The long-tailed owl has the second name “Ural owl”, since this representative was first discovered in the Urals. The Great Tawny Owl is a fairly large bird of the owl family. The body size varies from 50 to 65 centimeters in length, and the wing size can reach 40 centimeters with a wingspan of 120 centimeters. The upper part of the body is predominantly brown with spots of white and dark shades. On the lower part of the body the color is grayish with brown streaks. The feet are thick, grey-brown in color and feathered down to the nails. The facial disc is gray, framed by a black and white border. It has large black eyes. The tawny owl gets its name from its noticeably long, wedge-shaped tail.
Description and features
Among the feathered life of the planet there is a large family of owls. And it is not for nothing that its representatives have been considered a symbol of wisdom since ancient times, because by nature they are endowed with resourcefulness, practical intelligence and the ability to move unnoticed, that is, without making noise, through the air.
But at the same time, they themselves are always aware of what is happening. Their hearing is unusually fine thanks to the successful asymmetrical arrangement of the ear openings, which makes it possible to capture sounds coming from all sides.
In addition, the anatomical features allow these birds to turn their heads three-quarters of a circle in the horizontal direction, and in the vertical plane their vision is a full angle, which gives them additional chances to always be on guard.
This family includes eagle owls, scops owls, long-eared owls and other predatory types of fauna, grouped into three dozen genera. It is not without reason that many of these members of the bird kingdom (though not all) are considered long-livers, because their life span is up to 50 years or more.
Outwardly, these creatures look formidable, proud in their solitude and self-sufficient in everything. True, those of the people who got to know them better believe that at heart they are very susceptible and vulnerable.
The tawny owl is also a member of the mentioned family . These winged creatures have much in common with their relatives, but also have characteristic differences. Their characteristics and life will be discussed further.
The sensitivity of sound perception in owls is ensured by the special design of their hearing aid. And therefore they are able to hear how a beetle rustles in the grass and a mouse makes its way into its hole with careful steps. But in addition, peculiar antennas - hard feathers growing from the ears - help owls pick up noises of different tones.
Pointed upward at a certain angle, they resemble ears, and it is not surprising that many people think so at a superficial glance. However, the tawny owl does not have this feature. And only a fold of skin covers her auditory openings.
And the absence of these imaginary ears is one of the characteristic structural features of these birds, distinguishing them from their family members. The tawny owl's head seems disproportionately large. The beak is short, thin, neat, laterally compressed.
The facial disc, being outlined with clear contours, is expressed quite effectively. And the round eyes of the tawny owl especially stand out on it, imparting impressiveness to its entire appearance. The eyes of these creatures, fascinating with their mystery, most often have a dark iris.
But despite the fact that they add something special and extraordinary to the image of these creatures, there is an opinion that the rays of the natural spectrum are poorly perceived by them. Yes, there is no need for this, because their owners spend most of their lives in dense forests, and they are active at night.
And in remote places and in such gloomy times there is never too much sunlight. There is a hypothesis that these birds, like other owls, respond well to thermal radiation, although most scientists dispute this statement. The plumage of such birds itself is loose and fluffy in structure, and in color it is reddish or grayish with brown motley inclusions.
Taxonomy
Russian name
: Long-tailed or Ural owl
Latin name
— Strix uralensis
English name
— Ural owl
Squad
— Owls
Family
— Real owls
This species was first described precisely in the Urals - hence the second name of this owl - Ural (that’s what it’s called in Latin and English). But the name of the entire genus “tawny owl” has a twofold explanation. On the one hand, the word “tawny owl” can be interpreted as “an insatiable creature” (and indeed, all owls are very voracious), and on the other hand, “not food,” since since ancient times people were forbidden to hunt owls and eat them.
Kinds
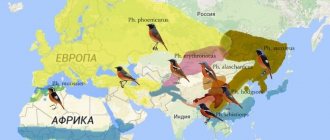
In the owl family, the described birds represent a whole genus, which is called the same as the birds themselves: tawny owls. It is divided into 22 species, the members of which have their own special characteristics, differing in habitat, plumage color and size.
