- Wild animals
- >>
- Mammals
The shrew should not be confused with an ordinary mouse, because it is not a rodent at all, but belongs to the class of mammals. Perhaps this is the smallest representative of this class. The shrew is a destroyer of hordes of all kinds of insects. The little animal has a very funny appearance, thanks to the proboscis on its face, looking at which you involuntarily smile.
Origin of the species and description
Photo: Shrew
The shrew is a mammal and belongs to the order of insectivores. This is the smallest predator from the shrew family. In appearance, the shrew is very similar to an ordinary vole mouse, but it is distinguished by the perky and peculiar proboscis on its face. The shrew family includes three hundred varieties of these unusual animals, united into two subfamilies:
- Shrews (have brown tooth enamel);
- Shrews (animals with white tooth enamel).
There are 21 species of shrews in our country alone. People have long noticed their harsh and aggressive disposition, so they nicknamed them “little devils.” If you go deeper into history, back in the seventeenth century, the scientist and zoologist Topsel described this animal as a predatory and ferocious animal that bites very hard, and every bite can be fatal. Let us describe in more detail some varieties of shrews.
The tiny shrew is the smallest mammal on Earth, its body length is from 3 to 5 cm. The animal is named because of the color of the tooth enamel, which prevents the rapid grinding of teeth. The color of the animal's fur is also brownish.
The shrew (dwarf shrew) is slightly larger than the previous one, its body length is about 7 cm. The color of its tooth enamel, as the name implies, is white. Meeting this animal is very rare; the color of the coat of this shrew species is gray.
The giant shrew is the largest representative of its family, the length of its body is about 15 cm, and its tail is 10 cm. The color of its coat can be either light gray or completely black.
Common shrews (water shrews) love the shores of freshwater bodies of water. A distinctive feature of such shrews is the coarse hairs on their limbs, which make them comfortable to move in the water. In addition, the fur coat of this animal is waterproof, it has a grayish tint, and on the abdomen it is of a lighter tone. In appearance, this shrew is very similar to a water rat.
Video: Shrew
Mouse-like shrews are active at any time of the day. Their fur is soft and silky. The color of their fur can be grayish, yellowish, brownish-brown and even black, their body is from 6 to 11 cm long, and their weight is only about 23 g.
American shrews are quite large compared to other shrews, have a short tail and powerful limbs. These animals are poisonous and have dark fur.
Forest shrews are small in size, but their fur is very pleasant, long and beautiful. Its shade is predominantly gray. The body length of this variety is no more than 10 cm, and the weight is from 3 to 12 g.
The Ugandan armored shrew has a unique skeleton in its structure. The length of its body can reach up to 15 cm, and the animal weighs 110 grams. The coat is rough, but quite thick, the color of the fur is gray.
Interesting fact: thanks to the amazing structure of the armored shrew's skeleton, the animal can overcome enormous loads on its body, which are a thousand times greater than the weight of the shrew itself.
Appearance and features
Photo: Shrew on the site
Despite the fact that there are a considerable number of varieties of shrews, and they all have their own specific features, there are still common characteristics of appearance inherent in the shrew family. In relation to the body, the animal’s head is quite large, the muzzle is elongated and pointed, and the nose turns into a small proboscis that is mobile.
The animal's paws are short and have five toes. The fur cover is thick and velvety. The length of the tail varies among different species; in some it is very short, in others it is longer than the entire body. The skull has a narrow and elongated shape, which is pointed closer to the nose. A unique feature of the shrew is the size of its brain; it is one tenth of the weight of the entire animal, which is much larger than that of humans and dolphins.
As such, there are no cheekbones in shrews, and the number of teeth varies from 26 to 32. Permanent teeth replace milk teeth at the embryonic stage, so newborn shrews are born with teeth. The longer incisors are located in front, especially the lower ones. Around the anal and genital openings there is something like a roll of leather. On the sides at the base of the tail there are glands that emit a specific foul odor.
Interesting fact: female shrews have from 6 to 10 nipples, and the males' seminal glands are located inside the body. Males have a fairly impressive genital organ, the length of which reaches seventy percent of the length of the entire body.
