Raising quails will allow you to provide your relatives with healthy eggs and dietary meat, and, if desired, make money from this type of household farming, which is becoming more popular every year in Russia.
Why quail?
Farm food is in extraordinary demand today. The imposed sanctions showed the dependence of the domestic economy on imports, but at the same time stimulated the production of local products.
Quail meat and eggs are in demand - they are tasty and healthy food, suitable even for small children and allergy sufferers. Unlike other branches of poultry farming, raising quail does not require significant initial costs or a large area for placement - per sq.m. The poultry house accommodates up to 200 birds.
In terms of food costs, quail are more profitable than chickens and geese.
At 30-40 days of age (the age of the clutch varies depending on the breed), the quail already begins to lay eggs. If you have 500 heads, you will have up to 15,000 eggs.
Description of wild quails
Appearance
This is a small bird of the pheasant family, partridge subfamily, order Galliformes. The weight of a common quail varies from 80 to 145 grams, with a body size of up to 20 centimeters.
The quail's wings are long, relative to the body - up to 35 centimeters in span. But the tail is tiny. The eyes are brown, the beak is brown.
The common quail has short, widely spaced legs. This structure allows it to quickly move along the ground.
Features of color
Wild quail has a camouflage color of feathers, allowing it to blend into the background of the earth's surface. This makes the bird less noticeable to predators.
The plumage color of wild quail is represented by a variegated combination of brown and yellow flowers. There are inclusions of ocher shades and dark spots.
The parietal region of the common quail is darker than the other areas, with a slight brown tint. Along it there are usually several stripes painted with ocher.
The male's crop is a brighter, reddish hue. This feature is needed to attract the attention of females during the mating season. Wild quail lacks such decoration. The color of her feathers is lighter than that of males.
The upper body of both sexes is darker than the chest area.
Behavior and voice
The difference between common quail and other species is that they can fly. Although they don’t like to do this, preferring to move by running. Their flight abilities are used during migrations.
Quails have an unusual voice, for which they are valued by bird lovers. Quail singing can often be heard during the mating season, when males call for females.
True, the sounds made by common quails can hardly be called singing. Rather, it’s wowing (sounds of “wa-wa-wa”) and screams.
Productivity
A feature of quails that makes them extremely valuable in the poultry industry is their great early maturity and high egg productivity.
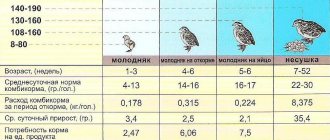
The female begins laying eggs 5-6 weeks after birth and is capable of laying about 3 hundred eggs in a year. For 1 kg of egg mass, approximately 2.8 kg of feed is consumed.
If we compare quails in egg production with chickens, considering the ratio of the female’s body weight to the annual volume of her eggs produced, then quails are 3 times more productive than chickens.
Table 1. Egg production and egg weight of female domestic quails at the beginning of laying.
At first, the mass of eggs is small (about 5 g), but by the age of two months it is compared with the mass of eggs of adult females, whose age reaches 4-5 months, and is approximately 10 g.
When raising poultry for meat, the emphasis is on its weight. Intensive feeding of meat quail breeds makes it possible to ensure that their weight is three times greater than the mass of egg breeds. At the same time, they will also rush, but they will start doing this later.
Quail varieties
Japanese or dumb
Quail is larger in size, the weight of some individuals reaches 250 grams. This species was domesticated by the Japanese in the 20th century. The birds are not susceptible to disease, have good egg production (about 300 eggs per year) and a high percentage of brood survival (85-95%).
Australian Black-breasted
As the name suggests, the chest of this quail is colored black. Loves high temperatures, about 25-28 degrees, and low humidity - 45-50%.
Harlequin
Males of this species have a contrasting pattern of white and black flowers on their heads. The craw, as well as the throat, is not the usual reddish hue characteristic of quails, but is painted with a white spot in the shape of an anchor.
Brown (swamp)
The main color of the feathers of this quail is brown, with black splashes. It chooses wetlands for habitat.
African blue
Males are distinguished by the color of their plumage in bright blue or sapphire colors. Quails of this species have a normal gray color.
Painted or Chinese
The smallest representatives of quails: weight from 45 to 70 grams, body size - no more than 14 cm. They are distinguished by their bright colors. The belly and large feathers on the wings are brown, the back is gray and blue, the beak is black, the legs are orange. These quails are bred mainly for beauty.
There were other types as well. At the moment they are considered completely extinct due to human intervention. This is a New Zealand and Canarian variety of quail.
