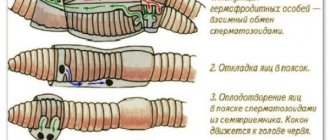
The movement of the worm occurs due to contraction of the muscles of its body, while the length and thickness of its individual parts change.
The movements of all parts of the body consist in the fact that some parts of it lengthen and thin, or, on the contrary, shrink and thicken. As a result of such alternating actions, forward movement occurs. First, its front part stretches forward, and then its back. When the back of his body pulls up, his front begins to move forward. This is how the earthworm moves, which can be observed by placing one individual on a paper sheet. Let's take a closer look at what makes the earthworm move.
Appearance and features
Earthworms (Lumbricidae) belong to the order of oligochaete annelids. Their body consists of separate annular segments (segments), the number of which depends on the age and size of the worm. There can be 80-300 segments. Moreover, there are constrictions both outside and inside. The creature's shape is maintained by the internal pressure of the liquid that fills their body from the inside.
The ventral side is flatter and lighter, the dorsal side is convex and dark. The front end of the body (with the mouth) has a pointed shape, the rear end (with the anus) is wider and blunt. Approximately in the middle, the worm's body is divided by a protruding belt, which is involved in the reproduction process.
Appearance
The size of earthworms living in Russia is 10-30 cm, sometimes larger. In Australia there live worms up to 1 m long, and in South America there are giants up to 2 m and 2.5 cm in diameter.
On a note! Earthworms are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive cells.
The body of these invertebrates is covered with mucus, which at the same time:
- protects skin from drying out;
- facilitates movement in the substrate, providing gliding.
During the cold season, invertebrates move into the deeper layers of the soil, and life processes slow down and stop (diapause). Little is known about the lifespan of these creatures. There is evidence that worms live on average 5 years, but no more than 10 years.
First night right
(Latin
jus primae noctis, German Recht der ersten Nacht, Herrenrecht
, French
Droit de cuissage, Droit de prélibation
, “the right to lay the thigh”), which existed in the Middle Ages in European countries - the right of landowners and feudal lords after the marriage of dependents peasants spend the first night with the bride, depriving her of her virginity.
In some cases, the peasant had the right to buy off this by paying a special tax. The same right existed in many cultures of the Indians of South America for sorcerers or for leaders, and perhaps exists among some tribes even now. The right of the first night for relatives of the bride and groom existed in some African tribes and among the Balearics on the Balearic Islands. Versions of the origin of this phenomenon
The philosophers Bachofen, Morgan, Engels saw in the right of the first night a remnant of group marriage. In the era when the paired family was already beginning to take shape, men still retained the right to all the women of their tribe. With the gradual development of culture, the circle of men who have the right to women becomes smaller, the exercise of this right is limited in time, and, finally, it comes down to only one wedding night, first for everyone, then only for the head of the family, for the priest, for the military leader and for the lord - in the Middle Ages. According to data cited by Friedrich Engels, among some peoples, friends and relatives of the bride and groom presented their original rights to the bride on the wedding night, and the groom stood only at the end of this row. This was the case in ancient times among the Balearics and some African tribes (Augils); at least until the end of the 19th century. this custom existed among the Barea tribe in Abyssinia. For others, an official, a representative of a tribe or clan - a cacique, a shaman, a priest, a prince - takes the place of a social group and enjoys the right of the first night. The emergence of the custom is probably associated with the fear of shedding blood during deflowering. It was believed that this act was associated with the loss of a large amount of mana and therefore harmed an ordinary person. That is why they invited a sorcerer or a leader (depending on the ritual).
Information about the existence of a phenomenon in the history of Europe
As proof of the existence of the right of the first night, they pointed to the Jungferzins
(to give virginity), preserved until the very last days of the reign of feudalism, as well as a ritual according to which the master, on the wedding day of his serfs after the wedding, had to step over the marriage bed or put his foot on it.