The body length of the largest of them in adulthood can exceed 70 cm. But most of their fellows are not so representative; they are two or more times smaller. Let's look at some of the varieties.
1. Tawny owl (also called gray owl). The species includes about ten subspecies. The bird is small in size, slightly larger than a crow. Her eyes are dark. The plumage is endowed with camouflage coloring to match the color of tree bark.
The shape of the wings is more rounded compared to other owls, and they themselves are wider and shorter. This bird is mainly a European resident, but is often found in Asia, mainly in the central and eastern regions of this continent, and has also been recorded in North Africa.
Its habitats are largely similar in terms of climatic conditions. This could be the southern edge of the taiga, the Mediterranean and other areas of Eurasia with similar conditions, where the bulk of the population is concentrated.
Such birds prefer to inhabit old forest areas with overgrown ancient trees, usually of deciduous origin, but sometimes coniferous. Often in the forest thickets at night the voice of a tawny owl .
This is a drawn-out, howling, melancholy “oooh.” This is how males scream, and their calls during mating time are easy to distinguish from the short and dull “kwi” that their girlfriends echo. The signals demanding food, which will be heard a little later, will be different - voiceless and hoarse “piuvik,” as children will call their parents.
The sounds produced by such birds are multifaceted and depend on their mood. They may have the purpose of attracting attention, expressing a threat, and also indicate a number of other states and desires of these creatures. And the timbre of their voices, even in films, became the personification of the night. Such winged creatures fly beautifully and elegantly, sometimes aiming upward, sometimes, on the contrary, approaching the ground.
2. The pallid owl is found in palm groves, rock gorges and desert areas of Egypt, Arabia, Israel and Syria. Unlike the previous variety, these birds are smaller in size (on average about 31 cm). Their coloring is also completely different, which, given their habitat, is completely natural. Against the background of sand and rocks, their yellow eyes and pale feather color make these creatures hardly noticeable to unwanted eyes.
3. The Chaco Tawny Owl is a resident of the wild, arid tropical region of Chaco, which is located in South America. That is why the bird got its name. This feathered creature can often be seen in the dry forests of this region on trees and in semi-desert areas, sitting on rare bushes or directly on the ground. Like all owls, such representatives of the genus are predominantly night owls and are active in the dark. The bird has a brownish-gray plumage with pretty white ripples.
4. The Brazilian owl is an inhabitant of the same continent as Chaco, and is also in many ways similar to the birds described above, but larger in size than the previous one (up to 38 cm). Birds are found not only in Brazil, as the name suggests, but also in Argentina and Paraguay. This bird lives in dense forests, has dark eyes and brown-red feathers.
5. The tawny owl is the largest among its relatives (average size 70 cm). The species name does not deceive; the striped tail of such birds is really long. It is wedge-shaped and reaches up to 30 cm, protruding significantly from under the wings when they are folded in a calm state.
The color of the birds' feathers is pockmarked, but quite light, with a complex pattern of dark stripes, a combination of brown and ocher shades with the addition of small spots. The singing of such birds resembles humming in consonance with low notes, where “yu” and “uv” are distinguished.
Sometimes birds make noises similar to the barking of a dog. For the first time, this type of winged fauna was scientifically recorded and described in detail in the Urals, and therefore, among other things, the species received the name: Ural owl . But the range of such winged creatures is not so narrow, but on the contrary, very extensive, since they are found in the lower reaches of the Vistula, in the Balkans and the Carpathians.
Birds are distributed all the way to the European north, more precisely Scandinavia, and in the east to the Pacific Ocean, including the Kuril Islands and Sakhalin. They prefer to inhabit sparse forests, as well as forest edges; they choose clearings and areas in the immediate vicinity of forest clearings as habitat areas.
6. The spotted owl is an inhabitant of the North American continent, measuring about 35 cm. According to the name, such birds are indeed motley in color. And on the clearly contoured face, wise and sad black eyes stand out.
