Ichthyophthiriasis is a disease that many aquarists call semolina. The name comes from the tubercles that form on the body of a sick fish. These tubercles are similar in appearance to semolina, but much smaller. The causative agent of the disease is the ciliate ichthyophthirius multifiliis belonging to the class Ciliata. It has an oval body, in front of it there is a mouth surrounded by cilia. Cilia also surround the entire body of the ciliate. Thanks to them she moves.
Reproduction of ciliates occurs by division. As soon as the trophonts mature, the pustule ruptures in the epithelium of the aquarium fish and comes out. After this, it sinks to the bottom and attaches to the ground, stones, plants, and decor. Next, a cyst is formed, inside which the process of division begins.
During the division of one trophont, about 2000 daughter parasites appear. They break the shell and swim in the water, looking for a new victim. If the young ciliate does not settle on the fish for several days, it dies. Parasites that find a new victim are located in the gills and the upper layer of the epithelium. There they grow. When they reach maturity, they leave the fish and the cycle repeats again.
The growth of equal-ciliated ciliates is influenced by the following parameters:
- The comfortable temperature for their development is 25 degrees.
- Low water temperature increases the time of cyst formation and the time to search for prey.
- Poor lighting increases the lifespan of young cells.
- At a water temperature of 30 degrees and above, ciliates die within 5 hours.
Pets who have suffered from ichthyophthyriasis acquire immunity. If the disease recurs, the fish will survive.
How does infection occur?
All fish, without exception, are susceptible to semolina disease. But most often the disease spreads in tanks where there is an overpopulation of fish.
Ciliates can get into an aquarium in several ways:
- From a reservoir along with a planted plant, along with soil, driftwood and water. To prevent this, everything caught from a reservoir must be processed.
- With live food.
- When relocating plants and fish from another aquarium, for example when buying new pets.
Table salt is the first remedy for ichthyophthirosis
Remember, back in the biology textbooks for the fifth grade, an experiment was described. Two drops of water with a thin isthmus between them, an amoeba was placed in one and salt was added. The amoeba immediately moved to where the water was fresh. That is, salt is harmful to microorganisms. Therefore, we want to tell you how to treat fish from semolina with salt. In fact, the method is good, twenty years ago I was the leading one, there was simply nothing else. The technique is simple: add one tablespoon of salt to 10 liters of water. The fish should survive in this solution for 3 to 5 days. There are methods for making a more concentrated solution, up to 1 tablespoon per liter. The fish are placed in it for 3-5 minutes, and then released into quarantine, where the salt concentration is normal. At this time, the main aquarium is cleaned and disinfected, that is, completely restarted.
Ichthyophthyriosis: symptoms and diagnosis
Pets suffer from semolina for about 2 weeks. If left untreated, all inhabitants die. The fry die on the 8th day. Livebearers and girardinuses are the least likely to suffer from ichthyophthyriosis.
As soon as the ciliates have entered the gill covers and the upper layer of the epithelium, the following symptoms appear in the fish:
- Anxiety.
- Pets begin to rub against plants and algae.
- They try to swim in the area of bubbles coming from aeration.
- When trophonts form, white tubercles become noticeable on the body of the fish.
- The pet often rises to the surface and swallows air.
At the last stage of semolina, the inhabitants of the aquarium do not react to external stimuli and refuse to eat. Sometimes during illness the corneas of the eyes are affected, which leads to blindness. When ichthyophthirius multifiliis leaves the body of an aquarium inhabitant, it breaks the capillaries. Because of this, blood clots appear on the body, gas exchange in the fish’s body is disrupted, the body is poisoned by the waste products of the parasites, and the pet’s death soon occurs.
UV sterilizer
A modern method of treatment and protection not only from many diseases caused by protozoa. A device that emits UV radiation, which leads to the death of microorganisms.
