As soon as a dog settles in the house, it immediately becomes interesting how old it is by human standards. This helps you better understand your pet and find the key to his soul. So, how can you find out how old a dog is in comparison to a human’s life? More on that below.
How to calculate a dog's age
There are many methods that allow you to find out the age of a four-legged pet in relation to a human one. But they are all quite arbitrary, since the life expectancy of a pet largely depends on the breed, nutrition, physical activity, the presence of chronic or congenital diseases, and the attitude of the owner.
Up to 2 years, veterinarians use the following coefficients to calculate the ratio of dog and human age:
- small breeds – 1;12;
- medium breeds – 1:10;
- large pets – 1:9.
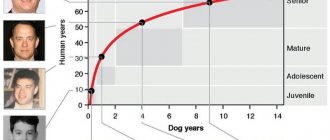
A one-year-old dog, especially small breeds, is an adult and can control its actions; for comparison, according to human criteria, this age corresponds to 10–13 years.
Table of the age ratio of people and dogs without taking into account breed
| Pet age (years) | Person's age (years) |
| 2 months | 1,2 |
| 6 months | 5 |
| 1 year | 10–13 |
| 3 | 28–32 |
| 5 | 38–42 |
| 7 | 47–50 |
| 8 | 54–57 |
| 10 | 63–66 |
| 12 | 73–77 |
| 15 | 85–88 |
| 16 | 87–90 |
| 20 | 94–97 |
New research into speech perception
Scientists recently conducted a new study. 12 domestic dogs of different breeds took part in it. They included border collies, golden retrievers and a German shepherd. Experts studied the brain activity of animals using a tomograph. It turned out that dogs also perceive the intonation of speech first, and then the meaning of words. Their brains process information in the same order as the human nervous system.
The dogs listened first to familiar words of praise, and then to unknown phrases spoken in both an approving and neutral tone. The tomograph data showed that the animals' brains first process the intonations of the voice, and only then react to the meaning of the words.
Stages of development - features
A pet goes through the same stages in its development as humans - toddlerhood, late childhood, early and late puberty, growing up, maturity, old age. But, unlike people, the formation of basic character traits and behavior is completed at 2 years.
How to determine the age of a four-legged pet:
- Milk teeth - begin to erupt in puppies older than 1 month, fall out at 4 months, the change of dentition ends at approximately 8 months.
- Molars – up to 2 years of age, dogs have sharp, intact teeth. The lower jaw wears down at the age of 4–6 years; after 7 years, teeth begin to fall out.
- Coat – young pets have a soft coat that is evenly colored. After 6 years, the coat becomes coarser and gray hairs can be seen.
- Eyes – in puppies, the eyes have a bright, uniform color, gradually the organs of vision become less transparent, and regular discharge is observed.
- Activity - up to six months, puppies are in motion almost all the time; with age, active games and long walks attract dogs less and less.
According to veterinary statistics, the average age of domestic dogs is 12–13 years.
Periods of a dog's life
The entire life of dogs can be divided into several periods:
- Lactic;
- Puppy;
- Teenage;
- Youthful;
- Mature;
- Elderly.
The dog experiences growth during the milking, puppy, and teenage years. So the smallest dogs, for the most part, fully grow by 10 months. Well, the largest breeds stop growing by 2 years.
Adolescence in tiny breeds begins at 10 months and ends on average at 8 years. However, in larger four-legged animals, adolescence ends much earlier; already at 3 years old, some dogs can be called mature, while medium-sized dog breeds go through the stage of adolescence at about 4 - 5 years old.
A small breed dog becomes full-fledged and mature after 8 years of age, and this period continues until the 12th year of life. The largest breeds reach maturity at 3 years old, and remain so for up to 6 years. The duration of maturity in average representatives of tetrapods ranges from 7 to 10 years.
Naturally, old age also comes to dogs; there is no escape from it. The youngest dog breeds may experience some age-related inconveniences only after 12 years. By the way, pocket dogs, which are constantly in the arms of girls, can live even more than 20 years, which cannot be said about other pets.
Medium-sized dogs begin to age rapidly after 8 to 10 years of age and can live in this state for about several years. Well, the largest four-legged animals already after 6 years enter the phase of old age and the duration of their future life will depend only on proper care.
