's eye with special Albucid drops, which are sold in any pharmacy. You need to drip every day so that your hamster's inflamed and swollen eyelids fully open.
Tumors and neoplasms
Tumors (malignant, benign), pathological growths on the body, legs. ears is a fairly commonly diagnosed pathology in rodents, which can develop for a variety of reasons. Bumps can appear due to injuries, severe bruises, or falls from a height. To begin treatment, you need to establish a diagnosis, so take your pet to a veterinarian.
For benign and malignant tumors, surgical treatment will be prescribed. If the cancer is localized in a hard-to-reach area (oral cavity), the tumor has metastasized, veterinarians recommend euthanizing the patient.
Albinos
Why do hamsters have red eyes? It happens that the most ordinary hamster parents give birth to a baby whose fur does not even have a hint of pigmentation. No type of color suits him. It is for such special animals that the name albino was created. Every species of rodent sooner or later encounters such unusual representatives. Albinos are also found among most creatures on Earth.
Such fluffies are considered very valuable, since genes are responsible for the presence of pigment, but its absence is a random and natural result. These little ones have red or pinkish eyes. In nature, such rodents have a hard time, since their white fur gives them away in a dangerous situation, so they do not live long. Well, in a cozy human house, hamsters feel calm and confident. The lifespan of pets is 3-4 years.
The health of albinos is quite fragile, which is worth remembering. The color of the coat and eyes are not the only differences from relatives; habits, character and size may also vary slightly.
All about infantile hemangiomas
What it is?
Infantile hemangiomas are the most common vascular tumors that are most often diagnosed in young children. They usually occur in the first weeks after birth, but in some cases the phenomenon can develop during the first months. According to statistics, infantile hemangiomas occur more often in girls than boys and more often in people with light skin than dark skin. Also, according to observations, vascular tumors often occur in premature babies, and the longer the period of prematurity, the higher the risks of its development.
Causes
The common cause is hypoxia, i.e. lack of oxygen in the tissues, which can be not only due to pathologies of the placenta, there can also be a hereditary predisposition, but we do not oppose it to hypoxia, it is an additional factor.
Symptoms
In most cases, the pathology is localized in the face and head, but it can also occur on other parts of the body and even on the mucous membranes and internal organs of the baby. The formations can be located on the surface or inside the skin. Most often, a hemangioma is visually similar to an iceberg - a small part of it is visible on the surface of the skin, and the main part is located in its deeper layers.
The main distinguishing feature of infantile hemangiomas is the way they change over time. So, at birth, the initial hemangioma may look like a bright spot with a vascular point or capillaries in the middle. Then, within 3-4 months, it actively grows and acquires a bright red color. When shouting, physical activity, or taking a warm bath, the tumor may swell and become more pronounced. After 4 months, growth continues, but becomes slow, and closer to a year it stops altogether. At the final stage, involution occurs, that is, the pathology begins to disappear on its own, 90% of tumors regress completely by 4-5 years.
At the stage of involution, the tumor gradually decreases, turns pale and after some time acquires the color of the skin (however, in some cases, a trace may still remain in the form of a light spot, scar or spider veins).
Medical tactics
By their nature, hemagiomas are absolutely benign and are in no way related to the presence of oncology, which must be urgently removed. But there is one “But”! Infant hemangiomas require mandatory medical supervision. The tactics for managing a patient with a vascular tumor will depend on the size, location, number of tumors and the presence of complications.
As a rule, for uncomplicated formations, a wait-and-see approach or “active non-intervention” is used. Its essence is regular monitoring by a doctor with recording of any changes (it is most convenient to take photographs of measurements with a ruler).
The frequency of examinations depends on the age of the child. The following rule is used here: the child's age in months must be equal to the examination interval in weeks. That is, a 3-month-old baby should be shown to the doctor every 3 weeks, a 6-month-old baby every 6 weeks, etc.
Very often parents begin to worry: “How can this be! The tumor is growing, but the doctor is doing nothing.” But specifically for hemangiomas, such tactics are completely justified, because the formation is more likely to regress on its own with minimal cosmetic complications. But surgical intervention, on the contrary, can have significant consequences.
Is treatment necessary?
