Deafness is a pathological process characterized by a sharp decrease in hearing, sometimes to the point of complete loss. Hearing loss in dogs is a common reason for owners to visit a veterinarian.
Lost hearing in a pet or the development of a pathological process over a long period of time does not always come to the attention of the dog’s owner. Despite this, the dog's behavior changes. She becomes less active and stops responding to loud sounds.
There are many reasons for the development of the disease. But it is important to remember that deafness, as a rule, indicates the development of serious diseases, so such a manifestation should not be ignored. It is necessary to understand what measures can be taken if a dog has developed or is developing deafness.
When to suspect deafness in a dog: alarm bells
The easiest way to tell is if puppies can hear. They begin to react to what is happening around them at about the 2nd week of life. If at this point the puppy still does not respond to sounds, then there is a high probability of congenital pathology.
It is more difficult to notice disorders in older age, since symptoms manifest themselves progressively and rarely include pain. Most of the changes are behavioral:
- ignoring nicknames;
- decreased activity and increased sleep duration;
- maintaining sound sleep during loud noises (the pet wakes up only from touching);
- fear from unexpected touches or sudden appearance;
- disorientation in space (the animal gets lost in its familiar surroundings or falls over while walking);
- disappearance of the reaction to “favorite sounds”: the click of the lock when the owners return, the rustling of a bag of food or the slamming of the refrigerator;
- refusal to play while walking and severe agitation in open spaces;
- scratching the ears and shaking the head, characteristic of ear infections.
If you notice one of the alarm bells, take your dog to the vet. The disorder, detected at an early stage, can be successfully treated. The thing is that by this time there is only a deterioration in hearing, and not its complete loss.
How to diagnose and determine the cause of hearing loss
Diagnosis of a dog’s hearing condition in a veterinary clinic is carried out according to the following action plan:
- First of all, the doctor examines the animal and checks its reaction to sound stimuli.
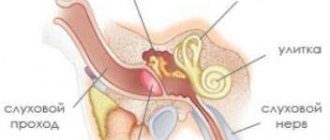
- After this, using an otoscope, the pet’s ear canals are carefully examined, the strength of the change in their structure and the presence of an inflammatory process inside the organ are determined. In addition, a close examination of the surface of the inner part of the auricle can determine the presence of foreign bodies stuck in the ear, damage or neoplasms of various origins.
- If after the examination the veterinarian still cannot make the correct diagnosis, then a head x-ray and other additional diagnostic measures are prescribed. For example, MRI results make it possible to see blockage of the ear canals and damage to the small auditory ossicles of the middle ear, and a neurological examination makes it possible to determine the condition of the auditory nerve.
The most accurate method for diagnosing hearing organs in animals and humans today is deservedly considered the above-described BAER testing, which is mandatory in many European countries when breeding pedigree dogs. Without a doctor's certificate indicating the absence of deafness, the animal is not allowed for breeding.
Classification of the disease
When treating deafness in dogs, it is important to understand its types. Congenital disorders are almost impossible to eliminate, but those caused by injury and disease are often curable.
Congenital and acquired
Congenital deviation exists from birth and is inherited. Such a pet is not familiar with sounds, so it easily adapts to the world around it without experiencing discomfort. Instead of hearing, it relies on the more developed sense of smell and touch.
The acquired form is more common. It occurs due to diseases, injuries to the hearing aid, neurological disorders and age-related changes. Hearing is lost gradually, and sometimes owners discover something is wrong only when the reaction to sounds completely disappears.
Temporary and permanent
Temporary hearing loss is reversible. Most often it is caused by sulfur plugs, which prevent the free movement of sounds. After eliminating the cause, the animal’s condition stabilizes.
An unfavorable prognosis is typical for the permanent form. This includes acquired and senile deafness in dogs, as well as irreversible complications caused by infections and injuries.
Single-sided and double-sided
If a dog has partially lost hearing, then this disorder is called hearing loss. Depending on the number of ears affected, the pathology is classified as unilateral or bilateral.
Sudden, acute, chronic
Sudden hearing loss is characterized by a sudden loss of normal function over several hours. This occurs under the influence of neoplasms, circulatory disorders, viral infections and injuries. Once the root cause is eliminated, hearing may be restored completely or partially.
If hearing loss lasts for 1-3 days, then it is classified as acute. Without timely help, the dog becomes completely deaf.
A chronic disorder lasts for several months. The condition may gradually worsen or stabilize at a certain stage.
Electronic examination BAER test
This method is recognized as the most informative in the world. It is given to dogs starting from one month of age.
Test conditions
The test is performed in specialized clinics equipped with the necessary equipment.
