Poultry farming » Chickens
0
2421
Article rating
Kira Stoletova
Some people raise broiler chickens not only on an agricultural farm, but also in the city on their own loggia. For many farmers, raising broiler birds at home is not just a hobby; for them it is both a food product and an income. Diseases of small broiler chickens are not uncommon nowadays. In order for chicken diseases to go away without complications, you need to know what symptoms of diseases can attack broilers and how to deal with various infections. Many novice poultry farmers are often lost and don’t know what to do and how to deal with chicken diseases. Diseases in chickens most often occur in very young chickens and this should be prevented.
Diseases of broiler chickens
In chickens, three stages of maturation can be noted during which the bird’s immunity has not yet strengthened: from the 1st to the 5th day after birth, from the 20th to the 25th and from the 35th day for 5 days. At this time, from the first days of life, broiler birds have a dangerous period when they are most vulnerable to infections. Diseases of chickens, their symptoms and treatment are the special care of the owner. When about 1.5 months have passed after birth, you can relax a little. After this period, the immunity of day-old chicks and future laying hens settles down and the individuals grow a little. No particular differences from diseases of ordinary adult laying hens and broiler birds were found. What diseases of broiler chickens are there?
Aspergillosis in chickens
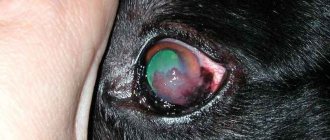
Diseases of baby chickens and their treatment. Aspergillosis is a fungal infection that affects the respiratory system of chickens. Birds develop wheezing, coughing, and uneven breathing. The pathogens enter the embryos through the shell. To avoid such a disease, you should avoid the development of fungal diseases in the litter of chickens. You should clean the areas around drinking bowls and feeders as often as possible. Aspergillosis occurs due to a fungus, but it can also be caused by other pathogenic microorganisms.
The infection can be transmitted within a few days through infected individuals and equipment. The young animals become apathetic and have no appetite. To treat this disease, you should contact a veterinarian who will prescribe the necessary medications. At home, aspergillosis should be prevented from the first days of life. The poultry house must be kept clean and the premises and equipment must be regularly disinfected.
Coccidiosis
With coccidiosis, which can occur in the intestinal, hepatic form, the organs of the digestive tract (stomach, intestines) are affected. The chicks look exhausted, sleep constantly, and move little. The mucous membranes are pale or icteric in the liver form of the disease. Feathers and down are tousled, the cloaca is contaminated with feces. The disease is accompanied by green, yellow, light brown diarrhea. Chicks quickly lose weight. Malfunctions in the functioning of the peripheral and central nervous systems are noted. Coccidiosis is characterized by very high mortality, especially among young broiler breeds.
Chickens with coccidiosis
Baycox and Coccidiovit are used for treatment. Medicines are added to drinking water and feed. These veterinary medications can also be given for preventive purposes. In addition, all necessary sanitary standards and hygiene in poultry houses must be observed.
Salmonella
Everyone has heard about this disease, even those who are completely unfamiliar with chicken breeding. Salmonellosis is an infectious disease that can be transmitted by airborne droplets through contact between healthy birds and infected individuals. Her signs are as follows:
- The eyes are swollen and watery.
- There is no appetite at all.
- Swollen feet.
- Diarrhea.
- Slow growth.
If you find signs of salmonellosis even in one individual, you should feed the entire livestock with chloramphenicol. In some cases, signs of salmonellosis may be completely absent or very vague, which makes it difficult to identify such a disease. Most often, the first manifestations occur a few days after infection. Prevention against salmonellosis should be carried out regularly. To increase immunity, broiler chickens are given mineral supplements. Sometimes a drug such as enroflon is prescribed. More details about diseases of broiler chickens and their treatment can be found in the photo or video.
Pullorosis
Pullorosis (bacillary white diarrhea) is a disease that disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Chickens experience profuse diarrhea, difficulty breathing hoarsely, shortness of breath, and cough. The stool has a watery consistency and is white in color. The plumage is matte and ruffled. The cloaca and tail are contaminated with dried feces. Appetite is reduced or completely absent. Sick broiler chickens are lethargic, inactive, and are far behind their peers in growth and development.
Chickens can be infected by contact, airborne droplets, or intrauterine means. The infection spreads with lightning speed and most often occurs in an acute form. In one-month-old chicks, pullorosis is diagnosed in a subacute, chronic form. The disease is provoked by dampness, lack of oxygen, unbalanced food, so it is necessary to provide the bird with an optimal diet and living conditions.