Power and dosage are selected individually. During illness, most likely, you will simply need to turn it on to constant radiation
.Method 1 (advanced-gentle)
For fish intolerant or intolerant of malachite. We are being treated with delagil. The treatment regimen is as follows: 1 tablet (250 mg) per 30-50 liters of water. After daily water changes of 25-30%, repeated applications are required in an amount equivalent to the changes to restore the concentration of the drug. Can be used with half the dose of malachite green (0.05 mg/l), then the cure occurs faster. If you need to use it without malachite, then it should be noted that the treatment is not quick and at a late stage of infection you may simply not have time to remove the ichthic from the fish. Keeping the temperature elevated and providing aeration is business as usual. Delagil does not damage biofiltration in the indicated doses. There have been cases of damage by delagil to stretching - from simple to fastidious, but this does not occur reproducibly, therefore, apparently, it depends on other factors (for example, pH, gH, etc.). Delagil is not always easy to find in pharmacies.
Method 2 (killer)
It is often recommended to use mixtures of malachite with antibacterial nitrofuran drugs to treat ichthic. Such mixtures often help in the fight against “unkillable” forms of ich due to the fact that nitrofurans not only suppress secondary bacterial infections, but also have a pronounced antiprotozoal (antiparasitic) effect.
This is exactly what SuperIckCure is in capsules - a mixture of malachite green and furacilin (nitrofurazone). Or 'just' a mixture of malachite with furatsilin - for example, the drug 'Malachite green' in the dosage according to the instructions + furatsilin at the rate of 1.5 tablets of 20 mg (this is the usual form of tablets sold in human pharmacies) for every 20 liters of water (which will correspond to the amount of furatsilin in branded drug SuperIckCure - capsules). When treating large fish (in particular red parrots) from tropical ichthic, you can add one and a half dosages of this drug, with the usual dose applied immediately, and the additional 'half' dose gradually.
When using malachite in combination with furazolidone, the latter should be added in the amount of 6-8 tablets of 50 mg per 100 liters of water.
It should be noted that nitrofurans have a detrimental effect on biofiltration, so these mixtures are strongly recommended for use in a leach tank. Or, if this is not possible, then be prepared for a disruption in the biological balance and, accordingly, regular intensive replacements to remove nitrogenous compounds until the normal functioning of biofiltration is established.
Moreover, during the course of these drugs, it is recommended to feed the fish to a minimum (preferably no more than once every 2 days) in order to avoid the accelerated accumulation of nitrogen compounds and poisoning of the fish with them. It is better to carry out replacements daily by 20-25% (or more) of the total volume.
Antipar (Agrovetzaschita) and FMC preparations, which are a mixture of malachite green, methylene blue and formaldehyde, are also not recommended for use in a general aquarium due to expected (due to the presence of methylene blue) biofiltration failures, or when using them, follow the recommendations given in the previous paragraph .
Any treatment and prevention will be more effective in a well-kept aquarium, where the fish are free from stressful situations. The causative agents of the disease ichthyophthyriasis can appear in almost every aquarium. But if its inhabitants are healthy, do not lack nutrients and oxygen, and live in favorable conditions, the disease has little chance of manifesting itself in the aquarium.
GUPPY DISEASES EXTERNAL SIGNS AND TREATMENT PHOTO DESCRIPTION VIDEO.
FIN ROT - DESCRIPTION TREATMENT SYMPTOMS VIDEO PHOTO.
How to treat semolina in fish
Before you begin treating semolina in fish, you should understand some of the characteristics of the parasite. In the body of the fish, the ciliate hides under the upper layer of the epithelium. Medicines can only overcome parasites that have escaped into the external environment. In no case should you exceed the dose of the drug, as this may negatively affect the condition of the fish. Equal ciliates react poorly to increases in water temperature. The first signs of semolina appear a few days after the parasite has entered the victim’s body.
If there is no result
First of all, do a water change again. This is very important, because endlessly adding different drugs to the same closed system is fraught with the complete destruction of life in it. If you have still not been able to achieve positive changes, try the following scheme. This is Sera Costapur in full dosage, and a nitrofuran drug is added to it. This is regular furazolidone. Almost all microorganisms, bacteria and protozoa are sensitive to it. Its dosage must be very carefully controlled, no more than one tablet per 15 liters of water. This is a very strong remedy, but it completely destroys all microflora. For about two to three weeks, the water will have an unpleasant yellowish tint, but since it is necessary to treat aquarium fish for semolina, it will not go away on its own, so you will have to be patient. Now for several days you can only monitor the condition of your pets. If there is an improvement, then you can calm down. However, in rare cases it happens differently.