Lebeau's theory
In the middle of the last century, a veterinarian from France A. Lebo developed his theory to calculate the age of a dog in relation to a human, which is based on the accelerated development of four-legged pets in puppyhood. In his calculations, he compared the period of puberty, maturity and average life expectancy in pets and people.
According to his calculations, the development of a dog at 12 months is the same as that of a teenager at 14–15 years old, 2 years correspond to 23–25 years of a person, each subsequent year of an animal’s life is equal to 4–5 human years. But in his calculations the doctor did not take into account the size of the pets.
Separation of dogs depending on body weight
| Group | Representatives | Weight, kg) |
| Small dogs | Toy terrier, pugs, Yorkshire terrier, Pekingese, Pomeranian. | No more than 10 |
| Average | American, English cocker spaniel, basset hound, bulldogs, dachshunds, husky. | 11–25 |
| Large | Labradors, greyhounds, Staffordshire terrier, German shepherd, husky. | 26–45 |
| Gigantic | Great Danes, Newfoundlands, Mastiffs, St. Bernards, Deerhounds. | More than 46 |
Calculation formula
The very first and simplest calculation method is still popular among many owners.
The calculation method is that 1 year of a dog’s life is equivalent to 7 years of a person’s life . In order to calculate the age of a four-legged friend, you need to multiply the number of years he has lived by a coefficient equal to seven.
Where did this figure come from? Back in the middle of the 20th century, veterinarians compared the average human life expectancy of 70 years and the average life expectancy of dogs, 10-12 years. Based on these indicators, it was concluded that a person lives 7 times longer than a dog.
A significant drawback of the “seven-year theory” is the simplicity, even primitiveness, of calculations without taking into account the stages of the animal’s physical and mental development and breed indicators.
Kleiber's Law
Klaiber put forward the theory that the rate of metabolic processes in a dog’s body is directly related to its weight - the larger the animal, the longer it will live. But in practice, everything happens the other way around: small dogs live about 4–5.5 years longer than representatives of large and giant breeds.
The rule of correlating the number of years lived with the heart rate does not work on dogs either - small dogs have a faster heart beat, but they live longer. The weight of an adult mastiff is almost 40 times the body weight of a Chihuahua, according to Kleiber's theory, a large dog should live longer, but in fact, a small dog will live 1.5 times longer.
Scientists have not yet been able to identify the exact reason for this discrepancy, but many veterinarians believe that this is due to some hormonal characteristics of the dog’s body. Representatives of small breeds produce more of a specific hormone that slows down the aging process than large pets, and the concentration of growth hormone is lower. All this leads to the fact that small dogs are less likely to suffer from age-related diseases, which also has a positive effect on the total number of years they live.
The ratio of 78 human years and the age of small dogs and large pets
| Size | Approximate age (years) |
| Small breeds | 14–17 |
| Medium breeds | 14–16 |
| Large breeds | 11–14 |
| Giant dogs | 10–11 |
For all other warm-blooded animals, Kleiber's law works - large individuals live much longer than small representatives of the fauna.
Why do small dogs live longer than large dogs?
This phenomenon still puzzles scientists, and they have yet to explain the relationship between a dog's body weight and lifespan. Generally speaking, large mammals like elephants and whales tend to live longer than small ones like mice. So why do small dogs live longer than large dogs?
Some researchers believe that the lives of large dogs are accelerating over time. Scientists have concluded that every 2 kg of body weight reduces a dog's potential life expectancy by about 1 month.
One likely reason for this is that larger dogs may become more vulnerable to age-related diseases more quickly, and that the increased growth of larger dogs may lead to a higher likelihood of abnormal cell growth and death from cancer. The researchers plan to conduct additional future large-scale experiments to better explain the relationship between size and mortality.
The Internet is simply teeming with requests from curious owners “how to determine how old my dog is by human standards?” Indeed, every pet owner, no matter if it is a dog, a cat or a guinea pig, is trying to figure this out.
Dog age table
Until about 3.5–4 years of age, dogs of all breeds develop equally, but then large pets begin to age rapidly. Therefore, modern gerontologists have concluded that the life expectancy of pets directly depends on its weight and size.
