Snails (Gastropoda lat.) are the largest group of gastropods. It is also one of the most diverse groups of animals, both in form, feeding habits, and habitat. There are more than 62,000 described living species of snails, and they make up about 80% of living molluscs. Estimates of total extant species range from 40,000 to 100,000, but there may even be as many as 150,000 species! There are approximately 13,000 genus names for both recently formed and fossil gastropods.
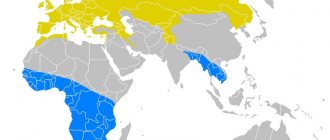
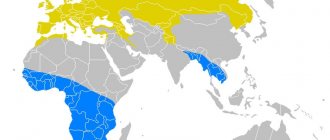
Snail habitat
The snail is often found on a continent that can provide it with high humidity.
She will feel optimally good in Europe, Africa or America. You can meet it in Russia or Asia. It does not live only in deserts and areas with eternal ice.
Reproduction
Most land snails are hermaphrodites. They have the full range of characteristics of both sexes. And they can produce both eggs and sperm.
There are also heterosexual species of mollusks.
The onset of sexual maturity, depending on the species, can vary from 6 weeks to 5 years.
Under unfavorable conditions, puberty may be delayed. This should be taken into account by those involved in shellfish farming.
Reproduction by parthenogenesis has been recorded only among one species of gastropod invertebrates. But many of them can reproduce through self-fertilization.
Based on their species, snails are viviparous or lay eggs.
Negative impacts and dangers
Despite their inconspicuousness, snails are a tasty addition to fish, crayfish, thrushes or moles, hedgehogs, and wild boars.
Storks, herons, and frogs can also attack. The animal is saved due to its slowness; it also does not appear in heavily lit areas, hiding in the grass.
However, in addition to external enemies, the snail may encounter disease. Reason for concern: white coating on the sink, burn, poisoning. Other dangers include a broken shell, prolapsed organs, or self-gnawing.
Price
You can buy grape snails in a specialized pet store or from private breeders. In the southern regions of Russia, mollusks are found in their natural environment, and it is not difficult to find a suitable specimen.
The risk for the owner is that unsanitary development conditions can cause infection with fungal diseases and mold. The soil substrate is often contaminated with parasites, which, together with the snail, will enter the home environment.
The purchase will be very inexpensive. The price of a grape snail is only 200-400 rubles. For a home nursery, a pair of gastropods is usually purchased. The owner should pay attention to the condition of the mollusk shell.
It should not have visible damage or developmental deformities. The life of a grape snail is interesting to observe. The little pet is unpretentious and attractive with its harmonious existence.
Types of snails
There are about 110 thousand species and subspecies of the snail. At the same time, 2,000 live in Russia.
The poisonous snail lives in the Pacific Ocean, its name is Geographical Cone.
Make no mistake about it, releasing a huge dose of insulin could be fatal for 10 people. If you are going on vacation to the Pacific or Indian Ocean coast, it is better to familiarize yourself with the photo of the snail in advance.
The smallest member of this society does not even reach 1 cm. Four individuals of Angustopila dominikae easily fit in the eye of a needle.
The large mollusk is the giant Australian whelk, weighing up to 18 kg and up to 1 m long. A predator that lives in northern Australia, Indonesia or Papua New Guinea.
It is worth paying attention to the species that live on our territory.
Body structure
The external structure of the snail may differ depending on its type, but there are common characteristics.
- The mollusk consists of a shell and a body, moreover, it has a clearly visible head, which has tentacles and the so-called snail’s foot.
- To protect the internal organs, the mollusk has a special mantle. It also helps to form and grow the shell.
- The snail's body is very elastic due to the absence of a skeleton. Its surface is equipped with quadrangular grooves that retain moisture well.
- To enable the mollusk to move on various surfaces, it has a well-developed sole with a pair of foot glands. They secrete mucus, which helps reduce friction when the snail moves, and at the same time contract in waves.
- The internal structure of the snail is not as complex as that of mammals. And yet, she has a heart, a digestive system, nerve nodes.
