Vision, smell and hearing are the basic senses, without which many living beings cannot exist normally. Cat ears have a specific structure and are able to pick up the smallest noises, so the auditory function of these animals is quite acutely developed, and ear diseases require mandatory treatment.
The photographs of ear disease in cats presented in this article are visual manifestations of various diseases and lesions.
It is strictly not recommended to self-treat pets and be sure to contact special clinics to receive veterinary care.
General symptoms of ear diseases in cats
The main signs of ear diseases in cats are easy for owners to identify; for this, it is necessary to regularly examine the animal.
Even if you have the necessary medications and remedies in your home medicine cabinet, you should not immediately begin treatment; it is better to entrust the diagnosis to specialists who focus on the following symptoms:- painful sensations in animals when palpating the ears;
- scratching the ear area and the ears themselves until bloody wounds appear;
- the animal often shakes its head and touches its ears with its paws;
- the pet has an unpleasant odor coming from the ears;
- the swelling of the outer part of the auricle is visually determined;
- During hygiene procedures, discharge from the ears is observed.
Read here Anemia in cats: main causes, symptoms, treatment options and best medications (90 photos)
To make a timely diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan, hygiene procedures should be carried out regularly.
A weekly examination of your pet will help you immediately identify a problem with the ears and contact an experienced veterinarian who will conduct an examination and the necessary tests.
Characteristic symptoms
Ear diseases in cats are manifested primarily by changes in behavior. You should watch your pet and if this happens constantly, then something is wrong with the animal:
- constantly tilts his head to the side;
- shakes his head;
- twitches his ears sharply, as if they were splashed with water;
- often and suddenly rubs the ear with a paw;
- presses his head against upholstered furniture, against the carpet;
- does not allow ears to be touched, runs away when the head is stroked;
- scratches the ears often and strongly, resulting in bruising;
- loses orientation in space, when walking the cat is constantly pulled to the side.
If this behavior is noticed in your pet, you should carefully examine the inside of the ears. There may be redness and ulcers in the ears, light or dark discharge, dirt in the form of dark crumbs, bloating and swelling. The diseased ear may smell unpleasant, and when you lightly press on its base, a sound similar to squelching can be heard.
Changes can occur in one or two ears at once.
If you notice that your cat’s ear itches or hurts, and she is worried, and any discharge or changes inside the auricle are detected, then the question arises - what to do and how to treat. There are many ointments, drops and lotions, but they cannot be used without clarifying the diagnosis. If they can cure one disease, then in another case they can cause harm and waste time.
If your cat has ear pain, you should find out how to treat it at home from a qualified specialist after conducting a series of examinations.
Ear diseases and ear canal diseases
It is quite difficult to independently determine what disease cats have near the ear; even experienced cat owners cannot do it.
Scratching and injuries can occur for various reasons, but they are often associated with diseases of the ears, which come in several types and require mandatory treatment.
Special instructions for treatment
Therapy begins only after the animal is diagnosed. A correct diagnosis improves the effectiveness of therapy. Independent attempts to get rid of diseases can only worsen the condition and cause an exacerbation of the disease.
It is strictly forbidden to clean cats' ears using hygiene sticks. Discharge and dirt can only be removed with cotton pads. If the doctor insists on surgical treatment, there is no need to refuse. It may be the only effective method of getting rid of pathology.
Injuries and wounds
A street fight for territory, a bite or independent, careless scratching can cause suppuration and inflammation.
You can treat the damaged areas yourself and seek help from a veterinarian who will carry out antibacterial treatment of the damaged area.
Complications of IT
- Periauricular cellulitis is manifested by hyperemia, edema, and local hyperthermia of the skin around the auricle. Pain is usually mild and systemic symptoms are usually absent, which helps distinguish cellulitis from malignant otitis externa.
