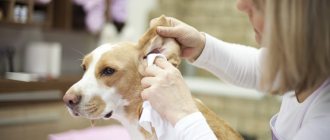
Head shaking in cats can occur for a variety of reasons, both simple and more serious. In many cases, your cat's head bobbing may simply be a symptom of a benign temporary abnormality, such as a stressful situation or overheating. However, it can also be a sign of a more serious condition that may require veterinary intervention.
Sudden head shaking in felines can cause stress, but there is usually no cause for concern. In this article, we will look at the common causes of this unusual behavior in cats and possible solutions. Let's start!
Ear problems
The most common reason your cat nods his head is due to ear problems. It could be simply a buildup of wax causing discomfort or hearing problems, or it could be something more serious, such as an ear infection. An ear infection can throw your cat off balance, and rocking is her attempt to get better. This is usually accompanied by other symptoms such as vomiting and lack of appetite. Another possibility is ear mites or fleas, and persistent itching can be uncomfortable for your cat.
© shutterstock
Check your cat's ears thoroughly for wax buildup, fleas, or mites. Gently wipe away excess wax, but stay away from cotton swabs as they can damage your eardrums. If there are any signs of redness, swelling or pain, it could be an infection and you should take your cat to the vet.
What could be the reasons?
Cats' ears are a very vulnerable organ. To solve the problem before it appears, every owner must understand how extensive the possible causes of the disease are. Among them:
- micro-trauma of the ear canal (improper cleaning, use of inappropriate products);
- the auricle is narrow in structure (features of specific breeds);
- blockage of the ear canal (due to polyps, foreign bodies, neoplasms);
- allergic skin diseases (to food or household chemicals);
- production of excess sulfur;
- inflammation of the ear canal as a result of past illnesses;
- the appearance of parasites (microscopic mites);
- development of fungal diseases;
- water getting into the ears.
Not every factor can be identified and prevented independently. Self-medication in such cases is contraindicated. Subsequent diagnostics is the task of a qualified specialist.
Reaction to medications
A bad reaction to medications can cause cats to shake their head and, in severe cases, even cause seizures. Your cat may have a bad reaction to certain medications, which is quite common even with medications approved for cats. Never give your cat medications that are not prescribed or at least approved by your veterinarian, as this can cause serious side effects. Reactions to medications are often accompanied by other symptoms, such as nausea or diarrhea.
If your cat is taking medication and you suspect that this may be the cause of his head shaking, ask your veterinarian if another medication is available.
Sulfur plug
If a cat scratches its ear all the time and shakes its head violently, it is possible that a large amount of wax has accumulated in its ear canal, and a so-called wax plug has formed. Naturally, the manipulation of removing excess sulfur can be done at home by soaking the plug with saline solution and carefully removing it with a cotton swab. But sometimes such actions can only worsen the animal’s health, so it’s better to play it safe and entrust the process of removing wax plugs from your pet’s ear to a specialist.
Genetics
Although it is quite rare, your cat's genetics may play a role in her head bobbing. This is especially common among purebred animals, where poor breeding practices among a small gene pool can result in unhealthy animals.
A good example of this is the Burmese cat. These cats sometimes suffer from an inherited condition called hypokalemic polymyopathy, which is characterized by weakness of the neck muscles that can cause head shaking.
© shutterstock
Treatment of cerebellar ataxia in cats
The chances of recovery and treatment methods for feline ataxia depend on the general condition of the animal and the reasons that caused the development of the pathology. The cat has the opportunity to fully recover and return to a healthy lifestyle if the owner consults a veterinarian in a timely manner.
The measures taken by veterinarians when diagnosing ataxia may be as follows:
- If the pathology is caused by a tumor, surgery is used. After its removal, the symptoms disappear.
- In case of poisoning, measures are taken to relieve intoxication. The animal is prescribed IVs, injections of vitamin B1, and diet.
If the pathology occurs against the background of brain defects, it can occur in mild, moderate and severe forms. The disease cannot be cured, but in mild cases it is possible to save the kitten. This will require full-time care.
Kittens are prescribed the drug "Gamavit" to strengthen the immune system. To improve the functioning of brain tissue, Glycine is recommended at a dosage of 250 mg, 1 tablet per day. The course of admission is 14 days.
Most often, the condition stabilizes after the kitten turns one year old.
Treating a pet for poisoning
Vestibular disease
Vestibular disease is characterized by sudden and somewhat severe disorientation in cats, which may be the cause of your cat's head bobbing. Common symptoms include falling or leaning to one side, bending or shaking the head, and often nausea and vomiting. This condition is caused by an abnormality in your cat's inner ear, the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance and coordination. The exact cause of this condition is not yet fully understood and diagnosis is made based on clinical signs.
