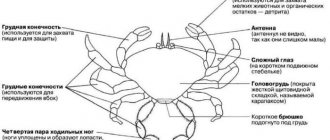
Crabs belong to the infraorder of decapod crustaceans. They have a small head and a short abdomen. They can be found both in fresh water bodies and in the seas. There are 6,780 species of crabs, all of different sizes and colors.
The smallest is the pea crab, the size of which does not exceed 2 mm. The largest crabs weigh 20 kg. Each has 10 legs and 2 claws. If he loses a claw, he can grow a new one, but it will be smaller in size.
They are omnivores, eating algae, mushrooms, crustaceans, worms, and mollusks. Crabs move sideways. For more information about the largest short-tailed crayfish, as crabs are also called, read our article.
Maltese freshwater crab, 150 g
As is already clear from the name, this crab prefers freshwater bodies of water, namely streams, rivers and lakes, lives in burrows, young individuals hide under stones. Their burrows are quite long, reaching up to 80 cm in length. They are his refuge not only from predators, but also from the cold.
Found in Southern Europe. An adult grows up to 5 cm in length, females are smaller than males. The Maltese freshwater crab lives from 10 to 12 years. He is omnivorous, can eat plants, frogs, and tadpoles, and will not refuse snails and worms.
Quite aggressive. There are no predators that feed only on this type of crab, but birds, foxes, rats, and ferrets can prey on them. However, the most dangerous enemy for them is man.
Maltese crab has been eaten since ancient times. One catcher can collect from 3 to 10 thousand crabs per season. They are under threat due to overfishing.
Sea hermit crab
The crustacean resident is not similar to its relatives in appearance and habitat features. The abdomen forms a sea shell in which the hermit crab is safely hidden. The Black Sea is rich in varieties of such organisms, living in communities of up to hundreds of individuals. During the stages of growth and development, Paguroidea exchanges a tight shell for a new one, which it captures from dying snails.
Blue crab, 900 g
Their homeland is North and South America. The blue crab chooses to live in shallow waters and river mouths. Selects sandy or muddy bottom. He needs warmth. He, like all crabs, is omnivorous. If there is not enough food, it can eat its own kind. Its width is from 18 to 20 cm, and its length is from 7.5 to 10 cm, males are slightly larger than females.
The blue crab received this name because of the color of its shell, which can be not only brown and gray, but also greenish with a blue tint.
He lives from two to four years. He spends most of his life hiding. It is preyed on by sea turtles, herring gulls and other animals. People also catch it, because... it is considered a delicacy.
Features of keeping crabs in a home aquarium
Before you get crabs, you need to study the features of their maintenance. Most of them need more than just an aquatic environment. They must have access to land, so the best solution is an aquaterrarium.
It combines an ordinary aquarium and a terrarium-paludarium. This type of home pond is more difficult to organize and maintain. Therefore, beginners rarely decide to keep crabs in an aquarium.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main arguments in favor of purchasing:
- longer life expectancy compared to fish;
- undemanding in maintenance and care;
- unpretentiousness in feeding;
- can live as solitary hermits;
- no need for large capacity;
- are highly decorative;
- have interesting habits, are the object of observation and study;
- inexpensive.
Crabs have few disadvantages:
- you should carefully monitor the purity of the water;
- it is necessary to control the pH of the environment;
- Do not touch the animal with your hands.
A big problem in breeding and keeping crabs at home is the almost complete lack of professional information. Even sellers in pet stores cannot give professional advice on how to care for a pet to a novice lover of aquarium exotics.
Content complexity
Professional and amateur aquarists note the unpretentiousness of crustaceans. But their maintenance and care are not so simple. Crabs need to create conditions similar to natural ones. Necessary:
- change water frequently;
- wash the soil, getting rid of food residues;
- monitor the mineral composition of the water, its pH, so as not to spoil the shell;
- properly equip the aquarium to provide the crustacean with freedom of movement and the opportunity to stay in the air;
- provide shelter;
- maintain air humidity.
An aquaterrarium requires outdoor placement of all devices, as sharp claws can damage tubes and cables.
You also need a lid, because arthropods are agile “acrobats” and can get out of the container.
Difficulties may arise with the selection of plants for the pool and dry land.
Crabs love to bite branches and undermine roots.
Average life expectancy
In their natural environment, crabs can live up to 20 years and reach large sizes. In captivity, the average life expectancy is 3-4 years. In good conditions, with experienced aquarists, they can live 5-6 years.
