441
no comments yet
0
Author:
Novikov Kirill.
Reading time: 33 minutes
The word “Indian” cannot be translated into foreign languages, because such a name does not exist in them. This term appeared in 1981, when domesticated musk ducks brought to the USSR from East Germany were first shown at VDNKh in Moscow. These ducks were given the popular name turkey due to the similarity of the red leathery growths on the head with the corals of the turkey, the most similar to which were the fleshy growths at the base of the drakes’ beak.
7 years later, in 1988, an exhibition of domesticated musky ducks from France was held at VDNKh. This variety of the breed was called “Barbary”; its ancestors came from wild South American ducks domesticated by Indians. Due to the similarity of French Muscovy ducks with the previously shown German ones, they also began to be called Indo-ducks.
In modern Russia, many varieties of the Muscovy duck breed, differing in plumage color, meat and egg production, are classified as indo-ducks.
Information for Beginners
Beginning poultry farmers can be advised to start breeding indo-ducks “for themselves”, and then, as they gain experience, start breeding them on a large scale.
Features of indo-ducks:
- Calm birds . This allows you to keep a large number of heads in a small area. Only in conditions of lack of food and water can drakes in crowded conditions show aggression towards each other.
- They quickly get used to their owners and territory . The grown young animals can be driven out to pasture. Indian ducks remember the road well, go out on their own and return without loss.
- Lower feed costs compared to other ducks . Turkey ducks consume large amounts of green matter during the day on pasture, so they require less grain feed.
- They can do without a pond . Despite their love of water, Indian ducks thrive and develop without open water: their ancestors in South America were tree-dwelling wood ducks.
- Immunity to traditional poultry diseases due to high immunity.
- High maternal instinct , which allows the poultry farmer not to interfere in the process of incubation, breeding and raising ducklings.
- There are no difficulties in the formation of uterine groups when kept on open range . It is enough to separate the females from the main herd of young animals and introduce drakes to them in a ratio of 3:1. Drakes will choose their own friends.
- The possibility of crossing Indo-duck drakes with female Pekin ducks to obtain quickly gaining weight mulards.
- Flight ability . At 3-4 months, Indian ducks are able to begin to take to the air. The problem can be quickly resolved by painlessly clipping the wings.
- Lack of noise and hubbub in the homestead . Indian ducks are not capable of making loud sounds.
Conclusion: breeding indo-ducks for a novice poultry farmer involves only their regular feeding and watering; no initial experience in handling poultry is required.
Duck diseases
If owners do not show enough attention to their pets, they may get sick. Most often, musky ducks are exposed to infectious, viral and parasitic diseases:
- rickets;
- lack of vitamins;
- cloacite;
- catarrh and goiter blockage;
- vitelline peritonitis;
- intestinal poisoning;
- cannibalism.
If you follow all the rules and conditions for keeping poultry and take preventive measures, then the immune system of Indian ducks will not allow various diseases to arise.
Information for poultry farmers
Poultry farmers include professionals who raise poultry on an industrial scale and amateurs who raise poultry at home.
If, after the first successful experience of breeding Indian ducks, there is a desire to continue doing this, then it is necessary to acquire knowledge on breeding, caring for and keeping birds.
How to distinguish a duck from a drake
You need to be able to do this to separate indo-ducks when they have reached 4-5 months of age. Separation must be done to form uterine groups of young animals.
Differences:
- The drake is always larger than the duck - it weighs more and is longer.
- Drakes hiss, ducks grunt and squeal.
- When picked up, drakes quickly calm down, ducks will scream and struggle constantly.
- The drake's head is larger and wider. The duck's head is smaller, neat, rounded.
- The drake's webbed feet are wider and its legs are thicker.
- When the drake is excited, the crest on the back of the head rises; in females it is smaller.
- Only in the drake can large fleshy growths appear at the base of the beak.
How to clip wings
Indians can fly. When the first flights appear among the young, all birds need to have their wings clipped.