The shrew has a very fast heartbeat, at rest it is up to 700 beats per minute, and in a state of fear it can reach up to 1200 beats. In general, scientists have noticed that these creatures are very unbalanced and nervous, so they can die even from a loud thunderclap.
Where does the shrew live?
Photo: Animal shrew
Various species of shrews have settled throughout our planet. They live almost everywhere, they can not be found only on the Australian continent, in the polar regions, New Zealand and New Guinea, as well as in parts of South America, which are south of countries such as Venezuela, Ecuador and Colombia.
These insectivorous creatures adapt to life in various territories:
- On flat areas;
- In mountain ranges (up to 4 km altitude);
- In deserts and semi-deserts;
- In tropical rainforests;
- In wetlands.
Each animal has its own domain, the territory of which it vigilantly guards to avoid encroachment by uninvited guests. If someone has invaded the shrew’s allotment, then a struggle for the hunting area begins, the outcome of which can be fatal for one of the rivals. Shrews enter into fights not only with their own kind, but also with mice and lizards.
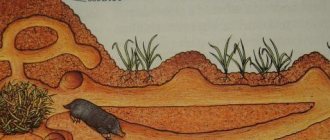
Burrows serve as a refuge and home for shrews, but they themselves dig them infrequently, but try to occupy someone else’s hole left by someone else. If they have to dig their own shelter, they make it shallow.
Insectivorous creatures love the hollows of rotten trees, where they also set up their homes. In their dens, shrews make soft and comfortable bedding from last year's leaves. We can say with confidence that shrews are sedentary animals that adhere to a certain territory throughout their short lives.
Shrew conservation
Photo: Shrew from the Red Book
There is only one species in the Red Book of Russia: the giant shrew. Indeed, the largest representative of the genus. Category 3 – rare species with low numbers and limited range. According to the IUCN, it falls into the reduced risk category. An inhabitant of deciduous and mixed forests of Southern Primorye, it was found in only three places: in the Lazovsky and Kedrovaya Pad nature reserves, as well as near lake. Hanka.
The international IUCN Red Book includes:
- The great-toothed shrew (S. macrodon) is a vulnerable species with a shrinking range. Several localities are known in the mountains of Mexico in forests at altitudes from 1200 to 2600 m. Found over an area of 6400 km², estimated range 33627 km²;
- The Carmen Mountains shrew (S. milleri) is a vulnerable species. It is found in the mountain forests of Mexico at altitudes of 2400 - 3700 m. The estimated range is 11703 km²;
- The Pribilof shrew (S. pribilofensis) is an endangered species that is found in coastal meadows only on one of the Pribilof Islands (USA) in the Bering Sea. The area of the island is 90 km². The number of species is 10,000 – 19,000;
- Sclater's shrew (S. sclateri) is a critically endangered species. There are 2-3 known locations in Mexico. Lives in forests whose area is shrinking. Nothing is known about the number;
- The San Cristobal shrew (S. stizodon) is a critically endangered species. Lives in damp mountain forests. One location is known in Mexico, fortunately in a protected area.
The conservation measures are not original: preserving undisturbed areas where animals could live in numbers sufficient to reproduce. Nature abhors a vacuum. Any ecological niche must be occupied, and even such ephemeral creatures that exist on the edge of the capabilities of warm-blooded creatures find a place for themselves. Even if not under the sun, but in the shade of other organisms, the main thing is that the shrew can survive.
