- Wild animals
- >>
- Birds
The bunting is a small bird of the passerine family, standing out among other birds with its bright yellow chest and head.
The bird was first described and qualified by the famous Swedish scientist Carl Linnaeus in the mid-18th century. Among ornithologists, the bunting is known by the Latin name “citrinella,” which translated into Russian means “lemon.” As you might guess, such an unusual name arose due to the yellow color of the bird.
Nutrition
— Advertising —
Bunting caught an insect
Buntings are granivorous birds and readily consume plant foods such as grass seeds (bluegrass, nettle, sorrel, clover, forget-me-not, dandelion, cornflower, yarrow, plantain) and cereal grains (oats, barley).
During the mating season, buntings may also eat grasshoppers, spiders, beetles and caterpillars. And parents bring semi-digested food in their crops to their chicks.
What does oatmeal eat?
Photo: Bunting bird
Oatmeal is not a picky eater. They feed with equal success on large quantities of plant seeds and grains of forage crops.
Most often birds prefer:
- wheat;
- oats;
- barley;
- plantain seeds;
- green pea;
- nettle;
- clover;
- yarrow;
- bluegrass.
In order to effectively collect seeds and grains, the bunting has a short but strong beak. Thus, the bird very quickly guts the spikelets and swallows the seeds. In just a couple of minutes, the bird is able to cope with a spike of wheat or select plantain seeds.
For several months of the year, the oatmeal needs protein food, and then the bird begins to hunt insects. To catch flying insects, the bird does not have enough flight speed and agility and only terrestrial insects are eaten. Buntings successfully catch grasshoppers, mayflies, caddis flies, small spiders, woodlice, caterpillars and unwary butterflies.
The need for protein food is due to the fact that it is necessary for laying eggs and feeding chicks. Therefore, birds begin to catch insects about a month before laying eggs. Thus, they ensure the strength of the egg shell and guarantee the normal development of the embryos.
After the young fly away from the nest, the need for protein food disappears and buntings stop catching insects, again switching to a vegetarian diet.
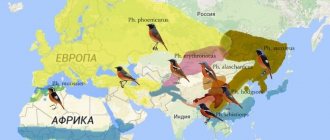
Distribution
Bunting sitting on a tree - photo
Area
— Advertising —
Buntings inhabit temperate regions in both Europe and Asia. Also, the bird was brought by humans to New Zealand, and spread well there.
Habitats
To live, buntings choose open spaces with sparse vegetation of trees and shrubs, for example, clearings, edges, forest parks, forest belts, clearings. During the winter cold, it willingly moves closer to people’s homes.
Instant porridge
If we talk about cereals in small bags with different flavors and even quick preparation, then it should be noted that this is a product made from chopped, later flattened oat grains. The composition contains added flavorings, of course, sugar, all kinds of dyes, various flavor enhancers, and inevitably preservatives.
Such a finished dish turns out to be very high in calories, because the flakes are quite small and they absorb much less liquid. Although cereal is quite safe, flavoring additives add extra calories. For patients with diabetes, such flakes will be harmful.
Kinds
Common oatmeal
Common bunting on a branch - photo
The species is similar in size to a sparrow, but with an elongated tail. The bird's body length is up to 20 cm, its wingspan is about 30 cm, its weight is 25-35 g. The male is a real beauty with rich golden-yellow plumage on his head, chest and tummy. On his neck, cheeks and forehead there is a noticeable pattern of olive-gray transverse stripes. The entire body is also decorated with streaks ranging from gray to reddish. The wings are dark brown. The beak is short and large. The female's color is lighter, with a green tint. The young are more similar to the females.
Dubrovnik
Oak bunting in its natural habitat
The species is common in Eastern Europe and Asia. The throat, belly and breast of this small bird are yellow. The wings, tail and back are motley, darker in males than in females. In summer, the males' head plumage turns black.
Bile oatmeal
The bilious bunting looks into the distance.
The bird's body length is up to 20 cm. The color of the plumage does not differ from the ordinary bunting. The gall bunting lives in Central Asia (China, Mongolia, Pakistan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Afghanistan). For the winter it flies to India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
Red-billed Bunting
Red-billed Bunting in a Russian forest - photo
Breeds in Greece, Turkey and Cyprus. For the winter he flies to Africa. The bird's body length is 16 cm, weight - 20 g. Outwardly it resembles a garden bunting, but the plumage on its head is gray-blue. The throat and breast are brown, the beak is pinkish-red. Singing consists of the sounds “du-du-dui”
Prosyanka
Her entire body is decorated with dark streaks.