Poultry health
Before breeding quails, you need to take care of their future home. There should be no drafts or dry, moldy air. Signs that conditions are not suitable for the birds will include occasional bald patches and patchy loss of feathers on the head or back.
If birds are exposed to unsuitable conditions for a long time, all of their plumage will become brittle. Eliminating drafts and creating optimal air humidity for quails will help correct the situation.
Juveniles should be raised separately from adults. The usual microflora, which necessarily accumulates on the body of an adult bird, can be fatal for chicks.
In addition to coop problems, their numbers also affect the health of the birds. If the house is small and there are a lot of birds in it, then they may start pecking each other. This leads to various injuries and death.
Keeping it clean
Keeping the cage clean is one of the main conditions for maintaining the health of the bird. It is necessary to ensure the cleanliness of equipment and equipment and remove debris from the cage on a daily basis.
In the hot season, it is necessary to wash feeders and drinkers with special care, and keep the bedding material clean: sand, sawdust. The accumulation of excrement and dirt in cells creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of external parasites.
There should be no empty spaces in the room that allow rodents to enter; emerging rodents must be exterminated. Birds that have died or been laid due to suspected disease should be safely isolated from other livestock.
Bird diseases
The main cause of non-communicable diseases is poor or unhealthy feeding of quail. Due to a lack of useful vitamins, these birds develop persistent vitamin deficiency.
The following symptoms are indicators of nutrient deficiencies:
- loss of appetite;
- throw back your head;
- neck stretch;
- lowering the wings;
- ruffled feathers.
You can cope with the treatment of such a problem yourself, without involving a veterinarian. To do this, you just need to create a balanced feed for the bird.
The most common infectious diseases of quail are:
- Newcastle disease;
- pullorosis;
- aspergillosis;
- colibacillosis;
- pasteurellosis;
- infectious diarrhea.
Preventing infectious diseases is much easier than treating them. For preventive purposes, you can install containers with soda or chlorine in the chicken coop. Good results in this case are shown by the use of ultraviolet lamps.
Unfavourable conditions
Unfavorable microclimate parameters that cause stress in birds include possible errors in caring for quails, feeding them, the presence of external irritants, and much more.
Stress can be triggered by irritants such as:
- hunger;
- sudden change in diet;
- loud extraneous noise;
- kept in a poultry house;
- unsuitable temperature and humidity;
- low oxygen concentration.
To keep a bird, it is necessary to create all the conditions for its normal existence. Any stressors must be removed.
Habitat
The common quail can be found throughout Europe, Africa, and western Asia. The only place where he cannot live is the polar latitudes.
The bird is migratory, travels to southern latitudes with the onset of April, and returns to its nesting sites in May. The wintering place of the common quail is the African continent, as well as the warm parts of western Asia.
There are sedentary quails, which originally lived in warm climate zones.
In Russia, the habitat of common quails is the plains of the middle part of the country, where they are warm enough and there is plenty of food.
For their life, they prefer grassy plains or mountain plateaus with tall grass. Grass and relatively flat terrain allow quail to hide and, if necessary, quickly escape from predators. In addition, the tall grass cover hides the laying of eggs well.
In the case of mountain plateaus, common quails rarely settle at altitudes above 2 thousand meters.
Reasons for the decline in species numbers
To this day, the common quail remains one of the main objects of interest for sport hunting enthusiasts. In the old days, poultry production in the southern regions of our country was of a commercial nature. This attitude towards birds on the part of humans has led to a sharp decline in the number of the species. A particularly significant decrease in the number of quails is observed in forest-steppe zones. Previously, these regions had the highest population sizes.
Another reason for the gradual disappearance of the quail bird in its natural habitat is the development of land for agricultural activities. Thus, the area of grassy meadows covered with dense vegetation is reduced. It is this environment that serves as a place for the quail bird to obtain food and reproduce.
Every year, a lot of quails die during haymaking with industrial machines. Birds often abandon egg clutches when human activity begins in the fields. The problem is that the active phase of work on farmland occurs precisely during the period when quail birds hatch chicks.
What does a person do to preserve the species? In order to increase the quail population, various environmental measures are being taken. As practice has shown, the most effective solution is to create conditions for breeding young poultry in nature reserves and special farms.
Lifestyle
The life of an ordinary wild quail is relatively short - about 6 years (you can find out about the life span of domestic individuals in the article “How long does a quail live”). Leads a daily lifestyle. At night, the birds gather in a small flock to avoid freezing, and hide in the grass or under stones and stumps.
When the slightest danger arises, common quails first freeze, almost completely merging with the surrounding vegetation. Then they quickly run away and hide, or, in extreme cases, take off. These birds are mainly attacked by foxes, ferrets, marmots, snakes, weasels, owls, and hawks.