Tags:
- Shrews
- Burozubochy
- Deuterostomes
- Bilaterally symmetrical
- Animals of Asia
- Animals of Alaska
- Swamp animals
- Animals of Eastern Siberia
- Animals of the mountains
- Animals of Eurasia
- Animals of Europe
- Animals of Transcaucasia
- Animals of Western Siberia
- Animals of the Caucasus
- Animals of the Kaluga region
- Animals of Kamchatka
- Animals of Canada
- Animals of Karelia
- Animals of the Red Book
- Animals of the Red Book of Russia
- Animals of the forest
- Animals of the forest-tundra
- Meadow animals
- Animals of Mexico
- Animals of the Moscow region
- Animals starting with the letter B
- Animals of Russia
- Animals of North America
- Animals of Siberia
- Animals of Scandinavia
- Animals of the steppe
- Animals of the Russian steppe
- Animals of the Subarctic Zone
- Animals of the Subtropical Zone of the Northern Hemisphere
- Animals of the tundra
- Animals of the Temperate Zone of the Northern Hemisphere
- Animals
- Shrews
- Shrews
- Endangered animals
- Red Book of the Amur Region
- Red Data Book of Kaluga Region
- Red Book of Kamchatka
- Red Book of Karelia
- Red Book of the Moscow Region
- Red Book of the Ryazan Region
- Red Book of Siberia
- Red Data Book of the Tver Region
- Laurasiotherium
- Insectivores
- Insectivores
- Placental
- Vertebrates
- Rare animals
- Rare animals of the world
- Rare animals of Russia
- Chordates
- Ghostostomes
- Quadrupeds
- Eukaryotes
- Eumetazoans
What does a shrew eat?
Photo: Mouse shrew
The shrew spends almost its entire life searching for food, because to maintain the required body temperature and replenish all energy costs, they need a lot of food.
Interesting fact: during the day, the shrew consumes a large amount of food, the weight of which is almost twice the weight of the animal itself.
The diet of these miniature predators consists almost entirely of insects. The shrew menu consists of:
- Slugs;
- Medvedok;
- Listoyedov;
- Spiders;
- Snails;
- Caterpillars;
- Woodlice;
- All kinds of larvae;
- Earthworms;
- May beetles.
The shrew can also attack lizards, small mice, and frogs. Water shrews happily eat small fish and amphibians. The hardest time for these small animals is in the harsh winter, when the ground freezes and it is very difficult to dig out anything from under the snow. In winter, shrews can also eat seeds of various plants, but rare specimens survive until spring.
A keen sense of smell and excellent sense of touch help the animals search for food. There is no division into the day of shrews into night and daytime; they are divided into periods of hunting and sleeping. The gluttony of animals, of course, is amazing, but their life depends on it, because the metabolism of these little ones is very intense.
Interesting fact: shrews will not last long without food; in the summer they can go without food for about 10 hours, and in the winter - only 3. After this time, the animal dies if it is not refreshed. This is how interesting their body is.
Features of character and lifestyle
Photo: Garden shrew
Even today, little is known about the habits and behavior of shrews, because they have not been sufficiently studied, because they lead a mainly twilight lifestyle and are almost all the time in the bowels of the earth. Males and females are practically indistinguishable in appearance.
By nature, these animals are loners, each of them has their own land, which they carefully protect from strangers. A shrew can fiercely fight for its allotment of land against uninvited guests; it is not afraid to attack larger mice and lizards. Her temperament is very aggressive and hot-tempered.
On the other hand, this animal is very unbalanced and timid, the shrew’s nerves are not right; it can literally be scared to death even by a thunderstorm. Hibernation is unusual for these animals, but when there is little food, the shrew falls into a kind of short-term torpor, and its body temperature drops sharply at this moment.
Short-tailed shrews, which are registered in Canada and the USA, and water shrews, which live in our country along the banks of reservoirs, are poisonous animals, the bite of which is very painful even for humans and causes swelling of the bitten area, and for many small animals such a bite is simply fatal.
As for the life expectancy of a shrew, it is very short-lived and is only about one and a half years. It has been observed that females live a month longer than males. This is the interesting and dual nature of shrews: on the one hand, they are very nervous and timid, and on the other, they are aggressive and unpredictable.
Methods of counteraction
Of the methods used today, the most effective can be considered the one that is safest for humans and pets. When there are few animals, then in order to get rid of shrews in a summer cottage, it is advisable to use preventive, physical and folk methods of repelling. If their population increases, which leads to serious crop losses, unfortunately, it will not be possible to do without radical control methods.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of the pest, preventive work is carried out:
- install a barrier in the form of a fine mesh made of plastic or metal along the perimeter of the garden (to a depth of 1.5 m);
- dig up the land to a depth of 20-25 cm;
- lay a fine metal mesh before sowing lawn grass.
