The word "desert" comes from the Latin "vastus", which means empty, lifeless. But in this seemingly uninhabited space, many species of living organisms live. To adapt to existence in harsh climatic conditions, desert animals have developed specific abilities. Most of them escape the heat in a simple way: their activity is confined to the cool night hours. During the day they try to hide in the shade or burrow. Many representatives of the fauna spend a particularly unfavorable time in hibernation. They hide and slow down their metabolism to save energy and water. Large mammals cool their bodies through evaporation. What animals live in the desert, and how did they learn to adapt to extreme conditions? You can learn about this from this article.
Characteristics of the desert
A desert is a special natural zone characterized by flat terrain, minimal vegetation and specific fauna.
Geographical position
There are sandy and clayey deserts; a special type of desert is the Antarctic. The largest desert on the planet is the Sahara. Its area is 11 percent of the total land area, and if we take into account the Antarctic desert, then about 20 percent.
Deserts are found in the temperate zone of the northern hemisphere and in the tropical and subtropical zones of the southern hemisphere. These areas of the Earth are characterized by a special climate with very little precipitation (about 200 mm per year).
The formation of deserts was natural: they appeared in those parts of the planet where there is very little or no moisture. The reason for such an arid climate is its proximity to the equator and separation from the sea by mountains.
A list of deserts in Africa and the world is presented in the photo.
Relief and climate
The relief of the desert zone is very diverse. Plains predominate, there are small hills, island mountains, river valleys and lake depressions. There are also rivers in the desert, however, they only cross this zone (Nile, Amu Darya), there are also drying up reservoirs (Lake Chad, Air). Groundwater is highly mineralized. The soil is poorly developed: there is little organic matter in it, and salts predominate in its composition.
The climate here is sharply continental, characterized by cold winters and very hot summers. Precipitation is rare: once a month, but it occurs less often - up to once a year (heavy rain may occur). Small rains simply do not reach the Earth's surface, evaporating due to high temperatures.
Russian desert
Russian deserts are located in the South-East of the country, closer to the city of Volgograd and stretch towards Kazakhstan, then sharply turn towards the Caucasus.
On the territory of Russia, a significant part of the deserts is located where the seabed used to be, this area is now called the Caspian Lowland. The relief here is very peculiar - lowlands are located throughout the entire territory, so the local landscape evokes strange emotions. Closer to the west you can find small hills made of sea salt.
Near the Caspian Sea there is a real desert with clay soil and completely flat terrain. In some places you can see sand, which is not blown away by the wind due to the roots of the elymus bush. An amazing fact is that the flora and fauna of the desert is much richer and more diverse than the northern part of our country.
Water bodies
The desert zone has a very dry climate, most of the precipitation that falls here evaporates, despite the fact that there is very little precipitation here. Therefore, there is a pronounced deficit of terrestrial fresh water, mainly transit rivers. There are small rivers here, but most of them dry up during the dry summer period.
The situation is further aggravated by the fact that the groundwater here contains a large amount of salt and is located at great depths. Thus, the rivers simply have nowhere to come from.
The peculiar relief of deserts contributes to the formation of lowlands and hollows, in which small lakes sometimes form. The water in them is saturated with salts, so it has a pronounced bitter-salty taste.
Indigenous people
Living conditions in the desert are close to extreme, but from time immemorial people have existed here too. The main difficulty of life in the desert was the lack of water and high temperature. However, there are no predatory animals here that could pose a serious danger to humans. Bedouins in the desert hunted kulans, goats and other local animals. The harsh living conditions contributed to the fact that people united and learned to stand firmly for each other.
The most ancient desert territory that was developed by man is located on the territory of the modern United Arab Emirates. Here, at present, as many centuries ago, local residents value their family most of all.
Climate
In some deserts, especially those located near the equator, there is heat and drought all year round, and the temperature there sometimes reaches +50 °C. Others, like the Gobi Desert in Mongolia, are cold and windy. There, high mountains block the path of warm, humid air flows, and in winter the temperature can drop to -20`C.
Gobi Desert in southern Mongolia
Animal world
The desert climate is extremely unfavorable, but the fauna here is very diverse.