The dog must be over 35 days old. An examination is prescribed if no abnormalities were detected during examination with an otoscope.
Preparation
The dog must be completely calm during the procedure; this can be achieved by administering small doses of anesthesia.
To avoid unpleasant consequences, the animal is not fed 10 hours before the procedure. This way he won't vomit under the influence of drugs.
Process
Each ear canal is examined separately. A special earphone is inserted into the animal's ear, which emits various sound signals. They may differ in volume, power, and playback frequency.
At this time, a special sensor reads the brain’s reaction to stimuli.
Duration
The entire examination takes no more than 15–20 minutes. During this time, the computer provides an accurate test result checking the right and left ear canals.
Price
The price for electronic examination varies from veterinary clinic to veterinary clinic. On average throughout the country, this amount does not exceed 2,000 rubles.
Causes of hearing loss in dogs
Hearing loss has many causes, so it is important to have your pet tested for the most common ones. This will help determine whether the situation is reversible.
Disorder from birth
Congenital anomalies are incurable. Animals with this diagnosis are excluded from breeding work and must be sterilized to prevent the transmission of the hearing loss gene to a future generation.
Injuries to the ear canal and ears, including cupping
Ear problems often arise due to injuries and mechanical damage. These include:
- Damage to the eardrum
. Its rupture facilitates the passage of harmful microorganisms that cause infections of the middle and inner ear. The eardrum is damaged by loud noises (exploding firecrackers), sudden changes in pressure (airplane travel), cotton swabs used for cleaning, and blows to the head. The affected animal experiences severe pain, and blood and pus are discharged from the ears.
- Incorrect docking
. If the breed standard requires complete removal of the ear, then such an operation can only be trusted by trusted surgeons. Any mistake can result in overgrowth of the ear canal.
A damaged membrane can be repaired through surgery. If the damage is minor, then it will heal itself.
Neurological disorders
Another cause of deafness in dogs is pathologies of the central nervous system: strokes, traumatic brain injuries, dropsy of the brain. Hearing loss here is secondary, so with timely treatment of the root cause, the pet begins to hear again.
Diseases and infections
If your dog has difficulty hearing, then it is worth checking for ticks, inflammation of the ear canal and brain. The most common conditions that cause hearing loss include:
- Otodectosis
. Ear parasites that feed on pieces of the epidermis cause severe itching. The animal scratches its ears until it bleeds, and brownish scabs and plaque appear inside the ears.
- Otitis
. Inflammation of the auricle is accompanied by swelling of the ear canal and purulent discharge. In most cases, only one ear suffers from the pathology.
- Meningitis
. The pathology can be recognized by extreme sensitivity to touch, fever, vomiting, gait disturbance and progressive paralysis.
All of these diseases can cause not only hearing loss, but also more serious complications. The pet may die before treatment begins.
Elderly age
Wear and tear on the body as a result of aging is natural and irreversible. Senile deafness in dogs appears after 7 years of age. At this age, animals have long known the habits of their owners, so they quickly adapt to communication through gestures and facial expressions.
Heavy contamination (plug)
In the absence of hygiene, dirt and wax accumulate in the ear canal. Over time, they form a plug that blocks the passage. A foreign object stuck in the ear can also cause a blockage.
Regardless of the reason, it is better to show the animal to a veterinarian, since self-removal may lead to the plug being pushed into the inner ear.
Adapting to your dog's daily routine
A dog with hearing loss may become afraid of approaching people or animals. Training will help soften the auditory startle reflex. During training, give your pet healthy treats - this will be a good motivation for him. Start by approaching your dog from different places, offering him a treat as you approach. Next, try waking your dog (in this situation, he can become very scared), but do it gently - and immediately give him a treat. A smart way to wake up a dog who can't hear is to walk vigorously (so he can sense your approaching footsteps) on the floor next to him or to gently tap his bedding.
Animals with predisposition
The risk group includes animals born from deaf parents. In addition to genetics, breed affects the likelihood of developing the disease. Most often, pathology is diagnosed in:
- Dogo Argentino;
- English and American bulldogs;
- terriers;
- beagles;
- cocker spaniels;
- Labradors;
- Dalmatians;
- marbled dachshunds;
- German shepherds and bobtails;
- boxers.
The color of the animal is no less important. Those with white pigmentation on the ears and head are more likely to be born deaf than their black-headed counterparts. This also includes albinos.
Hearing test
If you suspect that your dog cannot hear you, check its reaction to sounds at home. After receiving a positive result, you can seek help from a veterinary clinic to undergo a more detailed examination.