Traditional methods
Various homemade devices for scaring away animals and traps with bait are considered proven and quite effective in use.
To make the simplest mechanical repellers, ordinary household waste is used - tin, plastic or glass jars and bottles.
To remove shrews from the site, experienced gardeners advise:
- dig bottles into the ground at an angle of 45° or wooden sticks with tin or plastic cans on them. Under the influence of wind, a noise or hum arises in them, scaring away the animals;
- plant low-growing marigolds, onions, garlic, mint, lentils, hazel grouse, legumes and other plants that have a persistent aroma around the perimeter of the garden.
To scare away shrews, a pipe with a door that opens only inward is installed in the underground tunnel. Earthworms are placed in it as bait. After the trap is triggered, the animal is taken far beyond the boundaries of the summer cottage.
Physical
The most effective and simplest way to get rid of shrews in the countryside is with ultrasonic devices that affect the animals’ well-developed hearing organs, causing them to feel panic, forcing them to go in search of a quieter home.
"Grad 550 UZ" generates high-volume ultrasound, which has an uneven wave pattern, which prevents pests from becoming accustomed to the action of the device
Ultrasonic devices create sound of a certain frequency, which spreads over approximately 400-500 m2 or more (depending on the modification). For example, the action " Tornado OZV.01" is based on the settings of an electronic timer. A vibrating sound (lasting 10-15 seconds) is heard every 45-50 seconds and, amplifying many times, spreads over an area of up to 1000 m2.
Chemical
This method is the most radical way of pest control and is used when too many holes interfere with the normal growth of vegetables, cereals and other crops, and root crops literally fall into the ground.
These chemicals contain toxic substances that cause paralysis of the respiratory system, causing animals to quickly die.
Rodenticide preparations of domestic and foreign production
Among the most effective pesticides (rodenticides) are:
- "Hunter Antirodent";
- "Nutcracker";
- "Rat Death"
It is important to remember that children, pets and beneficial insects can be harmed by chemicals. When working with pesticides, you must strictly observe safety precautions and not violate the dosage specified in the instructions.
Social structure and reproduction
Photo: Baby shrew
As already mentioned, shrews prefer a solitary existence in their own isolated territory. These animals reproduce from one to three times a year. Gestation lasts 2-3 weeks. A litter can have from 4 to 14 babies, who are born blind and hairless.
The proboscis of newborns is poorly developed, so the babies look slightly snub-nosed. In a favorable period during the summer season, one female can raise about forty children, and some young animals manage to have their own offspring in the same summer.
Interesting fact: both parents build a nest for future offspring, although scientists have not yet established whether shrews are monogamous or polygamous.
On a soft bedding of dry leaves, babies grow and become stronger very quickly, and within a month they become completely independent. It is interesting to watch how a shrew and its offspring move in single file, holding each other’s tails with their teeth. From a distance it resembles a train, where each of the children acts as a trailer. If, after all, the cub manages to get lost, then he announces this with his squeak, the mother stops the “train” and looks for the loss, then the movement of the locomotive resumes.
It is worth mentioning the extraordinary ability of shrews, called the “Denel phenomenon”, it is characterized by a decrease in body size with the onset of autumn cold, the skull becomes flatter. In April its size increases again. This is how much unusual lies in the short life of such a miniature creature as a shrew.
Reviews from gardeners
Konstantin, 64 years old, Rostov
The simplest methods helped to scare away shrews from a summer cottage: acoustic and “aromatic”. Before the autumn digging of the garden, dried marigolds crushed into dust were scattered, and rags soaked in turpentine were buried along the entire border of the plot. Pieces of rotten fish were placed in the holes. In case the shrews bypassed the bait, additional metal reinforcement was dug into the garden bed at a slight angle to the ground, to a depth of 40-50 cm. A plastic bottle was placed on it, which moved with a light blow of wind, and the noise from the vibration of the steel rod scared away the animals. Champagne bottles, also at an angle, were buried in the ground - the effect was the same - an unbearable roar was heard.