In the Catalan original, Sugenheim ( Sugenheim, “Geschichte der Aufhebung der Leibeigenschaft”
, St. Petersburg, 1861, p. 35) quotes a decree of 1486 issued by Ferdinand the Catholic: “we believe and declare that gentlemen (lords) cannot also when the peasant gets married, sleeps the first night with his wife and, as a sign of his dominance on the wedding night, when the bride lays down in bed, steps across the bed and over said woman;
“Masters also cannot use the daughter or son of a peasant against their will, for payment or without payment.” Collin de Plancy in his Dictionnaire féodal
(Paris, 1826) pointed out that the canons of the Cathedral of Saint-Victor in Marseille were officially allowed to exercise the right of the first night in relation to their serf girls. The same Colin de Plancy cites the fact that the right of the first night was sold by one owner in Orleans for 5 sous, and by another feudal lord for 9½ sous.
Information about the existence of a phenomenon in the history of Russia
A number of historians of the 18th - early 19th centuries (Schlözer, Evers, Tatishchev, Elagin) saw an indirect indication of the existence of the right of the first night in Russia in the chronicle’s story about Princess Olga replacing the “princely right” with the black kuna. The very custom of giving a ransom to the landowner before the wedding persisted until the abolition of serfdom; This feed was known as the “brood marten.” In any case, according to the laws of the Russian Empire, landowners did not have the right to violence against newlywed serfs and for such facts they had to be and were sometimes brought to justice. Prince Vasilchikov in his book “Land Ownership and Agriculture” certifies that when he was the leader of the nobility, he more than once happened to encounter facts of similar violence of landowners against peasant women. In 1855, 6 years before the abolition of serfdom, Privy Councilor Kshadowski was tried and sentenced to a fine for using the right of the first night. However, laws protecting the sexual integrity of serf women from violence by their owners were rarely observed in Tsarist Russia due to the complete lack of rights of the peasants in the face of the arbitrariness of the serf owners. IN AND. Semevsky wrote that often the entire female population of some estate was corrupted to satisfy the master's lust. Some landowners, who did not live on their estates, but spent their lives abroad or in the capital, specially came to their estates only for a short time in order to take advantage of fresh peasant girls. On the day of arrival, the manager had to provide the landowner with a complete list of all the peasant girls who had grown up during the master’s absence, and he took each of them for himself for several days in order to deflower them.
Africa
According to data cited by Friedrich Engels, among some peoples, friends and relatives of the bride and groom presented their original rights to the bride on the wedding night, and the groom stood only at the end of this row. This was the case in ancient times among the Balearics and some African tribes (Augils); at least until the end of the 19th century. this custom existed among the Barea tribe in Abyssinia
South America
In many cultures of the Indians of South America, there was the right of the first night, which belonged to sorcerers and leaders. It reflected the social primacy of a person occupying a privileged position, but most often this was explained by the desire to ward off evil spirits by persons possessing the necessary power for this. Among the Ika, the sorcerer watched the progress of the wedding night; among the Patangoro, other men had the right to cohabit with the young woman. Among the Otomak, young men had to marry old women in order to learn the secrets of intimate relationships. These customs continued to exist among the Indians even after the arrival of Europeans.
In culture
- In the Hundred New Novellas, a 1462 work commissioned by the Duke of Burgundy, Philip the Good, the thirty-second tale tells of Franciscan monks from Catalonia who collected a “tithe” from women based on the number of sexual intercourse they had with their husbands. But since the Franciscans were forbidden to touch money, they were “forced” to receive their tithes “in kind,” that is, in the form of sexual intercourse. All women, without exception, paid their tithes, and only a few old women declared their reluctance to do this, inviting the Franciscan brothers to receive it in “fabrics, sheets, dummies, bedspreads, pillows and other similar things.”
- In Beaumarchais’s play “The Marriage of Figaro” (1784), which takes place in the author’s contemporary Spain, Count Almaviva, by a special decree, renounces the right of the first night regarding his subjects in honor of his young bride.