Basic actions:
- For the first time, it is better to do the trimming together - one holds the bird, the other trims it.
- It is better to clip the wings in a confined space - this will make it easier to catch the bird.
- After catching the bird, you need to press it to your body with both hands, leaving one wing free.
- The second person needs to pull the wing with his left hand and straighten it to its full length, take ordinary metal scissors in his right hand and trim all the flight feathers (the longest) on the wing by half the length.
- After trimming one wing, the indot duck can be released.
Trimming Features:
- It should be taken into account that the flight feathers of drakes are stiffer, so when trimming you need to use massive iron scissors.
- You cannot cut the flight feathers too short - blood may come out of the feather shaft and the bird will be hurt.
- In ducks, trimming the flight feathers can be done through one feather on both wings. This will allow them to better retain heat in the nest while hatching ducklings.
- The wings of all young animals are trimmed after the first flying bird appears. Wing trimming of an adult bird is carried out annually, after the end of molting.
How to choose a drake for the brood group
After dividing the young by gender, the leaders of the uterine groups need to be selected from the drakes. This should be done taking into account the following:
- You cannot choose the largest ones; they give a lower percentage of fertilized eggs.
- It is necessary to pay attention to the color of the males. An important condition will be the preservation of the characteristics of the breed standard in plumage color.
- You need to pay attention to drakes from the age of three months in the process of raising them. Active, fast-growing males are considered the most productive, and it is not necessary that they be the largest in the herd.
The history of the musk breed
Indians domesticated Indians in Mexico and South America. After European colonization, the breed was brought to Europe and gained great popularity among many poultry farmers.
The breed was not popular in Russia for a long time. The situation changed only in the 80s of the 20th century, when a large batch of musky ducks was brought from Germany to the USSR.
Today, Indian ducks are one of the most popular breeds in Russia and neighboring countries.
Note! Some people consider the turkey duck to be a hybrid of a turkey and a duck, but this is not true. Despite a certain external similarity, the musk breed has nothing to do with turkeys.
Methods of content
Several methods are known from the everyday practice of keeping Indian ducks in the homestead.
In cells
This method can be used by an experienced poultry farmer who does not have a lot of space for breeding indo-ducks.
Positive points:
- Rapid weight gain in a short time.
- No case.
- Economical consumption of feed and water.
- Full control over poultry production and slaughter.
- Year-round maintenance.
Difficulties:
- Initial costs for the manufacture of cages, the purchase of nipple drinkers, the manufacture of metal hanging feeders.
- The need to maintain a constant temperature in the poultry house at any time of the year.
- Supply and exhaust ventilation device.
Floor content
This method involves keeping young ducks indoors on deep litter. The method relates to industrial poultry breeding and is rarely used in households. Suitable for experienced poultry keepers.
Pros:
- Possibility of keeping large numbers of poultry in small areas.
- Fast weight gain.
- Economical consumption of feed.
- Year-round maintenance.
- Easy care.
Minuses:
- Poultry losses due to cannibalism.
- High energy costs for lighting, heating and ventilation.
Mulard ducks suffer from cannibalism. How to preserve livestock
Read
Indian ducks and mulards peck at each other. Solutions to the problem
Look
Mulards and Indian ducks plucking feathers from each other. Solutions to the problem
More details
Breeding in a poultry house
Keeping in the poultry house is seasonal - from the second half of October to the beginning of April, depending on the climate. In a household, it is so beneficial to maintain several brood groups, consisting of one drake and 2-3 ducks.
Pros:
- Preservation of breeding stock.
- Possibility of early spring receipt of day-old ducklings for sale.
Minuses:
- The need to spend on insulation, lighting, ventilation and deep bedding in the poultry house.
- The need to install partitions for separate maintenance of uterine groups.
Do you have a poultry house for winter keeping of turkey ducks?
Not really
Pasture maintenance
The most profitable way to breed a large number of turkey ducks is in the summer. The method is suitable for experienced and novice poultry farmers.