Veronica, 56 years old, Ryazan region
In the garden plot we did not decide to use poison or traps for humane reasons, so we save ourselves from shrews using the Grad ultrasonic device. I insert batteries into the device, seal it in a plastic bag and dig it near the holes to a depth of 10 cm. After 2-3 weeks I observe the complete disappearance of the pest. At the same time, ultrasonic waves do not have a harmful effect on animals and people.
Semyon, 48 years old, Krasnodar region
In my apiary in mid-November, a shrew got into the habit of emptying the hives. It is more dangerous than ordinary mice because it is small and very voracious. To drive it away, I placed a fine-mesh (size 6 mm) grate between the bottom and the lower body, but the tight holes prevented the bees from exiting. In March I replaced it with a mesh with 8-10 mm cells. In addition, I cleaned the hives of dirt and placed a pollen collector on the entrance. After that, all the problems with pests disappeared.
Natural enemies of shrews
Photo: Great Shrew
Shrews' small size makes them vulnerable to many larger animals. They often become victims of both nocturnal and daytime birds of prey. Weasels, ferrets and other small predatory animals can feed on shrews. They often become victims of attacks by foxes and ordinary cats and dogs.
These animals confuse shrews with mice, but, having taken such prey into their mouths, they immediately feel their mistake and often refuse such a snack. It's all about the fetid musky aroma that insectivores emit; because of it, many predators eat shrews very reluctantly and only when there are no other options for food.
One of the enemies of shrews is a person who destroys these animals, considering them pests of fields, gardens and vegetable gardens. Of course, the shrew is capable of damaging the root system of cultivated plants in pursuit of any insects, but it also brings great benefits to the land. With its proboscis, the animal skillfully loosens the soil, which is saturated with oxygen, while at the same time the shrew destroys entire hordes of harmful insects and their larvae.
Interesting fact: shrews destroy a large number of insect pests, even in places where birds cannot reach them.
Unfortunately, people see only harm in the activities of shrews, although this is not at all the case. Among other things, many shrews die during the difficult winter period due to lack of food, rarely surviving until warmer times.
Video
Experienced gardeners share educational information about the life activity of shrews and ways to repel these insectivores in the following videos:
Sources
- https://poklopu.ru/drugie-vrediteli/zemlerojka.html
- https://moypitomec.ru/dikie-zhivotnye/mlekopetayushhie/zemlerojka-foto-i-opisanie.html
- https://ogorodum.ru/kak-izbavitsja-ot-zemleroek-na-uchastke-samyj-jeffektivnyj-sposob.html
- https://luckclub.ru/pro-zemlerojku-kak-borotsya-s-zemlerojkami-na-sadovom-uchastke
- https://wildfauna.ru/zemlerojka
- https://urozhajnayagryadka.ru/kto-takaya-zemlerojka-i-kak-s-nej-borot-sya-na-ogorode/
- https://prusakam.net/zemlerojka/
- https://www.ivd.ru/stroitelstvo-i-remont/dacnyj-ucastok/kak-borotsya-s-zemlerojkoj-na-dachnom-uchastke-10-sposobov-59531
3 633
Population and species status
Photo: Shrew animal
As was said, shrews are widespread almost throughout the globe, with the exception of some areas, but the state of their population is quite ambiguous, it all depends on one or another variety of this animal. The population size of many shrews is stable and not subject to any threats, and some species are considered endangered and are listed in the Red Book.
If we talk about the shrew family as a whole, then only some species are considered endangered, and the numbers of other species do not cause any concern. We should not forget that these interesting insectivores have about three hundred varieties, so they are quite numerous and widely distributed across various continents, countries, regions and regions.
Reasons for appearance
Shrews, like other similar creatures, constantly carry out natural migrations in search of suitable places for their livelihoods. But this does not mean at all that it can appear in any area, since this requires certain conditions. Even if there is a lot of food in the area, but there is little moisture, the shrew is unlikely to appear. Hard soil that is not watered or does not have natural moisture does not allow the animal to dig long passages. Therefore, this animal is most often found near water bodies or in areas that are watered on a regular basis.
Shrew