Complex antibacterial drugs are used in therapeutic therapy: Tetracycline, Levomycetin, Biomycin. Baytril, Enroflox, Polimexin help well against this scourge.
Gumboro disease
Gumboro disease in broilers at home is not uncommon. Gumboro is also often called infectious bursal disease. Gumboro primarily affects young animals between 2 and 20 weeks of age. Symptoms of this disease are accompanied by damage to the bursa of Fabricius, and to a lesser extent to other lymphoid organs and the kidneys. Gumboro broiler diseases and its treatment regimen should be prescribed by a veterinarian at the first symptoms.
The infected individual should be transplanted to another room, and the chicken coop should be quarantined. Such a disease can be transmitted through one infected individual to another. Gumboro disease makes birds' immune systems vulnerable. There is no cure for this disease, but regular prevention is an effective method. Many farmers are vaccinating. For these purposes, live and inactivated vaccines are used to prevent chicken diseases and symptoms.
How do hybrid chicken breeds become infected?
There are three methods of infection among poultry:
- Airborne;
- Nutritional;
- Contagious.
Broilers often become infected from other poultry that already live on the farm. Moreover, viruses that appear on early maturing breeds of chickens often have a latent (hidden) form in other birds.
Therefore, the owner, as a rule, does not know that existing individuals are sick. The risk group includes young animals whose immune systems are still quite weak. As well as chickens kept in unfavorable conditions.
Dyspepsia in broiler chickens
The smallest chickens are susceptible to this disease. This disease occurs quite often among young animals. In simple terms, dyspepsia is the most common indigestion in chickens and the signs that they are sick are immediately visible. The reason for this may be an unhealthy diet that does not contain mineral supplements. With this disease, individuals lose all interest in food, they become incredibly lethargic and inactive. The main symptom of this disease is liquid droppings containing particles of undigested food. The cause of this disease can be the abuse of feed, a change in diet, as well as poor quality feed.
To prevent this disease, you should follow several rules.
- The temperature in the chicken coop should be warm at all times. A lot depends on temperature, but many novice poultry farmers forget about this.
- To combat the processes of decay in the bird's body, the most common ascorbic acid will perfectly help. You can also use a solution of manganese and baking soda.
These simple manipulations will help your pets fight the disease.
- Feed is given to chickens every four hours. The food should not contain fats or complex proteins. Only a strict diet, and nothing else. Make sure that there are no grains with rot or mold in the feed. Also, babies always need clean and fresh water.
- Think carefully about the arrangement of the area where your birds eat. Under no circumstances should chickens crowd together, fighting and scattering and soiling their feed, as often happens.
If chickens have indigestion, medicinal herbs will help. The method is simple, but that doesn’t make it any less effective.
Bronchopneumonia
Bronchopneumonia is really something to be afraid of, as this disease is dangerous for broilers. It entails a huge variety of different diseases, in some cases even fatal. If this disease is not treated in time, then bronchopneumonia can develop into other, more serious diseases, such as bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis, rhinitis, tracheitis.
Birds with this disease will have a painfully unkempt appearance, severe weight loss, a complete lack of appetite, and a depressed state. If the bird begins to cough and mucous fluid comes out of the nose, the disease is obvious. Although this is not an infection, mass mortality of birds is possible. Unfortunately, you cannot find a special drug for treatment in pharmacies. Therefore, you should immediately make the medicine yourself.
Here is the recipe for the most common medicine
One and a half glasses of soda ash must be dissolved in three liters of hot water. Next, add a solution of bleach (one glass per seven liters of water). The resulting composition must be allowed to brew, bring to a volume of twenty liters and treat the room. Birds do not go anywhere at this time. Nothing harmful will happen to them from this. To treat chickens, you can use penicillin, norfloxacin, and terramycin is also suitable. You can also use an infusion of mumiyo with honey, tinctures of ginseng and nettle. After a month, the chickens will begin to feel much better.
Hypovitaminosis
Chickens, like people, also need vitamins, and serious diseases can also occur due to a lack of microelements. These diseases are represented in large numbers. Like vitamins, hypovitaminosis is named after the letters of the Latin alphabet. If there is not enough vitamin A in the body of birds, pathology is formed in the embryo. Such birds have no appetite, growth stops, growth and development do not occur, the chicks are characterized by weakness and inactivity.
If the disease develops, there may be a lack of digestion, as well as damage to the nervous system.
