This beetle is found in Western Europe, in Russia to the Ural Mountains, and in Central Asia. This is a beautiful, large predatory beetle. The period of its activity occurs in spring and summer; in autumn and winter the insect hibernates. The odorous beetle is listed in the Red Book; its numbers are gradually declining due to the deforestation of broad-leaved forests. The “odorous” beetle gets its name from the stream of smelly liquid that it releases to protect itself from the enemy.
The odorous beetle is a small beetle with bright colors
What are the features of the life cycle
Before turning into a beautiful beetle, the insect goes through a series of transformations. Its life cycle includes the following stages:
- Egg. A female beetle can lay eggs 2-3 times per season. The period of active mating takes place in late spring and early summer. A clutch can contain up to 600 eggs. It all depends on the productivity of the female, weather conditions, and the amount of food supply.
- Larva. After a couple of weeks, large white larvae emerge from the laid eggs. They do not leave the egg shell for some time until they are covered with hard black scutes. After this, the larvae begin active hunting; we can say that they are more aggressive in search of food than their adult relatives and can search for food for themselves day and night. The larva undergoes several molts, and after that it burrows into the ground and pupates.
- Doll. By the end of summer, new cockchafers are formed from the larvae, but they do not leave the cocoon shells and overwinter until next spring. Next year, as soon as it gets warmer and the snow melts, adult young cockchafers will emerge from the pupae.
- Adult insect. An active and voracious predator. One beetle can destroy up to 600 silkworms during the summer. In the fall, at the end of the warm season, the insect burrows into the ground and hibernates, waiting for the next spring.
On average, the lifespan of the beetle beetle is 3-4 years.
Threat to beetles and protective measures
The number of entomophages is constantly declining in all known populations. One of the reasons why the odorous beetle is disappearing is the massive deforestation of forests, which are the habitat of the insect. Negative factors also include the use of insecticides in forests and the destruction of litter by grazing livestock in floodplain plantings. To prevent beneficial insects from disappearing, protective measures are being taken. The odorous krasotel is listed in the Red Book of Russia and Ukraine, it is included in the European Red List. In the habitats of ground beetles, the use of pesticides is limited, and new individuals are artificially populated.
What are some interesting facts?
This beetle is an interesting insect and has been the subject of research and observation by scientists for a long time. Among the most interesting facts regarding the fragrant beetle are:
Read on topic:
Features of the life activity of ladybugs
14.11.2020
Description of chironomids and their possible danger to humans
14.11.2020
What do cutworms look like and what harm do they cause?
14.11.2020
What do goliath beetles look like and can they be bred at home?
14.11.2020
- Attempts to breed this insect in captivity often ended in failure; the beetles did not lay eggs, but simply devoured each other.
The beetles are very beautiful, but dangerous; the bite can cause pain and irritation
- Due to an unsuccessful experiment with breeding gypsy moths in America, there was a sharp increase in the population of this pest. Significant damage was caused to the green foliage of the forests. In order not to use insecticides to treat the forest, a more humane decision was made to import a natural biological predator into the country.
- The beauty larva is twice as long as the adult;
- The coloring of the insect serves as a means of protection and repels potential enemies of birds and small rodents.
- The insect can live a relatively long time for individuals of its species, up to 4 years.
- Despite the attractiveness of the insect, you should be careful with it, it can bite and cause irritation with the poison that it releases from the glands on the abdomen.
- In 1919 in Germany, due to the presence of a large food supply, there was a real dominance of deciduous forests by beetles. As one of the eyewitnesses writes, rustling sounds were heard from all sides, both in the foliage and in the trees - the beetles were hunting for their prey. The forest has definitely come to life.
Larvae
The larvae of the odorous beetle are large, covered with black plates on top. There are dark dots on the sides. The jaws of the larvae are powerful, the paws are already becoming tenacious, which allows them to walk not only on horizontal surfaces.
Krasotel is active from May to September. In the spring, ground beetles travel long distances to find prey. During the day they are in shelter, usually under stones or in leaf fall. At night, insects go out hunting. When danger approaches, the beetle runs away or shoots liquid from the anal glands.
What does it eat?
The odorous beetle is an active hunter. Moreover, it can eat not only other insects, but even its own relatives. His diet usually includes:
- caterpillars;
- butterflies;
- small animals.
The beetle usually feeds on caterpillars.
The beetle looks for its prey in the grass, on the ground, in the crowns of trees, and in bushes. There have been cases when the beetle attacked chicks in nests that were not yet covered with feathers. If this predator catches its prey in a tree, then it prefers to go down and continue to eat its prey on the ground.
The beetle processes the prey with special digestive enzymes, its contents soften and become digestible for it.