Pros:
- Reducing the cost of purchasing feed by half due to the transfer of ducks to pasture green food.
- Producing a large volume of poultry meat during the summer season.
Minuses:
- The need to spend on fencing pastures, feeders, drinking bowls and shelters for ducks.
- To organize a pasture, you need a large area with a sufficient amount of grass.
- Pasture protection is necessary.
Walking keeping
Suitable for keeping Indian ducks at home. Requires daily attention and care of the bird. Suitable for beginner poultry keepers.
Rules of care
The answer to the question of what Muscovy ducks eat is simple: almost everything. The feed base will be wet mash: a mixture of chopped grass, tops, food scraps from the kitchen, grain and corn. The feed must be suitable for the age of the bird and its state of health. It is important to take into account the specifics of their intended purpose: Muscovy ducks for meat must be fattened according to different principles than indo-ducks, which are bred for other purposes. In terms of feeding, there are features that are worth knowing so that there are no problems with the duck:
- If there is a pond near the duckling house, then the amount of feed can be reduced. Ducks will get their own food by catching insects. However, in winter, mute fish should not swim in the pond due to weak sebaceous glands.
- Indo-ducks are naturally curious and can taste small sharp objects and swallow them immediately, which is why it is vitally important to keep the pen clean.
- Food and water should be warm, never hot, even if feeding occurs in winter.
- Birds start fights with other species of birds for food if feeders are shared.
- Indian women are prone to cannibalism. To prevent this from happening, it is important to monitor the intensity of lighting in the nest during egg laying.
Proper feeding should begin from the first days of a duckling’s life. On the first day, the ducklings eat crushed boiled eggs; on the second day, a mixture of eggs and porridge can be added to the diet. Gradually, chopped greens are introduced into the diet, and at the age of 10 days, ducklings can be fed potatoes.
Poultry house requirements
There are several of them:
- No sudden temperature changes in the room when the air temperature changes outside.
- No dampness or drafts.
- Relative air humidity no more than 75%.
- Maintaining an average temperature of +24 °C in spring and summer, +20 °C in autumn and early spring, +14-16 °C in winter.
- Availability of periodically switched on ventilation, cycle – one minute of work, 10 minutes of rest, maximum air speed of no more than 1 m/s.
- Lighting in winter is at least 10 hours.
- Deep litter in winter made of peat covered with straw.
- Availability of warm water for drinking during the cold season.
- Equipment of nests for oviposition, timely selection of eggs at low temperatures.
Feeding meat and egg-laying ducks and ducklings at home. Examples of diets depending on the period
Read
Types of drinkers for ducks and ducklings. Step-by-step instructions for making a device that does not splash water
More details
Ready-made feed for ducks. Comparative characteristics and consumption rates
Look
Possibility of keeping a duck in a city apartment. The only time this can be done
Further
Increased egg production
The number of eggs laid by a Muscovy duck may vary. There is no need to worry immediately if egg production decreases.
Muscovy duck gets sick, just like any bird
A decrease in egg production can occur in any poultry; this is influenced by several factors that need to be taken into account:
- lack of light;
- beginning of molting;
- incubation of eggs;
- invasion of rats or predatory animals;
- lack of space;
- moving nests around the house;
- diseases;
- heat or low temperature;
- lack of fresh air;
- unbalanced diet;
- obesity;
- shortage of drinking water;
- unproductive age of the laying hen.
Walking conditions
In contrast to pasture keeping of poultry, walking is considered to be a fenced and equipped area next to the poultry house.
Walking requirements:
- Mesh fencing to a height of 1.5 meters.
- The presence of a canopy over the exit from the poultry house.
- Fencing the paddock at the top with a net or regularly trimming the wings of the indo-ducks.
- Construction of an artificial reservoir or swimming pool at the request of the owner.
- No broken glass or small metal objects on the premises.
Requirements for baths:
- Shallow, wide metal containers with daily renewed water.
