Man has always been very interested in how animals see the world around them. In particular, what kind of vision do cats have? It is known that it is much sharper than ours. According to scientists - about ten times. Everyone also knows very well that cats see in the dark.
Thanks to this feature, as well as their glowing eyes, they even gained a reputation as beings of almost supernatural origin. In ancient times, somewhere they prayed to them, considering them to be deities, and somewhere they were sent to the stake as accomplices of witches.
© shutterstock
Features of a cat's vision.
Small cats have simply huge eyes, they occupy 1/3 of the size of the muzzle. It is worth noting that lions, tigers, and leopards have much smaller eyes and have a round pupil structure.
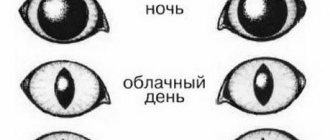
The cat's pupil is a real miracle. Like a filter in a camera lens, it narrows if the light is bright enough and expands if the light becomes less saturated.
Not only the light flux affects the width of the cat's pupil. If the animal is scared or hunting, the pupil stretches into a thread.
- Cats see much better than humans, but only at a distance of no closer than 2 meters; at a shorter distance, the image is blurry, and animals use vibrissae (special organs located on the whiskers) and sense of smell.
- Further than 20 meters, the image visible to the cat will also be blurred. Like any predator, a cat can see moving objects well within its jump range.
To imagine how cats see our world, just look at a blurry, poor quality photograph.
Vision and hearing: which is better?
Despite all the advantages of cat vision, it is not their strongest point, because... loses to such a feeling as hearing. The ability to hear is so developed that an animal, being at a distance of a meter from a sound source, can determine its location with an accuracy of several centimeters, and for this the cat will need only 0.06 seconds.
Felines can also hear sounds over long distances. At the same time, they detect sound deviations of one tenth of a tone; Thanks to this information, the animal forms an image of a prey making noise (its type and size).
There are a large number of myths and misconceptions regarding cat abilities. While scientists explain certain aspects of pet behavior, there are still many oddities that make the cat a mysterious creature. However, when it comes to the hearing and vision of furry household members, their perfection is beyond doubt.
Based on materials from www.hillspet.com
Color vision in cats
For a long time it was believed that most animals, including cats, have monochrome vision. Color vision is characteristic only of birds and some species of fish.
- Scientists were interested in what colors cats see, other than shades of gray.
- It turned out that cats perfectly distinguish shades of blue, green and yellow.
- Animals distinguish the color violet, but worse, since they lack the perception of red-orange shades.
If you imagine how cats see the world, the picture will be quite funny. All surrounding objects will be painted in green and blue tones.
Discovery five: THEIR EYES GLOW IN THE DARK!
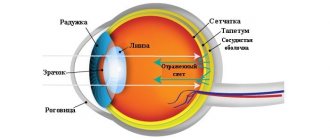
The whole secret of this miracle is in the so-called tapetum - a layer of the eye shell that captures light and directs it to the retina. That's why a cat's gaze seems so mysterious and even magical! Interestingly, you can calculate the color of the eyes by the color of the glow: blue pupils usually glow red, and yellow pupils glow green.
And now is the time to do...
How cats see their surroundings
Many owners have noticed that their pets love to watch TV. In fact, the image on the screen for a cat is a static object; in order for the cat to see movement on the screen, the frames on the TV must change at a frequency twice as high as the frequency perceived by the human eye.
Movements in games on tablets and phones are well perceived by the cat, and often pets like to “help” their owner play.
- Having already decided what colors cats see, it would be interesting to find out how cats see people.
- Zoologists have determined that cats adequately perceive the size of their owners, but if the pet is further than 6 meters from the owner, then it sees the person as a cloudy spot and recognizes it by smell and voice.
- A similar perception can be observed if a person is standing or lying down. The cat perceives static objects as a silhouette.
The cat has visual vision. She sees her surroundings within a radius of 270 degrees, and the slightest movement will immediately attract the attention of the animal.
An equally interesting feature is the cat’s ability to see in the dark.
Tips for choosing accessories based on color
In big cities, cats sit at home, without the opportunity to frolic in the fresh air. Owners want to diversify the life of their pets, pamper them and make them move. So that they don't become fat and lazy. This is where pet stores come to the rescue with a huge selection of toys.