The odorous beetle is extremely aggressive; if it eats a prey, it knocks its paws, makes noise and can even release a stinking, caustic liquid. If it gets on the mucous surfaces of the body, an allergic reaction may occur and a severe allergic reaction may begin. Therefore, after contact with beetles, you must wash your hands and keep its back part away from you.
Spreading
The distribution area includes broad-leaved and mixed forests of Europe to the south of England and Sweden. The eastern border of the habitat is the Southern Urals. A representative of the ground beetle family is found in Iran, Afghanistan, and the mountains of Central Asia. The insects are recorded in northern Africa. In Kazakhstan and Northern China.
In the 19th century, an experiment with silkworms took place in the United States; its result was a massive and uncontrolled spread of the pest. To combat gypsy moth caterpillars, Calosomasycophanta was introduced to North America. The beetle has acclimatized and spread to Canada and the United States. In Russia, it lives in the forest-steppe of the European part, in the forests and old parks of the Urals, Crimea, and Altai. The beetles were recorded in the Kaliningrad region, and in the Moscow region - in a single specimen.
Useful or harmful
The fragrant beetle is a beneficial insect. This is expressed in the fact that no one except him can cope with silkworms and poisonous caterpillars. It inhibits their uncontrolled growth and reproduction. Adult beetles destroy the caterpillars themselves, and its larvae have adapted to destroy silkworm nests from cobwebs.
FROM this video you can learn some interesting facts about these beetles:
In nature, there is no other natural biological “controller” for the growth of the population of harmful caterpillars.
Appearance
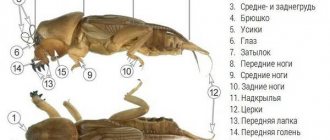
The body length of the insect is 35 mm. The beetle's body is elongated and its head is small. The beauty's eyes are large. The filamentous antennae are divided into 11 segments. The pronotum of the insect is dark blue. The greenish elytra with a golden tint have many parallel depressions. The ground beetle's abdomen is black, as are its legs. The limbs of the insect are well adapted for running. The beauty has quite powerful mandibles, which helps to hold the prey.
The most beautiful caterpillar in the world
Since we have already examined the most poisonous caterpillar in the world, we would now like to contrast it with the most beautiful and harmless one - the monarch larva. It is worth saying that even the name of this large caterpillar with a horn speaks for itself. A truly royal creature immediately appears, enchanting with its beauty and pleasing to the eye. Its main color is white and, if not for the bright yellow stripes on its back, the caterpillar would look like a zebra, because it is also completely covered with black thin stripes. She has three pairs of horns: two on her head, two on her tail and the same number in the middle of her body. They are located symmetrically to each other.
It is one of the most famous butterflies in North America. It is easily recognized by the characteristic pattern on its wings: black stripes located on a red background. The wingspan of the Danaid reaches 10.2 cm. This is one of the few insects that flies across the Atlantic Ocean during migration. In Russia, the species is found in the Far East.
Lemongrass is a long-liver in the world of butterflies
Gonepteryx rhamni, wingspan – 52-60 mm
Lemongrass, or buckthorn, is a rather inconspicuous-looking butterfly from the white butterfly family. Small dots are placed in the center of its wings, and the wings themselves imitate the shape of leaves on a tree. Nature has done its best so that these insects can hide from their enemies!
Males have a richer wing color than females. In the latter, the color of the wings is predominantly greenish-white. The development cycle of one individual takes about a year, which is a rare phenomenon in the world of butterflies. Therefore, lemongrass can safely be called a long-liver.
macroid.ru
Lemongrass lays 1-2 eggs on buckthorn leaves. Then green, smooth, slightly flattened caterpillars appear. Despite their great appetite and fastidiousness, insects do not cause much harm to trees.
How to attract lemongrass. Mostly butterflies feed on the nectar of dandelion, meadow cornflower, thistle, but they will not refuse cultivated plants. It is better to fight weeds that attract lemongrass in your summer cottage.
How to get rid of weeds - the secrets of “clean” beds Weed control is the main headache of all summer residents. Let’s figure it out together how to suppress the growth of weeds effectively and easily.
Fight with drugs
Pulled a muscle? Dissolve 1 tbsp. vinegar in 100 ml of water, moisten a piece of cloth with the liquid and apply to the sore spot for 30 minutes. The pain will subside. If you have a sore throat, prepare the following solution: add 1 tsp to 100 ml of water. apple cider vinegar and gargle every 1.5 hours.
After summer work, the skin of the hands often suffers. To get rid of cracks, mix your favorite hand cream with an equal amount of apple cider vinegar. Every evening before going to bed, rub the resulting product into your skin.
Here is a list of drugs trusted by gardeners.