- Placing containers under the sun to quickly warm up the water.
- No sharp edges on the sides.
- Availability of ladders for entering and exiting the water.
- The possibility of constructing baths in the form of small reservoirs with a concreted bottom and walls, a smooth descent into the water, and a water replacement system.
Requirements for the reservoir:
- The presence of a smooth sandy descent into the water.
- Shallow depth for quick water heating.
- The presence of natural vegetation and living creatures in the water.
The disadvantage of having swimming pools and ponds on paddocks is the constant dirt around them and the presence of a large number of flies.
In conditions of dense urban and rural development, it is recommended to abandon the installation of bathing areas or concrete the walking area.
Does your farm have access to a body of water with a natural ecosystem and sufficient vegetation?
Not really
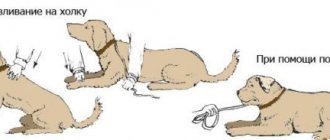
Wing clipping
Don't forget that Indian ducks, especially blue ones, still have the instinct to fly. Therefore, timely trimming of the wings is a guarantee that the bird will not leave the aviary. Only the flight feathers (tubular feathers) are trimmed.
Using sharp scissors, cut the feathers approximately to the middle. To prevent the duck from resisting and getting injured during trimming manipulations, it is enough to hold it tightly between your knees and straighten the wing.
Feeding and fattening
There are peculiarities of feeding indo-ducks at different periods of life.
Ducklings
Nutrition:
- The first day - boiled, finely crushed egg. Imported day-old ducklings must first be given water with diluted ascorbic acid powder for prevention.
- On the second day – add a small amount of additionally ground PK-5 or “Start” feed to the boiled egg.
- Gradual transfer over 3-5 days to completely feed on PK-5 or “Start” compound feed.
- Additives to mixed feed - cottage cheese, grated carrots, ground egg shells from the 5th day of life, 1-2 drops of fish oil once a day. Addition of greenery in the form of dandelion leaves, clover, woodlice, etc.
Drinking:
- use of vacuum drinkers up to 20 days of age;
- Accustoming to nipple drinkers from three weeks.
Fattening of young animals
A feature of fattening is the separation of ducklings of the same age from poultry in the farmstead.
Nutrition:
- Transition from feed PK-5 to PK-6 or from “Start” to “Growth” and “Finish”.
- Feed duckweed in large quantities as a source of protein.
- Additives in the form of beet and carrot tops, grass, ground shell rock, chalk.
- Fish and meat waste.
- Fresh small fish.
- Grain mixtures, ground into semolina, steamed corn.
- Grated beets, carrots.
Combined feeding ration per head (in grams):
| Stern | Spring | Summer |
| Grain mixture | 180 | 190-250 |
| Wheat bran | 25 | 25 |
| Greenery | 100 | 150-200 |
| Boiled potatoes | 40 | – |
| Carrot | 60 | – |
| Beetroot | 50 | – |
| Carrot or beet tops | – | 60 |
| Cottage cheese | 20 | 25-30 |
| Return | 20 | 20 |
| Hay flour | 15 | – |
| Meat and fish waste | 15 | 20 |
| Yeast | 1 | 2 |
| Bone flour | 4 | 4 |
| Shell rock | 6 | 6 |
| Chalk | 3 | 3 |
| Salt | 1.5 | 2 |
| Gravel | 2 | 3 |
Recommendations:
- To quickly gain weight during fattening, it is recommended to feed feed rich in plant and animal protein - duckweed, minced meat, fish oil.
- Fattening begins at one month of age and lasts for three months.
- After 120 days of feeding the young animals, the inducks begin to become obese and the feed is consumed ineffectively.
Barley as part of the diet of Indian ducks. How to give to chicks and adults correctly
Read
Apples in the diet of mulards and indo-ducks. Is it worth giving them on an ongoing basis?
More details
Inclusion of zucchini in the diet of mulards and indo-ducks. In what form should vegetables be added to the diet?