- In Mel Gibson's Braveheart (1995), the feudal lord of the Scottish independence fighter William Wallace claims his "right of the first night." To avoid the tyrant's advances, Wallace and his fiancee Marron are married in secret. Wallace recaptures Marron from the English soldiers trying to rape her. However, Marron does not have time to escape from the village and the local sheriff cuts her throat. Wallace confesses, but instead of surrendering, he begins to fight with the soldiers.
- In the painting “Le Droit Du Seigneur (The Right of the Lord)”
by
Jules Arsene Gardier
.
Disputes about the reality of the right of the first night
Some historians today are of the opinion that the right of the first night is a myth and such a right never existed.
A group of researchers explains its occurrence by the linguistic ambiguity of some historical texts, the authenticity of which is beyond doubt. For example, the “Book of Burgundian customs” (French Coutumier bourguignon
), compiled and annotated at the end of the 14th century, states that, according to one of these “customs” (we are talking about serfs), “when a man marries on someone else’s estate and brings his wife to himself, then if on the first night he forces her to lie under the master, then he loses nothing, for he acquires a woman for the master and includes her in his fortune.”
To understand this text, we need to remember the right to marriage dowry (French formariage), which compensated the landowner for the loss of the future offspring of the married couple if a serf peasant or peasant woman “married outside his domain.” According to the Book of Burgundian Customs, a serf could avoid paying such a ransom by forcing his bride to “lie under the master.” However, according to the above group, this simply means that the husband places his wife “in a subordinate position” in relation to his master, as a result of which he receives the right to own the future offspring of the newlyweds, refusing the traditional compensation for damages. The right of the first night is never mentioned in documents in itself, without substitutes compensating for it. Thus, in a document dated 1419, the owner of Larivière-Bourdet (in Normandy) declared: “In this case, I also have the right to collect from my people and others when they marry in my domain, 10 sous of Tours and a loin of pig along the entire spine and up to the ear, as well as a gallon of any drink added to this provision, or I can and must, if I consider it best, lie with the bride in the event that her husband or his messenger does not give me or my authorized one of the above-mentioned things." The historian Alain Boureau believes that this is a more or less humorous threat, the purpose of which is to emphasize the symbolic power of the feudal lord at a time when the original forms of serfdom have largely weakened. Buro believes that references to the right of the first night were used by feudal lords as a technique to obtain economic or political benefits. So, in 1538, the owner of the Louvi-Soubiron estate collected various fees and duties from the peasants, including cuissage
, - and all this with the goal of selling his fief as profitably as possible. In another case, the reference to cuissage was also used by the landowner in order to increase the list of his legal rights and thereby collect as much as possible from the peasants. The supposed existence of the right of the first night became a symbol of medieval barbarism and played an important role in shaping the idea of the Middle Ages - both in the perception of the general public and among historical scholars. In 1854-1858 in France there was a long discussion about the reality of the existence of the right of the first night. Jules Delpit published seventy-two proofs of the existence of cuissage in 1857. Catholic journalists argued that in reality this custom did not exist.
Information sources:
ru.wikipedia.org - right of the first night - Wikipedia;
dic.academic.ru - right of the first night;
lovestuff.ru - right of the first night;
factruz.ru - right of the first night.
Habitat
Earthworms live on all continents, with the exception of Antarctica, almost everywhere except deserts. In the soil of many areas of the Earth, the population of earthworms has grown significantly when people began to actively engage in agriculture there. For example, planting plants unusual for the region, in the root system of which there were already representatives of the species.
Worms breathe through the entire surface of their skin, so they prefer moist soils rich in humus (semi-decomposed plant debris). In too wet (swampy) areas there is little oxygen in the soil, and breathing is difficult. In dry, sandy soil, the mucus dries out and the worm may die.
Interesting! When it rains, worms tend to crawl to the surface because it becomes difficult to breathe in the soil. That is why, after a rainstorm, they can be seen in huge quantities on garden paths, on lawns and flower beds in parks.