As a diurnal bird, the quail seeks food during daylight hours. What a bird eats depends on its age. Young animals prefer to eat more insects. Older quails add plant seeds, leaves, young grass, and shoots to their diet.
Natural enemies of quails
Photo: Quail in nature
Quails are food for many predators of the forest and forest-steppe.
First of all this:
- foxes. They attack quails at night, when they are unable to escape the attack into the thick grass. Foxes are one of the most important enemies of quails, since they are the ones who primarily maintain the normal population of these birds;
- wolves. These large predators rarely leave the forest zone, but during hungry periods they are able to track down quails. Although, due to their large size and slowness, wolves can rarely catch a nimble bird;
- ferrets, weasels, stoats, martens. Agile predators are the best hunters of these birds, as they move as quickly as quails. But most of all they are interested in the chicks;
- falcons and hawks. They prefer to follow flocks of birds during seasonal migration, thus providing themselves with food for a long period of time;
- hamsters, gophers, other rodents. The quails themselves are not interested in them, but they do not mind eating eggs, so sometimes they destroy nests if they can get to the hatching eggs.
Natural enemies do not threaten the number of quails, which cannot be said about hunting, since because of it the species of common quail could disappear.
Breeding period
During the mating season, which begins in May, male quails begin to emit loud calling calls to attract females. Real battles often arise for the “lady’s” attention. The winner fertilizes the quail. Common quails do not create permanent pairs.
After mating, the female makes a hole in the ground, which she lines with dry grass and her feathers. Having built a nest, she sits down to lay eggs. One clutch can contain up to 20 white eggs with black specks.
When the clutch is finished, the quail sits down to hatch its offspring. After 17 days, the young appear. The chicks are covered with dense down, which prevents them from freezing. Color - red with dark stripes on the head, wings, and back. Weight at hatching: 5.5 grams.
Immediately after the last quail hatches and all the offspring dry out, they leave the nest with their mother. And learns to live independently. Common quail chicks grow quickly, becoming adults at 6 weeks.
Males of the common quail do not take any part in building the nest, incubating, raising and feeding the young generation.
Read about the characteristics of reproduction and egg production of quails in the article “When quails begin to lay eggs.”
Raising chicks
After hatching, the quail are placed in a wooden, cardboard or plywood box, which is covered with gauze on top. The air temperature in the first days is maintained at 35 ° C, and gradually reduced to 25 ° C until the age of 1 month. For the first two weeks, lighting is left for the quails around the clock, and then gradually reduced to 17 hours.
Hunting
Since wild quails are quite prolific birds, hunting them does not disturb the population size of the species.
Hunting common wild quail is not a difficult task, even novice hunters can do it.
It is recommended to go “on” before the birds fly away to the winter hut. At this time, a large number of wild quails gather in the grass on the banks of rivers. With the help of special noise effects, they force the flock to rise into the air, shooting at this time some of the individuals.
Many hunters go hunting for common quail with dogs. These helpers will find where he lives. They lift the caught bird, exposing it to the shot.
For hunting, either small-caliber weapons or small shot with a loose spread are used. Otherwise, when hit, you may end up not with a hunting trophy, but with minced meat. After all, these migratory birds are small in size.
Wild quail meat is more tender than domestic chicken meat. For which it is valued among gourmets.
Population and species status
Photo: Wild quail
Quail is a target for both sport hunting and hunting for meat. In the USSR, quail hunting became most widespread, so their destruction took place on an industrial scale. In the forest-steppe region, birds disappeared almost completely; At this time, two species of the pheasant family were destroyed. But thanks to their fertility, quails did not die out completely.
Their breeding played a significant role in preserving the population of the species. In the last century, the Japanese domesticated the Japanese quail and began breeding it in poultry farms. The bird has undergone almost no selection, and the species has survived in a huge number of individuals. Also, the number of quails began to decline due to another anthropogenic factor - the cultivation of agricultural land.
There are a number of reasons for the death of birds:
- firstly, this is the destruction of their natural habitat. Hens who cannot leave the nest while hatching eggs have died in dozens under the wheels of agricultural vehicles;
- secondly, treating seeds and plants that quail feed on with pesticides that their stomachs are not able to digest;
- thirdly, the destruction of their habitual habitats and their food. Plants, insects, and the comfortable territory of the forest-steppe ceased to exist during the mass cultivation of land in the USSR, which is why quails were deprived of the opportunity to reproduce and, accordingly, the population declined.
It is difficult to name even an approximate number of birds at the moment, but it is reliably known that the species is not on the verge of extinction and does not need protection. Thanks to widespread breeding on large farms and at home, quail have restored their population in less than half a century, and their numbers are growing.
