Just like in children, dogs change their milk teeth to permanent teeth, with only one difference - by the age of one year the puppy turns into an adult dog. Most physiological processes, including the change of teeth in dogs, proceed at an accelerated rate.
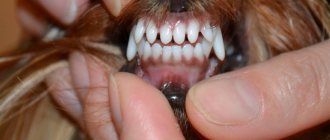
Dog puppies are born with no teeth in the mouth - with bare gums - and by adulthood they have 42 permanent teeth.
During their lifetime, dogs have two sets of teeth - milk and permanent. Moreover, regardless of the dog’s breed, the replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones occurs in the same sequence; the only difference is in the timing of the change of teeth. There is such a pattern - in dogs of large breeds, unlike dogs of small breeds, the change of milk teeth to permanent teeth occurs faster.
Milk teeth in puppies
The development of a puppy’s dentition is a long process, accompanied by serious stress for the body. Proper bite and teeth growth plays a key role in a dog's health throughout its life. The process of teeth formation and eruption is divided into stages that the owner needs to monitor.
You've probably noticed that puppies' milk teeth are very sharp. What is the reason? Many people believe that the reason for sharp teeth is obvious - the puppy must be able to tear and chew meat. Research by zoologists has shown that there are two more equally important reasons: natural weaning from mother's milk and the acquisition of skills to control the clenching of the jaws during a bite.
The mother feeds the puppies exclusively with milk until they are one month old, after which the babies begin to develop sharp teeth. Causing discomfort to the mother, babies are increasingly denied milk when they want to suckle and are forced to look for other sources of food. During play, puppies bite. Because their teeth are very sharp, strong clenching of the jaws leads to conflict situations and interference from the mother.
Symptoms of the onset of teeth change
At approximately 8 weeks of age, the puppy begins to shed its baby teeth. This period may be slightly delayed if the puppy is a large breed. Loose teeth occur because the molar tooth pushes against the baby tooth.
This is interesting! Most owners do not notice the key point in changing teeth. The baby tooth becomes loose and then simply “disappears.” Most often, the tooth falls out and is swallowed by the puppy while eating.
Symptoms of the onset of tooth loss can vary greatly. In many ways, the clinical picture depends on the dog’s temperament. Signs indicating a change in baby teeth usually appear as follows:
- Restlessness, whining, slight apathy.
- The puppy often rubs its muzzle with its paws.
- Poor appetite.
- Slight increase in temperature.
- Drowsiness.
- Diarrhea that does not lead to dehydration.
- The desire to chew and gnaw any objects.
- Resistance when trying to examine the mouth or feel the teeth.
- Smell from the mouth.
Normally, a puppy’s teeth change without alarming symptoms. The baby is constantly gnawing on something, but remains cheerful and active. During this period, you need to protect valuables from the pet’s attention, since the puppy will be attracted by the smell of shoes, wire braid, wood, etc.
Scheme of changing baby teeth in puppies
Almost all puppies are born without teeth; in rare cases, babies have incisors immediately after birth. Born completely helpless and toothless, the puppies are under the full care of their mother.
At about 2-3 weeks, the puppy's baby teeth begin to erupt. The pattern of changing baby teeth in puppies presupposes a certain order of eruption, but its disruption while maintaining the correct bite does not play an important role. Baby teeth grow in for a period of time until the puppy is ready to eat adult food.
The standard pattern for the eruption of baby front teeth looks like this:
- Middle central incisors on the lower and then on the upper jaw.
- Lateral incisors on the lower and then on the upper jaw.
- At about one month of age, the puppy's fangs erupt. According to the scheme, the lower and then the upper canines should erupt. In fact, canine growth can occur in any order.
Note! In total, the puppy should have 12 primary incisors, 6 on top and 6 below.
Sharp fangs become the first obstacle to continuing to suck the mother's milk. Experiencing hunger, against the backdrop of heightened senses, puppies begin to look for alternative sources of food. At this time, the breeder introduces supplementary feeding.
Permanent teeth
For adult dogs, the set must be complete and contain 42 teeth:
20 pcs. in the upper jaw:
- 4 molars;
- 8 premolars;
- 2 fangs;
- 6 incisors.
22 pcs. on the lower jaw:
- 6 molars;
- 8 premolars;
- 2 fangs;
- 6 incisors.