Comments (2)
Nikita
11.11.2017 at 12:45 |
A very interesting article, I of course knew that they perform some function, but why and why I learned from here, I also heard that some gardeners buy foreign worms for greater soil fertility!Answer
Yulia Expert Plodogorod
10/31/2019 at 11:27 pm |
Hello, Nikita! You are absolutely right, earthworms are very useful in open ground conditions. They restore even very depleted soil and clean it of chemicals. They are sometimes deliberately added to containers where compost is being prepared. This makes it possible to speed up the process and improve the quality of the resulting fertilizer.
We would like to note that when purchasing these creatures, it is important to make sure that the conditions are suitable for their normal functioning. Of course, worms of this type are highly adaptable, but they will be more effective under conditions of optimal temperature and other factors.
Also, you need to be careful about introducing creatures into your area that are not part of the natural ecosystem that is typical for a particular region. The fact is that without maintaining balance with the help of natural antagonists, species multiply intensively and uncontrollably. In the future, this may lead to overpopulation and destructive processes.
If there are too many earthworms, they will dig more intensively in search of food. This can harm plants, especially young ones that do not have a strong root system.
Answer
How do earthworms move?
The movement of the worm occurs in several stages and is associated with the structure of its muscular system. If you try to catch a worm that has sunk into the ground with its head end, the back half will remain in your hands, since the body will tear apart at the waist. Earthworms are able to go 80-100 cm deep into the soil.
Interesting! The severed back part of the worm usually grows back.
The role of bristles
On each segment of the animal’s body there are from 4 to 8 bristles - small thin outgrowths. They are placed at an angle towards the back half of the body. The worm moves in the ground like a spring. The pointed head end stretches, becomes thinner, and pushes the soil apart. At the same time, the bristles stand apart and hold the body. Then the back half is pulled towards the front.
The role of the longitudinal and oblongata muscles
The peculiarities of the movement of an earthworm in the soil are determined by the structure of its muscular system. Under the skin there are two layers of muscles:
- circular (ring);
- longitudinal.
Together they form a fused musculocutaneous sac (worm shell).
Rings
The longitudinal muscles are responsible for stretching the body, while the torso becomes elongated and thin. Ring - for reduction. At the same time, the body thickens and the segment shortens.
what do earthworms eat
Smile of the Cat
Earthworm nutrition. Earthworms feed mainly on half-rotted plant remains. They drag leaves, stems, etc. into their burrows, usually at night. Earthworms also feed on humus-rich soil, passing it through their intestines.
The peculiarities of digestion make earthworms detritivores, i.e. they feed on detritus - decaying plant organic matter (in combination with soil particles) located on the surface of the soil or in their underground burrows, as well as in the soil itself. Therefore, the coprolites that the earthworm leaves behind are lumps of soil enriched with nitrogen, microelements, and having low acidity due to the alkaline environment of its intestines. Because of its slowness and thoughtfulness, the earthworm does not have time (and is even embarrassed by prying eyes) to eat detritus, and therefore drags it into storage deep into the soil, saturating it with organic matter and feeding its smaller brothers. In addition, thanks to the numerous passages and burrows of earthworms, the air supply to the soil and all its inhabitants and plant roots is significantly increased.
More information Here) : http:*//humangarden.*ru/books/chervi.*htm - remove*
scarlet flower
old leaves
Yana Alexandrovna
While in the soil, earthworms feed on organic debris and constantly pass them through their digestive tract along with lumps of soil.
Moving on hard ground
In dense soil, the worm also moves with the help of muscles and bristles. At the same time, he swallows the earth with his mouth. Soil particles move through the animal's intestinal tract and nutrients are absorbed from it. Earthworms are detritivores.
Worms have no teeth. The throat sucks in the earth like an enema. The processed soil is pushed out of the anus. On the surface of the earth, on garden and park paths, you can see chains of small balls - coprolites - this is the waste of the worm's digestion. Moreover, in one day one earthworm is able to pass through its insides an amount of soil equal to its weight.
Important! Earthworms are the most important humus-forming creatures on Earth. During the digestion process, compounds of humic acids with inorganic substances (phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium) with low acidity are obtained. Thus, they saturate the soil with substances necessary for the growth and development of plants.