Preparations for the treatment of semolina:
Universal products:
- A solution of malachite green will quickly relieve the fish from the disease. Used in the form of baths.
- Sera Omnisan. Omnisan copes with the disease only in the early stages. Not suitable for stingrays, sharks, crayfish and shrimp.
- Sera Mycopur. Micopur is a conditioner against fungi (Saprolegnia), fungal diseases, skin and gill worms.
- The combination of drugs Omnisan + Mycopur acts on all forms of tropical ichthyophthyriosis.
Specialized products:
- AVZ Antipar. Treatment with this drug is carried out in a general aquarium, it is safe for vegetation, and has a wide spectrum of action.
- Aquayer Ichthyophthiricide - malachite green, does not contain formaldehyde, it is recommended to carry out treatment in a separate container.
- Sera Costapur - universal, for several types of skin parasites, not suitable for invertebrates.
- Rikka Ichthyocide - against all ichthyoparasites (Ichtyophthirius, Ichtyobodo (Costia), Heteropolatia, Chilodonella, Tetrahymena, Trichodina, Glossatella in fresh water, Cryptocarion, Brooklynella, Uronema in sea water), not suitable for catfish.
- Tropical CMF - against bacteria and fungi with a broad spectrum of action.
- For advanced cases, JBL Punktol ULTRA is suitable.
"Bicillin-5" - an antibiotic to fight the disease
This is a common human antibiotic of the penicillium group. However, if you are looking for options on how to treat fish for semolina at home, you will probably come across the recipe as a practical recommendation. The dosage when placing fish in a separate container is 500,000 units, that is, a third of a bottle per 10 liters of water. They need to be placed in this solution every day for 30 minutes for 6 days. In addition, the same portion is added to the general aquarium, only for 100 liters of water. This procedure is repeated for 6 days. However, I would like to note that this drug helps fight only a secondary bacterial infection, and not at all the semolina itself. Therefore, do not expect that you will be able to cure your pets this way.
Prevention of semolina in fish
To disinfect the aquarium, the inhabitants are transplanted into another container for 8-14 days. And where there was an outbreak of semolina, they raise the temperature to 29-30 degrees. If special preparations were used to treat semolina in fish, then the water is purified with a carbon filter.
To prevent the disease from starting again, some precautions should be taken. All new inhabitants and plants must undergo quarantine. The fact is that a newly acquired fish may already be infected, but the symptoms of the disease are not yet noticeable. After placing it in a community aquarium, semolina can begin to develop very quickly.
New fish should sit in a quarantine tank for 10-14 days. If nothing happened to the new pet during this time, then it can be placed in a common tank.
Causes of the disease
Often semolina ends up in an aquarium with water or new fish from the store. Large pet stores carry out quarantine, checking goods for the presence of aquarium fish diseases, while smaller stores may not notice parasites. Frozen food is no less dangerous, although there are much fewer cases of infection due to it.
Ichthyophthiriasis prefers to develop in water with average or elevated temperatures. At the same time, parasites adapt to any composition and severity. Freshwater fish with weakened immune systems are primarily infected. The cause may be stress, poor living conditions, improper feeding, or aggressive neighbors. Ciliates can be on the body of a healthy animal and wait for the right moment. Therefore, a normal appearance and bright, rich color does not mean that it does not pose a danger to other pets. Even if she does not get sick, other inhabitants of the underwater world, whose body will be weaker, may be susceptible to infection.
The causative agent of the ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis has several life forms:
- trophont - parasitizes the fish for some time, forms pustules, colloquially called semolina, ichthic and leaves the host;
- tomont - the form in which a parasite exists that has left the host;
- cyst tomite - the form into which tomont turns;
- theront is the form into which tomite turns and which infects the fish.
Photo 2 Life cycle of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis
The pathogen parasitizes on the body of fish and on the gill filaments
The disease is treatable.