- Malignant otitis externa (necrotizing) is a severe, potentially fatal complication of bacterial Otitis. It is most common in older patients with diabetes or people with weakened immune systems. In this case, the infection spreads to the base of the skull and surrounding soft tissue. There is severe otalgia and discharge from the ear. In the NSP - granulation, edema, erythema, necrosis (death) of the NSP.
Hematomas
Hematomas appear as a result of an impact due to the accumulation of dried blood under the skin of the animal, which appears after the rupture of blood vessels.
Swelling and swelling, darkening of the skin requires mandatory examination and further treatment; surgical intervention is often prescribed, which involves opening the hematoma.
Diagnostics
A comprehensive approach is required to make a correct diagnosis. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the results of the research, because bacterial otitis and otitis caused by ticks cannot be treated in the same way.
The doctor must collect all the data about the conditions of keeping and feeding the pet, chronic diseases, and behavior. A complete examination of the animal is carried out, the outer ear and ear canal are examined using an otoscope, and the doctor takes a swab from the ear for laboratory examinations.
Additionally, an x-ray may be prescribed, as well as an MRI; tomography will help determine inflammation of the middle ear at the very initial stages, when x-rays are uninformative.
Scabies mite
Outdoor cats are often exposed to ectoparasites, such as the scabies mite, which causes itching in the ear canal.
The presence of a lesion can be determined by undergoing laboratory tests and examining scrapings taken from the pet’s ears, after which special drug therapy is prescribed.
Causes
Various reasons can contribute to the development of the disease. Kittens and cats often suffer from otodectosis; this is a contagious disease caused by ear mites Otodectes cynotis. They are transmitted by contact with a sick animal and can cause otitis media.
In addition, pathology can result from:
- Bacteria: staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli;
- Fungi;
- Viruses;
- Allergy and autoimmune processes;
- Hormonal disorders.
In elderly pets, when examining the auricle, various types of neoplasms and polyps can be found, which also contribute to the development of the disease.
The cause of inflammation can be injury, structural features of the pet's ear, or a foreign object entering the ear.
Solar dermatitis
The tips of an animal's ears can be damaged under the influence of ultraviolet and solar radiation, which is typical for light-colored animals.
Seizures in cats - main causes, symptoms, first aid, treatment and choice of drugs (110 photos)- Polycystic kidney disease in cats - causes, diagnosis and symptoms of the disease. Treatment options and prevention of kidney disease (95 photos)
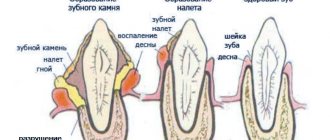
- Tartar in cats - signs of the disease and methods of fully treating tartar (125 photos + video)
Timely treatment of cat ear disease caused by solar radiation will prevent the development of cancer; most often, removal of the tips of the ears is prescribed.
Treatment of acute external otitis
To reduce pain, including before being examined by a doctor, it is recommended to use systemic painkillers, such as ibuprofen or paracetamol.
If the eardrum is intact, drops containing painkillers (for example, lidocaine) can be used. However, the advantage still remains with systemic anesthesia, and the issue of using drops with anesthetics is still controversial.
- For mild cases of ON, local agents containing acetic acid and/or glucocorticoid are indicated. Treatment is aimed at changing the environment in the NSP to a more acidic one, as well as reducing inflammation.
- For moderate cases, local agents are prescribed that contain an antibiotic or an antibiotic in combination with a glucocorticoid. The antibiotic must have activity against the most common pathogens of ONO - the drugs of choice are ciprofloxacin, neomycin, polymyxin B. If perforation of the eardrum is suspected, the use of drops containing aminoglycosides should be avoided.
- In severe cases, in addition to local therapy, the option of additional systemic antibacterial therapy is considered - most often oral forms of quinolones (ciprofloxacin or ofloxacin).
Drugs for local use remain the treatment of choice for ANO, as they allow creating a high concentration of the drug at the site of inflammation.
There are no randomized studies comparing topical and oral antibiotic therapy. But according to available data, the addition of an oral antibiotic to local antibacterial therapy for uncomplicated ANO does not have a significant effect on the course of the disease and recovery time.