Nutrition and touch
In addition to rotten vegetation, the worms eat rotten leaves, which they pull into their own underground burrows at nightfall.
Worms lack any complex organs of touch. But, if you shine a flashlight on a worm that gets out at night, it will quickly hide in the ground. This means that it can sense light through its nerve endings. He is also able to perceive smells, looking for edible, pleasantly smelling objects.
Business relevance
Breeding worms at home can hardly be called a popular type of business. But the low barrier to entry, ease of cultivation and care, as well as the availability of various sales sources indicate the prospects of organizing a vermifarm (a place where worms are grown). You can make money by breeding worms at home in various ways of organizing a business:
- Sales through our own retail fishing outlets. Not every fisherman likes to pick in the ground in search of earthworms, and besides, today it is not so easy to find enough of them. Many people simply purchase bait at special points. One individual today costs 1-3 rubles, and for full-fledged fishing you need at least 30 worms.
- Sales to poultry and fish farms, pet stores for feeding. For fish and birds, live food must be present in the diet. Earthworms have great nutritional value. Therefore, farmers, for example, those who breed Indian ducks at home, constantly purchase worms as food, moreover, you can negotiate with them on periodic deliveries.
- Sale of breeding stock for those who want to breed worms at home.
- Production of vermicompost, which can be obtained as a result of the vital activity of worms. Vermicompost is a valuable organic fertilizer, the best nutrition for any plants. Buying vermicompost is interesting for both ordinary summer residents and large landowners, farmers, and those who are looking for profitable business ideas with small investments. Vermicompost can be collected every 4-6 weeks.
- Sales to pharmaceutical companies for the production of medicines.
- Production and sale of vermicelli. Worm tea (vermic tea) is a product of the vital activity of worms and is a unique highly concentrated biohumate. Increases crop yields and has a protective effect on them.
Useful on the farm
Earthworms by their “profession” are natural soil looseners that optimize the soil structure and increase the level of fertility. When moving around the site, individuals make long, deep passages and holes. They stabilize air exchange through root systems and seeds. Invertebrates consume rotten grass and leaves, and dirt as food. This is a good prevention against the development of harmful insects and diseases. They saturate the soil with substances necessary for plants from the periodic table, such as:
- nitrogen,
- calcium,
- phosphorus,
- magnesium.
To read: Where it lives and how to fight clothes moths
Natural necessity
All animals have a circulatory system, starting with secondary cavities. It was formed as a result of an increase in vital activity (compared, for example, with Life in constant motion requires stable energetic muscle work, which, in turn, causes the need for an increase in the cells of incoming oxygen and nutrients, which only blood can deliver.
What is the circulatory system of an earthworm? The two main arteries are the dorsal and the abdominal. In each segment, looped vessels pass between the arteries. Of these, several are slightly thickened and covered with muscle tissue. In these vessels, which perform the work of the heart, muscles contract and push blood into the abdominal artery. The annular “hearts” at the exit into the spinal artery have special valves that prevent blood flow from going in the wrong direction. All vessels are divided into a large network of thin capillaries. Oxygen comes from the air, and nutrients are absorbed from the intestines. Capillaries located in muscle tissue release carbon dioxide and breakdown products.
The circulatory system of the earthworm is closed, since during the entire movement it does not mix with the fluid of the cavity. This makes it possible to significantly increase the metabolic rate. In animals that do not have a blood pumping system, heat transfer is two times lower.
The nutrients that the intestines absorbed during the movement of the worm are distributed through a well-formed circulatory system.
Its scheme is quite complex for this type of animal. Vessels run above and below the intestines along the entire body. The vessel running in the back is equipped with muscles. It contracts and stretches, pushing blood in waves from the back to the front of the body. In the anterior segments (in some species of worms it is 7-11, in others - 7-13), the vessel running along the back communicates with several pairs of vessels running transversely to the main one (usually there are 5-7). The circulatory system of an earthworm imitates hearts with these vessels. Their muscles are much more developed than others, so they are the main ones in the entire system.