During the day, when the heat reigns and the air temperature reaches its maximum, it is unlikely that you will be able to meet anyone except insects, lizards and a few birds. In the evening, the world of the desert comes to life along with its inhabitants.
Camel
Perhaps the most famous animal living here is the camel. Locals call it the ship of the desert. The camel received its nickname due to its inherent adaptability to local conditions.
The camel's body is capable of storing water and fat in its humps for quite a long time, so they can move for a long time without an additional source of nutrition. Because of this wonderful skill, locals use camels for cargo and passenger transport. In addition, in the east the camel is highly valued and is often used as currency.
fennec fox
A cute and funny animal at first glance that looks like a fox and a cat at the same time. The animal's muzzle with large, expressive eyes evokes particular affection.
The body of the animal is small, weighing no more than one and a half kilograms. A characteristic feature is disproportionately large ears and tail. Fenech has cat-like agility and can easily climb a tree. Makes peculiar sounds, peculiar only to him: they look like a roar, squeak, and snort at the same time.
Hunts birds and rodents at night, has speed and agility. It can also use plants and fruits for food. The fennec's body is designed in such a way that it only needs moisture from food, so the animal can go without water for a long time.
jungle cat
Back in Ancient Egypt, local residents used this animal to hunt ducks. These animals are excellent hunters, dexterous and strong, but they will not engage in a fight with an obviously strong opponent.
Externally, the jungle cat is similar to a domestic cat, but somewhat larger: the weight of an adult can reach 15 kilograms, the body length is about 80 centimeters.
Another name for this animal is the swamp lynx. The jungle cat makes sounds similar to a lynx and has distinctive tufts on its ears. The cat hunts birds, hares and other rodents in the dark.
Horned viper
This snake is one of the most poisonous on the planet. This fact has been known for a very long time, so local residents diligently avoid meeting her. The reptile's appearance is truly terrifying, mostly due to its impressive size and the presence of horns on its head.
The color of the snake can vary from olive to brown. The body length can reach 70 centimeters, the body is massive and thick. The viper uses a lateral movement to move. Reptiles live alone and pair up only for the breeding season. The snake practically does not need water and only during the breeding period does it find a place near a reservoir.
Gazelle Dorcas
A very beautiful, miniature and playful animal. The weight of an adult does not exceed 20 kilograms with a body length of about a meter. Nature has made it so that the gazelle can hide from its natural enemies - predators, so the animal can reach speeds of up to 100 km/h.
Gazelles live in herds of about 100 individuals and are capable of creating families. When danger arises, the gazelle makes a special loud sound, warning its fellow tribesmen.
These animals are perfectly adapted to the conditions in which they have to exist. They get all the moisture the body needs from plants they eat. Gazelles are able to survive in very high temperatures, with their peak activity occurring in the early morning and late evening.
Addax
Representative of the equine order. Addax tends to change the color of its coat depending on the time of year: in summer it is white, in winter it darkens to a brown tint.
Addax or mendes antelope
Dromedary or dromedary camel
Gazelle Dorcas
Dung-beetle
Horned viper
Varan
Aldabra giant tortoise
Yellow scorpion or deadly hunter
It won't actually kill a healthy adult, but it can cause serious pain, but it will succeed in killing children and the elderly. They are often sold as exotic pets, which is very dangerous.
African ostrich
Their legs are very strong and they use them to drive predators out of danger. They have excellent vision and the ability to hear well, which is their main defense mechanism. They feed mainly on grass and shrubs, sometimes also on small animals.
wild dog
African wild dogs are more densely populated in the southern savannas, but isolated packs are also found in central and southern Sahara. Wild dogs are successful in 90% of their hunts because they are known for their strong herding instinct; after the kill they make sure their old and sick and puppies are well fed.
Saharan cheetah
This subspecies hunts more in the dark than normal cheetahs, one of their many behavioral adaptations to survive the harsh climate of the world's largest desert. Another important adaptation is that they can withstand much longer periods of time without water, which they extract from the blood of their prey.
Fenech
Since the name of this species comes from the Arabic word - fanaka - the name of this animal actually means "fox". The Fennec fox is the smallest canid (members of the dog family, including wolves, jackals and other foxes) in the world. Fennecs have a very pale coat color, which helps them reflect most of the sunlight that falls on them.