Look
Grass in the diet of mulards and indo-ducks. Which one can be given and from what age
Further
Uterine group
Nutrition:
- Cereal mixtures of wheat, corn, oats, barley, triticale.
- Greenery.
- Roots.
- Minced meat and fish.
- Dairy products.
- Mineral supplements.
Combined feeding ration per head (in grams):
| Stern | Autumn | Winter |
| Grain mixture | 150 | 160 |
| Wheat bran | 35 | 40 |
| Greenery | 150 | – |
| Boiled potatoes | – | 50 |
| Carrot | – | 80 |
| Fodder beet | 70 | 30 |
| Cottage cheese | 10 | 12 |
| Return | 20 | 20 |
| Hay flour | 10 | 18 |
| Meat and fish waste | 10 | 8 |
| Yeast | 2 | 2 |
| Bone flour | 2 | 3 |
| Shell rock | 6 | 6 |
| Chalk | 3 | 3 |
| Salt | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Gravel | 2 | 2 |
Disease Prevention
Keeping small Indian ducks is not difficult. But there are still cases when chicks are exposed to various infectious diseases. Treating them can be a difficult task, because sick livestock must be carefully cared for. These difficulties can be avoided with the help of disease prevention, which will be reliable protection of the entire livestock from life-threatening diseases of ducklings.
The main thing in prevention is balanced feeding. You need food rich in vitamins and minerals. It is recommended to add chalk and ground shells to wet mash. But how many grams to add is determined strictly by the age of the duck. In the first month, one serving contains 1-3 g of these substances. At a more mature age - up to 8 years.
Features of egg laying and chick hatching
Basic:
- Eggs for laying must be collected, labeled and stored for 14 days at +11 °C in a horizontal position.
- To plant an Indian duck on a nest, you need to put 18-20 eggs in it.
- If the Indian duck cannot cover all the eggs with her body, their number can be reduced to 16 pieces when the Indian duck eats food.
- To place an Indian duck on eggs, the temperature in the poultry house must be at least +14 °C.
- It is easier to equip nests using old car tires, arranging a bedding of hay. It is allowed to organize nests in the thickness of straw.
- The nest must be limited at the top so that the drake cannot drive the indo-duck away from the nest.
- Near the nests there should be a feeder, a drinking bowl and a bath.
- The bath is necessary to wet the duck's feet and transfer moisture to the eggs.
- Hatching lasts 32-35 days.
- The duckling will remain in the nest until all the ducklings have hatched.
- Hatched ducklings must be placed in a brooder at a temperature of +32 ° C to dry, feed and wait for the rest of the eggs to hatch.
- After the end of incubation, all of her ducklings from the brooder are allowed to visit the indo-duck; further care of the offspring falls entirely on the indo-duck.
Mulards are birds for one season. Features of maintenance and diet, optimal growing period
Read
Productivity of mulards and indo-ducks. Comparative characteristics of meat and eggs
More details
Which breed to choose for breeding
There are two main categories of Muscovy ducks - wild and domestic. For breeding, it is recommended to purchase domestic ones, since wild ones have more freedom-loving dispositions and are less productive in meat and eggs.
Overview of the main breeds of Indian ducks for home keeping and breeding:
- Black Indians. The feathers are predominantly black with small splashes of green and purple on the back. Most black Indian ducks have brown eyes.
- Black and white Indian ducks. They are similar to birds of the previous breed with the only difference being that there are small white spots on the chest, head and neck. Eye color is light brown.
- White Indians. These birds have all the feathers white, and the paws and tip of the beak are yellow. This breed does not have a greenish tint. The eyes of white Indian ducks are usually gray-blue.
- Brown wild turkeys. The duck's body is a deep brown color, but the tips of the feathers may have white or black spots. Small white spots may also appear on the head and neck.
- Blue wild ducks. The feathers of the bird have a rich blue color with a slight green tint. The breed is rare, so these ducks are often kept at home as decorative birds.