Worms in a flower pot, what to do?
Elena*
Earthworms are bad. As long as there are nutrients in the ground, they are not dangerous, but as soon as everything is over (when everything ends), they are taken up by the roots, especially young roots. When earthworms started appearing in the pot, I tried everything, actara and potassium permanganate, and washed the roots. Everything is useless. It got to the point that I even left it with the washed roots in a bucket of water overnight. I thought they would choke. But no. When I lifted the plant (it was crescent asparagus) from the water, I saw a terrible picture. The worms hung like ropes attached to the roots. I removed them with tweezers. The drug CONFIDOR helped me. I spilled the soil twice with an interval of 1-2 weeks. Earthworms breed very quickly in a favorable environment.
Murmur
There is a drug called AKTARA. diluted in water. buy it at the store and use it to water pots of plants.
Alexander
fishing with a pot
Valentina Dylgina
If it's raining, that's fine.
Emilia Bilyauer
dilute a weak solution of potassium permanganate and pour it in
Vladimir Emelianenko
Throw it away quickly, it's a nightmare and unsanitary!!
compas
Digging and fishing... all year round, worms are useful for plants - they loosen the soil.
olga
The soil will have to be thrown away, the roots of the plant should be washed in a light solution of laundry soap. Rinse the pot and pour boiling water over it. Heat the new soil in the oven before use...
Irina*
I think that it is best to change the soil, even if it is purchased, you never know what kind of worms they are, what if you don’t get them out? Wash the pot, change the soil and let your palm tree rejoice.
Lydia
I had the same problem - three cacti were eaten (((they also recommended potassium permanganate to me... watered it, the fourth cactus still seems to be alive. Only the solution should be very weak
Vera Shelest
A slug crawled out of my purchased soil in a sealed bag. Lively, it immediately crawled to eat the leaves. This is the kind of land we pay money for! I now began to steam the soil on the stove in a saucepan. I advise you to remove the flower from the pot and steam the soil.
Katya Kotovich
these are most likely trimatodes (small, white), they are not so easy to get rid of, potassium permanganate will not help here, you need to completely clear the roots of the tree from the soil and wash the pot, otherwise the tree will die, these creatures live in the ground, they came to you that way, the seller did not checks the ground, eats everything, from plant roots and snails to the ground. so hurry up!
Alinka Malinka
Immerse the pot in a bucket of water for half an hour. . maybe so? Don't know.
Lady with a dog
I had the same story, worms are harmful, they feed on the most delicate small roots, pour very warm water (40-50 degrees) into a container and place a pot with a flower in it for 5-10 minutes so that the water level does not reach the top of the pot 2 cm after the worms will crawl out to the top You collect them for fishing, as advised above :0))) the only negative is that the ground gets wet through and through in cold weather, this absolutely cannot be done
Catherine
I also had rain ones. It's OK!
Marina Mirutenko
Earthworms are completely harmless! And they don’t eat any kaorns, they consume earthly organic matter and, passing through themselves, structure the earth. But they described how to bring others out.
Natalie Filini
Earthworm (Lumbricidae)
Length from 2-3 cm with thickness approx. 1 mm to 50 cm with a thickness of 1.5-2 cm. Approx. 300 species, widely distributed; most numerous in forest and forest-steppe zones. They live in the soil, are nocturnal, and crawl to the surface during the day after heavy rains. Soil formers. 11 species are protected. Earthworms (the family of oligochaetes) are usually considered beneficial organisms, but in a small pot of houseplants they can be harmful.
Harmful effects Normally, they feed on plant debris, but in a pot, when there is a shortage of fresh organic matter, they easily switch to living plant roots and underground shoots and rhizomes. Earthworms spoil the soil in flower pots with their liquid sticky secretions, clog the drainage, causing the soil in the pot to turn sour. If there are earthworms in the earthen coma, characteristic lumps of earth appear on the surface, thrown out by them from their passages. If there are earthworms in a pot, the plant becomes lethargic and stunted in growth.