American Cocker Spaniel. Description
Their kidneys are also desert-adapted and designed to minimize water loss from their body. In addition to its naturally strong sense of smell, the fennec fennec relies more on its incredible hearing.
Its ears are so sensitive that it can track its underground prey using sound! They can even climb trees to reach young birds and eggs if the tree has low branches.
Jerboa
A member of the rodent family, the jerboa is able to withstand the extremely harsh conditions of the Sahara Desert. His main defense is his amazing ability to jump and run at an average speed of about 25 kilometers per hour. Their diet mainly consists of desert plants, insects and seeds, from which they get all their moisture, so they don't need to drink much water.
baboon anubis
These baboons are found in many parts of Africa, but can also be seen in the mountainous regions of the Sahara Desert.
This baboon's coloration appears greyish-green from a distance, but closer observation reveals that it has a multi-colored "coat". Males are noticeably larger than females, with a large mane.
Anubis baboons survive well due to its diversified diet, which includes plants, birds and even small mammals.
Nubian Bustard
A subspecies of the bustard family. Males weigh over 4.5 kg, are about 75 cm long, quite large compared to females, 2.7 kg and are 63 cm long or so. They mainly feed on insects, but, if necessary, plant seeds. Due to habitat loss, their numbers have declined and they are considered endangered.
desert hedgehog
This desert hedgehog is a very small type of hedgehog with an average weight of 350 grams. When threatened by a predator, it strongly tenses the muscles that stretch the skin all over its body, causing its spines to stick out in all directions. The diet consists mainly of insects, but it may also eat eggs and vegetation for survival.
Slender Mongoose
The slender mongoose is also known as the black-tailed mongoose due to the black tip of its tail. It primarily feeds on insects, but its diet also includes lizards, rodents, snakes and birds. It can also kill and eat a poisonous snake, but does this only when there is a threat and climbs trees very well, compared to a regular mongoose
spotted hyena
The spotted hyena is also known as the "laughing hyena". The species is not yet endangered, but its numbers are rapidly declining due to poaching and habitat loss.
Compared to most other striped hyenas, this type has spots, but the color of its fur changes quite a bit as it ages.
Despite the fact that hyenas are scavengers, the spotted hyena primarily hunts its prey and this is the main reason for its high survival rate.
Considering the Sahara Desert and its hostile climate, it is difficult to imagine how these animals stay there. But over time, they evolved and adapted to this place, where every day is a race - a race for precious water, food and survival.
Source: https://joinfor.ru/zhivotnye-pustyni-sahara/
Vegetable world
Nature is very prudent: living organisms, including plants, are adapted to unfavorable living conditions due to their special structure.
Characteristic features of desert plants are:
- Low height.
- Fleshy leaves.
- Long roots.
Thanks to a powerful root system, the plant cover penetrates deeply into the soil and takes up the maximum amount of moisture, and large leaves do not allow moisture to quickly evaporate.
Cactus
Various types of cacti are the most common plants in this natural area. The shape and type of cactus can be varied; common features are the presence of a massive body and spines. Many cacti are long-lived and can survive for about a hundred years.
Baobab
A typical desert tree is the baobab tree. This plant is long-lived: it can exist for a whole millennium. The baobab has a powerful trunk and a developed root system, and its height depends on the amount of groundwater in the place where it grows: the more there is, the taller the tree.
Jojoba
The valuable medicinal plant jojoba grows in the American deserts. Essential oil is produced from its fruits, which is one of the most beneficial for skin and hair. Jojoba oil is widely used in cosmetology.
Prickly argan
Prickly argan grows in the Sahara Desert, mainly in Morocco. A unique healing oil is obtained from the fruits of the plant, which is used in cosmetology and medicine. The wonderful properties of this oil were known in ancient times, which is why the Arabs call it liquid gold.
Also, some types of grasses, camel thorns, and tumbleweeds grow in the desert.
During the rainy season, the flowering period of grasses begins. The desert landscape changes beyond recognition: the bright carpet of flowering plants amazes the imagination.
Water bodies
Unlike areas of broad-leaved or tropical forests, there are practically no large rivers or large bodies of water. However, there are exceptions - the Nile River, crossing the Sahara, the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers, filled with water from melting mountain glaciers and laid channels through the Karakum and Kyzylkum deserts. But dry, lifeless river beds tens and hundreds of kilometers long still predominate.