Quails are birds that are valuable both in nature and at home. In forest-steppes they form an important part of the food chain, and for people they provide tasty meat and eggs, which birds produce in large quantities. Quails are not difficult to keep, so people quickly learned to breed them on an industrial scale. Quail is one of the most “lucky” representatives of the pheasant family.
The common quail is a small bird the size of a thrush, which many people probably know. It is known that quails live in tall meadow grasses and have a quick, restless disposition. Some may think that there is nothing interesting about quail. But if you take a closer look at this bird, you will find that it is an amazing and extraordinary representative of wildlife.
Contents of step-by-step instructions:
Captivity
Involuntary features
Common wild quails get along well in captivity. The only thing is that no one keeps them until they are 5-6 years old. After 1-2 years of life, quails lay fewer eggs, and males fertilize them worse.
The quail begins to lay eggs 1.5 months after birth. Up to 300 eggs are produced per year from one hen. They are valued for their nutritional composition enriched with vitamins and microelements.
Breeding common quails at home began in ancient China. Then the trend moved to Japan, where the benefits of quail eggs and meat were discovered.
In addition to the edible properties of quail eggs and poultry meat, its manure is used as a nitrate-rich fertilizer. Some internal organs and bone cells of common quails have found use as a component of Asian medicine.
Common quails feed on what they eat in nature.
Optimal temperature conditions
As a heat-loving bird, quail loves temperatures from 18 to 25 degrees. At lower levels, it may die; at high levels, it will begin to lose its plumage.
The number of eggs produced and the weight of an ordinary quail depend on the comfortable temperature.
It is imperative to ensure ventilation of the room where wild quail live. This will help get rid of the ammonia that quail droppings produce.
Cell
To prevent birds from flying around the house in different directions, they are locked in cages. Housing for common quails can be purchased ready-made or constructed independently. The last option is discussed in the article “Building a quail cage with your own hands.”
Any type of cell must meet the following requirements:
- height - at least 20 centimeters;
- It is recommended to cover the top with a soft cloth - it will protect timid quails from injuries that they can receive when jumping during danger;
- The floor of the cage is made with a slight slope at one angle, where the eggs roll away as a result.
The size of the cage depends on the number of birds. It is calculated according to the principle: for every 10 quails - 0.2 square meters. For ordinary quails raised for meat, the cage is made a little larger.
Lighting
The activity of common quails is related to the length of daylight hours. For them it is necessary to organize a regime of light and darkness.
Wild quail sleep about 4 hours a day. But it is not advisable to do a night regime for this period, since the birds will wake up hungry and eat more food than normal. This may cause the goiter to stop working. It is better to divide the night cycle into parts of 2 hours with the same break between them.
There is no need to illuminate common quails with strong streams of light. For a cell with an area of 40 by 100 centimeters, one 40 W light bulb is enough.
Feeding
It is customary to feed adults 3 times a day. When using regular feed for quails, it is necessary to enrich it with cottage cheese, fish or soybeans. With an increase in protein composition above normal, it is possible to obtain eggs with two yolks.
Varieties of food and diet of quails
Quail food must contain:
- Grain, grain waste, leguminous and grass seeds - beans, vetch, peas, hemp seed, corn, buckwheat, poppy, oats, pearl barley, millet, wheat groats, millet, rice, weed seeds, sorghum and chumise, soybeans, lentils, barley , cake, meal, bran.
- Additives of animal origin - fat, quail blood or blood meal, fish and fish oil, fish meal, curdled milk, cottage cheese, bloodworms, mealworms, meat and bone meal, earthworms, maggots, eggs.
- Vitamins A, D, E, C, PP of group B - boiled potatoes, dandelions, cabbage, nettles, clover, alfalfa, herbal flour, green onions, carrots, beets, pumpkin, zucchini, pine needles and pine flour, garlic.
- Minerals - gravel, bone meal, chalk, table salt, shells, eggshells.
If the diet is not sufficiently complete and varied, the quail diet may include: premixes, protein and vitamin supplements, yeast and chiktonik.
If it is impossible to feed quails with compound feed, they can be fed with separate, pre-mixed feed (mash). Such mixtures should include grain, protein (protein), vitamin and mineral feed.