What is needed for treatment
First of all, these are medicines from world brands of aquarium products, for example, Tetra Contralck, SERA med Professional Protozol, JBL Punktol Red Plus, ZMF Ex-Rapid, immunostimulating drugs, for example, Preis Aquaristik Preis-Immun-Tonic, drugs containing ions various microelements, since sick fish lose them, which can cause other diseases. The full range of medicines and bioactive additives can be found on the pages of aquaMegaMall.ru
If it is not possible to use modern medications, you can use other medications, a list of which is given in the Treatment section.
Before starting treatment, it is recommended to clean the aquarium, thoroughly siphon the soil, and remove mollusks and crustaceans. The aquarium should be completely shaded, filtration should be turned off, and aeration should be increased.
It is highly desirable to have an outpatient aquarium without soil.
If many fish are affected, treatment is carried out in a common aquarium.
Photo 3 Appearance of the first pustule
Quite often you can find recommendations on forums to increase the temperature to 30˚C. Tetra GmbH specialists do not advise doing this, because if tropical ichthyophthyriasis occurs, such an increase will activate the parasite reproduction cycle, and if the gills are affected, the fish may die due to a drop in oxygen concentration in the water.
Symptoms
In the case of parasitism on the body, it is almost impossible to detect the disease in the initial stages. As the results of studies by Wilfred Haas and Bernard Haberl published in 199 in the journal Tokai J Exp Clin Med. showed, the parasite, penetrating under the skin of the host, releases specific analgesic substances, so the fish does not experience any discomfort. After penetration, the release of such substances stops, and the fish begins to show anxiety, characteristic symptoms:
- rapid breathing;
- the fish tries to hide in secluded places;
- begins to spend most of the time lying on the bottom;
- the fish begins to “itch” against various objects with sharp sliding movements;
- sometimes the fish begin to swim under the surface on their sides.
However, since the channel through which the parasite enters the body quickly tightens and becomes inaccessible even when examining the fish with a powerful magnifying glass, diseases can only be detected after the formation of small white tubercles on the surface of the body - pustules.
Photo 4 Botia in the initial stage of pustule manifestation
It is more difficult if the parasite settles on the gills.
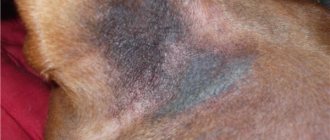
Photo 5 Gill filaments affected by ichthyophthyriasis
The photo shows white lumps - large mature trophonts. White vast areas are areas with completely destroyed gill filaments. The preserved gill filaments are dark cherry in color because they are filled with venous blood.
Treatment
When choosing a drug for treatment, you need to remember that drugs that contain formalin and malachite green in large doses are poorly tolerated by loaches, young characins, and labeos - therefore the concentration is reduced to 0.06 mg/l. True, this will make the treatment longer, but the fish will not be harmed.
The first method of combating ichthyophthirius was proposed in 1894 by Stills - he discovered the destructive effect of sodium chloride on the parasitic ciliate and used salt as a medicine. In 1972, Cross proposed an improved method of administering this treatment using a salt gradient. Salt in the form of large crystals was placed on the mesh bottom of an outpatient aquarium. The fish rushed to the upper layers, and the tomonts that left the owner sank to the bottom, where they died from the high salt content in the water.
Today, with the availability of much more effective drugs, this method is practically not used. Many studies have shown that modern trophonts and strays are much more resistant to sodium chloride than fish. However, professionals still advise adding a small amount of salt to the solution with the medicine. The fact is that fish infected with ichthyophthyriasis begin to intensively lose magnesium and sodium, so adding salt will help make up for the lack of essential ions.
“Old” methods of treatment include the use of formaldehyde. This substance is added to the aquarium water at a rate of 0.25 ml/l every other day until the fish recovers. In the intervals between application of the drug, the water is replaced. A method of treatment using formaldehyde baths was also practiced (data from the article by Brown and Gratzek for 1980). The affected fish is treated for an hour with a solution of 1.6-2.5 ml/l. The huge disadvantage of this method is that it is completely impossible to use in an aquarium, since formaldehyde kills algae and plants.
