Eye diseases in cats deserve special attention, as they often cause deterioration or complete loss of vision. Despite the development of other sense organs, blindness significantly worsens the animal’s quality of life. You can avoid troubles with the help of prevention and timely treatment, started immediately after the detection of alarming symptoms.
How can you tell if something is wrong with your cat's eye?
If there is something wrong with a cat's eye, it is easy to understand by its condition. The following symptoms will indicate the disease
:
- increased lacrimation and discharge of pus;
- redness of the mucous membrane and inflammation of the eyelids;
- photophobia, covering of the third eyelid and frequent blinking;
- pain on palpation;
- the appearance of itching;
- sticking of the eyelids after waking up due to the drying out of the accumulated exudate.
Depending on the cause of the malaise, symptoms may be supplemented by worsening appetite, apathy, severe thirst and fever. If you notice at least a few of the listed signs, be sure to schedule your pet for an examination at a veterinary clinic.
Wounds and open injuries to the eye.
Cause. Most eye injuries and wounds in cats occur as a result of fights with their fellow cats, falling on sharp objects, or strong blows leading to damage to the skin.
Clinical signs. During a clinical examination, the veterinarian notes a violation of the skin in the area of the injured eye, the presence of scratches, wounds, and bleeding from the injured areas.
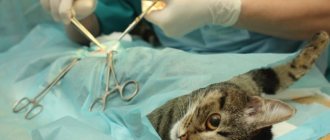
Treatment. The damaged area is washed with hydrogen peroxide, bleeding is stopped; in the presence of large wounds, pain relief and suturing are used, and antimicrobial therapy is administered locally. For complex and large eye injuries, eye microsurgery and sometimes removal of the damaged eye are performed.
Causes of eye problems in cats
Three groups of reasons are to blame for the occurrence of ophthalmic diseases. These include:
- infectious, due to the negative effects of viruses and bacteria;
- non-infectious, including tumors, injuries and allergies;
- congenital, associated with breed predisposition and poor genetics.
The risk group includes extreme-type Persians with pronounced breed traits. Due to increased tear production, which forms pathogenic microflora, their tear ducts are very often infected with bacteria.
Causes
Veterinary experts distinguish 2 main categories of causes of eye diseases:
- Disturbances in the functioning of protective organs and the eyeball itself. These include various injuries and burns, inversions and eversion of the eyelids, fusion and drooping of the eyelids, eye loss, blepharitis, neoplasms;
- Pathology of the organ of vision itself. These are: glaucoma, cataracts, conjunctivitis, keratitis, iritis, panophthalmitis, uveitis, etc.
All of them require urgent veterinary care, as they can become chronic, which is either very difficult to treat or incurable, and the organ will have to be removed.
Types of eyelid diseases and their treatment
Symptoms and methods of treating eye diseases in cats depend not only on the cause, but also on the area of the lesion. The main blow is always taken by the eyelids, which protect the more delicate layers from the aggressive influence of the external environment.
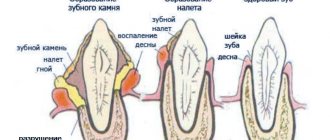
Blepharitis
Staphylococcal infections that enter the eye cause unilateral or internal blepharitis in cats. This disease is accompanied by severe redness and inflammation of the corners of the eyelid, as well as the discharge of purulent exudate. Dried pus gradually covers the entire affected area, causing thickening and ulceration of the skin.
In addition to infection, blepharitis can be caused by allergies or demodicosis. Inflammation is treated with antibiotics, antihistamines or acaricidal drugs.
Third eyelid prolapse
This term refers to the transparent nictitating membrane, which performs a protective and moisturizing function. It is located in the inner corner of the eye next to the nose. Its loss is accompanied by uncontrollable twitching of the eyelids, lacrimation and copious discharge of pus or mucus.
Pathology develops with infections, allergies, parasitosis, foreign objects and fusion of the eyelids with each other. To reduce it, they resort to surgery.