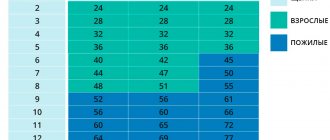
Table of the ratio of canine and human age indicators, depending on the size of the pet
| Dog age | Small dogs | Medium sized dogs | Large dogs | Giants |
| 1 | 13–15 | 14–16 | 13–16 | 11–13 |
| 2 | 21–24 | 23–26 | 21–23 | 19–21 |
| 3 | 26–28 | 27–30 | 27–31 | 26–27 |
| 4 | 30–33 | 33–35 | 34–36 | 3–37 |
| 5 | 34–36 | 35–37 | 38–40 | 40–43 |
| 6 | 39–40 | 40–42 | 43–45 | 47–50 |
| 7 | 43–45 | 45–47 | 49–51 | 54–57 |
| 8 | 46–49 | 49–52 | 53–56 | 63–66 |
| 9 | 50–53 | 54–57 | 59–62 | 68–72 |
| 10 | 54–57 | 58–61 | 54–67 | 75–79 |
| 11 | 57–60 | 63–66 | 69–73 | 84–88 |
| 12 | 62–65 | 67–70 | 74–78 | 90–94 |
| 13 | 65–67 | 72–75 | 75–78 | 98–102 |
| 14 | 69–73 | 75–79 | 85–89 | 105–110 |
| 15 | 74–77 | 80–83 | 90–93 | |
| 16 | 77–81 | 84–88 | 95–100 |
Dogs, especially large ones, do not live long, very rarely reaching 15 years of age, which corresponds to 100 human years. How long a pet will live largely depends on the owner. To prolong the life of a pet, it is necessary to feed it only high-quality products, timely vaccinations, antiparasitic treatment, more walks, and regular visits to the veterinarian.
Nuances of popular calculation methods
The average lifespan of dogs is 15 years - everyone knows this. Experienced dog breeders know that this figure is not entirely correct, since each animal has its own physiological characteristics due to its breed, congenital or acquired diseases, and even character.
Dog handlers agree on one thing - small breed dogs live longer, and it is normal for them to celebrate their 15th and even 17th birthday. Dogs of large breeds cross the threshold of old age at 10 years, but not far - thirteen years old is considered a rarity for them.
Therefore, dividing a dog’s life into periods is also conditional: a Jack Russell at 9 years old is still full of energy, and a Tibetan mastiff is already old. But an approximate description of the stages of maturation of dogs
will be useful to every owner:
- Infancy
, or neonatal period - these are puppies up to 1 month old. They begin to see, hear and try to walk. - Youth
lasts up to 1.5-2 years. This period is characterized by increased activity and accelerated development of the body and brain. This is the easiest time to train a dog, although you will have to overcome its teenage stubbornness. - Maturity
in different breeds is determined until approximately 8 years of age. This is the time of greatest physical strength and good health. From 2 to 8 years of age, females and males are allowed to be bred; in addition, service dogs do their job best in this period of life. - Old age
occurs between 8 and 10 years. Identifying the signs of aging is not so difficult: health problems appear, activity decreases, fangs wear down, and gray hair appears in the coat. In small breeds this process is slower, in large breeds it is faster.
The owner needs to select food, plan walks and activity of the dog in accordance with its age. Otherwise, the dog's health will deteriorate sharply.
First of all, the relationship between the age of a dog and a person is based on the average life expectancy. Rare pets live up to 15 years, so the transitional age in humans falls on the elderly in dogs. At the same time, a one-year-old dog is the equivalent of a 15-year-old teenager.
The lifespan of a pet depends on its breed, the presence of chronic diseases, genetic predisposition, body size, care and maintenance. The methods presented below are based on these and other factors.
Simplified
This method is the most popular, but the least accurate. A year of a dog's life is equivalent to 7 years of a person. The simplicity of this formula allows you to do without a calculator.
The coefficient was proposed in the 20th century after studying the average life expectancy. At that time, the life of four-legged pets rarely exceeded the 10-year threshold, and the life of their owners faded away by the age of 70.
A significant advantage of the method is its simplicity of calculation, but it is often criticized for the unreliability of the results obtained. The level of development of a one-year-old dog is higher than that of a seven-year-old child. Some breeds reach sexual maturity at 6 months, and at 1.5 years they are able to give birth to new offspring.
What is the best way to calculate a dog's years using a simplified method? When she is already an adult and has crossed the three-year mark, and this method is not suitable for teenagers.
LeBeau theory
In the middle of the 20th century, the French scientist LeBeau supplemented the simplified technique with new factors. He compared the average life expectancy, puberty and maturity. A comparison of human children and puppies showed that the latter mature faster. The difference smooths out only by 3 years.