The species is larger than other buntings. Length – 18-20 cm, wingspan up to 32 cm, weight – 40-56 g. Back – brownish-gray, belly – white. The legs and large beak are brown. The young animals are colored brown. Millet grasses live in Eurasia and northern Africa.
Yellow-browed Bunting
Yellow-browed Bunting photographed in the south of Kazakhstan.
Resident of coniferous and mixed forests of Siberia. A fairly large bird, up to 16 cm long, with a wingspan of 25 cm, and weighing about 23 g. The plumage on the back is brown with dark stripes, brown wings and tail, the underside is white. The male has a black head with a yellow “eyebrow”.
mountain bunting
Mountain bunting sitting on a rock - photo
Dimensions similar to the common bunting. The bird is colored brown and sexual dimorphism is not expressed in this species. Distributed in Europe, Asia and Africa.
Gray Bunting
Gray Bunting in the branches of a tree
The bird is found in Europe and is easily distinguished by the greenish plumage on the male's head and his yellow throat. The abdomen and back are gray. There are no streaks characteristic of the species on the lower part of the body. In females, only the breast is colored pale yellow. The song consists of the sounds “zru-zru”.
Garden oatmeal
Gray bunting on stone
Very similar to ordinary bunting. The body length is up to 17 cm, the wingspan is 22 cm. The color of the plumage is chestnut with dark streaks. The bottom is lighter than the back. The sides of the male’s head are yellow, and there is a black mask on the eyes. The species lives in western and southern Europe, on the islands of the Mediterranean Sea, and in northern Africa.
Yellow-throated Bunting
Yellow-throated bunting prepares to jump.
Native to eastern Asia. The male is distinguished by a black top of the head, a black mask on the eyes and a spot on the chest; his chest and “eyebrows” are yellow. The tail, wings and back are brown. The abdomen is white. Females are dull compared to males. The species is distinguished by a characteristic crest on its head.
Garden bunting
The garden bunting sings its song.
The species lives in Europe and Western Asia. The bird's body length is up to 16 cm, weight 20 - 25 g. Not as bright as the common bunting, although it is similar to it. The plumage on the head is greenish-gray. The song is simple and monotonous.
Jankowski's oatmeal
Yankovsky's oatmeal
Distributed in Korea and China. Does not exceed the size of a house sparrow. The back is brown, the belly is light. There is a noticeable chestnut spot on the chest. There are black feathers on the head and eyes, and the bird also has a peculiar dark “whisker”.
Oatmeal Kozlova
Kozlov's Bunting
A large species with a long tail. The male has black plumage on his head and white eyebrows. The top is chestnut, the breast is white, and the belly is gray. White stripes are visible along the wings. The birds have a blue-black beak and yellow legs. Found only in eastern Tibet.
White-capped Bunting
The plumage color of the female is pale.
Body length is up to 20 cm, weight is 25-29 g. The top of the head, neck and tummy of the male are white. There are also white spots under the eyes. The back is chestnut with streaks. The young are reddish-brown. The species is widespread in Asia.
Black-headed bunting
A black-headed bunting sits on a branch.
The species nests in the south of Europe, in the countries of the Middle East, the Arab Peninsula, and Transcaucasia. It is found at an altitude of 2000 m above sea level. The male is decorated with a black “hood”, yellow belly and lower back. The plumage of the female is gray with a slight yellow tint. The length of the bird is up to 19 cm, weight 30-33 g.
Oatmeal crumble
Baby oatmeal looks like this.
The species lives in northern Asia and Europe. The bird, according to its name, is small - up to 13 cm in length and up to 15 g in weight. Her characteristic feature is her red cheeks. The back of the bird is decorated with brown stripes, and the belly is black.
Oatmeal-remez
Thanks to its color, the bird easily takes refuge in the grass.
The bird's body length is up to 15 cm, weight is about 20 g. This species is easy to distinguish from its relatives due to its variegated color. The back of males is brown with black stripes. The breast and sides are brownish-red. The head is jet black with a tuft, white eyebrows and a white chest. The plumage on the head of females is brown.