Entropion of the eyelids
An alternative name for this disease is entropion. Most often it affects the lower eyelid, causing photophobia and excessive lacrimation. With entropion, it is very easy to understand that something is wrong with the cat’s eye, because she experiences severe pain due to prickly eyelashes and hairs.
The pathology is caused by congenital disorders, injuries and neoplasms. The problem is eliminated by excision of excess skin and formation of the correct palpebral fissure.
Ptosis
Characterized by involuntary drooping of the upper eyelid. The diseased eye opens only partially, and the palpebral fissure narrows. Ptosis occurs as a result of complications of inflammatory processes, paralysis of the facial nerve or weakness of the orbicularis muscle covering the anterior parts of the orbit. It is treated exclusively by surgery.
Lagophthalmos
External signs of lagophthalmos are similar to ptosis. The difference is that the eyelids cannot close. Because of this, the cat has to sleep with its eyes open. The causes and treatment are the same as ptosis.
Fusion of the eyelids with each other or with the conjunctiva
The first type of disorder is called ankyloblepharon, and the second - symblepharon. These pathologies develop from birth, with chronic blepharitis and as a result of mechanical damage. Both cases are accompanied by tissue scarring and the inability to open the eyes. To eliminate the fusion, the help of a surgeon is required.
Diagnostics
Your veterinarian will examine the eye, particularly to look for foreign bodies or signs of injury. The veterinarian will also make sure that the tear ducts are not blocked and that there is no swelling. The veterinarian will then measure your cat's tear production as well as eye pressure.
Your veterinarian may use a variety of diagnostic tests, including corneal staining, conjunctival tissue scrapings, and, in some cases, an eye biopsy. If conjunctivitis is a suspected symptom of another disease, your veterinarian may also do a blood test.
Pathologies of the fundus and lens
Ophthalmic diseases in cats can affect the fundus and lens. These organs are responsible for visual acuity, so when they are damaged, it becomes more difficult for the animal to catch objects at a distance.
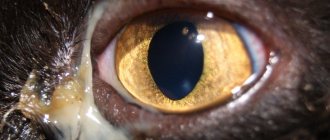
Cataract
It is characterized by a loss of transparency of the lens, impairing the ability to refract light rays. The main symptoms of cataracts are clouding of the pupil and iris, as well as a gradual change in their shade to bluish-gray.
The causes of the disease lie in congenital disorders, advanced infections, injuries and diabetes. At the initial stage, only damaged particles are removed, and at an advanced stage, the entire lens is removed at once.
Glaucoma
Accompanied by the appearance of a greenish cataract, redness of the mucous membrane and an enlarged pupil. The main cause of glaucoma is increased intraocular pressure. The pathology cannot be treated, but thanks to cryotherapy and antiglaucomatous drugs, its development can be slowed down.
Lagophthalmos
Lagophthalmos in a cat is manifested by the inability to completely cover the eyes with the eyelids.
Cause. Eversion and inversion of the eyelids, paralysis of the facial eyelid, hereditary shortness of the eyelids.
Clinical signs. During a clinical examination of a sick cat, a veterinarian notes a constantly slightly open palpebral fissure, lacrimation, and lag of the lower eyelid from the eyeball.
Treatment. Treatment of this pathology in cats is surgical, and it is necessary to first use antimicrobial eye drops and corneal protector medications.
Diseases of the cornea and mucosa, appropriate treatment
The cornea (cornea) acts as a refractive lens, the mucous membrane (conjunctiva) protects the visual organ from drying out, and the vascular membrane (uveal tract) saturates the retina with useful microelements. All these organs are very vulnerable, so after damage to the eyelids, they are the ones who suffer from the effects of negative factors.
Conjunctivitis
If a cat's eye is inflamed and swollen, and the conjunctiva has acquired a bright crimson hue, then most likely he has conjunctivitis. Its appearance is associated with infections and allergies, so antibiotics or antihistamines are used for treatment. If there is an abundant accumulation of pus and the presence of multiple follicles, surgery is performed.