Pathological deviations are possible - extra teeth or incomplete teeth. Owners of dwarf breeds need to show their pet to the dentist once every 2 years, since all small dogs are at risk for periodontitis.
How to help a puppy with teeth changes
How to help your puppy when changing teeth, relieve discomfort, avoid complications and protect your own things from “toothies”? In nature, canines get rid of their baby teeth in a quick and primitive way - they chew sticks and stones. The puppy will do the same if given the opportunity.
When living in an apartment, you need to make sure that the puppy has something to chew on. To prevent inflammation and delayed tooth change, the baby’s mouth should be examined daily.
You should be wary if:
- The gums turned red not only along the edge of eruption.
- An unpleasant odor appeared from the mouth.
- Teeth changed color.
- Gums are bleeding.
Contact your veterinarian immediately if your puppy has a fever or has completely refused to eat. In all other cases, as long as the pet’s health does not cause suspicion, your task is to feel sorry for and distract the pet.
What can you chew to relieve itchy gums?
During the period of teeth change, most owners, through their own carelessness, lose valuable things - shoes, headphones, notebooks and even phones. Furniture, floor coverings, door jambs, etc. are often damaged. How to prevent a “catastrophe”.
What can you give your puppy to chew to relieve discomfort:
- Durable toys - so that the baby does not get bored with the same objects, they can be changed every 2-3 days.
- Teethers are durable, specially shaped toys. The advantage of teethers is that they are safe; even if the puppy bites off a piece of the toy and swallows it, nothing will happen.
- Chewable treats (bones, sticks).
- Large articular bones (moslaks) with meat, spongy bones, raw and boiled cartilage.
- Raw vegetables and fruits.
- Wood, dry, preferably from fruit trees.
The best option to interest the puppy and teach him to chew only permitted objects is special treats and toys.
Bones are a good option if the puppy is in plain sight, but needs something to keep him occupied. Vegetables and fruits are the most useful toy. The puppy receives vitamins, coarse fibers and is accustomed to healthy food.
Prevention
Dental problems are quite easy to prevent if you approach your pet's health responsibly, starting from puppyhood.
Provide a complete, balanced diet, with the obligatory inclusion of solid food (exclude chicken bones).
To accustom a puppy to hygienic teeth brushing, if you miss the moment, it will be difficult to brush the teeth of an adult dog.
By periodically cleaning your teeth at home, you will be able to notice inflammation or looseness of the tooth at an early stage. Contact a specialist in a timely manner and preserve your pet’s proper bite.
If you notice that your dog has tartar, bring him to the clinic for ultrasonic cleaning.
I strongly recommend not to go to animal salons (grooming) for this procedure, but to go to a veterinary clinic. Since this procedure must be performed under sedation (light anesthesia).
This is necessary for several reasons:
- The procedure is painless, but the dog is very nervous and stressed.
- During brushing, drops of water and particles of tartar fly off. When a dog is nervous, it breathes unevenly and may inhale “tooth dust.” As a result, we get Aspiration pneumonia.
- In salons, this procedure is performed without sedation. And even if under it, there is not always everything necessary to safely carry out this procedure.
Already with a small puppy you need to start all these games with a stick, a ball, etc. This is not just fun, such games provide the necessary load on the jaw so that it develops properly.
When buying a purebred puppy, especially if it is brachycephalic, you need to be sure of the integrity of the breeder. Check the health of the puppy's parents to prevent genetic abnormalities in the formation of the bite.
Possible complications
As soon as the puppy begins to change teeth, the health of the oral cavity and the general well-being of the pet must be closely monitored. Some breeds have a tendency to delay the replacement of baby teeth and develop oral diseases.
If you do not have experience in keeping dogs, it is better to take your baby to the vet at the age of 8-10 weeks. Delay associated with possible complications may result in irreversible malocclusion.
Note! If you buy a puppy from a kennel, the breeder must provide x-rays proving that the baby will have full teeth. If they are trying to “prove” to you that the puppy’s full teeth are determined by the milk series, it is better to find another breeder.
Gum inflammation
Inflammation of the gums, these are the consequences:
- The eruption of teeth that are too large is a genetic factor.
- The formation of “hoods” of gums, under which food remains and rots.
- Poor nutrition.