The lifespan of crustaceans depends not only on the conditions of detention, but also on their type.
Spiny crab, 2 kg
It can be found in the northeast of the Pacific Ocean, in the Bering and Okhotsk Seas, in Kamchatka, near the Kuril Islands and near Sakhalin.
The width of its carapace is from 11 to 14 cm, females are slightly smaller - from 10 to 13 cm. It is covered with large and thick spines. Weighs from 800 g to 2 kg. The comfortable depth for them is 25 m, but in southern waters they go lower and can be found at a depth of up to 350 m.
When the water temperature drops, it can swim to river mouths, where it is not so cold. He was able to adapt to fresh water. Spiny crab is red or burgundy in color. Its meat is a real delicacy; it is sweetish, juicy, and filling.
Dutch crab
A unique crab that can adapt to salty and fresh water. Its modest size, no more than 3 cm, does not hinder the culinary interest shown by seafood connoisseurs. The meat of the animal is soft and juicy. The color of the crab is dark brown or terracotta in color. The surface of the shell has convex tubercles.
The Dutch crab is most often in active movement, searching for food. The creature Rhithropanopeus Harrisii, unpretentious in its diet, picks up everything that can be eaten - the remains of the feasts of its relatives, algae, any organic matter.
Dutch crab can be kept in a home aquarium
Snow crab opilio, 2 kg
Its other name is common snow crab , it lives off the coast of the Bering and Okhotsk Seas, and is also found in Canada, off the coast of Greenland, etc. It can be at a depth of 13 to 2 thousand meters.
The width of the crab is 16 cm, the leg span is up to 90 cm. Females are 2 times smaller than males. Their shell is reddish in color, covered in tubercles and spines. The snow crab opilio feeds on bottom-dwelling invertebrates. There may also be carrion. They have sweetish meat, which is high in protein and low in fat.
Hairy crab
The unusual inhabitant Pilumnus hirtellus is quite often encountered by divers off the coast of Crimea, in areas of rocks, rocky deposits, overgrown with algae. The name “hairworm” was given for the dense bristly cover on the reddish-purple shell measuring 22-28 mm.
It is interesting that the crab does not run away when meeting a person, but takes a fighting position, sticking out its claws. The organism of the sea dweller can withstand storms and low temperatures. You can see the crab in natural conditions at a depth of 10-35 m. The population is declining for a number of reasons, including illegal crab fishing in the Black Sea .
Hairy crab or "hairy crab"
Coconut crab, 4 kg
Despite the name, it is not a crab, but a type of decapod. It is also called the palm thief . They call him that because they used to believe that he could climb palm trees and cut coconuts from them, so that he could then eat the pulp of the broken nut. Moreover, if the coconut is not cracked, it easily opens it with its claws.
But biologists say that the coconut crab does not know how to get nuts, but does not mind feasting on “fallen animals” that were torn off by the wind.
The palm thief grows up to 40 cm. It has really strong claws with which it can crush small bones. It feeds on coconuts, pandan fruits, and other crustaceans. Lives in shallow burrows, which are lined with coconut fibers, sometimes hiding in rock crevices. Can climb a tree.
Lilac crab, or water lover
It is difficult to find a colored inhabitant, since it is reliably camouflaged among stones and vegetation and does not go onto land, which is why it received the name “water lover.” The inhabitant of Xantho poressa Olivi is so quiet that it can cover itself with sea pebble and hide for several days.
The size of an adult crab is approximately 6 cm. Strong claws, disproportionately large, are strong enough to turn over stones. The legs are small and weak, and the lilac crab cannot move with acceleration like other relatives.
The shades of the shell and claws are not only lilac, but also purple and greenish. It feeds on the same thing that other varieties of Black Sea crabs eat - carcasses of dead bottom inhabitants, aquatic vegetation.
Blue crab, 4 kg
This is also a craboid, i.e. looks like a crab, but belongs to hermit crabs. Externally similar to Kamchatka crab. Its width is up to twenty-two centimeters in males, and slightly less in females. Weight – up to five kilograms.
The body is red with a brown tint, tinged with blue, and the underside is yellowish-white, with orange spots. It is covered with spines; young crabs have tubercles instead of spines.
They live quite a long time, from 22 to 25 years. This species can be found in the Seas of Japan, Bering, and Okhotsk. Blue crab is eaten.
Rock crab
The self-explanatory name suggests where crustacean representatives are most often found. Grapsus grapsus crabs have the unique ability to cling to the surface of rocks with such force that even a powerful wave cannot tear the creature off.