Uveitis
With uveitis, a cat's eyes hurt a lot, so she constantly closes her eyelids and avoids bright light. Advanced inflammation of the uveal tract rarely responds to drug treatment, so the only salvation is removal of the affected organ. In the early stages, it is enough to eliminate the root cause and undergo a course of symptomatic therapy.
Keratitis
The main cause of inflammation of the cornea in cats is similar to previous pathologies. Most often, keratitis develops when infected with bacteria and viruses, so the victim is prescribed antibiotics or antivirals. In advanced cases, laser correction is used.
The inflamed cornea becomes blue or gray and dull, and the mucous membranes become noticeably red. A sick pet tries to avoid bright light and constantly rubs its face with its paws. Without timely help, keratitis can be complicated by cataracts or glaucoma.
Entropion of the eyelids
This is an incorrect position of the upper and/or lower eyelids, in which the free edge of the eyelid is shifted inward towards the eyeball.
Symptoms:
— Eyelashes and hair on the eyelids, when turned in, greatly irritate the eye.
— The cat squints its eyes a lot.
- There is severe lacrimation or purulent discharge. Constant irritation can lead to corneal injury.
Treatment:
1. Surgical. With spastic volvulus, therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease, but in some cases, after eliminating the cause that caused the spastic volvulus, it is still necessary to resort to surgical correction.
============================================================================================================================================================================================
Other pathologies
Less common eye diseases in cats include the following:
:
- Canaliculitis
, or inflammation of the tear ducts. Occurs when the ducts become clogged and is accompanied by profuse lacrimation. It is treated by washing the clogged lacrimal sac or removing it.
- Exophthalmos (proptosis) and enophthalmos
, or prolapse and retraction of the eyeball. Changes are visible to the naked eye. The organ is returned to its original position under general anesthesia.
- Panophthalmitis
. A most dangerous pathology that affects all eye tissues. Accompanied by an enlargement of the eye and the discharge of pus. To avoid brain infection, the affected organ is removed.
- Adenoma of the third century
. It is characterized by severe redness and thickening of the third eyelid as a result of inflammation of the lymph nodes. This makes it look like a cherry. The organ affected by the adenoma is sutured to its normal state or removed.
Due to the high likelihood of complications, it is better to entrust treatment to a veterinarian. Self-administration of drugs rarely brings the desired result. At best, you will simply smooth out the existing symptoms and complicate the diagnosis.
Symptoms of cataracts
The second most common disease is cataracts. As a result of natural aging or various metabolic processes in the body, clouding of the lens occurs.
- A cloudy lens is unable to perform its main function - accommodation of the eye.
- A specific symptom that should alert a cat owner is the appearance of shine in the eyes.
At the same time, the pet also squints, trying to reflexively increase visual acuity.
The photo of this eye disease shows a pronounced clouding of the eyeball, which every owner will notice.
When veterinary help is urgently needed
If something is wrong with a cat’s eye, the owner can provide first aid. After this, it is recommended to consult a doctor. This must be done even if the problem seems completely insignificant. After all, it is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own, and your mistake can result in premature blindness of your beloved pet.
Emergency assistance will be required if pus appears, high fever, signs of cataracts and glaucoma, burns or other health-threatening injuries. In these cases, it is recommended to contact the nearest 24-hour veterinary clinic without waiting until morning.
Keratitis
Keratitis is a lesion of the cornea of the eye. It can be caused by either trauma, including foreign body impact, or infection. The main symptoms of keratitis are:
- photophobia;
- profuse lacrimation;
- corneal clouding;
- accumulation of discharge in the corner of the eye.
When treating keratitis, it is important to exclude the possibility of its relapse : eliminate the cause of the disease. Effective drug intervention is impossible without the help of a veterinarian. Only a specialist can correctly determine the cause of the disease and prescribe the correct therapy.
Treatment at home
After the diagnosis is made, the mustachioed patient must be provided with the most comfortable conditions possible. Place it in a darkened room, away from noise sources, other pets, children and other irritants.