A striking detail of the materiality is the feather “frill”, which decorates the appearance and gives the birds their originality. It begins directly under the thin beak and looks like a wide scarf surrounding the bird’s neck. The voice of these creatures with a characteristic drawn-out “hu-hu-o” is also noteworthy.
7. The Great Gray Owl is even more long-tailed, because its size reaches up to 80 cm. The main background of the feathers of such birds is gray-smoky, the outfit is decorated with complex patterns, dots and inclusions. These winged creatures received their nickname due to the black spot under their beak, which resembles a beard.
Other striking features of the appearance are yellow eyes, as if with dark eyeliner, and a white stripe on the neck, like a thin collar. The facial contours of the birds are so clearly defined that the fluffy feathers on the back of the head and below resemble a cap.
Such creatures are found across a vast territory of Eurasia. In the west, their range begins from Prussia and further, stretching across the entire central zone of Russia, while capturing taiga forests and some mountainous areas, it reaches through Siberia and Mongolia to Sakhalin.
8. The African tsikkaba is a resident of the hot continent mentioned in the name. Such birds are found south of the Sahara on the fertile lands of this continent, populating plantations and forest thickets in river valleys.
These creatures have mostly brown plumage with white stripes and splashes, darker above, whitish below with the addition of gray and reddish tones. The contours of the face are outlined with a line in the shape of a heart. It has dark round eyes and a thin yellow nose. The wings of such birds are darker than the main background. They do not exceed 35 cm in size.
Reproduction
Gray owls form permanent pairs. The mating season in the south begins in February, in the north - in March-April. They use other people's nests (birds of prey or ravens) located in trees, updating and improving them. Sometimes they nest on high “breaks” of old trees and half-hollows.
The female lays 2 to 5 white eggs. Incubation lasts 28-30 days, during which time the female practically does not leave the nest. The male hunts, feeds the female and chicks.
When near a human or animal nest, gray owls behave aggressively, clicking their beaks threateningly, and sometimes can attack with their claws.
The chicks develop slowly. They leave the nest 3-4 weeks after birth, but remain close to the nest.
Lifestyle and habitat
Occupying a significant territory and a wide variety of regions on Earth, owls initially chose dense forests or simply deserted uninhabited areas for settlement, that is, areas of the planet whose area is currently shrinking every year under the pressure of industry and the spread of human civilization.
However, despite this, most species of such birds do not suffer much and remain prosperous and numerous. The reason is the extraordinary ability to adapt to changing conditions.
For example, the gray owl , the original inhabitant of the taiga and deep forests, is increasingly seen in forestry, found in parks, neglected gardens, and abandoned cemeteries, where it not only successfully exists, but also breeds.
The fact that all representatives of this genus from the owl family are voracious predators can be understood from the very name of the birds. Many etymologists believe that it comes from the word “gluttony.” True, there are other opinions.
It is assumed that the name of the birds should be translated from Church Slavonic as “not food”, that is, in modern Russian - “not food”. And this means that such birds, along with some other birds and animals, according to biblical canons, cannot be eaten. This is evidenced by certain lines of the Old Testament.
Basically, these creatures are loners, but the breeding period is an exception. The tawny owl is a bird that has no obvious dangerous enemies in nature, with the exception of especially large predators: golden eagles, hawks, eagles.
Therefore, if such winged creatures die, then the reasons for this are mostly natural, that is, illnesses and accidents. Since most of the described birds live sedentary (although there are also nomadic species), during severe winters in unfavorable climatic zones, they can die from a lack of adequate food.
And settling close to people, these poor fellows often become victims by running into power lines or colliding with vehicles. Such incidents are not widespread, but they are known.
These are twilight birds and faithful servants of the night. They usually stay awake from the evening until first light the next day. True, if the periods of darkness in a given region in northern latitudes in the summer are too short or absent altogether, the birds have no choice but to lead their lives and get food in the sunlight.
Having had their fill, the tawny owls go to rest for the day. True, there are exceptions, for example, the Great Gray Owl, which prefers to chase prey during the daytime and rests at night.
Interesting facts about the bird
The Great Tawny Owl is an amazing representative of the animal world, about which several truly interesting facts are known:
- The bird's voice may sound like a bark or a hum. The owl is distinguished by a large number of variations in the sounds it makes.
