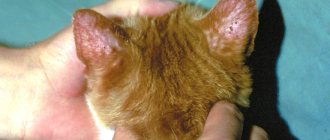
Feline herpes or rhinotracheitis is a severe contagious (infectious) disease of viral origin that mainly affects the respiratory system and eyes. The causative agent is Feline herpesvirus (FHV-1); this strain of herpesvirus is found in almost 90% of felines, but in most cases it is in the animal’s body in a dormant (latent) form. Rhinotracheitis in cats develops with a decrease in immunity or against the background of another pathology that weakens the body. This disease is zoonotic, typical only for animals; humans cannot become infected with feline herpes.
What is feline herpes virus infection?
Herpesvirus infection of cats, or rhinotracheitis, is a real tragedy for the cattery. Due to its high contagiousness (infectiousness), it is quickly transmitted between animals, and crowded living conditions provoke the growth of the epidemic.
Pathogen
The causative agent of rhinotracheitis is the herpesvirus FHV-1. After penetration into the body, it begins active reproduction inside cells, causing their destruction and death.
The danger of the virus lies not only in its contagiousness, but also in its resistance to external factors. It can survive in the environment for several days, and its death occurs only when disinfectants are used.
Routes of infection
Not only an outdoor cat, but also a domestic one can become infected with herpesvirus. Transmission of infection occurs when:
- direct contact with infected animals or objects;
- an insect bite that came into contact with a sick cat;
- the birth of kittens from an infected mother or during breastfeeding.
The pathogen is released along with biological fluids (urine, tears, saliva), so the owner can easily bring it home on his shoes. For this reason, you should not let your guard down, even if your pet never goes outside and has no contact with other animals.
Incubation period
On average, the incubation period takes about 5 days. Despite the absence of symptoms, a sick cat is capable of transmitting the infection to other animals within a day after infection.
Prevention
No product provides a 100% guarantee of the absence of infection. But the risk can be significantly reduced by using the following measures:
- Vaccination - starting from three to four months, kittens need to be given the complex vaccine Nobivak, Triket, Multifel in two stages. Revaccination of the animal annually. For kittens born from an infected female, three vaccinations are allowed - at four, eight and twelve weeks.
- Deworming must be carried out before vaccination, recommended once every three months. Helps avoid helminthic infestation, which significantly reduces the pet's immunity.
- Daily wet cleaning of premises with disinfectants. Handling care items, hands and clothing after handling sick animals.
- High culture of keeping animals, especially in nurseries and shelters. The premises must be of sufficient area; high density of pets is not allowed. Good ventilation, optimal temperature and humidity in the room must be maintained year-round.
- Isolate sick animals and provide them with a separate litter tray, food and water bowls.
- A complete balanced diet, special vitamin complexes are introduced into the food twice a year.
- Pets are not allowed to interact with stray animals.
- Mandatory quarantine for newly admitted cats.
1111
Causes of the disease
Immediately after infection, the disease occurs in a hidden (latent) form. Activation of the pathogen occurs with a sharp decrease in immunity. This occurs during pregnancy, severe stress, concomitant diseases, lack of vitamins, hypothermia and overheating of the body.
Herpes virus infection in kittens is more severe than in adult animals and can be fatal. Also at risk are Persian cats, who are vulnerable to the disease as a result of their breed characteristics.
Symptoms of herpesvirus in cats
The first warning signs appear immediately after the incubation period. These include:
- difficulty breathing and cough;
- inflammation and swelling of the larynx;
- frequent sneezing and profuse salivation;
- sores on the tongue and lips;
- purulent nasal discharge;
- conjunctivitis;
- the appearance of a third eyelid or film on the eye;
- redness and swelling of mucous membranes;
- mucous vomiting;
- temperature rise to 40°C.
The sick person becomes apathetic and loses appetite. When eating food and water, he arches his neck and tilts his head to the side to ease the pain in his throat when swallowing.
Classification by type
Symptoms and treatment for herpes in cats vary depending on the type. Depending on the severity of the symptoms and the speed of development, the infection is divided into 3 types:
- Acute
. It is accompanied by all the described symptoms, so it can be diagnosed quite quickly. Without timely treatment it becomes chronic.
- Chronic
. It is characterized by the appearance of inflammation on the skin, as well as alternating remissions and relapses. It can last for years, gradually disrupting the functioning of the central nervous system. Over time, the animal develops tremors in the limbs and manege movements, that is, an irresistible desire to walk in a circle. This type of pathology is fraught with ulcerative colitis and blindness.