To avoid further injuries, be sure to trim your cat’s claws and do not let him outside until he recovers. In addition to the basic treatment, which includes the use of eye drops and ointments, you will need to pay close attention to hygiene through rinsing.
Washing and hygiene
Washing is carried out using cotton pads, guided by the following algorithm
:
- Prepare all the necessary tools and preparations in advance to reduce the risk of traumatizing the animal with painful waiting.
- Wrap your pet in a thick cloth or find an assistant who can hold him during the procedure.
- Soak a cotton pad in the medicinal solution, squeeze it out and open the cat's eyelids.
- Gently move the disc over the eye, moving from the outer corner to the inner.
- Repeat the previous steps with the other eye, not forgetting to change the cotton pad.
The procedure can also be carried out using a syringe without a needle. To do this, you need to irrigate each eye with the solution under low pressure and gently blot them with a clean, lint-free cloth. After removing the accumulated dirt and soaking the crusts, you can begin applying the main preparation.
Drops and ointments
If something is wrong with a cat’s eye, then special drops and ointments will be required to normalize its condition. The list of necessary medications will depend on the cause of the disease:
- bacterial infection – Iris, Leopard, Levomycetin;
- viral infection – Anandin;
- fungal infection – Tetracycline;
- injuries - Traumeel.
The drops are instilled into both eyes at once, and the ointment is applied only to the disturbing area. After application, close the eyelids tightly and gently massage so that the product is evenly distributed inside. During treatment, it is recommended to wear an Elizabethan collar on your pet so that it does not inflict further injuries on itself when scratching.
Is it possible to use folk remedies?
Folk remedies can only be used as part of complex therapy. They do not fight the root cause, but only alleviate the patient’s condition by eliminating associated symptoms. It is also important to note that some herbs can cause an allergic reaction, so it is best to use them only under the supervision of a veterinarian.
Please note that the popular recipe with olive oil is extremely dangerous. Any oily substances create a very dense film. Because of this, new bacteria can quickly grow on the mucous membrane after treatment.
Features of treatment of pregnant, lactating and young individuals
Kittens, as well as pregnant and lactating animals, need gentler medications and lower dosages. Their immunity is weakened, so most antibiotics cause severe complications. Some of them can lead to miscarriages or stillbirths.
They also resort to surgery with extreme caution, since the anesthesia used can affect the course of pregnancy or the baby’s fragile heart. The indication for its implementation is a serious threat to life that exceeds the existing risks.
Prevention measures
Prevention of ophthalmic diseases in cats involves daily eye care. In the morning, the owner must carefully examine the animal and, using a napkin moistened with a special lotion, remove the discharge that has accumulated during the night.
It is better to feed your cat ready-made super-premium food that contains all the necessary nutrients and microelements. This will avoid the development of allergies, which often leads to chronic inflammation of the eyes.
You also need to carefully monitor the cat’s communication with its relatives, if possible, exclude self-walking, and isolate it from aggressive animals that can injure the eyes in a fight.
Do not neglect vaccinating your pet. Annual vaccination protects against many viral diseases that lead to partial or complete loss of vision.
All information posted on the site is provided in accordance with the User Agreement and is not a direct instruction to action. We strongly recommend that before using any product, you must obtain a face-to-face consultation at an accredited veterinary clinic.
Iritis (iridocyclitis)
Iritis (iridocyclitis) is inflammation of the iris and ciliary body.
Cause. Traumatic injury, inflammation spreading from the cornea, complications after eye surgery, infectious diseases.
Clinic. During a clinical examination, a clinic veterinarian notes a constriction of the pupil, dimming of the iris, photophobia, pain, and cloudy fluid in the anterior chamber of a sick cat. When conjunctivitis is associated with the disease, we note serous-purulent discharge.
Treatment. In order to restore pupil contraction, a 1% atropine solution, novocaine blockade, and antibiotics are prescribed. During treatment, eye drops and ointments with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects have a good effect.