Control methods Soil from the street can contain not only adult individuals, but also eggs. Therefore, it is better to sterilize garden or forest soil in one way or another before use. If plants are taken outside in the summer, place the pots only on pallets and so high that earthworms cannot climb into them. At the same time, worms rarely appear and successfully reproduce in pots with indoor plants due to the peculiarities of preparing soil mixtures and the watering regime. But if they have already appeared in the pot, you need to immerse the pot with the plant in warm water for half an hour - the worms will either crawl to the surface, where they can be easily collected, or drown. It is also quite easy to collect large worms when replanting. You can water the soil in the pot well with a pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Elena
you can decide here which worms are in your pot
[link blocked by decision of the project administration]
Who else lives in the soil?
The well-being of the soil is ensured by numerous soil inhabitants, but most of them are so small that we do not notice them. Healthy and fertile soil is full of life: bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoa, mites, springtails, larvae, worms, ants, nematodes, millipedes, enchytraeids and much more.
All depend on each other, many exist in symbiosis. Manipulations with herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides destroy established connections and the vacated living space is very quickly occupied by aggressive forms, most often pathogenic.
Worms feed on dead organic matter, but without soil microorganisms they will not be able to do this. Thus, the clean land beloved by many without a single weed is half dead, its biocenosis is disturbed, it requires constant labor and investment in the form of fertilizing, loosening, weeding, and watering. Instead of soil biota, gardeners work. And vice versa - if there is organic matter in the zone of plant roots, all soil living creatures will actively work there, providing the plants with everything they need.
Methods of gardening and gardening, of course, are everyone’s personal business. But there are already more than a dozen annelids in the Red Book of the Russian Federation, and behind them in the chain are all those who feed on them.
Before feeding live waste to worms:
Such as cleaning from
- cabbage
- potatoes
- carrots
- celery
- radishes
- radishes
- beets
- and so on.
In winter, you can save energy by freezing it all on the balcony. Now about the bones, such hard material for food in general is absolutely unthinkable, since our worms will never chew them without dentures. In order to feed it to the worms, you need to grind any bones
- apricot
- avocado
- cherry
- mango
- meat
- olive
- nuts
- peach
- fish
- plum
- date
- pistachios
- cherry
- eggshell
- etc.
All of them are quite hard, but in a ground state they are excellent as food for worms to grind food faster, as all birds do, which swallow small pebbles for this purpose. However, at home you can foolishly break something - in the sense of a blender, mixer or electric meat grinder. If you try to grind all the above listed bones, hard roots and branches of plants in expensive kitchen devices. Therefore, we collect such food separately and burn it in the fireplace at the dacha. But ash, chalk and sand in unlimited quantities are perfect for feeding our “suckers” not only for grinding food, but also for deoxidizing it. In a box vermifactory, at least half of the feeding should be wet waste paper. The second half includes all kitchen vegetable or fruit peelings, as well as water after washing off the remains of any food from the dishes. What do all the worms especially love? To further improve the appetite and love of sexually mature individuals of the “Angels of the Earth”, aphrodisiacs are highly desirable:
- coffee grounds
- tea leaves
- spoiled jam
- sweet remains of flour and confectionery products
- various meat scraps
- fish waste
- greasy napkins for wiping pans and pans
- our feces
- droppings and manure of all domestic animals and birds
Sources
- https://www.syl.ru/article/332655/chem-pitayutsya-dojdevyie-chervi-v-prirode
- https://TaraKlop.ru/chervi/dozhdevoj-cherv/
- https://faunistics.com/dozhdevoj-cherv/
- https://wildfauna.ru/dozhdevoj-cherv
- https://farm-worm.com/znachenie-chervej/
- https://travart.ru/dozhdevye-chervi
- https://zverila.ru/dikie-zhivotnye/vidy-dozhdevyh-chervej-i-sreda-ih-obitaniya.html
- https://zen.yandex.ru/media/rmnt/organicheskoe-zemledelie-dojdevye-chervi–osnovnoi-indikator-plodorodiia-5b713c39926e3100a8d6293d
- https://vermitechnologii.ru/chem-kormit-dozhdevyih-chervey/
Test on the topic: “Type of Annelids”
Time limit: 0
Navigation (job numbers only)
0 out of 10 tasks completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Information
The verification test task includes questions with one or more correct answers.