The length of the chitinous shell is almost square in shape, 6–8 cm. It is distinguished by the ability to run quickly in any danger. The direction of running is changed so often that they make the task of the pursuer many times more difficult, which is how they escape. The red color of the crab indicates its aggressiveness towards competitors and enemies. They feed on algae on rocky surfaces, dead fish, and dead birds.
Large land crab, 3 kg
Other names are brown or edible crab , because. it is reddish-brown in color. It is shaped like a closed pie. The width of the shell of an adult individual can reach 25 cm, but, as a rule, 15 cm, and it weighs up to 3 kg. The length is most often about 6 cm in males, almost 10 cm in females, and up to 15 cm in some individuals.
He lives in the North Sea, in the Atlantic Ocean. Prefers to hide in cracks and holes in rocks and is nocturnal. The large land crab feeds on crustaceans and mollusks, stalks prey or lures it into ambush.
His main enemies are octopuses, as well as people. They are caught in large quantities; in 2007, 60 thousand tons were caught around the British Isles, which is why this type of crab has almost disappeared there.
Swimming crab
It is impossible to confuse the swimming crab with its relatives due to its characteristic feature - wide legs transformed in appearance into flippers. The inhabitant of Portunidae has a clear advantage over other species.
The ability to swim well, quickly burrow, throwing sand at itself, does not make the crab an easy prey. Amazing eyes are planted as if on stalks that can extend and retract.
The swimmer is active at night and hides in the sand during the day. The color of the shell in gray-beige tones with a green tint contributes to ideal camouflage. The size of the underwater resident is only 3-4 cm. The sandstone is not liked by fishermen, who gave it the nickname “barber” for its brilliant ability to cut nets to not only release itself, but the entire catch.
The back claws of the swimming crab look a bit like oars.
Tasmanian king crab, 6.5 kg
The Tasmanian king crab , or, as it is also called, the giant Tasmanian crab , is one of the largest in the world, its width is up to 46 cm, and its weight can reach up to 13 kg. The males are especially noticeable in size, being 2 times larger than the females. It is light in color with red spots.
This type of crab can be found in southern Australia, at depths from 20 to 820 m, but it prefers depths from 140 to 270 m. It feeds on mollusks, starfish and crustaceans.
They are being hunted because... These crabs have a lot of meat and it tastes good. One of the representatives of this species was caught off the coast of Australia, which was named Claude. He was bought by the British Aquarium for 3 thousand pounds sterling. Despite the fact that he was quite young, he then weighed about 7 kg, but, according to experts, as he matures, Claude can become 2 times heavier.
The truth about the inhabitant of the Weymouth aquarium
As mentioned earlier, the world's largest crab, according to the owners of the aquarium, lives in the city of Weymouth. However, how did he get there and is he really the absolute record holder?
It all started when a family of fishermen caught a huge king crab off the coast of Australia. Its weight was about 7 kilograms, and the length of its shell was 38 centimeters. This made it one of the largest crabs caught in the last decade.
After the huge inhabitant of the seas, he bought a famous aquarium. And thanks to its advertising, it became the most famous crab on the planet. True, it cannot be said with certainty that this is the largest representative of crustaceans caught by humans. He's just the only one who managed to become a real star.
Kamchatka crab, 8 kg
Kamchatka crab is also a craboid, i.e. looks very similar to a crab, but belongs to hermit crabs. This is the largest crustacean living in the Far East. It is red-brown, yellowish below, and has purple spots on the sides. It grows up to 29 cm in width, plus limbs that reach 1-1.5 m.
For life, he chooses an area with a sandy bottom, depth from 2 to 270 m. He likes to live in cool water of medium salinity. He prefers to lead an active lifestyle, constantly moving.
They tried to breed Kamchatka crab in the Barents Sea, after several unsuccessful attempts everything was successful, it began to reproduce successfully there. The Kamchatka crab feeds on sea urchins, crustaceans, mollusks, small fish, and starfish.
Herbal crab
A lover of lagoons, estuaries with abundant algae, in which he usually hides from enemies or for hunting. The triangular shell of a greenish tint is 7-8 cm wide. The claws are short, strong, and can break the finger of a careless catcher. It moves very quickly, reaching speeds of up to 1 m/sec.
Appears on sea beaches, when in danger, buries itself in the sand and runs into the water. It dives into the sea to depths of up to 40 m. It feeds, like other species of Black Sea crabs, on dead organic matter, algae, small bottom organisms, and does not disdain its relatives.