- Latent
. Characterized by the absence of symptoms. It can become acute when exposed to certain factors that reduce the body’s defenses.
When treating the acute form, recovery occurs within 1-2 weeks. If, at the time of contacting the veterinary clinic, rhinotracheitis has become chronic, then it will take much longer.
After recovery, the pet acts as a carrier for up to 3-6 months, since the pathogen remains in its secretory glands. Under certain factors, he himself may become ill if the virus enters the active phase again.
Medicines that help remove alcohol from the body
If a person is able to take pills on his own, then this method should also be used to quickly eliminate the symptoms of intoxication. Adsorbents, enveloping and diuretic drugs, and drugs for restoring intestinal microflora can help.
Sorbents and enveloping agents
Simple over-the-counter medications can help speed up the removal of toxins from the body. The most popular of them are “Smecta”, “Enterosgel”, “Polysorb MP”, “Filtrum”, white or black activated carbon. Emptying the bowel helps effectively eliminate the symptoms of alcohol poisoning.
Diuretics
It is better to use Lasix or Veroshpiron. These drugs do not flush potassium from the body, which is important for the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system. Plain water, herbal decoctions, green tea, fruit drinks, and juices have a diuretic effect. Water is needed for detoxification and restoration of water-salt and electrolyte balance.
Preparations for restoring intestinal microflora
Alcohol, especially its surrogate types, has a destructive effect on the beneficial intestinal microflora. Fermented milk products (kefir, fermented baked milk, bifidok, tan, ayran) will help restore it. But for the best effect, it is advisable to take probiotics. “Smecta”, “Bactistatin”, “Hilak-Forte”, “Bifidumbacterin”, “Bifiform”, “Lactobacterin”, etc. are sold without prescriptions. Read the instructions carefully: an overdose of probiotics can do a disservice.
Other drugs to eliminate alcohol intoxication
If the degree of poisoning is not higher than the second, then to improve your well-being you can take Alka-Seltzer, Metadoxil, Zorex, Limontar, Biotredin. These drugs relieve hangover symptoms, eliminate headaches, and accelerate the elimination of ethanol from the body. To normalize the condition, it is advisable to ventilate the room and take a contrast shower without sudden temperature changes.
Diagnostic features
It is not possible to cure the disease at home. Do not wait for complications to appear and contact the veterinary clinic at the first signs of discomfort.
Symptoms of rhinotracheitis are similar to other infections, so before starting treatment it is important to determine the actual pathogen. What symptoms are NOT characteristic of herpesvirus:
- intense inflammation of the gums, a large number of ulcers and lameness - the likelihood of calcivirosis;
- absence of conjunctivitis and preservation of appetite – bordetellosis;
- alternating eye damage - chlamydia;
- very loose stools with a pungent odor - distemper.
At the appointment, the veterinarian carefully examines the mustachioed patient and collects anamnesis, clarifying the clinical picture from the owner. In addition to the examination, to make a diagnosis you will need:
- general and biochemical blood tests that determine the general condition of the body;
- antibody test and PCR study confirming the presence of the virus and its type;
- smears taken from the eyes, pharynx and nasal sinuses, helping to exclude pathologies with similar symptoms.
After receiving all the results, the veterinarian determines the form of the disease and selects a treatment plan. Please note that it is prohibited to stop taking medications until you receive appropriate instructions from your doctor! Otherwise, the pathology may become chronic.
Consequences of the disease
The cessation of symptoms of rhinotracheitis and conjunctivitis almost always occurs. There are no serious consequences, and the cat returns to an active life. After severe conjunctivitis, persistent defects may remain on the cornea of the eye, which impair its transparency.
Virus carriage remains in most cases. It is impossible to completely get rid of it, and the animal poses a threat to its relatives. It is difficult to detect carriage after an infection; PCR results may be false negative.
Treatment methods
Treatment of herpesvirus in cats is carried out at home under the supervision of a veterinarian. The first improvements are noted within a couple of days from the start of taking the prescribed medications.
Drug therapy
The main goal of therapy is to increase immunity. Thanks to this, the body copes with the virus on its own. The sick animal is prescribed:
- antibiotics and sulfonamides that eliminate concomitant infections;
- anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, expectorant and antiemetic agents;
- intramuscular injections of vitamins A, B and C;
- immunomodulators;
- medications for rhinitis, conjunctivitis and laryngeal diseases.
Glucose drips are given for severe dehydration and exhaustion. In such cases, the mustachioed patient is placed in a hospital until his condition normalizes and his previous appetite returns. Another option is for a nurse to come to the sick person’s home every day.