At home
You can check your pet while sleeping. Try dropping a bunch of keys on the floor, clapping your hands loudly, or shouting your nickname loudly. The lack of reaction will confirm those who have concerns.
A deaf puppy will help determine its aggressiveness. He does not hear the squeals of other babies during painful bites, so he is not able to control their strength. Also worth noting is the barking itself. Dogs, deaf from birth, cannot bark, so they communicate using howls and squeals. Be careful: some breeds cannot bark at all, the most famous being the Basenji and Shiba Inu.
Research in a veterinary clinic
To make a diagnosis, the doctor examines the reaction to sounds and examines the ears with an otoscope. If a pathology is detected, all further studies depend on its cause:
- X-rays and MRIs showing damage and blockage;
- neurological examinations aimed at studying the auditory nerve.
A more informative research method is electronic testing using the BAER test. In European countries, passing it is a mandatory condition for obtaining permission to breed the breed.
Electronic BAER test
The minimum age for the study is 35 days. The testing duration takes about 15 minutes. Although painless, subjects are given a small dose of anesthesia. This eliminates anxiety and inadequate reaction to demonstrated sound signals.
During the procedure, the dog is wearing headphones through which various signals are given to him. Based on the results of the bioelectric response of the brain stem, the veterinarian determines the type of hearing loss and its cause.
How to test your hearing
To make a diagnosis of “deafness,” the pet owner should know about the most characteristic manifestations of this disorder, and an examination with a veterinarian and additional diagnostics will help confirm the guesses. There are several ways to test a dog's hearing, but first of all, it is worth examining changes in the animal's behavior and visual manifestations of the disorder.
Find out what to do if your dog's ear is red inside.
Signs of deafness in an adult dog
Obvious symptoms of hearing loss in dogs will include the following behavioral characteristics:
- lack of reaction to sounds that previously always attracted the dog’s attention (for example, the barking of relatives, the click of the opening door or refrigerator, the conversation of strangers under the door);
- lack of reaction to the nickname, which is why many owners feel that the pet is simply ignoring them;
- decrease in usual daytime activity: the dog sleeps more, and in order to wake it up, you have to touch the body;
- decreased emotionality when walking on the street, which is expressed in a refusal to play (deafened dogs often look around);
- fright if the owner unexpectedly approaches and touches the animal.
In cases where deafness is associated with ear diseases, frequent shaking of the head and scratching of the pet's head are additionally identified. Sometimes, against the background of developing deafness, owners note the dog’s disorientation in space, with imbalance, excessive excitability and anxiety.
Important! To confirm your suspicions about your pet's deteriorating hearing, try throwing a bunch of keys next to your sleeping dog. If the pet jumps up, raises its head, or at least wags its tail, there is no reason to panic.
BAER test
The BAER test is a diagnostic method, the essence of which is to measure the bioelectric response of an animal’s brain to various sound stimuli transmitted to its ears using special headphones. Such testing can be carried out as early as 35 days of age of the puppy, and its additional advantage will be the ability to determine both bilateral (complete) deafness and partial (unilateral) disorder, with the establishment of the root cause of the existing disorders. Clicking sound signals of varying power and volume form a curved line that displays the very reaction of the brain to what is happening.
The duration of testing is 10–15 minutes, it is practically painless and even without the use of anesthesia will not cause severe discomfort in the dog. The results of the BAER test are printed on a special form and given to the owner along with the doctor’s signature and the clinic’s seal. In addition to the conclusion, graphs of the study of each ear of the animal are attached.
Electronic testing is often used in cases where a regular examination of the dog did not bring the desired results and the reasons for hearing loss are in no way related to inflammation in the ear canals (you can verify this using an otoscope). For maximum reliability of the results obtained during the BAER test, the animal must be completely calm and relaxed, therefore, especially emotional dogs have to be given short-term anesthesia, excluding food consumption at least 8-10 hours before performing this procedure.
What treatment might help?
If the pathology turns out to be acquired, then treatment is based on eliminating the cause that caused it. Inflammations caused by infection are treated with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Foreign objects are carefully removed with tweezers or surgically. More serious intervention is required to excise tumors. Small wounds heal on their own after treatment with an antiseptic, so to restore hearing you need to be patient.
The blockage is removed by mechanical or medicinal cleaning, using preparations to dissolve earwax. After receiving detailed instructions from your veterinarian, this is easy to do yourself.
Hearing aid for pet
Congenital anomalies are rarely corrected by hearing aids, while acquired ones (with the exception of senile deafness) can be successfully treated with conventional treatment. The high price of such devices is often unjustified, so they should be purchased only if you have the financial opportunity.