Treatment of hemangioma (including surgery) is justified in the following cases:
1. The neoplasm is localized on the face, and there is a high risk of severe cosmetic defects.
2. Hemangioma is located in the area of the eyelids, nose, lips and throat, thereby interfering with the normal functioning of these organs.
3. The tumor has reached a large size and is subject to constant friction (for example, with a diaper).
There are several specific syndromes in which hemangiomas are combined with other developmental anomalies. In this case, the pathology requires not only elimination of the tumor, but also the use of other treatment approaches.
In some cases, to determine treatment tactics, the doctor prescribes additional examinations:
- Ultrasound (to assess the structure and depth of the tumor);
Dopplerography (to study blood flow);
blood tests (to assess clotting);
- MRI, etc.
Another cause for concern for parents is the bleeding of hemangioma. Since this formation is vascular, bleeding is possible, but it is unlikely that it will occur spontaneously. Bleeding can occur due to injury, cut, or tumor injury. If such a situation occurs, the bleeding must be stopped using a pressure bandage and, if its flow does not stop for a long time, seek medical help.
According to various data, only 10-30% of childhood vascular tumors require treatment.
Let's summarize which hemangiomas require treatment:
prone to ulceration and bleeding;
large in size and fast growing;
localized on the face and other open areas of the body, thereby representing a pronounced cosmetic defect;
located in the area of the eyes, nose, lips, genitals and interfering with the normal functioning of these organs;
posing a threat to the child’s life (very large or located on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract);
accompanied by other anomalies;
located in places subject to frequent friction (for example, in the groin area);
In modern medicine, several treatment options for infant hemangiomas are used: medications (drugs for oral administration), external (ointments, gels) and surgical. Let's look at each method in more detail.
Systemic therapy
In evidence-based medicine, two drugs are most often used to treat hemangiomas:
A drug from the group of beta-blockers. The main indication for its use is the treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system. However, it is also suitable as systemic therapy for complicated hemangiomas, as well as for the treatment of hemangiomas localized on the face and disrupting the functioning of organs.
Pros: speed of achieving the desired effect (a positive result is visible literally the next day).
Cons: the possibility of side effects from the respiratory and cardiac systems of the body; presence of contraindications for use.
The drug is a systemic glucocorticoid. It is used mainly for hemangiomas that threaten the child's life.
Pros: has an anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effect, due to which tumor growth quickly stops.
Cons: Due to the need for long-term use, it may cause side effects.
Note that any systemic therapy begins within the hospital, under the strict supervision of specialists. The duration of treatment is up to 6 months.
Local therapy
Two groups of agents can be used in local therapy:
1. External beta-blockers (Timolol, Propranolol).
The use of these drugs is advisable for small hemangiomas. The drug has good antitumor effectiveness combined with low absorption (practically does not penetrate into the blood) and an almost complete absence of side effects.
2. External glucocorticoids and the antitumor drug Imiquimod.
The drugs show positive results on limited lesions, but are not the drugs of choice due to the high risk of complications.
Surgery
The classical surgical method of excision for hemangioma is used extremely rarely. At the moment, the most preferred methods are laser surgery and cryotherapy. Lasers have proven themselves to be effective in the treatment of ulcerated, shallow tumors, as well as for eliminating residual effects after a course of systemic therapy.
Cryotherapy is also used on small, shallow tumors, but this method can be accompanied by pain, burns and scarring.
In conclusion, I would like to remind you once again that in most cases, infant hemangiomas do not require treatment. The most reasonable tactic is “active non-intervention” with regular monitoring by the attending physician.
Life expectancy of albinos
The white hamster with red eyes is found in every breed of rodent. Hence the different life expectancies of albinos.
- Djungarian hamsters live for about two to three years. Some individuals live for four years.
- The lifespan of a Syrian is three years. There are rodents that live up to six years.
- Campbell's species rarely lives for more than two years.
- The lifespan of a Roborovsky hamster is two and a half years.
- The shaggy dwarf rodent rarely lives more than two years.
The lifespan of a snow-white animal depends not only on the breed, but also on the conditions of detention, nutrition and care. If you feed your pet high-quality food, show it to the veterinarian on time, and keep the cage clean, then its life expectancy increases.