Procedures
When treating herpes virus in cats, special attention is paid to ulcers on the cornea. Further ulceration is fraught with loss of vision, so it is very important to prevent the pathological process before the situation worsens.
To eliminate ulcers, use antiviral ointment acyclovir and antimicrobial ointment tetracycline. The surface of the eyes is treated 5-6 times a day for a week.
Additionally, the affected areas are washed with chamomile decoction and miramistin. During the procedure, it is recommended to wrap your pet tightly in a towel or blanket. This will prevent injury to the mucous membrane or your hands when pulling out an unhappy animal. After immobilizing your mustachioed pet, proceed to the following steps:
- Take a sterile cotton pad and soak it in the prepared solution. Remember that you need to use a different disc for each eye.
- Gently wipe the affected areas and surrounding area. If large drops flow abundantly from the disk, squeeze it out to remove excess.
- Repeat the procedure several times and let the solution absorb. If necessary, apply acyclovir or tetracycline to the eyelid and massage it lightly. After this, the cat can be released. Perform the procedure at least 3 times a day.
For severe coughing and other breathing problems, steam inhalation may be required. At home, warm and moist air that appears in the bathroom after taking a hot shower or filling a bath is suitable for this. To get a positive effect from the procedure, just keep your pet in a tightly closed bathroom for 10-15 minutes.
Therapy at home
After identifying the herpes virus FHV-1, the veterinarian will prescribe specific treatment for the cat. There are no drugs to suppress the virus itself; therapy is symptomatic.
Complex therapy for this infection includes:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antiviral agents;
- immunostimulating drugs;
- nasal drops to ease breathing;
- medicines for the treatment of eyes and mouth;
- maintenance therapy.
First of all, it is necessary to isolate the sick animal, provide it with a separate litter tray, bowls for food and water. He should be given proper care. To prevent complications from developing, avoid hypothermia of the sick individual.
Dietary food during illness, preferably from a special line of wet food. Food should be given warm to stimulate the appetite, as the cat's sense of smell is weakened due to nasal congestion.
If a cat refuses to eat and drink completely for more than three days, it is necessary to use droppers (in a veterinary clinic) or subcutaneous infusions, which can be administered independently as prescribed by a doctor. Use saline, glucose, and Ringer-Locke solution to prevent dehydration of the body. B vitamins and ascorbic acid are often added to the infusion mixture. In severe cases, hospitalization of the animal to a veterinary clinic is indicated.
To facilitate the breathing of a sick individual, the use of air humidifiers, inhalations and nebulizers helps well. The nose and mouth must be cleaned of mucus and pus and treated with special animal products. If ulcers have formed, use Iodinol, Chlorhexidine, Solcoseryl gels and ointments, Actovegin.
To combat nasal congestion, there are special drops Anandin, Maxidin, Interferon, and others.
Antibiotics are used to prevent complications and additional infections. Usually these are third generation cephalosporins - Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin. Along with this therapy, probiotics (for example, Villot probiotic drink) should be introduced into the animal's diet.
Antipyretics are used only when the temperature rises above 40 degrees Celsius - Ketofen, Loxicom, others.
It is strictly forbidden to give paracetamol-containing products to animals.
Immunomodulators and antiviral drugs
In the treatment regimen for rhinotracheitis for cats, it is necessary to use drugs aimed at increasing the body’s immune forces - the immunomodulators Immunofan, Fosprenil, Polyoxidonium, Cycloferon. Veterinary drugs – Anandin, Roncoleukin, Gamavit, Gamapren.
Antiviral drugs are used to reduce clinical signs of infection. The following methods are used:
- Systemic antiviral prescriptions - Famciclovir is an antiherpes drug used to treat humans. The method of administration is oral, safe for animals, and has an excellent therapeutic effect. The use of antiviral serums for cats (Vitafel-S, Globfel) is indicated.
- Therapy of conjunctivitis using antiviral drops and ointments. Sometimes the damage to a cat's eyes during the course of the disease is significant, even requiring surgical removal. Therefore, it is necessary to pay special attention to their treatment. Using eye drops for people Cidofovir, Trifluridine, Idoxuridine will help prevent the development of keratitis.
Animal care
During drug therapy, the pet should be isolated from other cats for 2-3 weeks. During this time, healthy individuals must be vaccinated to prevent further spread of the herpes virus.
In addition to taking medications, the patient will need comfortable living conditions and a nutritious diet. To destroy the virus from surfaces in the house, steam treatment is carried out. It is recommended to clean the tray and food bowls belonging to the infected person with a chlorine solution, and throw them away after treatment.