In the center of the Sahara there is a unique complex of 18 lakes called Ounianga, although here the average annual precipitation rarely exceeds 2 millimeters. These lakes were formed due to underground water flows in those distant times when the climate of the Sahara was still humid.
Even proximity to the ocean is possible. For example, the Namib Desert stretches for 2000 km along the African coast.
But the most famous water bodies of this unique world are the oases. In these places, groundwater comes very close to the soil surface. In oases you can find not only water, but also an abundance of food. Oases can look like small ponds surrounded by date palms, or like real cities inhabited by large numbers of people.
Arctic deserts are distinguished by the almost complete absence of swamps and a very small number of lakes. Glaciers are a kind of water body here, which are formed as a result of climate influence. Arctic glaciers reflect the sun's rays, so the planet is not heated to dangerous levels by the sun.
Birds and insects
Like other living organisms living in the desert zone, birds manage to exist thanks to the adaptability of their body. The feathered inhabitants of the desert are characterized by a special structure of their kidneys and thick plumage that protects them from the heat.
Sandgrouse
Representatives of this order live in Asia and North Africa. Powerful wings help birds travel long distances in search of food and water. In his thick plumage, the male hazel grouse brings water to the female and chicks.
Bustard
The bustard is a very large bird that lives in the deserts and semi-deserts of Eurasia. The height of the bustard can reach one and a half meters, the wingspan is about 2.7-2.8 meters. Males are much larger than females.
The bird uses shoots and fruits of plants, insect larvae, and various worms for food. It leads a predominantly sedentary lifestyle, but in search of a more favorable habitat it can travel quite long distances.
Ostrich
The ostrich is the largest bird on Earth and lives mainly in African deserts. The name of the bird translated means camel sparrow. Surprisingly, the ostrich is simultaneously similar to these two animals.
The bird is truly enormous in size: the average height of an adult is about 2.5 meters, weight is about 50-75 kilograms, the record weight is 130 kilograms. It is noteworthy that despite such impressive size, the ostrich’s brain is about the size of a walnut: the bird has very low intelligence.
The ostrich compensates for its lack of intelligence with caution; while eating, it often raises its head and assesses the situation; in case of the slightest danger, the bird begins to run away. The running speed is very high, the ostrich can accelerate to 70 km/h; during the chase, it can turn sharply without changing speed, or fall sharply to the ground.
Saxaul jay
The saxaul jay is a small bird that lives in the deserts and semi-deserts of Eurasia. The jay's weight does not exceed 90 grams; an adult has a dull color, predominantly sand and brown.
Rodents
Many desert animals are constantly in danger and struggling to survive. Rodents are small representatives of fauna. Their activity increases with the onset of dusk, when the heat subsides. At this time, the search for food begins.
Jerboa
This is a small mammal that belongs to the order of rodents. It adapts perfectly to any climatic conditions, so it also feels good in the hot desert. The length of the animal can reach from 4 to 25 cm. A special feature is its tail, which is 3 times larger than the body length. Searches for food at night and sleeps during the day. The diet includes fruits, grains, roots of bushes and trees, as well as small insects, worms and larvae.
It has developed limbs, thanks to which it runs quickly and escapes from enemies. The muzzle is large, flattened on the sides. The sense of smell is practically absent, but thanks to their long whiskers they find food for themselves.
Interesting fact! All the jerboas were clean. They can brush their fur up to 30 times per day. And the smallest representative fits in a tablespoon.
Spiny mice
An amazing animal that reaches a length (including tail) of only 14 cm. The head is small with large black eyes like buttons and round ears. The rodent's back is covered with light spines, like a hedgehog's.
They are usually gray or pale yellow. White and soft hairs grow on the lower part of the body. Males differ from females in that their fur is longer and forms a kind of mane on their neck.
Spiny mice can shed their skin when in danger. It is not as durable as other mice. Regeneration in rodents occurs quickly and scars do not form at the wound site. They live in Saudi Arabia, Africa, the islands of Crete and Cyprus.