Poultry farmers often notice a lack of vitamin A when night blindness occurs. To compensate for the lack of vitamin A, you can use herbal flour, carrots and greens. If there are not enough vitamins of group D in the bird's body, calcium-phosphorus metabolism is disrupted. This affects the health of their bones. The birds are weak, have diarrhea, their legs are shaking, and the birds may limp severely. At home, you need to follow proper feeding, rearing and maintenance of birds. If there is a deficiency of the vitamin, veterinarians advise adding fish oil to the main food. In addition, walking will be very useful. Fresh air, grass, warm sun.
A lack of B vitamins causes the following problems in birds:
- Various apathies
- Gastrointestinal upset may occur
- Conjunctivitis
- Developmental delay
Green food, sprouted grains, meat, fish, bone, and grass meal are full of this vitamin. It is a good idea to give birds complex vitamins.
Rickets
Lack of calcium and vitamin D can lead to rickets in chickens.
Signs of the disease:
- chicks fall when walking;
- development slows down;
- passive behavior.
For recovery, chickens are intensively fed with vitamins and premixes with a high calcium content.
You can avoid rickets by following a number of rules:
- not too dense seating of young animals in cages;
- walks in the open air;
- balanced diet.
Newcastle disease
Russian scientists more often call this disease “whirlwind”. Birds develop a cough, apathy, strange coordination movements, drooping wings, a sickly appearance, ruffled feathers, and weight loss. There is something else that is characteristic of this disease. Sick individuals can stagnate in the same place. Newcastle disease is considered infectious and infected individuals must be isolated from healthy chickens.
If measures are not taken, the entire population may be affected by this disease. There are currently no special medications for Newcastle disease. Sick birds should be immediately placed in a separate room to avoid spreading the infection. You can study Newcastle disease in more detail in the video.
Bird flu
The disease is incurable and very dangerous for both broilers and humans. It affects the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract.
The infection usually manifests itself as follows:
- cough;
- runny nose;
- sneezing;
- elevated temperature;
- general weakness;
- stomach upset.
A sick chicken is immediately slaughtered. Bird flu can be prevented by maintaining hygiene and sanitary standards in the poultry house.
Mycoplasmosis
Mycoplasmosis manifests itself in broilers with cough, runny nose and lacrimation. If the disease continues for a long time, pus accumulates in the eyelid area and tumors may appear. Even after treatment, recovered birds continue to be considered a source of infection and can infect healthy birds simply by being nearby. It is necessary to treat sick birds with an antibiotic called Tylosin and, in addition, it is worth using medications of the tetracycline group.
It is worth considering that your birds will not be completely cured, because mycoplasmosis still remains in the body for life. The best way out is timely vaccination of all birds and isolation of sick ones. To avoid problems with young animals in the future, you should carry out proper care and regularly clean the chicken coop. How to treat broiler chickens with mycoplasmosis can be studied in detail in the photo or video.
How can hens and chicks get sick at home?
Chicken diseases are divided into two large groups: parasitic and infectious. The latter are transmitted from carriers of the infection, for example, other birds. Common infectious diseases include:
- Smallpox.
- Coccidosis.
- Imaginary case.
- Infectious bronchitis.
- Colibacillosis.
- Salmonellosis.
- Pseudo-plague.
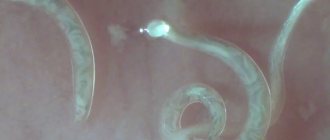
Parasitic diseases of laying hens and broilers occur due to the penetration of helminths, tapeworms and other dangerous parasites into the body.
Marek's disease
Marek's disease affects individuals from birth to 5-6 months. At an early stage, this disease does not manifest itself in any way, but later the birds develop uncoordination, curling of the fingers, and damage to the joints of the legs. A month after the disease, the birds die. Treatment for this disease is impossible, but the carcasses of these birds after heat treatment can be used for food.
To prevent Marek's disease, it is necessary to vaccinate in a timely manner, improve the maintenance, feeding and care of broilers. Joints can be affected due to calcium deficiency in the body. Review the diet of broiler chickens.
Possible reasons
Broiler chicken is a precocious hybrid of domestic chickens, which was obtained by interbreeding. The main causes of disease in poultry are:
vitamin deficiency: most often D, A, B;- lack of calcium in the body;
- staying in a room with low temperature, high humidity and lack of sunlight;
- creation of excessively sterile conditions in the habitat;
- overpopulation of chickens;
- emergence of infectious diseases.
Chicken pox
The disease is transmitted by rodents, as well as various skin parasites. Raising broilers once they are diagnosed with chicken pox becomes impossible. This disease affects the mucous membrane and internal organs of chickens.