Cane oatmeal
Reed Bunting
A resident of Europe and Asia. The body length is 16 cm, the wingspan is up to 23 cm. The head and throat of the bird are black, there is a light stripe on the neck. The belly is white. The back is gray-black with brown stripes. The tail is also decorated with light stripes. Juveniles and females are distinguished by the absence of black feathers on their heads.
Japanese oatmeal
Japanese bunting - photo
The body length of the species is up to 14 cm. The male is colored in gray-green tones with black stripes on top. His belly is green and yellow. The female is practically no different. The birds have a large, gray beak. The species breeds only in Japan.
Taiga bunting
Taiga Bunting, photo from eastern Russia.
The species is widespread in China and northern Russia. The birds' head and throat are black. The back is reddish-brown with dark streaks. There are white stripes above the eyes and from the beak to the crop.
Habitats
Buntings readily populate clearings, forest edges and clearings.
Birds often choose trees and bushes along roads in open areas as shelter. In open landscapes, they are able to detect the enemy in advance and fly away. Birds are not afraid of people, so under suitable conditions they can live even in the city. In winter they live in harvested gardens and fields or on the outskirts of populated areas. Bunting can also be found in the mountains, where it rises only to the subalpine zone. Migratory birds fly to Mediterranean countries or Western Europe . They return to their homeland in March or April. At this time, buntings unite in large flocks with sparrows, finches or other types of small birds, and go in search of food.
Male and female: main differences
A male and female bunting bask together.
Sexual dimorphism is pronounced in buntings during the mating season. The male dresses in his most luxurious outfit: golden-yellow plumage of the head, chest and belly, chestnut back and wings, olive-gray stripe patterns all over the body. The female, in contrast, is painted in faded greenish-yellow shades.
In autumn, males molt, and the bright yellow plumage is replaced by brown with rare yellow patches. This is why it is much more difficult to distinguish between female and male buntings during this period.
Features of reproduction
In common buntings, sexual maturity occurs at the age of one year . They begin nesting in mid-spring. From the warm countries in which the birds spent the winter, the males are the first to return. They find a place for a nest, sit not far from it on the top of a bush or tree, and begin to sing for a long time. In this way they announce that the place is occupied and invite females.
Ten days after the males, the females arrive, and after some time they begin to build a nest.
Bunting nests
Birds choose forest edges or young coniferous growths for their homes.
They do not settle in forest areas, because the small birds have many enemies there. During the breeding season, buntings choose a suitable depression among the bushes and begin to build a nest . It takes them a lot of time to arrange their home. To make the nest strong, birds use leaves and dry stems of cereal crops as building materials, adding a small amount of lichen and moss to them.
Buntings camouflage their home from prying eyes with the help of soaked stems of large herbaceous plants, which are added to the nest structure. Along the edges, the ends of these plants remain unwoven, due to which the birds’ home is almost invisible among the bushes.
Particular attention is paid to the bottom of the nest. It is carefully lined with horsehair or small roots . If construction takes place during the rainy season, the birds try to put as much hair as possible on the bottom. In such a nest the chicks will feel very comfortable.
The nest of buntings is made in the form of a small bowl and reaches a height of 80 mm and a diameter of 130 mm. To provide the chicks with good protection, the depth of the tray should be at least 50 mm. In this case, the babies will not fall out of the nest.
Nesting and chicks
During the season, the common bunting lays eggs twice. The first clutch occurs in mid-spring, and the second in early summer. Each clutch contains from two to six “thick” eggs. They can be of very different shades - pink, light purple, bluish-gray or rusty brown. The eggs may have a dark pattern in the form of spots, specks, commas, or curls. The largest egg measures 23 mm, and the smallest one measures 15 mm.
The female sits on the nest after laying the penultimate or last egg . The female incubates them alone. The male does not help her, since he is responsible for food by flying for food.
After twelve to fourteen days, the chicks appear. They are covered with thick grayish-brown or reddish down and have a crimson-red or pink mouth.
Both parents feed the offspring. But after some time, when the babies have not yet left the nest, the female leaves them with the male, and she begins to build a new nest for the next clutch. The young animals leave the “parental home” already on their twelfth or thirteenth birthday.