North African gundi
These small animals live in rocky deserts and semi-deserts. Shelter is found in crevices, under rocks. Their ribs are able to flatten, so they are able to crawl into narrow crevices of rocks. They have small and flat ears, as well as large eyes.
The length of their body is 16-23 cm, and the tail is from 1 to 6 cm. The fur, like that of a chinchilla, is soft and fluffy, it perfectly protects animals from cold and heat.
Gundis travel long distances to find food. They feed on plant seeds, grass, leaves, and stems. They live in families. With peculiar cries they notify their relatives of the approaching danger.
Desert hedgehog
The desert or long-eared hedgehog lives in the semi-deserts of Africa. Body length 13-27 cm, weight up to 500 g. The needles on the back are thin and short. The muzzle is covered with light hair, the eyes are small and black, and the ears are quite large. This small desert animal comes out to hunt after dark.
Eats locusts, centipedes, spiders, scorpions. Thanks to its strong jaws, it deftly grabs its prey and pulls it out from under the soil.
Rare species
Uncontrolled human intervention in nature causes irreparable harm to it. This happened with deserts: many of its inhabitants are now on the verge of extinction.
Baybak
The baybak is a species of ground squirrel native to the deserts of Eurasia. Today, these animals are practically exterminated due to uncontrolled hunting of them.
The baybak is a fairly large rodent: the body length is 50-70 centimeters, the weight of the male can reach 6 kilograms. The animal consumes plant foods for food, preferring soft ones: oats, clover. The boibak does not require water; the moisture received with the food is sufficient.
Varan
The monitor lizard is a huge lizard. Currently, there are several species of these animals; they mainly inhabit the desert zones of Australia, Asia and Africa. The monitor lizard population is rapidly declining.
These animals are dangerous predators. Their huge jaws and sharp fangs are capable of destroying almost any mammal. Monitor lizards do not get full for long and can go without food for several days.
There are several varieties of monitor lizards, the largest of which live in the deserts of Australia. The length of these individuals can reach 6-7 meters. Relatively small monitor lizards live on the territory of Kazakhstan. All monitor lizards are active during the day; at night they hide in their burrows. The monitor lizard is an aggressive predator; it attacks everyone it can cope with: smaller brothers, mammals, birds, insects.
Jeyran
The gazelle antelope has the status of an endangered animal and is listed in the Red Book. Their habitat is the deserts of Kazakhstan.
Dzheyran is a graceful and slender animal. The average height of an adult is 50-70 centimeters, weight up to 30 kilograms. The head of males is decorated with long curved horns. The color of the animal is brown-sandy, the back is darker, the legs are almost white.
Animals eat plant foods, preferring cereals. The body is adapted to obtain the necessary moisture from the food it eats. Antelopes are active during the day, and in the midday heat they are most often located close to the reservoir.
Scorpios
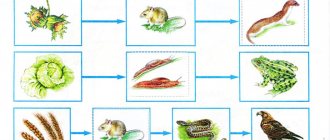
Centipedes are followed by the second link in the chain called “Who Eats Who in the Desert.” Scorpions often become killers of small arthropods, so they rightfully occupy third place on the list. They are found only in hot countries, however, science knows of 1,750 different species. Only fifty of them are poisonous to humans. Their unique feature is recognized by their long history: they are the most ancient of terrestrial arthropods. By studying scorpions, you can learn a lot about the evolution of animals, trace their development path from a marine lifestyle to a land one. Like centipedes, these desert animals, whose names are known to everyone, are nocturnal, hiding in rock crevices during sunny hours. Fast running and strong claws help them kill insects and arachnids.
The meaning of the desert for nature and people
The natural area is of primary importance for human agricultural activities. Livestock farming is very developed here; vast areas of the desert serve as pastures for domestic animals. Sandy deserts are the most valuable in this regard - there is enough fodder for livestock even during the dry season.
The warm climate is very favorable for growing many crops. In oases, with proper watering, white gold - cotton - is successfully grown. Delicious melons, grapes and other fruits and vegetables are also grown here.
Deserts and semi-deserts play an important role in the planet's ecosystem. Researchers have found that the soil of these places is very rich in carbon, and the atmospheric nature of the gas has been established. Thus, these natural areas participate in the formation of the planet’s carbon balance.