Getting a pet without studying the physiological characteristics of the animal is a big mistake. Even our most common pets - cats, dogs, hamsters - have unique biological properties for their species, and therefore require unique care. Often the level of content does not take such nuances into account. The structure of a hamster is no simpler than that of any other mammal; it is the same gentle creature and sensitive to the world around it. Therefore, before taking responsibility for the comfort, health and life of the baby, please study the nature of the little furry. Today, as part of our article, we will talk about what structure a hamster has and what a hamster’s skeleton looks like.
Hamster oral cavity
The main uniqueness of Khomka is its legendary cheek pouches. These are very developed, capacious muscle cavities. They begin with a gap near the lips inside the mouth, the bottom of the natural pocket is in the neck near the shoulder joint. If they are stuffed to capacity (can hold 18g of food), the size of the head increases by 2 times.
The animal uses natural pockets in two ways:
- to eat the provisions stored there in the near future in a secluded place;
- or to transfer the spoils to an improvised barn, “for a rainy day.”
To unload the contents, the glutton has to forcefully squeeze out the contents with his paws. Bags also play a role in defense: to appear larger and scarier, their owner inflates his cheeks with air.
Baby's paws
The animal has four legs. The front ones are small, but very strong. When living in the wild, they often dig the ground. There are 5 toes on the paws. Four of them are clearly visible, but the last one is almost invisible, since it is not sufficiently developed, although all 5 toes are visible in Djungarians.
As for the rear pair of limbs, they are less developed. In nature, the rodent throws away the dug soil with its hind legs so that it does not interfere with it.
Teeth
Those unfamiliar with the anatomy of the rodent are sure that it has only 4 teeth - 2 visible incisors on top and bottom. In fact, there are still small molars, 6 on each jaw. Designed for chopping food.
But the entire group of rodents lack fangs. There is a void between the incisors and chewing teeth - scientifically called a diastema.
Huge incisors are curved in the shape of an arc. The front part of the yellow color is not plaque, not caries, but the natural shade of an exceptionally hard layer of enamel, which is the cutting blade on the edge of the tooth. There are no roots, so the incisors are able to constantly grow. Regeneration of incisors in rodents is critical because the tip of the tooth is constantly worn away.
If your pet's diet contains a lot of soft food, grinding and sharpening of the incisors does not keep up with their growth, and then the latter reach unacceptable sizes. Subsequently, it will become difficult to close the mouth, gnaw, chew, which is fraught with the most tragic consequences. To save your pet, you need to go to a veterinary clinic, where they will perform an operation to shorten the incisors.
We described in more detail about the structure of a hamster’s teeth and how to shorten the incisors at home in this article.
To prevent critical cases, wooden sticks, solid food and toys should always be present near the hamster. For dessert, treat yourself to some kozinaki.
The upper part of the molars consists of tubercles, ridges, and folds. The thickness of the enamel here is not the same. When teeth wear down, sharp projections of harder enamel remain. Thanks to this property, a sharp, uneven relief is again obtained on the surface of the teeth.
Cognitive Features
For rodents, it is difficult to formulate a general description of their mental capabilities. Here everything depends on the breed, conditions of detention, and the age at which the animal was taught to be handled. The frequency of communication with the owner and the types of games that were offered to the pet are of great importance.
You will be interested to know what kind of memory these fluffies have. Scientists have proven that cheekies are able to remember events, which affects their behavior in a certain situation. For example, some Homas perform a ritual of greeting their owner: they go to the edge of the cage and quietly squeak or rub their paws. At the same time, having noticed a stranger, the same animal hides in the house.
Good memory is also evidenced by the fact that rodents begin to respond to their name over time. You just need to choose a short nickname and repeat it more often.
Sometimes there are talented hamsters that are very trainable. This phenomenon is based not only on the good memory of rodents, but also on their natural curiosity. If you place a tasty treat at the end of the maze, the homa will definitely find it. Next time he will cover the same path even faster, which proves the ability of these pets to learn.
In order for the learning process to go well, you should choose the right time for classes. Animals with a twilight lifestyle do not like to be disturbed in the morning or during the day, but training can begin in the evening.
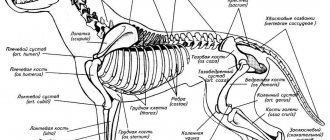
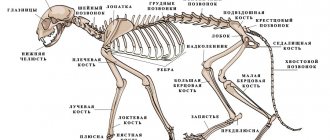
Animal skeletal system
It should be understood that the hamster's skeleton is extremely fragile. Khomka likes to climb tall objects, and quite often he can make a risky jump if he can’t get down or urgently needs shelter. His musculoskeletal complex cannot, like a cat’s, absorb shocks and shocks. Therefore, limb fractures often occur.
Features of Fluffy's Paws
The front legs are small but strong. In nature, rodents often dig hard ground with them. “How many fingers does a hamster have?” - a trick question. You can see 4 toes on these paws. There is a 5th, but it is not developed (rudiment). The hind limbs are weaker; with them it throws the dug soil behind itself. The skeleton of the Syrian and Djungarian hamsters has normally formed 5 fingers.
How to determine gender?
Sometimes the issue of gender of acquired or born individuals is fundamentally important for breeders. In ordinary hamsters, it will be much easier to determine the sex; as for dwarf breeds, to determine the sex you need to be guided by certain external distinctive features.
- The animal must be lifted by the scruff of the neck with its belly facing you. This body position will force the hamster to spread its lower limbs.