The traditional method of treatment is the use of malachite green, sometimes with the addition of formaldehyde. It is important to remember that only malachite green has an effective healing effect in the form of a zinc-free salt of malachite green oxalate. The fish are treated with a solution at three-day intervals, transferred to an outpatient aquarium with water containing 0.001 ml/l of the substance. Carbon filters are not used; enhanced aeration is installed.
Treatment in the form of baths is also used, increasing the concentration - up to 0.02 ml/l, bath time - thirty minutes.
The disadvantages of malachite green include, first of all, the fact that the substance is a carcinogen not only for fish, but also for humans.
In combination with formaldehyde, malachite green is pre-dissolved in formaldehyde at the rate of 3.5 grams per liter. This solution is added to the aquarium at the rate of ¼ milliliter of solution per liter of water. Treatment is performed three times with a 3-day interval.
In 1992, information appeared that feeding fish with malachite green added to food was quite effective against trophonts. In 1996, this information was confirmed with the caveat that the method can only be used in the initial stages of the disease and applied only to fairly healthy fish.
The literature on aquarium husbandry quite fully describes attempts to use such substances for treatment as:
- copper sulfate (Brown and Gratzek, Straus;
- quinine, acriflavine, drugs containing mercury, quinacrine, chloramine-T (Cross).
However, it turned out that all these substances are ineffective in the fight against ichthyophthyriasis.
Of great interest is the course of treatment tested and shown to be effective in the Leningrad Zoo in the treatment of young animals (size from 3 to 5 centimeters) and adult bots, mystus, acanthophthalmus, fractocephalus, goldfish, pacu, pseudoplatistoma. Positive reviews about this method are presented in large numbers on various aquarium forums. Successes have been noted in curing small characins and small carp-toothed species.
With this method, the aquarium is completely shaded and, if possible, the temperature is lower than normal by two degrees.
- Delagil is added to an outpatient aquarium at the rate of 1 tablet (250 milligrams of active substance) per 40 liters. Water (if scaleless fish are treated, the dose is reduced by 1/3), then half the standard dose of malachite green is added.
- After 12 hours, without changing the water, add another ½ standard dose of malachite green.
- After 12-24 hours (shorter interval for tropical forms of ichthyophthyriosis and with heavy shedding), replace 25% of the water and add ½ dose of Delagil and ½ dose of malachite green;
- Next, repeat the procedure described in paragraph 2 and repeat the cycle until the rash disappears;
- After the pustules disappear, the cycle is repeated at least twice.
One of the advantages of delagil is that it does not have a detrimental effect on biofiltration, which is important when treating in a community aquarium.
The following even more gentle method, in which the composition is used in 30 liters of water, is very effective in the initial stages of the disease:
— metronidazole – 250 mg;
- nystatin - 500,000 units per 50 liters of water;
- erythromycin - 250 mg.
The treatment regimen is the same as for treatment with delagil.
Treatment with ciprofloxacin gives good results. Pre-prepare a stock solution - 1 tablet (500 mg of active substance) per 80 liters of water. Prepare a therapeutic bath with excellent aeration and place the fish for three hours, then transfer it to an outpatient aquarium, the water in which is subjected to UV sterilization. The duration of the therapeutic bath is no more than five hours. The next day, the procedure is repeated, the water in the outpatient aquarium is completely replaced, and the aquarium itself is thoroughly washed. The treatment cycle is five days. In especially severe cases it may be increased.
In the absence of industrially manufactured drugs, treatment with a mixture of malachite green and nitrofuran agents works well. This is exactly the composition of the drug SuperIckCure produced by Aquarium Pharmaceuticals. You can prepare it yourself. Malachite green is taken in standard concentration, nitrofurazone (furacilin) at the rate of 30 mg (one and a half standard tablets) per 20 liters of water. For the treatment of large tropical fish, the dosage can be increased by one and a half times, and the usual dose is applied immediately, and the excess is added gradually. When replacing nitrofurazone with furazolidone, add 8 tablets of fifty milligrams per hundred liters of water. When treated with nitrofurans, feeding is limited to at least once every two days. Water changes are carried out daily, replacing 25% and replenishing the loss of medicine.