Note! The last two varieties of the breed produce fewer eggs and meat.
Egg incubation
At low winter temperatures in the poultry house, the turkey duck will not sit on the nest. In this case, it is recommended to hatch the ducklings using an incubator and raise them in a brooder. The number of fertilized eggs depends on the number of ducks in the brood group. If there are 2 ducks per 1 drake, egg fertilization is 100%, if there are 4 ducks – 60%.
Recommendations:
- The eggs are laid in a preheated incubator.
- The eggs are laid horizontally.
- Marks are made on each egg to control the turning over.
- Ovoscopy is performed on the 10th day, empty ones are removed.
- On day 14, all incubator vents are kept open to allow carbon dioxide to escape.
- The eggs are first cooled daily, then sprayed, then the incubator is closed.
Incubation modes:
| Incubation day | 1-7 | 8-14 | 15-30 | 31-36 |
| Temperature, °C | 38 | 37.6 | 37.6 | 37 |
| Humidity, % | 60-65 | 45-55 | 45-55 | 70-80 |
| Rotate once a day | 2-3 | 2-3 | 2-3 | No |
| Cooling | No | 5 minutes 1 time per day | Gradually increase to 15 minutes 2 times a day | No |
| Spraying | No | No | from 14 to 21 days, spray with warm water once a day, from 22 to 30 days, 2 times with warm water | 2 times a day with warm water |
Carrying out forced molting
After 4-5 months of egg-laying, indo-ducks undergo a molting stage, then a new egg-laying cycle begins. Natural molting proceeds slowly for them - from 4 to 5 months.
In order to speed up this process, it is recommended to adhere to the following procedure:
- Day 1: remove food, leave water and light;
- Day 2: exclude food, water and light;
- 3rd day: give 50 g of grain, water, light for 3 hours (from 8 to 11 o’clock);
- Day 4: exclude food and water, light for 3 hours;
- Days 5-19: constant water, feed at the rate of 100 g of grain per head per day, light for 4 hours (from 8 to 12 hours);
- 20-30 days: gradually replace grain with mixed feed at the rate of 100 g of feed per head per day, light for 6 hours (from 8 a.m. to 2 p.m.);
- 30-40 days: feeding at the rate of 130 g of feed per head per day - 20 g of grass meal, light 8 hours (from 8 to 16);
- from 41 days: gradually increase the feed supply to 200 g and then feed ad libitum.
Increase daylight hours by 1 hour per week, adding 30 minutes on Monday and Thursday, until reaching 14 hours (from 8 a.m. to 10 p.m.).
Raising ducklings
After hatching, the ducklings are placed in a brooder. Temperature conditions in the brooder:
- first week – from +28 to +32 °C;
- the second – from +24 to +28 °С;
- third – from +22 to +24 °C;
- fourth and further – from +17 to +20 °C.
Recommendations:
- The survival rate of ducklings in the brooder is 100%.
- When ducklings are in a brooder, it is necessary to monitor them and prevent pecking of weaker and smaller ducklings by separating them behind a low partition. Wounds should be treated with hydrogen peroxide.
- The brooder should have infrared lamps, vacuum drinkers, feeders, and openable vents for ventilation.
- Bathing facilities are not permitted.
- It is recommended to change the water in drinking bowls frequently: under the influence of infrared lamps it quickly fades.
- The ducklings are fed 6 times a day, every 2 hours, for 20 minutes. Uneaten food is removed from the brooder, otherwise it will quickly deteriorate under the influence of infrared lamps.
- Regular sanitization of drinking bowls and feeders is necessary.
- After the third week of being in the brooder, the vacuum drinkers are removed from the ducklings and they begin to accustom them to nipple drinkers, if floor-based housing without walking is planned in the future.
Feeding mode:
- in the first week 6 times a day every 2 hours;
- the second – 5 times;
- the third – 4 times;
- from one month of age – 3 times a day.