On the coast, crushed shellfish, jellyfish washed up on the sand are a favorite delicacy of herbal crabs. It has been noted that Carcinus aestuarii Nordo is sensitive to the level of salt in the water.
The saltier it is, the more comfortable it is for the inhabitant. Another name for the crustacean is the Mediterranean crab. Previously it was considered a commercial species, but now with the status of “rare” it is also included in the Red Book.
Herbal crab is in the Red Book
Japanese spider crab, 20 kg
The span of one pair of legs is up to three meters. It can be found in the Pacific Ocean, near Japan, at a depth of 50 to 300 m. Its body length is up to 80 cm, and with its legs up to 6 m, it weighs from 16 to 20 kg.
It's not so easy to catch him, because... with its claws it can seriously injure. Japanese crab is a delicacy. Once upon a time, 27-30 tons were caught per year, but now the fishery has been reduced to 10 tons, during the breeding season of crabs, i.e. in the spring, you can’t touch them.
They themselves feed on both plant and animal food, and do not refuse carrion. Their natural enemies are octopuses and squids.
22 3
sand crab
The most leisurely inhabitant of Xantho poressa in comparison with other relatives of the Black Sea. At the moment of danger, it does not run away, but freezes, imitating a small pebble at the bottom. The shell size is 5 – 6 cm. The reddish-orange color contributes to good camouflage.
If the crab is nevertheless disturbed, the inhabitant will begin to click its claws in a threatening pose. When losing its weapon in the fight against an enemy, the crab is able to grow new claws.
Loves rocky surfaces, where it is easier to hide. Due to the sluggishness of the sand crab, the population is decreasing; the inhabitant is easy prey for humans and natural enemies.
Sand crab is the smallest
Origin and description of the species
Photo: Kamchatka crab
The Kamchatka crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) owes its name to its external resemblance to crabs, however, according to the zoological classification, it originated in the process of evolutionary development from hermit crabs belonging to the Craboid family, the general genus Paralithodes.
The main difference from crabs is the shortened fifth pair of walking legs hidden under the shell, as well as the irregularly shaped, asymmetrical abdomen with chitinous scutes in females. A short pair of limbs in hermit crabs serves to hold the shell. In the process of evolution, the Kamchatka crab stopped living in a shell and therefore the need to hold it disappeared. The fifth pair of legs is used to clean the gills.
The crab moves with the help of four pairs of limbs, moving them in turn. It moves at a fairly high speed, the direction of movement in this species is to the side.
The abdomen, bent and shortened, has small plates and microlegs, the asymmetrical arrangement of which confirms the origin of the arthropod from species in which the abdomen is twisted in a spiral shape.
Video: Kamchatka crab
The senses of touch and smell are provided by the front antennae with sensitive cylinders located on them. This species feature has a significant impact on feeding behavior, helping in the search and selection of food.
As the individual grows, a change in the frame skeleton occurs, or molting. The frequency of molting at the beginning of life, especially during the development of larvae, is high and occurs much less frequently, up to 1-2 per year in an adult, and by the end of life it happens only once every two years. How often crabs should molt is regulated by special glands located on the eyestalks. Before shedding the old frame, the soft parts of the arthropod are already covered with a still weak, pliable shell. The Kamchatka crab lives on average about 20 years.
What do they eat?
They feed on plant matter and particles of animal remains, for which it is nicknamed an omnivorous scavenger. He is not a predator, does not hunt, but only collects decaying dead remains along the bottom. The crustacean feeds on small fish, carrion, various aquatic crustaceans, marine invertebrates, algae, macroalgae, and detritus. The crab is a spider by nature as a cleaner, so it carefully collects the remains of vegetation and living creatures. May eat live shellfish. Crab is caught for human consumption as it is considered a great delicacy in Japan and throughout the world. In life, the spider crab leads a calm lifestyle, wanders in search of food, and calmly moves among stones and potholes. Deprived of the opportunity to swim. His claws serve him as knives, with which he can tear apart necessary objects and attach them to his shell.
The crab regularly sheds its shell, which is replaced by a larger shell. The largest crab caught was 40 years old. How crabs interact with each other is not fully understood. It has been established that they lead a solitary lifestyle and have little contact with each other. Living in artificial conditions, in special aquariums, animals are isolated from any communication with their own kind.
Their sensory system is quite developed. Crabs living off the coast of Japan are called decorator crabs. They received this name for their love of collecting various objects and attaching them to their shells. This method helps them better camouflage and protect their existence.