You have already taken the test before. You can't start it again.
The test is loading...
You must log in or register in order to begin the test.
You must complete the following tests to start this one:
results
Correct answers: 0 out of 10
Your time:
Time is over
You scored 0 out of 0 points (0)
| Average result |
| Your result |
Categories
- No category 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- With answer
- With a viewing mark
- Task 1 of 10
1.
The body of annelids is formed
Right
Wrong
- Task 2 of 10
2.
A process that allows an earthworm to quickly repair damaged body parts
Right
Wrong
- Task 3 of 10
3.
The oligochaete worms include
Right
Wrong
- Task 4 of 10
4.
Appears for the first time in annelids
Right
Wrong
- Task 5 of 10
5.
Features of the earthworm's circulatory system
Right
Wrong
- Task 6 of 10
6.
Oxygen enters the earthworm's body through
Right
Wrong
- Task 7 of 10
7.
Excretory system of annelids
Right
Wrong
- Task 8 of 10
8.
Type of nervous system of an earthworm
Right
Wrong
- Task 9 of 10
9.
Features of the earthworm's digestive system
Right
Wrong
- Task 10 out of 10
Appearance on soil
Earthworms are best known for crawling out of their burrows onto the ground surface en masse after heavy rains. Because of this, they are called rain. It is not known for certain why this happens, but there are opinions that the following factors may contribute to this:
To read: How to use Regent cockroach repellent
- They seek warmth as precipitation causes the temperature inside the soil to drop several degrees.
- They need oxygen and moisture, which become more abundant in the upper soil layers after rain.
- Worms move to a new place, and it is much more convenient to do this on a moistened surface. Dry soil injures them, friction causes severe injuries to invertebrates, even if they move at low speed.
- Rain makes the soil more acidic, and the worms are forced to temporarily get out so as not to die in an unsuitable environment for them.
- Worms are afraid of the sound of rain, because the vibration it creates is reminiscent of the sounds of the approach of their direct natural enemies in the food chain - moles. This feature is used by experienced fishermen who need earthworms as bait. They insert a stick with an iron sheet attached to it into the ground and begin to swing it strongly in different directions. Due to this, vibration is created, under the influence of which invertebrates quickly crawl out of their holes. This is where people collect them.
Suitable soil
The earthworm usually prefers areas with moist and loose soil. They are suitable for humid subtropics, the banks of various rivers, ponds and reservoirs, as well as wetlands. In the steppes, soil subspecies of earthworms are most often found. Litter types usually live in forest-tundra and taiga. Most of their representatives are in broad-leaved coniferous belts.
An important role for them is played by the reduced acidity of the soil. Loams and sandy loams have this characteristic, which is why these invertebrates love them. If the acidity of the soil rises above 5.5, such areas become deadly for these annelids. The reproduction function normally occurs only in moist conditions. If the weather is hot and dry for a long time, they burrow deep into the ground, where they cannot reproduce.
Comparison of annelids and roundworms, their similarities and differences
| Characteristic | Roundworms | Annelids |
| Symmetry | Double-sided | |
| Number of cells | Multicellular | |
| Digestive tract | Mouth, pharynx, intestines and anus | |
| Form | Non-segmental | Long body, divided into segments |
| Reproductive system | Dioecious | Hermaphrodites and dioecious |
| Nervous system | Pharyngeal ganglion with ventral and dorsal nerves | Peripharyngeal ring with ventral nerve cord |
| Circulatory system | No | Closed |
| Excretory organs | Through intracavitary fluid and tubules | Metanephridia |
| Body cavity | Primary | Secondary |
Also, roundworms in their life cycle often use intermediate hosts for full development. This is not typical for annelids. Annelids differ from roundworms by the presence of a closed circulatory system, represented by ventral and dorsal vessels.