- "Fozalon". Refers to organophosphorus insecticides with enteric contact action. It has high initial toxicity, creates a deep effect, and maintains high plant protection efficiency at low temperatures down to 12°C. Adults and larvae die within two days after using the drug. Not phytotoxic.
- "Aktara". A fast-acting, highly effective insecticidal agent that is used to spray the vegetative part of plants and treat the soil. Thanks to the active ingredient thiamethoxam, the drug does not accumulate in the soil. Regular use allows you to keep any harmful flora under control throughout the season.
- "Decis". This enteric contact insecticide is used in case of sudden mass attacks of the most harmful insects. It instantly kills any pest from flies, aphids and butterflies to sawflies, butterflies and beetles, with the exception of Colorado beetles, which die within 4-5 minutes. Remains on plants after rain, duration of protection is 14 days from the date of treatment. In one application, migrating insects are exterminated in whole batches.
- "Kinmiks". An insecticidal preparation based on beta-cypermethrin, a low-toxic household poison with a wide spectrum of action. Destroys mature individuals and larvae. The active substance enters the digestive organs, paralyzing insects, as a result of which they die.
- "Sumi-Alpha". A highly effective insecticidal agent belonging to the pyrethroid group. It has broad insecticidal and high lethal activity, repellent, antifeedant, and paralyzing effects. The drug can be used in combination with various types of fungicides or insecticides. The duration of protection is 14 days.
Spraying berry bushes with poisons is extremely effective and guarantees the death of the vast majority of caterpillars. However, this method has disadvantages:
- the use of such drugs can cause intoxication if a person consumes processed fruits;
- It is necessary to constantly change insecticides, since pests eventually develop immunity to the active substances in their composition.
Even modern varieties of gooseberries, obtained in the 21st century, included in the State Register, zoned in a particular region, quite often suffer from or are affected by various pests. Fortunately, at the moment there are a huge number of means of combating crop enemies, both chemical and folk (by the way, no less effective). Let's talk today about the most dangerous and common diseases and pests of gooseberries, as well as measures to combat them.
Ways to control various insects
To detect pests on bushes, it is necessary to monitor the plant from early spring. Green caterpillars on gooseberries begin to appear at a temperature of 16-18 degrees. How to get rid of them and what methods will be the most effective.
Sawfly
A common pest is the sawfly, which has a black head and yellow legs, making it attractive. The insect is most dangerous for gooseberries and currants. It destroys the plant in 2 weeks. The pest control method has several stages.
- In autumn, all fallen leaves are destroyed.
- Old dried branches are cut off.
- The soil is dug up to destroy the larvae that have lain down for the winter.
- The space under the bushes must be mulched.
- Before the buds appear, the soil is sprinkled with a mixture of two glasses of ash, one spoon of mustard powder and one spoon of ground black pepper. The soil is covered with film.
- You can also pour boiling water on the ground to destroy the pupae.
If the caterpillars have hatched from cocoons and come to the surface, they must be collected manually.
Spoiled bushes do not bear fruit for 2 years, since the growth buds do not develop. To avoid the appearance of sawflies, you need to plant tansy or elderberry next to the gooseberry bush. Insects also do not like the smell of turpentine, kerosene and gasoline.
Ognevka
The small butterfly has gray upper wings and appears harmless. She lays eggs in the buds or buds of the plant. Caterpillars eat flowers and prevent the ovaries from appearing. As a result of their activity, cobwebs appear on the shoots, the berries are eaten away from the inside, and the plant dies. To remove pests, you can use folk remedies.
- It is recommended to regularly dig up the ground under the bushes to destroy the larvae.
- Plant tomatoes and mint in close proximity to the plants.
- If you place a piece of roofing felt or roofing felt under a bush, ground beetles will appear in the area, eating moths and sawflies.
To save plants from pests, you need to leave enough space when planting. Good air exchange contributes to the health of the bushes, and the distance between them prevents insects from spreading quickly.
Moth
The bright orange caterpillar with black dots and head attracts attention. Pests completely destroy the leaves. After hatching, they begin to lay eggs three weeks later.
The emerging larvae eat the remaining leaves. The moth overwinters in dry fallen leaves and emerges in early spring. To combat it, you can use chemical or folk methods.
After hatching, they begin to lay eggs three weeks later. The emerging larvae eat the remaining leaves. The moth overwinters in dry fallen leaves and emerges in early spring. To combat it, you can use chemical or traditional methods.
- Be sure to get rid of fallen leaves in the fall and dig up the ground under the bushes.
- Plants should be treated with self-prepared decoctions of chamomile and shag.
- The bushes need to be sprayed with karbofos. The first time the treatment is carried out with the appearance of the caterpillars, the second time - 20 days before picking the berries.
Pests eat gooseberries, destroying not only the leaves, but also the fruits. The first sign of the appearance of a moth is holes in the green mass of the bush.