Nitrofurans kill biofiltration, so treatment is carried out only in sedimentation tanks.
One of the most effective methods of treatment with bicilin-5 was proposed by V. Mikhailov. The aquarium is shaded, the temperature is set in a narrow range of 25˚C-26˚C. For 6 days, a solution of bicilin-5 is added every night (500,000 units per 100 liters). The antibiotic is poorly soluble in water, so the solution is first prepared in warm (28˚C) water and immediately added to the aquarium. After adding the drug, the fish are not fed. Only live food is allowed in the morning.
It is not recommended to carry out treatment in general aquariums where Echinodorus, Vallisneria, Aponogetona, Barclay are planted - these plants do not tolerate the drug well.
Treatment with Bicilin-5 in the form of baths. The solution is prepared at the rate of 1,500,000 units. per 10 liters of water, add to a darkened outpatient aquarium immediately after preparation. Bath time – ½ hour. The full treatment cycle is 6 days.
There are also non-drug treatment methods that allow you not to affect the ecosystem that has formed in the aquarium. The method is quite troublesome and is usually used in cases where rare plants are planted in a common aquarium and there is a danger of damaging them with fish medicines. To do this, you will need two jigging aquariums, an outpatient aquarium for fish with pronounced symptoms. Fish with rashes are placed in an outpatient aquarium and treated according to one of the above schemes, and other inhabitants are placed in the first tank, in which they are kept for 12 hours, after which they are transferred to the second tank, and the first is thoroughly washed and dried. After being kept in the second tank for 12 hours, the fish and other inhabitants are transferred to the first tank, and the second is washed and dried. I repeat the procedure cyclically for 12 days. The water is subjected to enhanced filtration using dolomite filters.
Currently, methods of treating ichthyophthyriasis aimed at destroying trophonts have not received proper distribution. The difficulty of fighting them is that the parasites lie under the skin, which makes the direct effect of drugs inaccessible. In 1983, experiments were carried out on the delivery of medicinal substances directly to the location of the infusoria. Immersion in surfactant solutions, osmotic shock, and vacuum infiltration (Post and Vesely) were used. The results were negative. In 1988, work began to search for substances capable of infiltrating through the skin. It was shown that toltrazuril is able to penetrate the skin and destroy trophonts: the therapeutic dose was 10 mcg/ml, the treatment time was 3 days with daily immersion of the fish in a medicinal bath for 4 hours. Mechlhorn's research in the same year showed that the drug had a detrimental effect on trophonts, but was completely harmless on theronts. Schmakhl's studies conducted from 1992 to 1996 showed high effectiveness in the fight against trophonts of the triazinone substance HOE 092 V. Treatment was carried out by analogy with treatment with toltrazuril using quinine as a food additive. The tested koi and cardinal carp were completely cured.
Many practicing aquarists advise adding 5 drops of iodine tincture per hundred liters of water during treatment - in their opinion, this significantly enhances the healing effect of the medicine.
UV sterilization has proven itself well in the fight against ichthyophthyriosis. These devices perfectly kill free-floating forms of parasites, which can become active after cleaning the soil, general cleaning of the aquarium, water changes, and planting, which is accompanied by strong stirring of the soil. This method requires a pump capable of creating a strong current that will capture pathogens and, along with the flow, transfer them to the UV sterilizer.
Prevention/interesting for experts
It is important not to transfer new fish to a community aquarium without quarantine. It is interesting to note the described cases when fish that had previously recovered from ichthyophthyriasis acquired a kind of immunity and retained parasites on their bodies that were in a latent state, but in relation to fish that had suffered transport stress, they turned out to be pathogenic and the newly introduced fish became ill, and aquarists believed that it was the introduced fish that became cause of infection.
An important preventive measure is the immediate removal of dead individuals from the aquarium - the trophonts almost immediately leave the corpse and are quickly encapsulated.