The basis of treatment for otomycosis is NSP toilet and local antifungal therapy - the drugs of choice are clotrimazole and miconazole. Systemic antifungals are indicated for patients with suspected invasive fungal disease.
General recommendations
- During treatment, the ear should be protected from water - while bathing, a cotton swab soaked in petroleum jelly or glycerin should be placed in the ear.
- It is necessary to refrain from water sports for 7-10 days.
- You should limit the wearing of hearing aids and headphones as much as possible until the pain completely subsides and there is no discharge from the ear.
How is acute external otitis treated at the Rassvet Clinic?
For ONO, we give preference to local empirical therapy. An important stage of treatment is the toilet of the NSP, performed by an otorhinolaryngologist. In the clinic, we perform it under a microscope, which makes the procedure less traumatic and more effective. During the procedure, pathological discharge and granulations are removed from the ear canal, which in turn increases the effectiveness of local treatment.
Our otorhinolaryngologists select medications for local treatment based on otoscopy and medical history. Not only the effectiveness of the antibiotic against the most common pathogens is taken into account, but also their side effects and possible drug resistance.
We prescribe systemic antibiotics only when indicated. First, compared with local therapy, systemic antibiotics may increase the likelihood of drug resistance. Secondly, the use of only oral agents without local antibacterial therapy may lead to relapse of the disease, which is likely due to lower concentrations of antimicrobial drugs at the site of inflammation.
Acute external otitis media resolves within 7-14 days. With a longer course or repeated changes of tactics during the treatment period, frequent relapses, we always exclude other diseases, including immunodeficiency states and oncology.
Parasitic otitis media
Otitis in cats develops against the background of inflammatory processes and damage to the ear canal by endoparasitic mites.
Parasites live in or around the ear canal; their waste products cause a severe allergic reaction in the pet, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process.
Prevention
In order to prevent the cat from falling into the ear mite trap again, you should monitor its health and, for the purpose of prevention, fulfill some mandatory conditions.
After any water procedures, you need to not only wipe the cat’s fur, but also be sure to dry its ears from the inside . This will prevent the formation of a damp environment and make it possible to keep them clean.
Your cat's ears need to be cleaned daily. It is contraindicated to do this with cotton swabs, so as not to drive the sulfur mass even deeper. But cleansing with lotion should become an essential part of caring for your pet. During this manipulation, you need to monitor for the presence of abnormal sulfur secretions.
Mites in the ear
Avoid contact with wild or street animals. For a domestic cat, such exposure will become the root cause of infection with various types of ticks and infectious diseases.
Organize wet cleaning of the house using antiseptic agents twice a week. With its help, it will be possible to exterminate those parasites that entered the house on the soles of shoes or outer clothing.
Video on the topic
Cleaning your cat's ears
You should acquire a useful habit: make an appointment at the veterinary clinic once a month. During a structural examination, the doctor will pay attention to all the details in the cat's health, which will prevent any diseases and maintain his health.
If, however, the pet could not be saved, then if the first symptoms of tick infestation are present, you should immediately contact a veterinarian. If for some reason this cannot be done, then you can use the service of calling a veterinarian to your home.
Have you encountered ear mites on your cat? Leave questions for the veterinarian in the comments. All articles..
Tumors and neoplasms
Tumors and polyps in cats develop on the middle and inner ear, on the skin lining the ear canal.
The diseases are typical for older animals; malignant neoplasms require mandatory surgical intervention or the selection of special therapy.
What pathologies can affect a cat's ears?
Basically, the ears are affected by various parasites and mites. No less rarely, inflammatory infectious processes in the ears are diagnosed in animals. Hearing problems also arise as a result of injuries. The cat may suffer:
- otodectosis - a dangerous and serious disease that requires immediate treatment;
- otitis media and other pathologies of the outer and inner ear;
- eczema;
- dermatitis;
- hematomas, abscesses;
- tumors of different nature and degree of malignancy;
- necrosis.