Feeding ration (grams per head):
| Stern | 1-10 days | 11-20 days | 21-30 days |
| Compound feed | 25 | 70 | 110 |
| Greenery | 15 | 60 | 90 |
| Food waste | — | 15 | 40 |
| Needles | 0.3 | 1 | 2 |
| Boiled potatoes | — | 10 | 15 |
| Cottage cheese | 3 | – | – |
| Return | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| Powdered milk | 2 | – | – |
| Eggs | 10 | – | – |
| Duckweed | 10 | 15 | 20 |
| Fish fat | 0.3 | 1 | 2 |
| Meat and bone meal | 0.5 | 1.5 | 3 |
| Yeast | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| Shell rock | 0.5 | 1.5 | 3 |
| Chalk | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| Gravel | — | 0.5 | 1 |
| Live weight of ducklings, grams | 200 | 500 | 800 |
After 30 days of age, the feeding ration is similar to that for fattening.
Month-old ducklings are placed in a mesh box without a bottom, installed outside on the grass. Part of the box is shaded. At night, the box is insulated with a blanket, leaving room for air. After a week, if there is no danger from cats, dogs or foxes, the ducklings are given free range on the grass.
Expert opinion
Novoselova Sofya Ivanovna
Farmer. 20 years of experience.
Ask a Question
It is not recommended to let ducklings of the same age go out into the wild with poultry. A separate area with grass, feeders and drinkers is organized for the ducklings.
The installation of baths is carried out no earlier than 1.5 months of age, when the bodies are fully feathered.
How to make a nest
Separate “apartments” must be prepared for laying hens and future mother ducks.
- For the nest, you can take a thick cardboard box or put together a box measuring 30*45 cm from scrap materials.
- It is better to place the nest in a darkened corner.
- For insulation, lay natural fabric on the bottom. Synthetics are contraindicated.
- You can “house” 3 Muscovy ducks in one nest. Oviparous females must be separated from egg-laying females.
Important! Do not allow ducklings to get into a nest with females hatching eggs. There is a risk that the “mother” will abandon the clutch and begin caring for other people’s chicks.
Indo-duck weight
From observational practice:
| Age (days) | Duck, weight, kg | Drake, weight, kg |
| 14 | 0,28 | 0,32 |
| 30 | 0.45 | 0.85 |
| 45 | 1.65 | 1.72 |
| 60 | 1.95 | 2.65 |
| 75 | 2.6 | 3.5 |
| 90 | 2.7 | 3.8 |
| 105 | 2.8 | 4.0 |
| 120 | 2.8 | 4.1 |
At the age of over 120 days, Indian ducks eat food without gaining weight. Feeding them becomes unprofitable.
Appearance
The body of the Indian duck is elongated, the chest is wide, the neck is strong and short, the head is of medium size with warty red growths characteristic of the species. They say that if you rub them, they will smell musky. The eyes are small. The head is decorated with long feathers. At the moment of excitement, the warts become much brighter, the bird hisses, and the feathers on its head stand on end.
Indian duck head
Separately, it should be noted that the Indian duck has large, strong wings; the bird easily flies from place to place. And it's easy to understand if you look at her legs. Because of them, the bird looks like a living mockery of nature - its beautiful, massive body rests on short, crooked, webbed legs.
Appearance of the bird
Slaughter time
70-90 days after hatching is the optimal time for slaughtering birds such as musky ducks. Breeding and keeping them for a longer period of time is not profitable. This is explained by the fact that after reaching the age of three months, ducks begin to eat a lot (disproportionate to the weight they gain). By the 90th day, the average weight of the female reaches approximately 2.5 kg, the drake - 5 kg.
Actually, the slaughter itself is carried out by cutting the veins through the open beak with scissors. Next, the carcass is hung to drain the blood. Then it must be kept for 3-4 hours until the fat hardens. The carcass is freed from the feather using conventional technology. That is, first the large tail and flight feathers are removed. Then the back, sides, tail, chest and neck are cleaned. At the final stage, the wings are plucked and the stumps are removed.