- The task of determining sex comes down to establishing the distance between the genital organs and the anus of the individual. Females will have no fur in this area in most cases. As for sexually mature males, their stomach in this area will always be wet. This is due to the active work of the glands.
- In females, the distance will be minimal, the gland is practically not visualized. There will be two rows of nipples extending from the breast. In males, the gland will be pronounced; one can note its external resemblance to the navel. In addition, there will be a significant distance between the anus and the genitals.
The tail is an important detail
The tail of hamsters is relatively short. In some species it reaches a length of 12 mm. On average, the length is 7–10 mm. It happens that females, angry at males, gnaw their tails even more.
The main purpose of the organ is to protect the anus from infections. Constantly pay attention to its condition, because the disease, called after its main syndrome - “wet tail”, is notoriously popular. The diagnosis is diarrhea or diarrhea, the cause is sanitary conditions: poor quality food, dirty water or a carelessly cleaned cage. This is a serious disease - 90% of cases are fatal. Don't hesitate to make an appointment with your veterinarian as soon as you notice a wet tail.
Cover
Includes a description of the hamster's fur. The coat is soft, short and very thick. Gives the animal volume and smooth lines of the body and head. The legs including feet, tail and ears are covered with shorter and sparse hair.
Flaws
Sparse, uneven, wrinkled coat. The ears, tail and paws are not covered with hair.
Vices
Large areas of the body without hair.
Monitoring your hamster's normal body temperature
For this subfamily, the normal temperature is between 37.5 °C and 38.5 °C. Measurement is performed rectally: a thermometer is inserted into the anus. Measurement time - 5 minutes.
A hamster's body temperature is below normal - a sign of a developed infection. To provide first aid, fill a heating pad with warm water, wrap it in a cloth and place the patient in it for 10 minutes. After the procedure, wrap it in a heated cloth. In this form, it is advisable to take your pet to a veterinarian as soon as possible.
If the temperature is elevated, move the rodent to a cool place: near a windowsill or refrigerator. Also, do not delay visiting the doctor - some kind of infection is probably beginning to develop.
A miniature hamster is a special animal; it is better to study its physiology and structure of the hamster in more detail before purchasing. Agree, this short excursion into the biology of a rodent has taught you several new lessons on caring for the tiniest member of the family.
Did you like the article? Share with friends: [supsystic-social-sharing id=”1"]
- Related Posts
- How to determine the age of a hamster
- Hamster carrier, how to transport a hamster
- Bitten by a hamster
« Previous entry
Care and maintenance at home
The natural habitat of Djungarian hamsters extends to semi-fixed sands, as well as gravelly-cinquefoil, wormwood, grass-desert and xerophytic zones of the steppes of North-Eastern Kazakhstan and Central Asia, including the territory of the central regions of Asia, as well as the Western Siberian District.
Therefore, the conditions for keeping this animal in captivity should be as close as possible to natural ones. Maintenance experience shows that Djungarian hamsters, despite the ease of maintenance, still require competent and constant care.
How many jungarians to have?
According to experts, it is permissible to keep only one animal in one cage, regardless of gender. This is due to the fact that these animals are quite territorial and in limited space, capable of showing aggression towards each other.
As a result of keeping several animals in one area, they develop a feeling of permanent stress. In this state, they are capable of inflicting injuries on each other, sometimes incompatible with life. Therefore, each animal purchased for the purpose of further maintenance must be housed in a separate cage.
Selecting a cage and filling it
Keeping Djungarian hamsters at home does not involve any special problems; it is enough to choose the right cage and fill it correctly. The most suitable cage for this small animal may have dimensions of 300x500 mm. A special cage made of transparent plexiglass is also suitable. The pet's cage must contain:
- Bedding in the form of finely sifted sand or medium-sized compressed sawdust. These materials are quite cheap, but at the same time they perfectly absorb moisture and also absorb unpleasant odors. It is not recommended to use cotton wool, paper napkins, newspapers, rags, etc. as bedding.
- Special toilet for keeping small domestic rodents. Special absorbent components are poured into such trays. Typically these are called fillers.
- Holes that can represent various roots, plant branches and tubes.
- Holiday house. This can be the most primitive structure made of wood or other environmentally friendly material.
- A wheel with transverse protrusions and without a grid in the bottom.
Harm to a person - a farmer
It’s not hard to imagine the enormous harm wild hamsters cause to agriculture, farmers, gardeners and gardeners!
The huge number of pests and the ability to adapt to any conditions allow them to infest all rich territories, and the ability to build complex burrows makes them difficult to catch and destroy.
Everything that is grown in the garden is a delicacy for them, and hamsters will not give up so easily. Farmers face a serious struggle for their harvest!
In addition, wild hamsters can bite humans or domestic animals and livestock, which will most likely result in infection with various infections (up to 30 types), and possibly death.
The fleas that live on them and suck blood are no less dangerous. Rodents pose a serious threat, but the fight is all the more important!
Sense organs
The senses of domestic mice are not as developed as those of their wild relatives. Their vision is not sharp.
The structure of the sense organs has the following features:
- The eyes are spherical in shape. They do not react to blue and green colors. Mice see yellow and red.
- The ears pick up high-frequency sounds.
- Focus on smells. The nose helps to distinguish “friend” from enemy, find food, and determine its location.
- In the dark, their whiskers help them navigate.
If a mouse is frightened, its urine acquires a special smell, signaling danger to members of the pack. In this case, the animals begin to run away and look for shelter.
Females react to female urine. The urine of males affects all members of the family.
The limbs have special glands that secrete secretions. It is needed to mark your territory.
Article on the topic: How long do Syrian hamsters live at home?