Table 2. Quail's need for some elements
| Elements, mg | Units | Quail age (weeks) | ||
| until 6 | from 6 to 12 | adults | ||
| Calcium | % | 1,30 | 0,60 | 4,50 |
| Phosphorus | — | 0,75 | 0,60 | 0,70 |
| Magnesium | — | 0,02 | 0,04 | 0,04 |
| Potassium | — | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,50 |
| Manganese | mg/kg | 90,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 |
| Selenium | — | 1,00 | 1,00 | 1,00 |
| Iodine | — | 0,40 | 1,20 | 1,20 |
| Zinc | — | 65,0 | 75,0 | 75,0 |
| Iron | — | 8,00 | 20,0 | 20,0 |
| Copper | — | 2,00 | 3,00 | 3,00 |
Meals depending on the time of year
In winter, feeding is carried out not only with compound feed, but also with sprouted oats, wheat, millet and green onions. They serve as additional sources of vitamins and minerals.
In summer, the amount of green food can be easily increased by spinach, green salads, clover flowers, nettles, alfalfa, beet leaves and cabbage. They increase feed digestibility and nutrient absorption. To properly feed quails, green food must be thoroughly chopped. Earthworms can be used as animal food.
Diseases
general information
Like any bird, a quail can get sick. The reasons for the development of pathologies are often non-compliance with the requirements for keeping poultry, poor-quality or missing feed, and unsanitary conditions.
Quail diseases, methods of getting rid of them and preventive measures are well described in the article “Symptoms and treatment of quail diseases.” Let's look at common ailments.
Salmonellosis
An infectious disease that occurs when there is poor ventilation of the room and large crowding of quails in one cage. It happens that the disease occurs due to poor quality food.
Symptoms: liquid droppings blocking intestinal patency.
There is no treatment. Only destruction of the population with mandatory disinfection of the cell with a 3% chloramine solution or 2.4% sodium hydroxide solution. Calculation: liter of solution per square meter of area.
Prevention: frequent cleaning, fresh water in drinking bowls, high-quality ventilation, fresh high-quality food, correct calculation of the cage area for the number of quails.
Colicbacteriosis
Infectious disease of epidemiological type. The causative agent of the disease can be in water, feed, sand.
Symptoms: the bird is lethargic, sleepy, and often falls on its feet.
Treatment: antibiotics (“Enronit”, “Lexofron”), acidophilic yogurt.
Prevention: vaccination, keeping cages clean.
Pullorosis
The infection mainly affects young animals.
Symptoms: inactivity, chicks sit on their feet. When tremors begin, they try to cluster in the corners of the cage. Dried droppings are observed in the anal area, blocking the exit of feces.
Treatment: destruction of the population, disinfection of the cell.
Prevention: prevent chickens from hypothermia, clean the cage regularly.
Aspergillosis
A disease that can affect quails at any age.
Symptoms: in adult quails the disease occurs in a latent form. Young animals experience general lethargy, blue beaks and paws, and increased thirst.
Treatment: antibiotics, vitamins, antifungal drugs (“Amphotericin”, “Itraconazole”).
Prevention: fresh food, water, disinfection and cleaning of cages.
Newcastle disease (pseudoplague)
The disease mainly affects young animals. It develops quickly, the death of diseased quails occurs in 2-15 days. The cause of infection is sick birds, contaminated eggs, or food.
Symptoms: There are two forms of the disease. In one there is a rise in temperature, paresis, paralysis, weakness, and bloody diarrhea. The other form does not show itself in any way.
Treatment: only population replacement with cell disinfection.
Prevention: keep the new bird in quarantine for two weeks. Boil eggs well for feeding quails. Feed them only high-quality food.
Nutritional Features
To find food for itself, the quail bird rakes the earth with its paws and scatters it to the sides. Trying to answer the question of what quail eat, it is worth pointing out that most of the food consists of animal food. Birds prefer to eat caterpillars and various insects, worms, and small invertebrates. As they grow older, they increasingly switch to plant food, consisting of:
- seeds;
- grains;
- shoots or leaves of bushes and trees.
This feature should be taken into account by those people who intend to breed quails. At an early age, birds are always given more animal food. The amount of plant components is gradually increased.
The chicks grow and develop quickly. For this reason, in addition to standard components, their food should include proteins, vitamins and other beneficial compounds. You should not resort to the use of exotic types of food. Compound feed is quite enough if it is selected correctly. It can be replaced by:
- crushed grain;
- sunflower;
- meat and fish meal;
- boiled vegetables;
- soybeans
Classification
Today, people know about two dozen species and many subspecies of quail. Most of the species belong to the tooth-billed partridges, which are common in North America.
The common quail (Coturnix coturnix) belongs to the partridge subfamily and is divided into 8 subspecies:
- c. africana;
- c. confisa;
- c. conturbans;
- c. coturnix;
- c. erlangeri;
- c. inopinata;
- c. parisii;
- c. ragonierii;