An interesting feature of the snail is that it is able to regrow missing body parts. Moreover, even the loss of part of the head and tentacles is not fatal for it. On average, a mollusk will need 3 weeks to recover and grow the missing organ.
Sink
For a land snail, the shell is an integral part of the anatomy, integral with its body. It is present in the life of the mollusk from birth and acts as a house.
The shell is made of calcium carbonate. It increases in size as the snail grows, and its internal hydration occurs with the help of glands for the production of mucus.
When reaching full size, the adult builds a thickened lip, which is located near the “entrance” to the shell. From this moment on, the work of the snail’s body will be aimed not at its growth, but at the reproduction of offspring.
The purpose of a mollusk shell is to protect its rather delicate body from various mechanical damage when moving. Also in his “house” he hides from natural enemies, cold and heat. The mucus inside the shell prevents the snail's body from drying out and softens its friction against the internal surfaces.
If you place the snail with the top of the shell down, there will be a columella on the right edge of the mouth. This is a section of the shell colored in a color characteristic of a particular species of gastropod.
In young specimens, the columella is covered with a mantle, and to see it, you will need to move the snail's body a little. This should be done very carefully, preferably with a cotton swab.
An adult snail has a sufficient gap between the mantle and the columella, so the latter is clearly visible.
Seeing the columella is important for determining the species of the mollusk.
Apex is the top of the shell, its narrowest, closed part. Curls begin to emerge from it, increasing with each revolution. In different species of Achatina, the apexes differ in color, shape and degree of pointedness.
The growth is called the thin place of the mouth. It is very fragile and can break under even slight mechanical pressure.
During development, when the mollusk has not yet reached its full size, the growth has the appearance of a yellow, not yet colored area. Over time, it acquires a certain color and becomes harder.
There are snails that hibernate during the winter, but this can happen at any time (for example, due to lack of moisture).
To retain moisture inside the shell during sleep, the mollusk seals its “house” with a special barrier made of dry mucus (epiphragm).
Respiratory system
The lungs of the mollusk occupy a significant part of the body, covering the mantle region. There are a large number of tiny blood vessels present here.
The cavity inside the mantle is filled with air, while it is connected to the external environment by a single small hole (pneumatic bridge). With its help, air enters the lungs, and gas exchange processes occur through the vascular walls.
Heart
The heart of the snail is located in the posterior part of its mantle cavity. It has two departments:
- azygos atrium,
- and the ventricle with the aorta.
The heart is located inside a transparent sac (pericardium) and is located asymmetrically with respect to the body.
The movement of hemolymph occurs through the only vessel of the mollusk and the capillary system due to cardiac contractions.
Digestive system
The structure of the digestive organs of the snail has significant differences from what we are used to. In its oral cavity there are about 25 thousand tiny teeth (radula), which work to grind food according to the principle of a grater.
The radula and jaws of gastropods are located in their pharynx. The secretion of the salivary glands ends up here.
The snail's esophagus has a shortened shape and is connected to a large crop, which passes into a relatively small stomach. It seems to “grasp” the liver, located in the upper part of the shell.
The snail's intestine consists of a loop-shaped and hindgut. And the hole for removing waste products is located on the right side, near the breathing hole.
It should be said that the snail liver performs not only the function of a digestive gland: this organ also absorbs processed food.
The only kidney of the mollusk has a connection with the pericardium and the mantle cavity. There is a special valve that opens when waste is removed from the body.
Nervous system
The internal structure of the cochlea allows us to conclude that it does not experience pain. This is caused by its lack of brain, spinal cord and nerve endings.
Ganglia (types of nerve ganglia that replace the brain of a mollusk) are part of the nervous system of gastropods, which has a nodular scattered type. But they cannot fully replace brain functions.
Sense system
The tentacles on the snail’s head (there can be 1–2 pairs of them) are the organs of perception of the world, including the visual. The eyes of mollusks are usually located on the upper stalk-like processes (ommatophores).
The lower pair of tentacles is the land snail's organ of touch. They also help her distinguish odors.