In order not to buy bright and useless ones in vain, the owner must remember the peculiarities of cats’ vision. This knowledge will help you choose accessories for your pets. Cats are good at distinguishing objects of green, blue, yellow and green and gray colors. Therefore, they will run after such toys with excitement. And, most likely, to react indifferently to beautiful and fashionable reds. The cat will react the same way to beds and feeders. Green and blue will become his favorite ones, he can simply ignore the rest.
Cat's night vision
It would be a mistake to say that cats see in complete darkness. Like any mammal whose eyes see only by reflecting light from the retina, a cat needs at least a minimal light source.
However, it is worth considering that due to a special layer located behind the retina, the sensitivity of a cat’s eye in the dark is 8 times higher than human perception.
- In ancient times, being a small predator, the cat could not hunt during the day, as there was a danger of becoming prey to larger enemies.
- Therefore, cats turned into nocturnal predators, and, consequently, in the process of evolution, vision developed, adapted to hunting in the dark.
- And due to the vascular layer located behind the retina - the tapetum, vision became sharper.
By the way, cats owe this special layer – the tapetum – the fact that their eyes “glow” in the dark. This is also one of the reasons to give cats mystical abilities.
In fact, minimal rays of light are reflected from the tapetum and create a “glow” effect, similar to reflective signs on the road. If the darkness is truly complete, your pet’s eyes will not “glow”.
Therefore, to the question “can cats see in the dark?” can be answered as follows: in complete darkness, a cat does not see and orients itself with the help of whiskers, but the fact that “pitch darkness” for a person is by no means darkness for a cat.
Differences with human vision
Of course, it's all about the brain. Unlike humans, cats have developed areas of the brain that are responsible for hearing and smell, so vision in cats is worse than these senses. In humans, most of the neurons are taken away by hand motor skills.
Unlike other creatures, a cat's vision is an auxiliary sense, and not the main one - hearing and smell are considered the main ones. Evolution put everything in its place due to the fact that the cat is considered an animal that hunts from an ambush. That is why she does not need a far-sighted gaze of several kilometers.
Dogs see better than cats, and this is also due to brain development. The structure of the limbs and their work in the cat family is much more complex, therefore, together with the development of areas responsible for hearing and smell, there is no room left for vision on the surface of the cerebral cortex in cats, and they see worse.
Cat's vision problems
Eye diseases in cats are quite common. Moreover, owners do not always immediately notice the problem, because even a cat with poor vision is perfectly oriented in space, using its tactile organs and sense of smell.
There are three types of eye diseases in cats: infectious, traumatic and age-related.
Infectious diseases include:
- Conjunctevitis;
- Iritis;
- Keratitis.
Infectious diseases are more common in cats that roam outside. When contacting wild relatives, a cat can become infected. If symptoms appear, contact your veterinarian immediately.
Traumatic diseases:
- Injuries;
- Burns;
- Turn of the century;
- Entry of a foreign body.
Age-related or pathological diseases can develop as a complication after injury or infection, or if the animal is predisposed.
These include:
- Glaucoma;
- Cataract;
- Dacryocystitis.
Most often, you can determine that a cat has vision problems by its behavior. The animal hides from bright light, rubs its eyes, and shows anxiety. Changes in your pet's behavior are a reason to consult a specialist. Advanced diseases of the visual organs can become chronic, and the cat can go blind.
Now it’s easy for you to imagine how cats see the world and not be surprised that a cat’s eyes glow in the dark or that a pet “talks to a brownie.”
Does your pet see something we don’t see?
Whiskered pets were often accused of conspiring with the forces of evil, attributing magical abilities to them. But over time, most of the superstitions were explained by felinologists.
Differences from human vision and perception
Having figured out what kind of vision cats have, it is easy to identify its main differences from humans. Possible superpowers are confirmed by a wider viewing angle, faster perception speed and clearer visibility in low light.
Most owners have noticed more than once how their pets stare at one point for a very long time or suddenly jump up and start running around the room. At such moments, their pupils dilate and their fur stands on end. This behavior makes you very uncomfortable and even a little scary.
Photo of how a cat sees
Perception of the world
Nature has provided for the use of each organ in accordance with its purpose. For hunting, it is more important for a cat not to miss the movements of the prey, and factors such as coat color and body length do not play a role.
The animal’s hearing organs, which distinguish sounds by their height and strength, help them to more fully perceive the surrounding space. In addition, they have excellent sense of touch and sensitive vibrissae organs located on the muzzle and tail.
For cats, smells play an even more significant role than vision. It is important for an animal to smell new objects, and not just look at them. However, visual perception is a real survival mechanism.