Currant glassberry
Small pests remain inside the branches even in winter. If signs of this pest appear, you need to start treating the bush. Control measures are as follows:
- To get rid of glass, carry out sanitary pruning in spring and autumn. Do not leave stumps, burn cut branches.
- In May-June, loosen the soil and further process it with the following mixture: 300 g of ash, 200 g of tobacco dust, a tablespoon of pepper and mustard. Scatter three tablespoons under each bush.
- When the butterflies begin to emerge, spray the bushes with a decoction of tansy, infusion of celandine or dry mustard. Treat the bushes with a chemical preparation only after harvesting.
Whatever methods of struggle are chosen, the main thing is to achieve the desired result. If spraying does not help the first time, then the procedure must be repeated.
Willow woodborer – Cossus cossus (L.)
The butterfly's forewings are gray-brown to dark gray with a marbled pattern and vague gray-white spots, as well as dark transverse wavy lines. The hind wings are dark brown with matte dark wavy lines. The chest is dark on top, whitish towards the belly. The dark abdomen has light rings. The male has a wingspan of 65-70 mm, the female - from 80 to 95 mm. The female's abdomen is completed with a retractable, clearly visible ovipositor. The caterpillar is cherry-red immediately after hatching, and later turns flesh-red. The head and occipital plate are shiny black. An adult caterpillar is 8-11 cm (most often 8-9 cm), then it is a yellowish meat color, brown on top with a purple tint. The yellow-brown occipital scute has two dark spots. The breathing hole is brown. The egg is oval-longitudinal, light brown with black stripes, dense, 1.2 mm in size.
Rice. 1. Willow wood borer adult (https://www.en.academic.ru)
The caterpillars damage the wood of fruit trees: pears, apple trees, plums, cherries, quinces, apricots, walnuts, oriental persimmons, European olives, wild olives (Olea oleaster), mulberries, roots and trunks of sea buckthorn, as well as willow, poplar, aspen, alder, ash, birch, beech, oak, maple, elm (Ulmus suberosa), oleaster, etc. Butterflies appear in nature starting from the end of June, mainly in July, and depending on the geographical location, in some places even before mid-August. They fly slowly in the late evening. A year lasts a maximum of 14 days. During the day they sit in a characteristic position with their chest reclining on the lower part of the trunk. Females lay eggs in groups of 15-50 pieces in bark cracks, damaged areas, cancerous wounds of trunks at heights of up to 2 m. The total number of eggs per 1 female: up to 1200 pieces. The caterpillars hatch after 14 days. First, the bast tissues are eaten together. On older trees with thick bark in the lower part of the trunk, the caterpillars eat out individual long, irregularly running oval tunnels in the cross section only after the first wintering. The walls of the passages are destroyed by a special liquid and are brown or black. On thinner trunks with smooth bark, the caterpillars penetrate the wood earlier, usually within a month after hatching. The caterpillars push wood chips and excrement out through the lower hole. At the end of the growing season, when the leaves fall, the feeding of the caterpillars stops, which overwinter in the tunnels until the leaves bloom, i.e., until April - May, when the caterpillars continue to feed in separate tunnels again until the fall, overwinter one more time and finish feeding. They pupate either at the end of a circular passage, where a flight hole closed with wood chips is prepared in advance, or in the ground, near a damaged trunk, in a cocoon of wood chips. The pupal stage lasts 3-6 weeks. Before departure, the pupa, with the help of spines, protrudes halfway out of the flight hole or out of the cocoon so that the butterfly can more easily leave the exuvium. The duration of development of one generation in the northern regions of the European part and Siberia is 2-3 years, in the Crimea and the Caucasus 1 year, in the Primorsky Territory 2 years.
Rice. 2. Willow woodworm caterpillar (https://www.upload.wikipedia.org)
The willow woodborer is distributed throughout Europe, mainly in the middle and southern parts. It is found throughout the forest zone of the European part of Russia, in the Caucasus, Siberia, and also in the Far East. Known in western and northern China and Central Asia. In the steppe zone - in floodplain forests, shelterbelts, gardens and parks. In the Caucasus and Transcaucasia they are found up to the upper limit of the forest, in Turkmenistan and Tajikistan in oases and tugai forests along river banks, less often in mountain forests. As a result of damage by willow borer, trees weaken, are colonized by other stem pests and dry out.
Control measures:
whitewashing the trunks, covering wounds on trees with garden varnish, coating the trunks with clay and casein glue with the addition of an insecticide; cutting down weakened trees infested with caterpillars. In gardens for the preservation of individual inhabited trees, chemical. treatment of trunks during the hatching period of caterpillars, if possible - introduction of insecticides into caterpillar passages.