In other cases, veterinarians recommend getting used to the problem, not giving in to panic, and raising your pet in new conditions.
Prevention and care for pet ears
But still, you shouldn’t despair: in any case, it is within the owner’s power to prevent the progression or occurrence of deafness in their pets.
Proper ear prevention and care helps achieve this goal:
- At least once a week, you should carefully examine your dog's ear canals. If earwax deposits are noticed there, they are removed. But! This should be done as carefully as possible, trying not to injure the delicate skin and cartilage. We would advise you to first soften the “garbage” using sterile vegetable oil or Vaseline oil (sold at any pharmacy).
- If brownish deposits are found in the dog’s ears, indicating the presence of mites, measures to eliminate the latter must be taken immediately, without waiting for the condition of the ear canals to worsen. Moreover, today in any veterinary pharmacy or pet store you can buy almost a hundred types of products to combat ear mites.
- If your pet’s hearing has become worse as a result of an ear injury (we wrote above about how to determine this), it should be immediately shown to a veterinarian.
How to keep and raise a deaf dog
The main task of the owner is to provide his pet with a rich and fulfilling life, despite the difficulties that arise. Four-legged pets learn quickly, so during adaptation it is enough to adhere to the following tips:
- Avoid pity. Due to regular indulgences, the dog will quickly “sit on the neck” and lose independence.
- Be consistent. Don't jump from one exercise to another without waiting to complete the previous one.
- Use gestures and facial expressions. You can watch them in a training video or come up with them yourself.
- Buy a vibrating collar and an ultrasonic whistle. These tools make training much easier.
Touching must be taught very gradually in order to develop a positive reaction. To awaken an animal, you just need to put your hand to its nose. Feeling a familiar smell, he will wake up and not be afraid of the surprise.
It is recommended to fence the territory of a private house with a fence, and place the sleeping place away from noisy rooms. When approaching the dog, use loud claps. They create vibration, eliminating fright due to sudden appearance.
Be sure to attach a tag to your collar with your phone number and animal's name. When walking in the dark, use a flashlight or a glowing bracelet so your dog doesn't lose sight of you. Remember that he cannot hear the sounds of cars or other dangerous objects, so always take a leash with you.
Diagnostics
The veterinarian completes a complete history of the dog, including any medications that may have damaged the ear or caused chronic ear disease.
Early onset of the disease usually suggests congenital defects (congenital causes) in predisposed breeds.
Brain disease, on the other hand, is a slowly progressive disease of the cerebral cortex, usually caused by frailty or cancer, which prevents the brain from registering what the ear hears.
Bacterial cultures and hearing tests, as well as testing the sensitivity of the ear canal, may also be used to diagnose the underlying condition.
Preventing hearing problems
To prevent hearing problems, it is recommended to avoid hypothermia, avoid colds and keep your ears clean. Seek help from a veterinarian for any alarming symptoms without waiting for complications to develop.
If your pet is diagnosed with deafness, sterilize it and do not allow it to be bred. Remember that when one deaf puppy is born, the entire litter is sterilized. This eliminates the transmission of the pathogenic gene to subsequent generations.
A deaf dog is not much different from its healthier counterparts. Thanks to its developed sense of smell and touch, it is often superior to other animals. The owner can only help her develop these skills through regular training. The new method of communication has many nuances, but over time you can get used to it.
The article is for informational purposes only. Contact your veterinarian!
Do you like the article? 178
Changing your dog's environment
If your dog is losing his hearing, you will need to learn new ways to communicate with each other. As hearing loss develops, work on adding hand signals to verbal commands. If your pet suddenly becomes deaf, hand commands should be used more intensively. Whatever it is, don't despair. If your dog was well trained before losing his hearing, he will quickly master any new exercises. She, like you, just needs to get used to the lack of hearing. Remember this and continue to train her.
A dog with hearing loss should not be allowed to roam unattended. If your dog suddenly loses his hearing, or if it happens gradually, make sure he is always on a leash. If she spends time in the yard, she should be tethered or have a fence installed so she can move around freely in a safe environment. When you leave the house, keep your dog on a leash.
In addition to the leash and collar, your dog will need to update its identification tags. Post one with your contact information, and on the second indicate that the dog cannot hear. If you are worried about losing your dog, consider purchasing a collar with a bell. Maybe it's time to think about a microchip.
There are several ways to help a deaf dog in everyday life. In the evening, you can attract her attention with the help of light. You can light a lantern in the yard when it is time to enter the house. The overhead light in the room can be turned off, on and off again to alert the dog that the family is going to bed. In addition, do not forget about your pet’s excellent sense of smell. By using different scents in your training, you can help her associate your command with a specific scent.