Otodectosis
This pathology is caused by mites that parasitize the auricle and ear canal. A pet becomes infected with ticks through contact with a sick relative. Moreover, it is impossible to see a tick with the naked eye. Accumulations of parasite waste products are found in the ears.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- severe itching of the skin, while a large amount of deposits accumulates inside the ear;
- severe redness and scratching of the ear;
- anxiety due to severe itching and pain;
- the appearance of brownish scabs in the ear;
- dissemination of a strong foul odor;
- constant tilting of the head to the side affected by the infection.
If therapy is refused, the course of the disease becomes more complicated and is accompanied by:
- inflammation of the middle and inner parts of the ear, threatening deafness;
- the appearance of hematomas;
- perforation of the eardrum;
- inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
To get rid of the pathology, an effective veterinary drug BlochNet max is prescribed. It must be dripped into the ear, 4-6 drops, several times with a break of 5-7 days. The medicine should be injected into both ears, even if the mite has affected only one.
In the absence of this drug, the veterinarian prescribes antiparasitic and antibacterial agents. They treat the ears until the symptoms of the pathology are completely relieved. Self-medication of otodectosis is very dangerous.
Otitis
This is an inflammation of any part of the ear. In cats, the disease is a typical consequence of otodectosis. The most dangerous is otitis media, which affects the inner ear. Symptoms of the disease:
- redness of the inside of the ear;
- the appearance of a strong unpleasant odor;
- the appearance of purulent or even bloody discharge;
- a sharp decrease in hearing (moreover, some cats may experience periodic hearing loss);
- due to ear pain, the cat cannot chew solid food and especially dry food (preferring soft food instead);
- There is copious discharge of mucus or pus from the eyes;
- inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes is observed.
The most dangerous complication of otitis media in cats is meningitis. Without urgent treatment, it ends in death. Treatment depends on the form of otitis and includes the following measures:
- To get rid of purulent otitis media, antibiotics, hydrogen peroxide, and chlorhexidine are used. It is necessary to rinse the auricle with these medications.
- For chronic otitis media, veterinary antibiotics and compresses based on Dexamethasone are used.
- Wetzym veterinary drops are used to treat otitis externa.
- In case of fungal infection, a solution of phosphoric acid is prescribed, which needs to be used to treat the ears.
- With allergic otitis media, you first need to establish the cause of the disease, and only then prescribe certain pills.
Dermatitis and eczema
Dermatitis can occur due to skin damage from fleas and ticks. Because of this, the pet is constantly itching behind the ear. Numerous wounds and ulcerations appear on the auricle itself, which bother the animal with very severe itching. Scratching causes the affected area to increase.
Dermatitis can also be caused by a severe allergy to food or some environmental factors. With eczema, the skin of the ear swells and swells. Foul-smelling exudate accumulates inside the cavity. The pet constantly tilts its head and tries to get rid of the obsessive itch.
Exudate and other deposits are removed with hydrogen peroxide or a solution of baking soda. Wet areas should be lubricated with astringent preparations:
- lapis;
- Pyoctanin;
- picric acid;
- boric acid;
- zinc ointment.
For very severe itching, Cardiazol is prescribed.
Hematomas and abscesses
These diseases are associated with trauma to the animal. Hematoma is a consequence of mechanical damage to the auricle. Hematoma can be found especially often in cats in the spring, when they fight for a female. A cat may have not only bruises, but also scratches and other types of injuries. The ear can also be injured after a fall from a great height.
A hematoma appears as a result of a closed injury to the auricle. The affected area hurts very much. The pet is restless, presses his ear and does not allow him to be touched. The stages of development of a bruise are no different from those that occur in humans. The inflammatory process can develop after blood leaves the blood vessels. Due to untimely provision of assistance, suppuration and infection occur.