The behavior of a hen when an animal or person approaches is very interesting. She flies up onto the branch of another tree and begins to emit alarm signals in the form of a jerky squeal or a long, high-pitched whistle. If the chicks have already hatched, then, in order to distract a potential enemy from their home, the parents fall into the grass and, pretending to be a wounded bird, begin to crawl to the side.
In autumn, birds of all ages gather in flocks and look for habitats in open spaces where food is more available. The average lifespan of the common oatmeal is about three years.
Content
Oatmeal caught in the hand
Buntings are always kept one at a time in spacious cages at least 60 cm long. For the first two weeks of life in captivity, it is forbidden to move the cage with oatmeal or cover it with thick cloth, so that the bird gets used to it and sings.
After this period, the cage should be left in well-lit places and often taken out into the air so that the oatmeal does not lack sunlight. Otherwise, her beautiful plumage will begin to fade and fade.
Daily bathing and fresh water to drink are also necessary for this little bird.
In captivity, buntings can form pairs and nest. In one clutch the female has from 4 to 6 eggs. She incubates them for two weeks. The chicks are fed insects.
Nutrition
Oatmeal caught an insect
The basis of oatmeal's diet is millet, canary grass, oatmeal, rapeseed, grass seeds, except those that contain fatty oils (for example, sunflower). Mineral feed, greens, pieces of fruits and vegetables are also added to the daily diet.
They love to eat oatmeal and animal food, mealworms, ant eggs, maggots, and insects. Such complementary feeding is especially important during the period of molting and active singing. At this time it should make up half of the diet.
Natural enemies of buntings
Photo: What oatmeal looks like
The bird has many natural enemies. In particular, the bunting is hunted by such feathered predators as hawks, kites, gyrfalcons and owls. Due to the fact that buntings are not very agile in the air, they become easy prey for aerial hunters. The only thing that saves the bunting is caution, the ability to hide in bushes and tall grass, and also the fact that the bird does not rise too high.
On the ground, oatmeal faces no less dangers. The maximum height of a bird's nest is about a meter. Consequently, all types of terrestrial predators (including domestic cats) can easily feast on eggs or young chicks. Quite often, foxes and badgers specifically track down the nests of buntings and eat the eggs and chicks. Due to their small size, the birds cannot prevent this in any way, although the male tries to protect the nesting site.
Modern chemicals used in agricultural holdings can also harm poultry. Eating grain treated with chemicals, birds are poisoned and die before leaving offspring.
Interesting fact: In recent years, people have caused considerable damage to oatmeal. Fried oatmeal is considered an exotic and highly desirable dish in many European restaurants. Since the bird has a tiny weight, it is placed in a cage installed in a dark room. When under stress, oatmeal begins to eat continuously and within a few days increases its weight by 3-4 times.
The bird is then drowned in red wine and fried whole, including its entrails. The cost of one such fried bird can reach up to 200 euros!
How is it made?
In order to obtain flakes, the oat grain must first be peeled and all hard flakes removed, and then steamed at a very high temperature.
When the grain swells, it must be passed through smooth rollers, which will flatten it and turn it into thin plates. This technology is used precisely for the purpose of making the porridge take little time.
You will also be interested in the 10 most expensive gems in the world (photo and price)
The degree of processing directly affects the three stages of cooking Hercules flakes:
- A quick cooking process lasting from 2 to 5 minutes.
- Average cooking will take from five to 15 minutes.
- Long cooking will take from 15 to 25.
In terms of usefulness, the leading position is given to flakes that take the longest time to prepare, because then the main valuable properties of the plant are preserved due to the least additional intervention.
What princes are similar to them.
The warbler and passerine families are very similar to the bunting in their habitat, body size and shape, way of life and nutrition. However, warblers feed on insects, and sparrows have a characteristic call. Together with passerines, they are classified into the passerine order of birds. Slavaceae are a larger family of the order, and in addition they are distinguished by a wide variety of colors.
Also within the same family you can see a large difference in beak shape. In some breeds it is thinner and elongated, in others it is short and blunt. As for sparrows, they cannot be confused due to their short legs and hopping gait, gray-brown color and cone-shaped beak.
Oatmeal on the Christmas tree
Lifespan.
At home, bunting can live for several years; in the wild, it is hunted by predators, which causes a rapid change of generations. The average lifespan of an individual in the wild does not exceed three years, but genetically it is capable of living longer. Incredibly, the oldest bird recorded in Germany lived for 13 years!
Grey-headed Bunting