Protect your pet from stress and drafts. Place it in a warm and quiet place, protected from intrusion by other inhabitants. Anxiety has a negative impact on well-being and can cause a relapse.
Bowls for food and water, as well as the toilet should be located close to the bed. Thanks to the proximity of these objects, the cat will not have to waste energy moving around the apartment. The saved strength will help in the fight against the virus.
Diet and nutrition
A weakened body needs nutrients, but a stuffy nose without smell and a sore throat seriously complicate feeding. You can stimulate your appetite with the help of wet canned food - their strong and tasty smell is much more attractive than dry food. In the future, the granules can be returned by choosing a brand with good calorie content.
When feeding naturally, use light meals that do not injure the mucous membranes. The diet should include:
- boiled chicken or beef mince;
- raw quail eggs;
- watery porridge;
- unrich meat broths;
- pureed vegetables that have undergone heat treatment.
Serve food often (4-5 times a day), but in small portions. This will eliminate prolonged fasting and heaviness in the stomach. The temperature of the food should be at room temperature.
Don't forget about water. It should be changed twice a day. If you do not have this option, purchase a drinking fountain with automatic filtration.
Can a person become infected?
The herpesvirus FHV-1 is dangerous only for the cat family. It cannot be infected by four-legged animals of other species or humans, so you should not be afraid of the sick person and avoid close contacts.
Despite this, it is worth considering that infection works in the opposite direction. A dog or its owner walking outside can bring the virus into the house on their paws and shoes. For this reason, it is very important not to neglect prevention and vaccinate your pet upon reaching the appropriate age.
Is feline herpes contagious?
There is absolutely no reason for humans to be afraid of becoming infected with feline herpesvirus; this virus only affects cats
, which eliminates the possibility of disease in other pets.
The infection is most active in the cold season and can easily be contracted by:
- Unvaccinated;
- Those with poor health, as well as those who have recently suffered from hypothermia;
- Animals that are regularly poorly fed have an increased susceptibility to the virus;
- Persian and related breeds;
- Kittens.
Prognosis and complications
Herpes in kittens causes death in 20% of cases. Also at risk are pets with an advanced form of the pathology. Weakened animals die from acute dehydration or bronchial pneumonia caused by secondary infection. In all other cases, a positive prognosis is given.
If treatment is delayed, the disease develops into a chronic form, fraught with the following complications:
- inflammatory processes in the lungs, bronchi, trachea and sinuses;
- dry eye syndrome and vision loss;
- miscarriages or stillborn kittens;
- intestinal atony, accompanied by constant constipation;
- pathologies of the central nervous system (gait disturbance, muscle spasms);
- deep ulcers with scarring and subsequent death of corneal tissue;
- destruction of the jaw bone;
- leukemia, or blood cancer;
- viral immunodeficiency.
It is much safer to vaccinate your pet against the virus in advance with a special vaccine that provides passive immunity against the pathogen. Although vaccination does not guarantee one hundred percent protection against infection, it significantly alleviates the course of the disease if it does appear.
Preventive measures
To prevent cats from becoming infected with viral rhinotracheitis, it is enough to follow sanitary standards for caring for animals. If you entered the house from the street, put your shoes in a closet with the doors closed, and do not forget to wash your hands. Avoid contact with stray animals. A new pet must be quarantined in a separate room for 2-3 weeks, after which it is allowed into a group with healthy cats.
Vaccination is the main preventive measure to prevent the spread of the feline herpes virus. Healthy kittens are vaccinated from the age of three months or after changing teeth. The use of a vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies and prepares it to quickly respond to future infection. Live fragments of the virus contain the vaccines Leucorifellin and Felocel. Kittens are not vaccinated with them due to the appearance of a runny nose and watery eyes within two weeks after vaccination. It turns out that animals actually become ill with rhinotracheitis. Inactivated vaccines Quadricat and Nobivak, in which pathogenic microorganisms are killed, are safer. After vaccination, it takes time for the pet’s immunity to provide protection against the disease.
Unfortunately, the vaccine only protects against the type of virus included in it and does not prevent infection with another type of feline herpes. Therefore, it is not completely effective. The pet will get sick, but the illness will be less severe. Animals that have recovered from viral rhinotracheitis are vaccinated annually to avoid relapses of the disease.
Viral rhinotracheitis poses a danger to domestic cats due to its transience. Sometimes the disease leads to irreparable consequences. It is better, without wasting time, to take your pet to an appointment with a veterinarian and follow the entire prescribed treatment regimen. A caring and patient attitude towards an animal during illness will speed up its recovery.