Each type of mollusk has a set of tentacles necessary for life in different conditions. Bivalves and spadefoots, for example, use them to move underwater and burrow into the ground. Also, with the help of tentacles, they regulate the flow of water with food particles going into the mantle cavity.
Aquatic species of snails have one pair of appendages, and their eyes are located at the base of these tentacles.
The land snail's eyes are located at the top of the "eyestalks". The structure of the eye itself is also unusual. This is a kind of bubble, inside of which there is a lens (a spherical lens to which the optic nerve is attached from below).
The mollusk cannot boast of excellent vision. He can distinguish objects 1 cm away from him quite well. But he sees everything else as blurry spots of light, and besides, he does not distinguish colors.
Both pairs of tentacles have very good sensitivity. A small touch is enough for the snail to quickly push its “telescopes” into its head. The same reaction will occur to too bright light.
There are unusual types of mollusks. The structural features of the snail Euglandina rosea, for example, include an increased number of tentacles. This predator (also called a wolf) uses an additional pair of appendages to hunt small animals. With them she explores the space ahead, “sniffing out” prey by the smell of its mucus.
Grape snail
The leg size is no higher than 0.5 cm, width up to 20 mm. The shell does not exceed the threshold of 0.55 cm, and is equipped with up to 5 turns. The age of a snail is limited to 20 years.
Habitat – European part. The breed is famous for its distribution and breeding at home. It can withstand temperatures that drop to 7 degrees below zero. The snail spends the winter in hibernation, covering its shell with mucus.
At home, a glass jar with good ventilation will be enough for her. Bisexual, bred by crossing. Eats fruits and vegetables.
They are actively bred on special farms for the further preparation of delicacies, cosmetics or pharmaceuticals.
Historical data
The habitat of Achatina is the equatorial part of East Africa. Not without human help they moved to Madagascar, Seychelles, India, and Sri Lanka. In Indochina, they spread throughout the entire territory in just 10 years.
Once in the United States, they managed to destroy most of Florida's farmland in a few months. Every effort was made to destroy them. Because of this, Achatina is prohibited from being brought into the United States and kept as pets. Violators of the ban face a five-year prison sentence and a huge fine.
India and Taiwan faced the same problems. Hindus destroy millions of snails every year. However, local residents of these countries began to eat them with pleasure, inventing various dishes. Achatina soup is popular in India as a healing remedy for lung diseases.
Snail coil
A freshwater animal with a brick or red shell. Actively lives in aquariums of fish lovers. Its height does not exceed 4 cm. It feeds on pollutants in a pond or aquarium, cleaning it of rotten plants.
Subspecies of this individual: horned, horned red, Far Eastern, wrapped or keeled.
Nervous system
If you touch the snail, it immediately retracts its tentacles and then hides its entire body in its shell. This response to stimulation occurs through the nervous system of the snail. Like other animals, the nervous system of the grape snail unites and coordinates the activities of individual organs and regulates all life processes occurring in its body. The sense organs associated with the tentacles help the grape snail move and get food. With shorter tentacles, it feels food and soil, and also distinguishes odors. At the ends of the longer tentacles are small eyes.
garden snail
As the name suggests, this is a headache for summer residents.
The gastropod is a lover of fresh vegetables, spoiling the harvest, which causes the death of the young plant. During the day she hides, and at night she crawls out to feed. The most unpretentious look in living at home. Eats everything that grows in the garden.
However, it is difficult to call it a pest. In addition to her excellent appetite, she is also a good orderly who is ready to process the remains of vegetation.
Behavior
All species of Achatina are nocturnal animals. During the day, they can crawl out only in damp, cloudy weather. They are able to remember their actions for one hour and return to the places where they found food.
Young individuals are more nimble and fearless, while older ones prefer to hide in secluded places and crawl out of the shelter only to search for food. Achatina perfectly recognizes its owner and reacts to him, freely crawling along his hands.
You can learn how to handle and care for these cute animals in our section Contents and Care.
Neretina snail
A popular aquarium species, brightly colored, no more than 3 cm tall.