The condition usually occurs suddenly and can occur in cats of any age. Although there is no specific treatment, your veterinarian will likely prescribe antibiotics or antifungal medications since there is likely some kind of infection in the inner ear. The condition is short-lived and usually goes away within a few days.
Sarcopid mites
If your cat's ears are shaking, this could be a sign that she has another type of mite. Such mites can spread not only in the ear area, but also in other parts of the cat’s body. They cause another feline disease, notoedrosis.
The head is affected first, then the entire body. The skin at the site of infection becomes dry and dense, covered with a crust, and the crust subsequently cracks.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to show the cat to a specialist. He will take a sample from the surface of the skin for analysis. Only the outermost layer from the inflamed area is scraped off; ticks can be seen there.
Both types of ticks provoke severe itching in the animal, forcing them to scratch the skin until it bleeds. Scabies that affects the ears can lead a cat to deafness or meningitis; in especially severe cases, the death of the pet can occur.
Final thoughts
Although sudden head shaking in a cat can be alarming, there is usually no serious cause for concern. The problem is usually easy to fix at home, and your cat can quickly bounce back. However, if the problem persists or worsens and is accompanied by other symptoms, it is a good idea to take your feline to a veterinarian for a check-up.
Posted by Christian Adams An American expat living in Metro Manila, Philippines for over a decade, Christian is a lifelong cat lover and the proud father of two rescue cats, Trixie and Chloe. Both girls used to be among the crowds of homeless people who roam the cities and countryside. Three-year-old Trixie was rescued from a litter found under a neighbor's porch, and two-year-old Chloe was brought home by Christian's young son, Henry, who discovered the crying kitten in the parking lot.
Diagnosis of ataxia in a cat
The main stage in diagnosing pathology is a complete history taking. The veterinarian must determine whether the animal had injuries or whether it suffered from infectious diseases. If possible, find out information about heredity and the course of pregnancy if we are talking about pathology in a kitten.
The animal's nervous system is assessed and tests are taken to identify viral pathogens. It is recommended to do an MRI of the brain to see tumors or areas of bruising. It is necessary to examine the ears using an otoscope.
As soon as there is a suspicion that infection is occurring in the area of the brain or spinal cord, a test for leukocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid is required.
Diagnosing disease in pets
Treatment on an outpatient basis and at home
It is important that therapy is carried out comprehensively. The treatment regimen is developed depending on the cause that caused the development of the disease. In this regard, the dosage of drugs may differ even if we are talking about the same form of pathology.
The following medications are most often prescribed:
- vitamin complexes, B vitamins;
- to eliminate infections - antibiotics;
- for swelling of the brain - diuretics;
- Hepatoject for liver dysfunction;
- to improve blood circulation in the brain - Cerebrolysate;
- saline solutions in droppers to relieve intoxication.
Physiotherapy and massage are recommended for the animal. If the spinal cord is affected, surgery is required.
Important! You should not try to treat yourself. A sick animal requires professional advice from a veterinarian. The severe form cannot be eliminated using folk methods alone without an integrated approach.
Vitamins for full recovery
Rules for cleaning ears
Once a month, your cat's ears need to be cleaned to prevent ear diseases. To do this, it is important to choose a time when the animal is completely calm. Sudden movements can damage the skin. To cleanse, take saline solution and heat it to body temperature.
Moisten a cotton pad and carefully wipe the inside and outside of the ear. Then you need to drop a few drops (3-5) of warm solution and very lightly massage the skin nearby. After this, use a cotton swab to carefully clean the ears of dirt.
If the animal is not given, the procedure is carried out by a veterinarian.
How to identify pathology
Understanding that your pet needs your help is quite simple. First of all, as mentioned above, pay attention to how often the cat scratches its ears and shakes its head. For example, if a pet repeats the procedure several times per hour, then this is a clear sign of discomfort he is experiencing.
It is worth paying attention to the pet’s behavior. If you have ear diseases, your cat may become more aggressive and nervous. In some cases, on the contrary, the pet becomes lethargic and apathetic. Loss of appetite and refusal to play are equally alarming signs. Pay attention to how the cat reacts to your touching his ears.
Be sure to inspect your pet's ears. If they have diseases, cats can scratch their outer parts, as well as the area behind the ears, until they bleed. Dirt appears inside the ear canal, and the skin begins to peel off. In advanced stages of the disease, an unpleasant odor and discharge appear.
I myself have encountered ear problems with a cat only once. He scratched himself a lot and shook his head, and there was a smell of pus coming from his ear. Upon examination, it turned out that the problem was a deep scratch that the pet received during another skirmish with a “competitor.” To initially treat such damage, I use hydrogen peroxide, and then treat the affected area with zinc ointment. It quickly dries the damaged area, allowing the wound to heal faster.
If there are ear diseases, the cat becomes more aggressive, he may even bite and scratch the owner if he touches the affected area