- The average life expectancy in natural conditions is 10 years; in captivity (with good care) the life of a bird can increase to 20 years.
- The silent movement of owls is not just a talent, but well-functioning flight mechanics combined with the unique structure of their wings. The edge of the owl's wings is covered with a bristly border, and the outer side is covered with soft plumage - all this muffles the sounds of the air being cut during flight.
- Even in comparison with the flight of other owls, the tawny owl differs in its flight style. Typically, when flying, an owl's body is parallel to the ground, while the Ural beauty slightly lowers its tail.
- If the year turns out to be rich in the number of rodents, the owl stores supplies to feast on and rest.
- The average daily amount of food is 125 g.
- In mountainous areas, the owl is found at an altitude of up to 1.6 km.
- If a lost chick is found, a person should not touch it. If the tawny owl is not injured, it can return to the nest on its own.
Owls have always enjoyed the love and respect of humans. These noble and beautiful birds do not pose a threat to the economy and, on the contrary, regulate the number of rodents, as the main carriers of various diseases.
Still have questions about the Tawny Owl or have something to add? Then write to us about it in the comments, this will make the material more useful, complete and accurate.
Nutrition
The diet of such predators consists mainly of small animals. The menu features depend on the habitat, and preferences depend on the variety of these owl representatives. The largest of the species are consumed as food by medium-sized birds and mammals, small squirrels and all kinds of rodents: voles, mice, rats.
An adult tawny owl of impressive size is quite capable of pleasing itself and catching black grouse or hazel grouse for dinner. Frogs, shrews, various reptiles, and fish also become victims of such feathered predators. Smaller species seek out appropriate prey or even feed on insects.
Such birds hunt not far from their nests, and in search of prey they usually do not move more than a quarter of a kilometer away. If they are large enough, they tear their victims into pieces for ease of absorption, and they are quite capable of swallowing small prey whole.
Tawny owls are also domesticated. Exotic lovers often take such pets into their homes to keep. And then the unusual guests are fed small game, pieces of meat, and sausage. Owls can be quite dangerous, because they are still predators.
And forgetting about this is fraught with consequences. They eat with wild pleasure, tearing the bloody delicacies into small pieces and scattering them around them, thereby creating a considerable mess.
And if white mice live in the house, hamsters or the owners keep other small animals, it faces considerable danger. After all, the hunting instinct of their winged, voracious neighbors will certainly push them to cruel reprisals.
But in general, owls are considered the least bloodthirsty and the most balanced. Although it is strongly recommended that prospective owners take such birds from nurseries, because it is more difficult for wild individuals to suppress the call of nature and instincts.
Long-tailed Owl in the Red Book
On the territory of the Russian Federation (a large part of the bird's range), the great owl is often found, despite being classified as a protected and rare species.
Beginning in the second half of the 20th century, the owl expanded its habitat to the south and west and significantly restored its numbers.
Main causes of extinction
Despite the caution and peaceful nature, the following dangers exist for the existence of the tawny owl, leading to the extinction of the species:
- the spread of poaching;
- cutting down old forests and planting new plants (owls prefer more sustainable ecosystems);
- destruction of the food supply.
Rodents make up almost the entire diet of owl animals; in addition, medium-sized predators and large rodents (rats) can feast on small mammals. Significant extermination of mouse-like rodents increases competition for food supply and negatively affects the number of birds.
Current population situation
The species is included in the Red Book of the Russian Federation, and is also listed in the regional books of the Moscow, Lipetsk, Tver, Ryazan, Tambov regions and the Republic of Tatarstan.
The bird belongs to rare nesting species (category 3) due to its fluctuating numbers due to its direct dependence on the volume of other rare animals that make up the food supply.
Do you need to take protective measures?
The following bird protection measures are currently applied:
- identification of permanent nest sites;
- formation of artificial nests;
- organization of reserves.
However, the greatest benefit in protecting vulnerable animal species remains the fight against poaching and increasing the biological literacy of the population.