Due to the variety of color, it is divided into 4 subspecies: zebra (striped), brindle (colored in the form of stripes), olive (nicknamed due to the color of the olive) and horned (owner of antennae-horns).
An unpretentious individual that can live for several days without food. Picking up rotten plants and waste from the life of other residents.
However, it does not tolerate direct ultraviolet rays or strong heating of water (up to 25 C).
Pamper your baby with calcium-containing products - it will make her happy. After all, a mollusk lives only a year with proper care. Hard water in an aquarium can shorten an already short life.
Color
The color of snail shells can be varied - plain, striped, with spots, patterns. In some species, the patterns may be indistinct, blurry, while in others they may be contrasting with a clear shape. Stripes can also be:
- axial - located vertically,
- spiral - located horizontally,
- diagonal,
- zigzag.
You will not find two completely identical snails; each individual of a certain species has its own unique pattern, which has common species features.
Snail Achatina
Until recently, its habitat was exclusively on the African continent. Today this is one of the favorites, classified as pets.
And it’s not surprising: the size reaches 20 cm. The weight is half a kilogram. Color brown, different shades. There are also completely white individuals.
This subspecies is a hermaphrodite, ready to lay eggs up to 6 times a year, from which up to 200 babies will subsequently hatch.
Accustomed to wandering at night and sleeping during the day, she is ready to change her lifestyle by increasing the humidity in the aquarium. Life expectancy is limited to 10 years.
Land and sea snails lay eggs, freshwater snails lay viviparous mollusks
Most terrestrial species have both female and male reproductive cells (they are hemaphroditic). They don't actually need to mate with another snail to reproduce because self-fertilization is possible. Parthenogenesis is especially important in areas where there are few partners. After mating, the females lay about 80 white eggs in a moist underground nest. Newly hatched snails have fragile shells and take about two years to mature.
Photo: Shutterstock
Some terrestrial gastropods “shoot” so-called “love arrows” at their potential partner. But this is rather an element of the mating dance that precedes the process of reproduction.
Most aquatic snails have male and female species. Freshwater females give birth to live young. Young animals look like smaller copies of adults. They develop quickly and mate at a young age to compensate for the lack of a larval stage.
But snails that live in the marine environment, like their terrestrial counterparts, lay fertilized eggs. They can lay eggs every month.
Breeding snails at home
For a snail to live in, it is better to purchase an aquarium of 20 liters per snail or a terrarium if it is land-dwelling.
The “house” should be closed with a tight lid, which will have holes for oxygen supply. Choose a place out of direct sunlight.
Soil: peat, coconut substrate, soil for flowers, sawdust or tree bark.
The temperature in the aquarium is not lower than +25. Maintain high humidity levels by misting with water from a spray bottle.
Don't forget about drinking water and cleanliness in the aquarium.
It is worth feeding vegetables, herbs or fruits. Eliminate inedible food scraps from the communal table. Feed in small doses. Add eggshells to the diet to maintain calcium in the snail's body.
Proper care and care make the snail completely domestic, which gets used to and recognizes its owner.
Sense organs
Eyes
On the head of Achatina there are two pairs of movable horns. The small beads at the tips of the upper horns are the eyes, the lower horns are the olfactory organs. The eyes distinguish the outlines of objects within 1 - 3 cm.
Snails navigate in space not only with the help of their blind eyes, but also with the help of light-sensitive body cells. They play an important role in determining the degree of illumination of surrounding objects. They don't like bright light. Therefore, they try to hide from the sun’s rays under snags, in foliage, or bury themselves in the ground.
Organs of touch and smell
An important role in the life of Achatina is played by small lower horns, which act as a nose. Without them, it is difficult for them to find food and assess the condition of the litter. Since the snail does not have hearing organs, these horns completely compensate for its absence. Also, at the tips of the tentacles of the sole and front of the body there are small tubercles that are able to recognize the smells, shape and structure of objects. Thus, snails can detect the smell of gasoline and acetone from 4 cm, and the smell of potential food from 2 meters.