Known Facts
- There are legends about how a huge crab pulled a sailor to the bottom and ate him. Of course, this is a big fabrication. Despite its menacing appearance, the crustacean is very peaceful.
- A young spider crab can only grow to adult size if it sheds its hard outer shell. The old shell is discarded, revealing the soft inner shell, which the crab stretches to a large size before it hardens.
- If he loses a leg, he can grow a new limb.
- Some species coexist with sea anemones. Their body is insensitive to burns. In this way, the spider crab protects itself by hiding in the numerous tentacles of sea anemones.
- Can be found on the shore after the surf. However, spider crabs cannot survive without water.
- One type of crab, the spider, is used exclusively for food by plankton.
Life and Molting
When a king crab transforms from a larva into an adult, its skeleton skeleton changes several times. This type of molting occurs frequently at first, and becomes less common as they grow older. The new shell grows under the old one, and when it is shed, it begins to grow stronger, absorbing calcium salts from the water until it reaches the desired state. The chitinous walls of internal organs also change. The color of the mature shell is red-brown, with purple spots on the sides. The abdomen is distinguished by a white and yellowish tint.
When molting occurs, the Kamchatka crab spends time in shelter until the new frame gets stronger. This period is favorable for the growth of the animal. When the shell is hard, the arthropod cannot change in size, and only when it is still soft is this possible. The result is impressive growth.
The animal moves on four pairs of legs with good speed, sideways. The average lifespan of an individual is 20 years.
Brown crab
An endangered species, crab fishing is prohibited. Large carapace of a brownish-burgundy hue, approximately 10 cm long. The claws are of more saturated tones. During the day it is passive, hiding among reefs. At night it searches for prey among small crustacean inhabitants, mollusks, and does not refuse organic carrion.
Natural enemies
Adults are practically not afraid of anyone, because arthropods are protected by a hard chitinous cover in the form of a shell. In addition, special needles in the form of spikes are located on the surface of the carapace. Only large mammals can overcome such protection. Young individuals cannot boast of such protection, so they have many enemies. These are predatory fish:
- halibut;
- cod;
- bulls.
As well as sea otters and octopuses, other large arthropods.
The most vulnerable time is molting. Therefore, during this period, he hides in secluded places so that no one can reach him.
Man is not a natural enemy, but the fact that many people bypass the law and catch these animals without a license may indicate that man will become enemy number one for underwater inhabitants.
Thanks to established state quotas, today the catch of Kamchatka crabs is limited. The state is trying to curb population decline so that arthropods can reproduce and maintain populations.
Nutritional Features
The main diet of the Kamchatka crab is urchins, mollusks, worms, stars, various types of fish, plankton, as well as various types of crustaceans. It should be noted that such an arthropod is an omnivorous predatory inhabitant. Young Kamchatka crabs prefer to feed on hydroids. The claw on the right side of the animal is designed to destroy the hard shell, and using the left claw, the crab eats the soft and tender internal components.
Reproduction
Males reach sexual maturity at 10 years, females at 7-8. The appearance of offspring is associated with the molting process. In due time, eggs form on the females’ legs, close to the abdomen. Having migrated to shallow water in separate groups, females and males meet and take a joint pose, reminiscent of a handshake - he holds her with his claws and does not let go until the female has finished molting. Thus, the male can protect his girlfriend during the period when she has a soft shell.
This lasts approximately three days, a maximum of a week. When the female's molt is completed, the male throws out a ribbon with spermatophores, which wraps around the female's legs. The male releases the female and goes to a secluded place to molt himself. Over the course of a season, he can enter into relationships with several representatives of the opposite sex.
The female, after a few hours (sometimes it takes several days), spawns eggs. There are many eggs, tens or even hundreds of thousands. They meet the ribbon, fertilization occurs. After this, the eggs attach to the mother's legs. This happens easily, since the caviar is sticky in texture, and the abdominal legs of the female have villi that hold it.
The development cycle of a new crab takes almost a year, until next spring. When the next spring migration begins, the larvae hatch from the eggs and set off for free swimming. At the same time, new eggs are formed in the female’s body to begin the next cycle. The fate of the larvae is very dramatic - driven by the current, they float around in sea water for a couple of months, while only about 4-10% of the total mass survives. These larvae, having passed the sieve of strict evolutionary selection, find a mud bottom, end up in algae thickets and live there in relative safety for three years. During this period they molt several times.
Having matured a little, the young move to the sandy bottom. Having reached five years (maximum - seven), young king crabs begin to migrate in separate junior groups.