According to the theory, a year of a dog’s life by human standards is equivalent to 15 years, and 2 years to 24 years. After 3 years, the coefficient decreases to 4 and remains unchanged for all subsequent years.
Comparing several important factors gives a more accurate indicator, but still loses due to the omission of animal size. Using a single coefficient for everyone is wrong, since giant breeds live shorter lives than small ones.
How to calculate a dog's age by human standards using LeBeau's theory as an example:
The dog is 7 years old, therefore, to 24 years (2 dog years) you need to add 5 (7 years minus the first 2 years) times 4, that is, twenty. It turns out that the seven-year-old dog is 44 years old.
Metabolic Law 3/4 (Kleiber's Law)
In 1930, the Swiss scientist M. Kleiber calculated the relationship between body weight and the rate of the aging process of the body. According to the proposed law, the lifespan of an animal directly depends on its weight. The smaller the body size, the faster the body wears out.
This theory is confirmed by the short life expectancy of rodents and the long life of elephants. Despite its success, Kleiber's law did not correspond to the rule for how years are counted in dogs of different breeds. The relationship between the average life expectancy of a Chihuahua and a Great Dane does not correspond to the postulates put forward and has an inverse relationship.
Metabolic law had to be modernized. Biologists have discovered a direct relationship between the rate of aging and the concentration of the IGF-1 protein. This element is produced by liver cells. It is responsible for the growth and development of organs and tissues.
The lower its concentration, the slower the body ages. The minimum concentration was found in small breed dogs.
In order to calculate how old a dog is by human standards, it is necessary to take into account its weight and the average life expectancy assigned to the breed:
- less than 10 kg – 16 years;
- 10-25 kg – 14 years;
- 25-45 kg – 12 years;
- more than 45 kg – 10 years.
In human age terms, that's 78 years. This is the average life expectancy of people around the world.
In the first years, the difference between animals of different breeds is minimal. Dimensions have little effect on puberty and maturity. The imbalance in the coefficients appears after 5 years, when the rate of aging in large breeds begins to actively increase.
Comparative table of dog and human years
It is preferable to determine the years of a dog by human standards using the modified LeBeau and Kleiber law. To do this, it is enough to know the age of the animal and its breed. Below is a table of dog ages based on all the important factors listed earlier.
Main causes of premature death
The causes of premature death can be congenital defects, but also acquired diseases.
Congenital diseases:
- Cryptorchidism and disorder of sexual dimorphism;
- Incorrect body proportions and height;
- Irregular tail shape (docked, carried over the back or ring-shaped);
- Incorrect muzzle shape (too short/long or blunt);
- Droopy or soft ears, malocclusion;
- Coat problems;
- Weak pigmentation and blue eyes;
- Excessive excitability, cowardice or lethargy.
But there are also acquired health problems caused by improper care:
- Insufficient amount of physical and intellectual activity;
- Improper maintenance (the dog is constantly in a cramped room - an apartment or an enclosure);
- Incorrect selection of food or diet in which the dog does not receive enough vitamins;
- The dog was not allowed to recover from the birth and was bred again;
- Dangerous work with risk to life;
- Physical activity when the dog has not yet recovered from any wounds or injuries.
Factors influencing life expectancy
1. Small dogs live a much longer life than representatives of large breeds. Why is this happening? It’s simple, because to maintain the basic functions and physiology of the body, small pets expend much less energy than large dogs. Large four-legged dogs often experience heart problems, because their heart beats much faster than that of small pocket dogs.
2. The sex of the animal also affects the average lifespan. Bitches live a little longer than males due to their physiological characteristics, endurance and body structure.
3. During sterilization and castration, four-legged companions no longer feel natural needs and joys, but they also do not expend energy on finding a partner and love pleasures. That is why their life is calmer, and therefore longer. Untreated animals often develop cancer of the genital organs.
4. The right choice of diet also plays a role in the duration of a dog’s existence. Balanced specialized food can extend the life of a pet by several years. That is why you should definitely contact a veterinary clinic so that specialists can select the optimal diet for your pet of a certain breed.
5. A healthy and proper lifestyle is important not only for humans, but also for dogs. Long walks in the fresh air, an active lifestyle, a good and friendly atmosphere in the family - all this is the key to a long life for a pet.
6. Regular examinations by a veterinarian will help identify the presence of hidden diseases and infections and promptly vaccinate the animal.