It will not be possible to avoid gum inflammation, to a greater or lesser extent. The main thing is to control the process and prevent its rapid development.
In case of severe inflammation, the puppy is prescribed procedures to maintain oral hygiene, or, in extreme cases, anti-inflammatory drugs.
conclusions
The first teeth appear in 20-30 days - 32 pieces or 28 in some breeds. Teeth change begins at 2-4 months, and molars grow in by 7 months. Pathologies are possible and most of them are correctable if detected in a timely manner. Control over the process rests with the owner, and the doctor can only help solve the problem.
Please follow and like us:
Nikitin Sergey
I write about dogs based on the experience and knowledge gained during my studies as a veterinarian, work in my specialty, and simply from observing my pets.
Types of bite and its disorders
To control whether your puppy’s teeth are growing correctly, you need to know the types of bites and their disorders. Note that for some breeds, minor malocclusions caused by genetics are allowed by the standards.
The following types of bite are distinguished:
- Correct or scissors - the teeth of the lower jaw are hidden under the teeth of the upper jaw without gap or friction.
- A flat bite or pincer bite is normal in some breeds. The upper and lower incisors meet in a straight line.
- Underbite is always a violation. There is a gap between the incisors of the lower and upper jaws when closed, larger than the breed standard allows.
- Snacking is normal for some breeds. The incisors of the lower jaw protrude in front of the incisors of the upper jaw.
The bite is considered normal if:
- The dog has all its teeth.
- The canines close together, except for breeds for which a strong overbite is acceptable.
- The dog's incisors are straight and strictly parallel.
Note! Almost all breed standards require that the dog have all teeth consistent with the dental chart.
Bite disorders are considered:
- Curvature or misalignment of the jaws.
- Lack of teeth.
- Curvature of canines and incisors.
Note! For most breeds, a gross defect is the visible teeth or tongue when the dog's mouth is closed.
Feeding a puppy during the teething period
Feeding a puppy during the period of teeth change should be as gentle as possible. Because there is a risk of inflammation, make sure that your diet does not include foods that are too rough or difficult to digest.
If your puppy experiences obvious discomfort while chewing, switch him to food that can be licked. Over the course of several days, while the baby's fang is erupting, his health may deteriorate significantly. If you refuse food, try switching your puppy to a completely liquid diet, for example, broths and fermented milk products.
How to feed your dog correctly during this period?
When puppies lose their baby teeth, there is no need to specifically change their diet. The pet continues to be fed with the same food. Dry industrial food partially removes plaque and also massages the gums when grasping granules.
With natural feeding, the resulting food may be too soft. In this case, the pet should additionally be given special treats that will create a load, strengthening the periodontium. In addition, soft food lingers to a greater extent on the enamel, gradually forming tartar.
Expert opinion
Kuzmenko Olga Olegovna
Information about the expert
Ask a Question
It is not recommended to include additional mineral supplements (including calcium) in your pet’s diet without consulting a veterinarian (especially when feeding industrial feed).
Is it possible to get vaccinated?
Veterinarians strongly recommend postponing vaccinations while teeth are changing. While the baby's molars are erupting, his immunity is in a constantly tense state. Before vaccination, anthelmintic measures must be carried out. The complex load may be too severe for a weakened body.
Vaccination against a background of strained immunity can lead to contracting the viral disease from which they are trying to protect the puppy or to developing an incomplete response.
Once the weakened virus enters the puppy's bloodstream, the immune system should not destroy it too quickly. In this case, the leukocytes responsible for “remembering” enemy cells simply will not have time to do their job.
Dental care for puppies
Puppies' milk teeth are different in structure and shape (from their molars), so they require special care. Puppies' dental care is carried out using a durable, rubber toy. In pet stores you can find special teethers that will help your puppy reduce discomfort and keep his teeth clean.
As an alternative, you can use special, hygienic treats. Typically, treats are made from dried tendons or meat. With natural feeding, you can give the puppy large bones that he can starve, but cannot chew. While the puppy is playing with the bone, he needs to be supervised.
When a puppy's teeth have changed, he must be taught adult hygiene. It is important to understand that not all adult dogs need regular teeth brushing, but getting your dog used to the process of brushing as a puppy is essential. If your pet eats properly, regularly receives hygienic treats and has the opportunity to chew sticks/bones, you won’t have to worry about dental health until the age of 5-6.