For hematomas, the cat is prescribed cold. An open wound should be treated with disinfectant solutions. If there is bleeding, it is important to apply a pressure bandage to the ear to reduce the rate of blood flow. An abscess always appears when there is an open wound or intense infection of the affected area of the body. Dust, sand, and earth almost always fall on an open wound.
If the affected area is large and the inflammatory process develops rapidly, surgical treatment is indicated. The doctor cleans the wound of fibrin and blood clots. After cleansing the wound, a sterile dressing is applied. This event is carried out using local anesthesia. It is necessary to prevent the animal from scratching its ear.
For hematomas, ointments are used: Levomekol or Lecomycetin. In case of severe suppuration, Vishnevsky's liniment and ichthyol ointment are used. Additionally, antibiotic therapy is used.
Ear tumors
They are rare in animals. But precisely because pet owners know little about the peculiarities of the development of tumors, they turn to the doctor only when the tumor is in an advanced stage and the choice of effective treatment methods is small.
Ear tumors in cats are divided into malignant and benign. The main symptoms of malignant tumors in the ear:
- a pronounced putrid odor emanating from the ear;
- the appearance of areas of baldness;
- the appearance of wounds in the auricle, from which a large amount of discharge of a different nature comes out;
- ear deformation.
Malignant pathologies of the auricle often occur in cats over the age of 10 years. Sometimes those animals that spend a lot of time in the open sun develop cancerous lesions of the ears. Carcinomas are prone to metastasis, sometimes this process develops rapidly.
Characteristic symptoms of benign ear tumors:
- severe itching of the ear, causing the animal to constantly scratch the ear and often tilt its head;
- slight discharge from the ear is observed;
- the ear increases in volume, and significant swelling forms inside the shell.
Benign neoplasms most often appear in animals over 7 years of age. Most often the ear can be affected by osteoma, ceruminoma and atheroma. Benign formations lead to an uncomfortable state of the animal.
If the tumor is a polyp, it is removed surgically. The same treatment is prescribed for all other types of neoplasms. Subsequently, it is recommended to take a course of antibiotics. To reduce pain, analgesics and NSAIDs are used in veterinary medicine.
Treatment for ear cancer may require removal of the ear canal or pinna. In the presence of metastases, chemotherapy is used. The prognosis for the course of a benign neoplasm is favorable. A cancerous tumor detected and removed in time can be treated, the outcome of which is favorable. In the presence of metastases, the prognosis worsens.
Necrosis
This is the name for progressive tissue death that develops as a result of hematoma or infection. As a result of tissue death, the ear turns black. It is impossible to cure such a disease. Surgeons decide whether to remove the affected part. If this is not done, the animal may develop gangrene and sepsis.
Foreign bodies
Owners of animals who suffer from pain that appears as a reaction to foreign bodies located in the ear canal turn to specialists.
These can be specks of dust and specks, grass seeds or organic plant remains; experienced veterinarians know how to treat ear diseases in cats and carry out the necessary manipulations to alleviate the animal’s condition.
Read also
Subcutaneous mite in a cat (Demodicosis)
Cats of different breeds and ages, both domestic and outdoor, can suffer from this disease.
Worms in cats: symptoms, signs and treatment
The first signs of infection may be absent for some time or resemble manifestations of other diseases
Sterilizing a cat: at home or in the clinic?
Sterilization is an intervention as a result of which an animal (a cat in particular) loses its ability to reproduce
Symptoms and signs of rabies in a cat
A person becomes truly afraid only when a cat bites him until he bleeds.
Ringworm in a cat: Treatment and symptoms
Ringworm is a serious infectious disease. When a cat gets sick itself, it transmits the disease to its owners.
Photos of ear diseases in cats
- Ringworm in cats - main signs, symptoms, prevention and treatment of ringworm in cats (105 photos)
Pancreatitis in cats: first symptoms, nutritional nuances and treatment options (125 photos and videos)
- Subcutaneous mites in cats - first symptoms, treatment options and real photos of examples of parasite damage (110 photos + video)
Help the site, share with friends