Distinctive symptoms of chicken pox
- Strange red spots appear, which then turn into scabs.
- Individuals may experience an unpleasant odor.
- Apathy in chickens.
- Chicks have difficulty breathing and swallowing.
This disease can be treated only at the initial stage, when the symptoms have just appeared, so there is no need to waste time. For treatment, you can use galazolin, boric acid and furatsilin solution. But there are farmers who prefer not to bother with treatment, slaughtering sick birds so that the disease does not spread to the rest of the birds.
Aspergillosis
If sanitary standards for keeping chicks are not observed, Aspergillus fungi may appear in the litter, on the walls, in feeders and drinkers. Spores penetrate the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, eyes, and gastrointestinal tract. In adult livestock, muscles are affected. Meat and egg products are discarded. When the eggs are opened, mold is found inside. Aspergillosis is an infectious disease, transmitted through food, drink, and air.
- The chickens become apathetic.
- They refuse food.
- They feel thirsty. They drink a lot of water.
- There is a lack of coordination and muscle tremors.
- Broilers sneeze and produce foam and mucus from their beaks and noses.
- The beak becomes blue.
- The chicks quickly lose weight, their sides sag, and their stomachs tighten.
- Body temperature rises to 41 C.
The bird dies on the 3rd day. There is no treatment. As a preventative measure, livestock are given medications containing iodine. The substance is an antiseptic. It will not allow the fungus to develop in the body. The following drugs are used as prophylactic agents:
- “Iodinol” – make a solution of 1*0.5; chickens are given 0.5 ml; therapy is continued for up to 10 days; week break; therapy is repeated;
- "Lugol" - the drug is administered by aerosol.
- carry out feeding with iodized milk;
- "Nystatin" - 400 units. 1 liter of water; carry out short-term desoldering for 6 minutes.
If aspergillosis is detected, the livestock is disposed of. The bodies are disposed of. The chicken coop is disinfected with an iodine solution. Prepare a 10% solution. There should be at least 10 ml per 1 m3. Birds are treated as a preventive measure. The fungus may be in the plumage.
Constipation in broilers
Constipation in young animals is quite common if the feeding regime is not followed and prohibited foods are used. The causes of constipation in young animals can be the consumption of flour feed and the lack of gravel in the feeder. Constipation can be caused by factors such as: overheating or, conversely, hypothermia of the chicks. Failure to comply with the conditions of detention can cause a lot of problems for young animals. It is very important to monitor the temperature of newborn chicks to prevent constipation.
To keep day-old chicks, a brooder or a special box is used, which is covered with a cloth to retain heat, leaving only a small hole for air to pass through. The first days after birth, the young are illuminated around the clock to maintain daylight and warmth. If chickens are sick and rearing becomes difficult, then their diet needs to be reconsidered; it may be deficient in potassium or other microelements.
Disease Prevention
It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it later. Follow a few rules for caring for and keeping birds at home, then raising young animals will become an easy process.
Useful tips for raising broiler chickens
- Cleanliness of your broilers. Birds must be clean, well-groomed, and well-fed. Food mixtures should not stick to the paws. Feeding should be done with high-quality and fresh food. If the feed is moldy, it should not be given to broilers. For active growth, special supplements and vitamins can be added to feeding.
- Disinfection of the chicken coop. Don't forget that your broilers need a clear area for eating and drinking and a clean sleeping area. The feeder is changed as needed. Perches are cleaned at least once a week. It is necessary to treat the walls and floor against mold so that the individuals do not get sick, then the cultivation will be carried out according to all the rules.
- Timely quarantine of all sick chickens. This way the infection will not spread to other healthy individuals. Caring for a sick broiler chicken should be regular.
- Vaccination of all individuals. Many vaccines are given on the first and second days after the appearance of young animals.
- Newborn chickens should be placed on a heated bedding in a room where the air contains at least 17% oxygen and the temperature is about 30-32 degrees.
- If individuals are cramped in a small room, then in such conditions there is a greater likelihood of contracting infectious diseases.
- You can feed young animals with saturated drinking water with vitamin C and glucose (ascorbic acid - 2 g/l, glucose - 50 g/l), this measure helps chickens well against diarrhea.
- To make newborn chicks feel great, you can use special feeding, about 6 times a day. The diet contains low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt and whey. At the same time, all these products should not mix with each other.
If you follow all these measures, raising chickens will not seem difficult to you and you will avoid many problems.