However, you cannot predict the various oral diseases that affect the teeth. Brushing the teeth of an adult, untrained dog is torture for both the pet and its owner. Usually, untrained dogs have their teeth cleaned under anesthesia.
What is diarrhea?
The main sign that we are not talking about episodic diarrhea, but about a full-fledged disorder, is the daily frequency of stool. Diarrhea is loose stool that occurs in paroxysms: three times a day or more often. At the same time, the water content in feces, normally 50-80%, increases to 95%1.
Diarrhea can be acute or chronic.
Acute form
(up to 14 days) may appear as a result of poisoning, eating allergenic foods2, intolerance to certain foods, medications, or the entry of certain viruses and bacteria into the body2.
Chronic
(from a month or more) - as a result of taking antibiotics, laxatives. The cause may also be certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract2.
The second most important sign is the condition of the stool. Color, consistency and the presence of impurities may indicate various diseases. For example, watery and loose stools, as well as a greenish tint to the stool, indicate the development of an intestinal infection. The cause of loose stools that are light in color and clayey in appearance may be damage to the small intestine and its initial sections.
Breed characteristics of tooth change
There are breed specific characteristics of teeth changing. If your pet is applying for a show career, it is better for a veterinarian to monitor the process of changing teeth and bite formation.
Before purchasing a puppy, it should be examined by a veterinarian, since gross malocclusions are immediately visible and they do not “resolve” with age, but only get worse. Upon first request, or preferably in a package with documents, the breeder must provide a photograph of the parents’ bite (sometimes two generations are considered) and an x-ray of the puppy’s jaws.
German Shepherd
German Shepherd – the bite is formed according to a standard pattern. Correct bite - only scissors. The teeth must be complete. Any malocclusion is regarded as defects or gross deficiencies.
Labrador
Labrador – the requirements are similar to those above: correct bite and a complete set of teeth.
Spitz
Spitz - requirements depend on the subspecies. The smaller the Spitz, the higher the risk of problems associated with changing teeth.
Spitz dogs have a common overbite, overbite and underbite, although only scissor bites are allowed by the breed standard.
Jack Russell Terrier
The Jack Russell Terrier is a working dog that must have a full set of teeth and a correct bite.
Laika
Laika is a working dog that must have a full set of teeth and a correct bite. Laikas often have problems developing their bite, since this type of dog is still considered a breed group. Simply put, your pet’s blood may be mixed.
Dachshund
The Dachshund is a working breed, so according to the standard, it must have a full set of teeth and a correct bite.
Yorkshire Terrier
The Yorkshire Terrier is a very problematic breed in terms of health, teeth change, and bite formation. Very often, Yorkies have to have their baby teeth removed because they do not fall out in a timely manner.
Dental problems occur even at a young age. To prevent various diseases of the oral cavity, a veterinarian should examine the dog at least once every six months.
Pug
The pug is a problematic breed in terms of health and teeth change. The standard bite is a pincer bite—the incisors meet in a straight line. A small undershot is allowed, up to 3 mm. Underbite and scissors are deviations. Pugs often experience delays in the loss of baby teeth and crooked incisors.
Diagnostics
When you take your dog to the vet, diagnosis always begins with a history.
Be prepared to answer questions like these:
- When and what alerted you, what were the first symptoms you noticed?
- Tell us everything about your pet's nutrition.
- Have you noticed a preference for softer foods?
- Do you give your dog a hygienic teeth cleaning? If so, what is used for this?
- Smell from the mouth?
- Lately, has the dog opened its mouth reluctantly, with effort, or normally?
The next step is inspection.
- The doctor looks at the general condition of the dog: coat quality, fatness, behavior.
- Inspection of the mouth.
- Counting the number of teeth.
- Bite assessment, taking into account breed characteristics.
- Definition of permanent and temporary (baby) teeth.
- Assessment of the condition of the gums and oral mucosa.
Sometimes color tests are performed to visualize the pathological process, for example:
The Schiller-Pisarev test is carried out using a special solution based on iodine. This solution affects the surface of the gums. If there is no inflammatory process, then nothing will happen, it will not become colored. Otherwise, the gums become dark brown, which indicates inflammation.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is always necessary to take an x-ray.