Prevention of ichthyophthyriosis will be effective only if it is comprehensive. It should include:
- preventing the possibility of contact of ciliates with fish - strong currents;
- diagnostics and initiation of treatment in the early stages of development - constant monitoring of the fish;
- treatment with drugs that increase the redox potential of water, for example JBL Ektol crystal, SERA ectopur, sold at aquaMegaMall.ru - promotes the activation of dormant cysts, weakens Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in all forms of development, increases susceptibility to drugs: the application of such drugs in accordance with the instructions from manufacturer helps to quickly identify parasitic infusoria and increase the effectiveness of treatment;
— quarantine measures..
Quarantine measures - you cannot immediately introduce newly acquired fish into a common aquarium. It should be placed in a separate vessel for 2-3 weeks at a temperature (if possible) of 24˚C. At a temperature that is optimal for the parasitic ciliate, I. multifiliis will be able to go through several development cycles during this time and visually appear on the body of the fish.
Experienced aquarists advise not to use soil in quarantine aquariums - on a clean glass bottom you can clearly see trophonts and formed cysts.
Manufacturers from Southeast Asia, faced with the problem of complaints from European consumers regarding cases of fish infection with ichthyophthyriasis, came up with an original way of preparing live food. The food is placed in a container in which the fish also swims in a compartment that communicates with the general volume of the vessel and has holes sufficient for the penetration of the mobile form of the ciliate, but not sufficient for the passage of food. If the fish does not get sick within five days, food is given to the rest of the fish.
Effective quarantine measures include measures aimed at interrupting the cycle of infection with I. multifiliis. The most infectious form upon contact is the free-swimming theront. To reduce their mobility, add a little salt to the water. The fish itself is periodically transplanted from one vessel to another. Such a transplant every day for seven days is sufficient to break the parasite's reproduction cycle.
In the 21st century, work began, as a result of which it is expected to obtain effective drugs against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, the mechanism of action of which is based not on chemical effects, but on the biological level. The most promising work is using genetic engineering methods. Research in this area has revealed that the ciliates that provoke the disease are very variable and exist in the form of several strains, that is, lines isolated at a certain time in a certain place and differing in the nature of the subtle biochemical processes occurring. This difference still prevents the creation of a serum against ichthyophthyriosis that would be effective against all strains.
More encouraging are the results of studies aimed at studying the interaction between the genomes of ciliates and the symbiotic bacteria living in them.
Photo 6 A – Tomont. B – theront. Small blue dots are symbiotic bacteria.
It has now been established that certain changes in bacterial RNA genes entail a loss of the ability of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis cilia to move. The mechanism of this phenomenon has not yet been established, and laboratory research is also quite expensive, but scientists continue to work in this direction and, perhaps, a medicine will soon appear that selectively affects only parasites, without affecting fish, plants, or shellfish. The use of such a medicine, as noted by Dr. HY Sun, who conducted the research, will make it possible to treat fish even in a severe stage of the disease in a community aquarium without harm to all its inhabitants.
The ongoing work on studying the motor reactions of theronts is of practical interest. It turned out that these single-celled organisms are characterized by eleven behavioral models, of which the most important for the fight against parasites are:
- Movement towards the owner; During such a movement, the theront can analyze what is happening in the external environment and make a decision in the form of two models of behavior - stopping and continuing to move towards the owner, the second model - stopping and changing the direction of movement;
- Upon reaching the host, the theront moves for some time along the surface of the host’s body and then, in a certain area, begins to penetrate the skin.
Research has shown that decisions are made by theront based on the concentration of amino acids and as yet unidentified high molecular weight substances from the skin of living fish. Theronts showed no reaction to dead fish. Bernard Haberl and Wilfred Haas, who are carrying out this work, believe that it will soon be possible to create substrates that will attract theronts to a greater extent than fish and thus localize them in one place for destruction.
Of great interest are materials on the use of loricariid catfish to combat ichthyophthyriasis. Swarming in the ground, catfish capture cysts of parasitic ciliates; under the influence of hydrochloric acid in the gastrointestinal tract, the cysts die.
Research conducted by specialists from companies producing products for aquarists contributes to the constant updating of medicines for ichthyophthyriasis and more. Therefore, it is advisable to follow updates on the range of medicines on the pages of aquaMegaMall.ru